View fulltext
View fulltext
Copolymerization of acrylonitrile (AN) with hydrophilic monomers is one of the research directions in the preparation of fouling-resistant polymeric materials. In this study, poly(acrylonitrile-co-maleic acid) copolymer (P(AN-co-MA)) membranes were prepared by 60Co γ-ray-induced copolymerization of AN and MA in a dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)/water mixed solvent. A phase inversion method was then applied. The effects of the solvent on the monomer conversion and molecular weight of the copolymer were investigated. The dependence of porosity, hydrophilicity, Zeta potential, and anti-fouling properties of the copolymer membranes on the molar feed ratio of maleic anhydride (MAH) was also studied. The results showed that in the DMSO/water mixed solvent under a mass ratio of 3∶2, the monomer conversion rate could reach over 80%, and the molecular weight of the obtained copolymer was close to 220 000. The porosity and hydrophilicity of the copolymer membrane increased with an increase in the molar feed ratio of MAH. The adsorption capacity of the copolymer membrane under a molar feed ratio of MAH of 30% for bovine serum albumin was only 52.1% of that of the polyacrylonitrile (PAN) homopolymer membrane. This study provides a useful reference for preparing PAN-based anti-fouling membranes with a controllable structure and properties using a radiation technique.
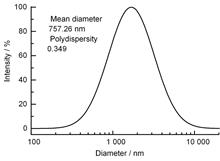
Epoxy resin (EP) and its composites have extensive applications in the nuclear industry. The study of their radiation effects can provide critical guidance in developing radiation-resistant epoxy resin materials. In this study, an epoxy resin was synthesized from tetrahydrophthalic acid diglycidyl ester and methylhexahydrophthalic anhydride. Boron nitride (BN) particles with two average particle sizes (7.5 μm and 757 nm) were used as filler to prepare two BN/epoxy resin composites. The possible bond cleavage of the crosslinking structural units of epoxy resin was investigated through density functional theory. The mechanical and thermal stability properties of the two BN/epoxy resin composites before and after gamma-ray irradiation under different absorbed doses were studied. The results showed that of all the chemical bonds consisting of a crosslinking structural unit, the C-C of the isopropyl unit had the minimum bond energy, making it easily breakable and leading to a breakdown of the polymer crosslinking network. When the absorbed dose exceeded 250 kGy, the tensile strength and thermal decomposition temperature of the epoxy resin and its composites noticeably decreased. The mechanical strength of the composite epoxy resins after irradiation depended on the combined effects of the BN particle size and the amount of added BN. When the absorbed dose reached 1 100 kGy, n-BN/EP with a mass fraction of 3% exhibited the highest tensile strength and thermal decomposition temperature. Therefore, adding a small amount of submicron-sized h-BN can improve the radiation resistance of epoxy resin. This work has theoretical and practical significance for the development of radiation-resistant epoxy resin composites.
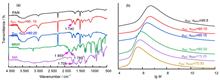
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) powders with different itaconic acid (IA) contents were prepared using aqueous precipitation polymerization with IA as the second monomer. The powders of the copolymer P(AN-co-IA) were then subjected to electron beam (EB) irradiation treatment at room temperature and under an air atmosphere, with an absorbed dose ranging from 25 to 200 kGy. The chemical structure of P(AN-co-IA) was characterized using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The effect of the IA content on PAN cyclization and the effect of EB irradiation on the thermal properties of the P(AN-co-IA) powders were investigated using differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis. The results showed that EB modification promoted the cyclization of PAN through a free radical mechanism, enabling cyclization at lower temperatures. In contrast, IA modification triggered cyclization through an ionic mechanism. Both modification methods synergistically promoted cyclization; however, their synergistic effect gradually decreased with increasing absorbed dose and IA content. The coefficient of influence was defined as the decrease in the exothermic enthalpy per 10 kGy increase in the absorbed dose. When the absorbed dose was less than 100 kGy, EB irradiation significantly affected the decrease in the exothermic enthalpy; however, the influence decreased rapidly with increasing absorbed dose. Moreover, when the absorbed dose exceeded 100 kGy, the rate of decrease of the coefficient of influence became reduced.
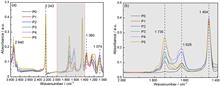
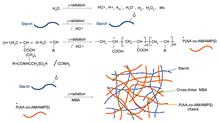
Starch-based super absorbent polymers (SAPs) were prepared using the gamma-ray co-irradiation method, where two comonomers were grafted and cross-linked. Incorporation acrylamine (AM) and 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid (AMPS) into the SAP was confirmed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The thermal decomposition behavior of the SAP was studied using thermogravimetric analysis. The salt tolerance was significantly improved by introducing AM and AMPS monomers into the SAP. The absorption rate of the SAP with AMPS in normal saline increased from 46 g/g (without AMPS) to 81 g/g when the ratio of AA:AMPS was 3:1.
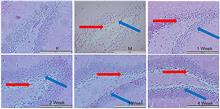
Herein, we investigated the effects of different courses of electroacupuncture on learning and memory in mice with radiation-induced brain injury, and elucidated the underlying mechanisms. Sixty 4-week-old male C57/BL6J mice were randomly divided into the blank group, model group, electroacupuncture group 1 (7 d), electroacupuncture group 2 (14 d), electroacupuncture group 3 (21 d), and electroacupuncture group 4 (28 d). Except the blank group, all groups were irradiated with X-ray (8 Gy, 2 min) to construct the radioactive brain injury model. The electroacupuncture group was injected with "Baihui," "Fengfu," and bilateral "Shenshu" points, and the intervention was performed for 7, 14, 21 and 28 days according to the groups, respectively. After electroacupuncture, the Y-maze test was conducted to assess the learning and memory of mice in each group. Neuron morphology and synaptic ultrastructure in the hippocampal DG region were observed via Hematoxylin-eosin staining and transmission electron microscopy. Protein expression levels of the Notch signaling pathway components Notch 1, Hes 1, and ASCL 1 were detected via Western blotting. The results revealed that, compared to those in the blank group, the learning and memory function of mice decreased significantly in the model group (p<0.01). The number of neurons in the hippocampal dentategyrus (DG) region decreased and their arrangement was disordered. The number of synaptic vesicles in the presynaptic membrane decreased, the rate of synaptic interface decreased, the thickness of the postsynaptic density (PSD) decreased, and the synaptic cleft increased significantly (p<0.01). Compared to those of the model group, the learning and memory function of mice in electroacupuncture group was significantly improved (p<0.05, p<0.01). In the electroacupuncture group, the number of neurons in the DG region increased, with neurons neatly arranged. The rate of synaptic interface in the DG region improved significantly in all groups (p<0.01), the PSD thickness of mice in groups 2, 3, and 4 was significantly increased (p<0.01), and the synaptic cleft in groups 2, 3, and 4 was significantly decreased (p<0.01). Compared to the blank group, Notch 1 (p<0.05) and Hes 1 (p<0.01) protein expressions were significantly increased in the model group, while ASCL 1 protein expression was significantly decreased (p<0.01); compared those in the model group, the expressions of Notch 1 and Hes 1 proteins in electroacupuncture groups 2, 3, and 4 were significantly decreased (p<0.05, p<0.01), and the expression of ASCL 1 protein was significantly increased in electroacupuncture groups 3 and 4 (p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively ). In conclusion, different courses of electroacupuncture can ameliorate the damage in learning and memory function caused by irradiation in mice, which is associated with improving the ultrastructure of synapses in the DG region and regulating the expression of related proteins of the Notch signaling pathway.
This study was conducted to evaluate the application value of a degradable liquid fiducial marker (LFM) in image-guided radiotherapy. In vitro experiment: using a solid fiducial marker (SFM) as a reference, the visibility, artifact, and optimal injection volume of an LFM under different cone beam CT tube voltage conditions were evaluated. In vivo experiment: using the SFM as a reference, the stability and degradation status of the LFM in nude mice were evaluated. Nude mice implanted with tumor cells were randomly divided into four groups: single fraction radiotherapy group (16 Gy/fraction) without LFM injection, single fraction radiotherapy group (16 Gy/fraction) with LFM injection, 2 fractions radiotherapy group (8 Gy/fraction) with LFM injection, and 4 fractions radiotherapy group (4 Gy/fraction) with LFM injection. The impact of LFM on tumor growth was evaluated based on the irradiation results. Compared with SFM, the LFM artifacts were significantly smaller (all p<0.05), and the visibility met the clinical differentiation requirements. The best imaging quality was achieved when the injection volume was 10 μL. The displacement of the LFM centroid relative to the spinal cord in the nude mice was significantly greater than that of the gold fiducial marker ((0.22 ± 0.03) mm vs. (0.17 ± 0.02) mm, p<0.05); however, it was always smaller than a pixel size. The results indicated good stability. The actual degradation rate of the LFM was highly consistent with the theoretical degradation rate. The LFM had a relatively smaller impact on tumor growth in the single fraction radiotherapy group but a greater impact in the fractional radiotherapy groups. LFMs have certain clinical applications and promotional value, and they are expected to replace SFMs in the future.
Herein, we established the fingerprint of Ligusticum chuanxiong, and the effects of different 60Co-γ irradiation doses on the eight active components of Ligusticum chuanxiong were investigated. A stock solution of the eight standard reference substances in Ligusticum chuanxiong were analyzed using a SHIMADZU Shim-pack GIST C18 chromatographic column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm). Different doses (3 kGy, 6 kGy,10 kGy and 15 kGy) of 60Co-γ irradiation were used to treat Ligusticum chuanxiong. After these treatments, the fingerprint of Ligusticum chuanxiong was obtained via liquid chromatography. The similarity was evaluated using the Similarity Evaluation System for Chromatographic Fingerprint of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2004 A edition), and the results indicated that the similarity of each component in Ligusticum chuanxiong was >0.988. After irradiation at <10 kGy, the contents of the eight active components in Ligusticum chuanxiong exhibited no evident differences, and the results indicated the stability and reliability of the method. Thus, this study provides a theoretical basis and support for the use of irradiation technology in the quality assurance of Ligusticum chuanxiong and the formulation of irradiation standards for Ligusticum chuanxiong.
The effects of 60Co γ-ray irradition (absorbed dose: 0 kGy, 5 kGy, 15 kGy, 20 kGy, 30 kGy, and 50 kGy) on the pH, solubility, free amino acid content, and structural characteristics of Procambarus clarkiibyproducts were studied. The results showed that irradiation reduced the pH value of the byproducts of the Procambarus clarkii, namely, the pH value decreased from 7.93 to 7.22. With increasing absorbed dose and water content, the solubility of the byproducts of Procambarus clarkiiincreased, with the highest solubility reaching 35.71% and the lowest being 16.23% in each treated sample. Irradiation could increase the content of free amino acids in the byproducts of Procambarus clarkii, and when the absorbed dose was 50 kGy, the content of free amino acids reached 34.66%. Through UV and infrared scanning revealed that the absorption characteristic absorption peaks of the byproducts did not show significant changes before and after irradiation, but the absorption intensity changed.
This study investigated a method of measuring the absorbed dose rate of γ-ray in air using a Φ7.5 cm×7.5 cm NaI(Tl) detector. Simulation of the NaI(Tl) detector using the Monte Carlo method was performed to obtain the γ-ray energy spectrum of the detector in the energy range of 50 keV~2.5 MeV. The G(E) function was used to calculate the air-absorbed dose rate of radioactive sources. When solving the G(E) function, the influence of the Kmax and the optimization factor M on its calculation of the air-absorbed dose rate was considered, and the solution of the G(E) function was optimized to improve the calculation accuracy. The relative deviation S of the air absorbed dose rate calculated by the optimized G(E) function from the theoretical standard value was less than ±1%. Finally, after the comparison of experimental measurements, it was found that the relative deviation between the calculated air absorbed dose rate of the G(E) function and the measured results of the dose rate meter was less than ±10%, indicating that the optimized G(E) function value of the NaI(Tl) detector can be used for the application of air absorbed dose rate measurement.
In this study, the issues of unclear characteristics of dose differences in multi-frequency and large-sample bioelectromagnetic exposure systems were studied. For this, four contrast simulation environments were established using Sim4Life. The frequency points in the simulation were set to 1.8, 2.4, 3.6, and 5.8 GHz, respectively. The scattering field and whole-body average specific absorption rate (WBASAR) values were simulated and analyzed. The results revealed that the WBASAR value for experimental animals was influenced by the electromagnetic scattering of adjacent animals, and the spatial distribution of the WBASAR value was similar to the trend followed by the excitation field distribution. The excitation field was the primary factor causing the variation in the WBASAR distribution. In addition, the WBASAR distribution varies with frequency, and a higher ratio of body size to wavelength inhibits the WBASAR variation. Furthermore, a design suggestion for the exposed platform was proposed to reduce group dose uncertainty based on the variation characteristics. Overall, this study provides a dose evaluation basis for the design of electromagnetic exposure systems.
The multi-channel parallel diode structure is effective in obtaining X-ray with low energy, large area coverage, and high dose rate in laboratory conditions. In this study, the dose uniformity of single- and five-ring structures was studied based on a point source model. The results showed that the radiation field was primarily focused on the projection position of the ring in the plane near the ring; as the distance increased, the radiation was gradually dispersed to other regions. In the case of single ring structure diodes and z < 15 cm, 80% of the area of the dose homogeneously increased and then decreased with the increasing distance, whereas the total dose in the calculated region decreased gradually. Considering the dose uniformity and total dose, the optimal experimental region of single ring diode radiation field was z = 7-9 cm. A smaller inner ring radius will only enhance the dose near the projection point of the ring; however, the uniformity of the dose on the plane will decrease. A larger inner ring radius will also decreased the dose near the projection point of the ring center. When the outer radius of ring was 10 cm, the optimal inner radius was 8-9.5 cm. Compared with the single ring diode, the dose uniformity of the five ring diode can be greatly enhanced, and the dose uniformity of radiation field and effective experimental region can be improved. Moreover, in z = 11-17 cm, the five-ring dose uniformity did not exhibit significant fluctuations.