View fulltext
View fulltext
The long-term, slow reaction that occurs when polyethylene (PE) is exposed to oxygen after ionizing radiation is known as post-radiation oxidation, which significantly affects the long-term performance of radiation-modified PE materials. In this study, an ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) film, a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) film, and a low-density polyethylene (LDPE) film were selected as typical PE materials and irradiated with γ-rays. Subsequently, the carbonyl products of the post-radiation slow oxidation reaction were quantitatively analyzed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and by varying the temperature, oxygen partial pressure, and absorbed dose. The effects of these factors on the oxidation behavior of PE after radiation were systematically investigated. Post-radiation oxidation was clearly observed in the UHMWPE and HDPE films. Meanwhile, the LDPE film showed weak post-radiation oxidation, which could be maintained for a long time at room temperature, with the highest reaction rate occurring at 50 °C. However, above 70 °C, the oxidation reaction could only be maintained for a few hours. Additionally, a significant positive correlation was observed among the post-radiation oxidation reaction, oxygen partial pressure, and absorbed dose. This study not only offers a new perspective for understanding the post-radiation oxidation reaction of PE but also provides guidance for improving the accelerated-aging evaluation of radiation-modified PE materials.
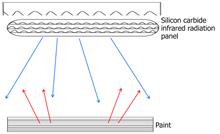
Stator bars are crucial components in motor production. The traditional process used for curing the surface paint of stator bars has a long cycle, low efficiency, and high energy consumption. Infrared radiation curing is a method that can potentially overcome these issues. This study investigated the curing behaviors of three types of paints (low-resistance, high-resistance, and red enamel paints) on the surfaces of stator bars under infrared radiation. The paint samples were prepared using an epoxy glass cloth plate as the substrate material and a silicon carbide infrared radiation plate as the infrared radiation source. The cured paint was characterized via infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The degree of curing and the electrical properties of each sample were measured and compared with those obtained using the traditional curing process. The results indicated that the degree of curing of the three types of paints after curing by infrared radiation was higher than that under the traditional curing process by 8.98%, 10.33%, and 10.40%, respectively, and that the surface drying effect could be achieved in 2 min. The electrical properties and surface morphologies of the paints were shown to satisfy the standard performance requirements. The paints cured by infrared radiation exhibited good electrical properties. The study thus demonstrated the high efficiency and practicability of the infrared radiation curing method, as well as its wide potential applicability.
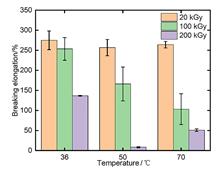
In national defense, aerospace, and nuclear power fields, the service environments of polymer materials in equipment are complex and necessitate high requirements for their radiation resistance and thermal stability. Therefore, studying the aging behavior of polymer materials in a coupled radiation-thermal environment is crucial. In this study, F2311 rubber material was subjected to aging tests in the temperature range of 36-70 °C, with an absorbed γ dose of 20 kGy, 100 kGy, 200 kGy. The effects of the coupled temperature and absorbed dose on the mechanical properties of F2311 were investigated. The gaseous products released by the F2311 material and their kinetic laws were determined using gas-phase infrared spectra. The experimental results showed that the mechanical properties of the F2311 elastomer deteriorated rapidly in the radiation-thermal environment. Radiolytic outgassing was inevitable, and the gaseous products included corrosive halogen hydrides. Gas-phase infrared spectroscopy can quickly identify and quantitatively analyze gaseous products to trace and supervise the service reliability of equipment. This study is expected to provide a basis for the study of coupled multifactor aging and compatibility of fluorine rubber.
Electron beam irradiation processing has become an important component of the nuclear technology industry, with low-energy electron beam increasingly being applied in processes such as coating curing, wastewater treatment, and food preservation. Accurate measurement of irradiation parameters is essential to ensure irradiation quality. However, at present, standardized protocols for electron beam dosimetry below 300 keV have not been established. As a result, parameter measurements are often benchmarked against the 10 MeV electron linear accelerator, which introduces systematic biases due to inconsistencies among measured objects. In this study, a novel method for measuring low-energy electron beam energy, combining experimental testing and mathematical simulations, was applied to electron beams with energies below 300 keV. Additionally, an absorbed dose measurement device based on calorimetry was developed. Relationships between absorbed dose and beam intensity, displacement velocity, and other parameters were explored to obtain absolute measurements of absorbed doses from a low-energy electron beam. The energy parameters of low-energy electrons were experimentally determined using a dose step-stacking method, combined with simulations of energy deposition depth distribution curve, then the low-energy electron absorbed dose parameters were measured in the range of 140 keV. The low-energy electron absorbed dose parameters were measured using calorimetry in the range 1-120 kGy, and measurement uncertainty was 11% (k?=2). This study provides a reliable measurement method for low-energy electron-beam irradiation processing.
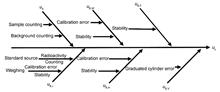
Bsaed on the requirements of "Standard examination methods for drinking water — Part 13: Radiological indices" (GB/T 5750.13—2023) as well as domestic and foreign uncertainty assessment guidelines, this paper presents the uncertainty evaluation of gross α and gross β analyses in actual water samples. By analyzing the uncertainty sources, combining various uncertainty components, and calculating the expanded uncertainty, the contribution of each uncertainty component to the total uncertainty was discussed. The analysis results for the water sample are gross α: (1.01±0.14) Bq/L (k=2), gross β: (0.60±0.09) Bq/L (k=2). The uncertainty sources mainly originated from the net counting rate, counting efficiency, and chemical recovery, which account for 52.3%,19.8%,and 20.0% in gross α , respectively, and 59.9%, 19.0%, and 13.6% in gross β, respectively.
This study investigates the degradation of pyridine in coal chemical wastewater using electron beam (EB) irradiation and explores the impacts of absorbed dose, initial pyridine concentration, and pH. We examined the efficacy of EB irradiation alone and in combination with oxidizing agents (H2O2, PMS, O3) on pyridine degradation, the performance of EB synergistic process and the mechanism of pyridine by EB irradiation were studied. Our findings reveal that at an initial pyridine concentration of 50 mg/L, absorbed dose of 5.0 kGy, and pH=7.0, the removal and mineralization efficiencies reached 90.88% and 6.05%, respectively. The addition of oxidizing agents significantly enhanced these efficiencies; removal rates were 94% with H2O2, 96% with PMS, and 93% with O3, while mineralization rates were 12%, 9.3%, and 10%, respectively. The EB combined with PMS showed the highest degradation performance, followed by EB/H2O2, EB/O3, and EB alone. Quenching experiments confirmed that the degradation mechanisms involve ?OH, eaq-, and H? radicals, with ?OH playing a major role in attacking and breaking down the pyridine ring.
The germination-promoting effects of low-temperature plasma produced by dielectric barrier discharge on Lycium barbarum (L. barbarum) seeds and the optimal treatment process were investigated using a pin-plate dielectric barrier discharge plasma reactor. The distance between the fixed needle plate electrode and the sample liquid was 5 mm. The effects of dielectric barrier discharge plasma on L. barbarum seed germination were investigated at different discharge times, discharge voltages, and electrolyte types. In this single-factor experiment, the response surface was used to optimize a seed treatment protocol for L. barbarum, and the effect of dielectric barrier discharge plasma on seed coat structure and properties was investigated by observing seed coat morphology and measuring the contact angle. Under discharge conditions including a discharge time of 1 h, a 35 kV discharge voltage, and 150 mL of 0.2% aqueous Na2SO4, the germination rate of treated L. barbarum seeds was 86.67%, and that of untreated seeds was 33.33%, an increase of 53.34%. The treated seed vitality index was 600.58, and that of untreated seeds was 206.9, revealing an increase of 65.55%. After treatment, the seed coat became smooth, its texture was rough, and seed hydrophilicity was enhanced. This study provides a clean and efficient method to improve plant seed germination rates.
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of 60Co-γ irradiation sterilization on the quality of Fructus forsythiae. The medicinal powder of Fructus forsythiae was used at different doses. Ingredient concentration,high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) finger print and antibacterial activity of water extract against Staphylococcus aureus were used before and after irradiation for comparison. A near-infrared spectrum (NIR) consistency model of Fructus forsythiae was established by near-infrared spectroscopic methodology and the optimum dose of 60Co-γ irradiation was investigated. The results showed that there was very significant difference (p<0.01) in the contents of the two compounds (forsythiaside A and forsythiaside I) compared to unirradiated samples. The similarity of HPLC fingerprints was decreased. The water extract's effectiveness against Staphylococcus aureus before and after irradiation in each sample showed no significant difference (p>0.05). The NIR consistency evaluation model was established to determine the irradiated samples. The microbial populations could be reduced to a lower degree at 5 kGy absorbed dose irradiation. 60Co-γ irradiation sterilization would affect the quality of Fructus forsythiaeat 10 kGy dose. It is recommended that the irradiation sterilization dose not exceed 5 kGy.
This study investigated the mutagenic effects of 60Co-γ radiation on different Lycium materials. The annual spikes of four species of Lycium, i.e., Z29, Z62, T3, and Z99, were treated with 0 Gy, 20 Gy, 40, Gy 60 Gy, 80 Gy, and 100 Gy of 60Co-γ radiation. Subsequently, their survival rate, growth traits, and physiological and biochemical indexes were measured and analyzed statistically. The results showed that as the absorbed dose increased, the survival rate, stem diameter, and plant height of all four materials decreased significantly compared with those of the control group (p < 0.05). The survival rate of T3 was zero at 80 Gy and 100 Gy. Meanwhile, Z29 exhibited zero survival at 100 Gy, and Z62 and Z99 exhibited survival rates below 10% at 100 Gy. Linear-regression ANOVA results revealed LD50 values of 47.54 Gy for Z29, 49.38 Gy for Z62, 23.99 Gy for T3, and 49.60 Gy for Z99, thus highlighting the reduced tolerance of T3 to 60Co-γ radiation compared with those of other Lycium materials. The optimal absorbed dose for Z99 was 40 Gy, whereas those for Z29, Z62, and T3 were 0 Gy-40 Gy, 0 Gy-20 Gy, and 20 Gy-40 Gy, respectively, thus indicating distinct preferences. 60Co-γ radiation resulted in growth-inhibitory effects on all Lycium species, which intensified as the absorbed dose increased. The absorbed doses at 20 and 40 Gy had less effect on the growth of the test materials. These findings offer valuable insights for the genetic enhancement and breeding of Lycium.
This study investigated the dosimetric results and gamma passing rates of jaw-automated tracking (JAT) techniques in volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) plans for patients with multiple brain metastases. From August 2017 to March 2020, 15 patients with multiple brain metastases were enrolled in this study at Yunyang People's Hospital. For each patient, a VMAT plan was created using both the JAT and jaw manual fixed (JMF) techniques. Plan quality was evaluated by comparing the conformity index (CI), homogeneity index (HI), and dose to organs at risk, including the whole brain and brainstem. Evaluation indicators and dose distributions were compared between the JAT and JMF groups. The results indicated that the JAT plans demonstrated better HI (0.060 vs. 0.080, p < 0.05) and a lower mean dose for the whole brain (853.8 cGy vs. 893.4 cGy, p<0.05). Additionally, the JAT plans exhibited reduced dose exposure in V10 (56.1% vs. 60.2%, p < 0.05) and V20 (28.5% vs. 29.5%, p < 0.05) compared to the JMF plans. No significant differences were observed between the two groups in terms of CI and maximum dose to the brainstem. In conclusion, VMAT plans utilizing JAT techniques can enhance HI and decrease dose exposure to the entire brain.
The incidence rate of central nervous system (CNS) diseases is increasing annually. One of the most important obstacles encountered in the course of drug treatment for such diseases is the physiological barrier of the brain itself, the blood-brain barrier (BBB). However, the biochemical and physical methods currently used to alter BBB permeability have several side effects. Evans blue (EB) was used as a tracer to investigate the relationship between different pulse microwave parameters and changes in BBB permeability, using tissue homogenization and fluorescence observation methods. BBB permeability increased with brain field strength when the number of pulses was 20, the pulse width was 750 ns, and the brain field strength was either 10 or 12 kV/m. Notably, EB leakage was 1.8 times that of the control group, which was a statistically significant difference (p<0.01). When the brain field strength was 10 kV/m and the pulse width was 750 ns, as the number of pulses increases, the BBB permeability first increased rapidly; however, when more than 20 pulses were applied, BBB permeability reached a constant value, and EB leakage was 1.9 times that of the control group, which was statistically significant (p<0.01). Lastly, when the brain field strength was 10 kV/m and the number of pulses was 20, as the pulse width increased, BBB permeability first increased rapidly but then increased with a slower rate, at pulse widths of 750 ns and 1 000 ns, respectively. The EB leakage was 1.7 times that of the control group, with statistical significance (p<0.01). The dose-effect relationship between the pulse microwave parameters and BBB permeability changes was further obtained through data fitting. This study provides data support for medical applications and the safety protection of pulsed microwaves.
The aim of this study is to create an association-rule prediction model for acute radiation dermatitis (ARD) in patients who underwent radiotherapy after radical breast-cancer surgery and to evaluate the clinical application value of the model. Data were obtained from 800 patients who underwent radiotherapy after breast-cancer surgery at the First Affiliated Hospital of Hebei North University between June 2014 and June 2024. The patients were randomly segregated into a model group and a validation group at a 6∶4 ratio. The FP-growth algorithm used in association-rule analysis was used to process the baseline dataset of the model group. An ARD prediction model was created based on effective strong-association rules. Internal validation was performed based on the model group. The C-index and a calibration curve were used to evaluate the consistency of the ARD association-rule prediction model. External validation was performed based on the model and validation groups. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for predicting ARD in the two groups were constructed. The difference in the area under the curve (AUC) between the two groups was evaluated. Based on the ARD association-rule prediction model, the incidence of ARD in patients with specific baseline-data combinations of“body mass index ≥ 28 kg/m2,”“serum albumin level < 45 g/L,”“chemotherapy history (yes),”and“average irradiation field area ≥ 15 cm2”ranged from 42% to 77%. The ARD association-rule prediction model with the highest incidence rate was validated. Based on internal validation, the C-index of the model is 0.883 (95% CI: 0.703-0.919). The calibration curve shows good consistency between the predicted and actual values. Based on external validation, the AUC predicted by the ARD model for the abovementioned two groups are 0.856 (95% CI: 0.701-0.892) and 0.839 (95% CI: 0.715-0.922), respectively. The ROC curve fitting is relatively ideal (χ2 = 3.224,p = 0.216), and the difference in the AUC is not statistically significant (p = 0.157). The ARD association-rule model yields accurate prediction results and demonstrates high main-prediction efficiency; thus, it can contribute significantly to the prevention and treatment of ARD.
Lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries have attracteded extensive research interest as key energy storage solutions, owing to their favorable energy and power densities coupled with remarkable long-term cycling and storage stability. These batteries are primarily composed of four parts: cathode, anode, diaphragm, and electrolyte, each of which plays a decisive role in the electrical performance of the batteries. This paper comprehensively reviews the impacts and potential applications of radiation exposure on the four primary components of these batteries, focusing on the current status of research and application of irradiation technology with respect to cathode defects, anode synthesis, defects and surface modification, diaphragm synthesis, non-grafting modification and functionalized grafting, polymer solid electrolyte synthesis, and modification and in-situ curing. Furthermore, it discusses the prospects for the application of irradiation technology in the various main materials, Irradiation technology can significantly improve the battery material's electrical performance and reliability, and it may become a promising means of battery performance improvement. Furthermore, this paper delves into the relationship between radiation exposure and potential failures in full batteries, thereby providing insights into the implications of radiation effects on battery technology under extreme operating conditions.