View fulltext
View fulltext
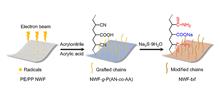
Herein, a bifunctional nonwoven fabric sorbent containing thioamide and carboxyl groups was synthesized via radiation grafting of acrylonitrile and acrylic acid, followed by modification with sodium sulfide, to selectively recover Au(Ⅲ) from the acidic solution. A polyethylene/polypropylene skin-core-structured nonwoven fabric was used as the substrate. The structure and properties of the sorbent were characterized using infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy, contact angle measurements, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction. The adsorption performance of the sorbent was determined through batch adsorption tests. The results indicated that the sorbent exhibited excellent Au(Ⅲ) adsorption capacity over a wide pH range (2-7) and demonstrated good selectivity for Au(Ⅲ) in the presence of coexisting metal ions, with selectivity coefficients ranging from 55.00 to 2 429.17 and a gold recovery ratio of 98.5%. The adsorption followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic and Langmuir isotherm models, with an Au(Ⅲ) saturation adsorption capacity of 133.91 mg/g. Au(Ⅲ) could be reduced to crystalline Au(0) during the adsorption process. Moreover, the modified nonwoven fabric could be effectively removed via simple high-temperature treatment, facilitating Au recovery.
To explore the influence of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) matching reference point selection on target accuracy in intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) for breast cancer and aimed to provide a reference for clinical application. We conducted a retrospective analysis on breast cancer patients who underwent postoperative radiotherapy between January 2020 and October 2020. CBCT images for image-guided radiotherapy, different matching reference points, and the location of computed tomography (CT) image registration were used to divide patients into the sternum (control group 1), thoracic (control group 2), and sternum-thoracic + target (team) groups. CBCT alignment was confirmed by three different registration methods. After matching, the matching error and spatial displacement of the metal clip at the boundary of the operative cavity in CBCT and target CT were measured and recorded. A total of 528 sets of matching errors and spatial displacement data of metal clips in the target area were obtained for 22 enrolled patients. Independent sample nonparametric tests were used to analyze the significant differences in the three groups of data, and the distance of metal clips in the three groups was calculated. The matching errors of the sternum and study groups were statistically significant, except for the rotation error in the direction of the X-axis (p>0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in the matching error between the thoracic vertebra and the study groups (p>0.05). After the sternum group was matched with the study group, the displacements of the metal clips in the target area of CBCT and CT in the X, Y, and Z directions were as follows: (1.59±1.61) mm and (1.23±1.19) mm (p=0.045), (1.65±1.44) mm and (1.89±1.52) mm (p=0.006), and (1.13±1.18) mm and (1.37±1.31) mm (p=0.999), respectively. The thoracic vertebra group was matched with the study group, and the displacements of the metal clips in the target area of CBCT and CT in the X, Y, and Z directions were as follows: (1.51±1.83) mm and (1.23±1.19) mm (p=0.002), (1.69±1.84) mm and (1.89±1.52) mm (p<0.001), and (0.91±1.28) mm and (1.37±1.31) mm (p=0.003), respectively. Moreover, the 3D vector distances of metal clips in the three groups were (3.16±1.92) mm, (3.62±1.92) mm, and (2.52±1.53) mm, respectively. The selection of optimal reference points for IMRT CBCT automatic registration of breast cancer should simultaneously include the sternum, thoracic vertebra, and target area of the affected side. Placement of a metal silver clip in the intraoperative cavity can improve the matching accuracy of the target area of breast cancer radiotherapy.
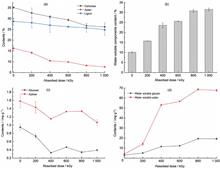
Rapeseed straw was used as raw material to investigate the changes in the lignocellulosic components, types and contents of degradation products after different absorbed doses of 60Co-γ-ray irradiation, and the enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation characteristics were evaluated in this research. The results showed that the contents of cellulose, xylan and lignin decreased, the total amount of water-soluble components increased, and the pH of water extract gradually decreased in the rapeseed straw with the increase of irradiation absorbed dose. The total amount of four types of small molecular fatty acids in the degradation products of rapeseed straw gradually increased with the irradiation absorbed dose increasing, reaching a maximum of 9.25 mg/g after 1 000 kGy irradiated. The total amount of nine types of small molecular aromatic degradation products first increased and then decreased, reaching a maximum of 0.22 mg/g in 800 kGy irradiated rapeseed straw. The cellulose conversion rate and glucose concentration of rapeseed straw by enzymatic hydrolysis increased with the increase of irradiation absorbed dose. The cellulose conversion rate decreased and the glucose concentration in enzymatic hydrolysate gradually increased with increasing substrate concentration. The cellulose conversion rate for enzymatic hydrolysis was 57.55% and ethanol conversion rate was less than 10% of 800 kGy irradiated rapeseed straw at 15% substrate concentration in separate hydrolysis and fermentation. Irradiation combined with water extraction significantly improved the enzymatic and fermentation efficiency of rapeseed straw. The cellulose conversion rate and glucose concentration for enzymatic hydrolysis were 71.62% and 40.38 mg/mL, respectively, the ethanol conversion rate was 64.00% after 48 h of separate fermentation, and the glucose in fermentation broth was completely consumed for 800 kGy irradiated rapeseed straw after water extraction at 15% substrate concentration.
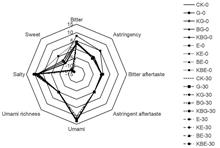
To explore effective measures to control the flavor of spicy salted duck irradiated by 60Co-γ ray and electron beam, the effects of antioxidants and irradiation temperature on the flavor and electron beam were studied using electronic nose and electronic tongue detection techniques. Radar analysis, principal component analysis (PCA), and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) were performed on the E-tongue and E-nose experimental data. The results indicated that there were significant differences in the flavor of spicy salted duck samples with different treatments (p<0.05), and the differences in taste of irradiated spicy salted duck mainly showed bitter taste, astringency taste, and sweet taste. The main differences in odor were W2W (aromatic compounds and organic sulfides), W1W (inorganic sulfides), W1S (hydrocarbons), W5S (nitrogen oxides), and W2S (alcohols and partial aromatic compounds). The flavor characteristics of each ice-temperature treatment group were closest to the control group, followed by the flavor characteristics of each antioxidant group. No obvious synergistic effects were observed on the flavor of irradiated spicy salted duck with ice temperature and antioxidant treatments. Ice temperature and antioxidant treatment could control the flavor change of spicy salted duck to a certain extent. This study provides theoretical support for selecting flavor control methods for spicy salted duck.
Patulin is the most common mycotoxins present in apple juice, and is very harmful to consumer health and economic development. Herein, we investigated the degradation of patulin and promotion of flavor component in apple juice by glow discharge plasma (GDP). The results showed that when the DC voltage was 550 V and the current range was 10-90 mA, the degradation rate of Patulin in apple juice reached 92.89% after treatment by glow discharge plasma for 15 min. After 30 min of GDP treatment, no significant change in the soluble solids and phenols of apple juice was observed, while the electrical conductivity, redox potential, and the color value of apple juice increased, with a slight decrease in pH. After 20 min of GDP treatment, 38 compounds were detected in apple juice by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry (GC-MS), including 8 esters, 7 alcohols, 20 aldehydes and ketones, and 3 others. Two new components,viz. acetophenone and 6,10-dimethyl-5,9-undeundene-2-one were detected compared with the control; both are sweet and fragrant essential oils, which could make the apple juice taste more delicious. The results of this study can provide the basis for applying GDP in the degradation of patulin and promotion of flavor components in apple juice.
Electron beam (EB) irradiation is an efficient method for avoiding microbial contamination affecting food quality. To explore the properties of Litopenaeus vannamei after EB sterilization, samples were irradiated at an absorbed dose of 0-12 kGy using a 10-MeV backward wave linear accelerator and tested for protein, fat, and amino acid content; pH; volatile saline nitrogen; textural features; microbiology; and organoleptic satisfaction. The results showed that the protein content and fat content were in the normal range. In the optimal absorbed dose range (6-8 kGy), TVB-N, which characterizes the freshness of shrimp, was apparently lower. Further, most of the amino acids peaked; textural features such as chewiness and cohesiveness were significantly enhanced; no microbial colonies were detected; and both color and taste were relatively better. These results suggest that EB irradiation sterilization is an effective method for microbiological control of food, and it results in greater freshness without degradation of the properties of frozen Litopenaeus vannamei in terms of nutrient content and other properties.
Nuclear accidents, although unpredictable and devastating, can be mitigated through well-formulated evacuation plans. An efficient evacuation of residents from hazardous zones to safer locations can be ensured through such plans. To address the vehicle path planning challenge under nuclear accidents, this paper proposes a method based on the hybrid ant colony algorithm (HACO). Cumulative radiation dose is used as a key assessment metric. Initially, a model estimating the average time for evacuating a route within a given time window is designed using a fuzzy network. In addition, a time-varying dynamic radiation dose model is proposed by incorporating the cumulative radiation dose calculation. The ant colony algorithm's iterative process is enhanced by the incorporation of the simulated annealing algorithm, while the heuristic approach of A* algorithm is employed for neighborhood searches. This integration results in an enhanced capacity for global optimization of the algorithm. For refining the local search capabilities of the algorithm, Pareto ordering is implemented. Additionally, the pheromone update method of the ACO algorithm is adjusted to account for the impact of distance on pheromone increments. Upon employing the HACO algorithm, simulation results indicate a 31% improvement in average convergence value and 30% boost in stability over the conventional ACO algorithm. These enhancements are instrumental in fortifying the planning of evacuation routes in the event of nuclear accidents.
Deuterium(D)and tritium(T)have been regarded as the first-generation fuels for achieving commercial fusion energy. However,the utilization of the radionuclide tritium introduces concerns related to radioactive safety. This study sought to investigate methods for estimating airborne tritium sources following a fusion reactor incident. An algorithm that combines an adaptive Kalman filter with a deep feedforward neural network was developed to determine the tritium release height and rate. By utilizing observed data both pre- and post-filtering as inputs,the neural network's predictions for the tritium release rate were analyzed. The findings indicate that filtering significantly lowers the prediction errors. Considering a 20% monitoring error,the average relative error for the estimated release height is approximately 3% and that for the release rate is approximately 4%.
The performance of tritium-based nuclear batteries based on two different energy conversion modes, the irradiated voltaic effect and irradiated photovoltaic effect, was studied by using the Monte Carlo method. The influence of the geometrical-physical parameters of energy conversion materials on the electrical output performance of batteries wais investigated. Single-layer and stacked-layer tritium-based nuclear batteries were designed and prepared. The effects of increasing the tritium source intensity and adopting the stacked-layer configuration on the enhancement of the electrical output of the batteries were analyzed. The simulation results showed that Si, SiC, and GaAs photovoltaic modules could be used for irradiated voltaic effect tritium-based nuclear batteries and that their respective optimal thickness parameters allow the electrical output performance to be optimized; the optimal thicknesses were 3.8 μm, 2.2 μm, and 1.7 μm, respectively. For irradiated photovoltaic effect tritium-based nuclear batteries, the thickness of the ZnS:Cu fluorescent layer could be adjusted to maximize the emitted fluorescence irradiance and optimized the electrical output performance. The experimental results showed that increasing the radiation intensity of the tritium source and adopting the stacked-layer configuration could effectively enhance electrical parameters such as the maximum output power of tritium-based nuclear batteries. The maximum output power of the stacked-layer nuclear battery could reach 106.138 nW, which was an increase of more than 64% compared with that of the single-layer configuration.
In this study, biological ash samples were prepared by establishing a high-capacity microwave integrated device for carbonizing and ashing. Radioactive nuclides in biologically derived ash samples using high-purity germanium gamma spectrometry were directly measured for rapid determination of γ radionuclide activity concentration in environmental bio-samples from nuclear power plant surroundings. A comparison with the traditional ash preparation method was also conducted. The results showed that the microwave-ash preparation method can improve the preparation efficiency of biological samples by approximately 2 to 5 times, with a relative deviation of less than 14.8% for parallel samples and a spike recovery rate ranging from 87.0% to 116%. A paired T-test revealsed no significant difference between the two methods. The proposed method has the advantages of high accuracy, high analytical efficiency, simple operation, greater security, and environmental friendliness. It is an ideal method for quickly determining γ radionuclide activity concentration in biological samples.
The effect of the total ionizing dose (TID) on the static random access memory (SRAM) is conducted on the 60Co radioactive source in the China Institute of Atomic Energy. The study explores the influence of the device process size, dose rate, temperature and total dose on TID. The results indicated that within a certain range, the dose rate had little influence on the TID of the device. The larger the characteristic size of the device, the greater TID effect, while the higher temperature, the weaker the total dose effect. In addition, the typical dose rate and the uniformity of the source are achieved. The research of the paper provide an insight into radiation hardening, particularly in the aerospace and the nuclear industries.