View fulltext
View fulltext
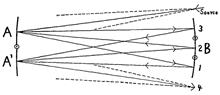
As it can simulate the absorption environment of gas molecules and provide a long absorption optical path, optical gas absorption cell has been widely used in gas molecular spectroscopy, trace gas detection and other fields. The development of optical gas absorption cell is reviewed from the perspectives of normal temperature and variable temperature in this work. Firstly, the principle and application of White cell, Chernin cell, Herriott cell and Circular multipass optical gas absorption cell used in room temperature gas measurement are introduced, and the corresponding advantages and disadvantages are analyzed. Then, the technology, main performance indexes, structure characteristics and applications of the optical gas absorption cell used in variable temperature gas measurement are described. Finally, the future development of optical gas absorption cell is prospected.
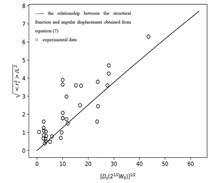
In order to study the influence of outer scale and inner scale of atmospheric turbulence on the spot wander characteristics of Gaussian beam under strong fluctuation conditions, the variance expressions of beam wander of Gaussian beam in focusing and collimating conditions are derived firstly by using the modified von Karman spectrum, and verified by experimental data. Then, according to the derived beam wander expression, the characteristics of beam wander under different inner and outer scales are studied using numerical analysis method. The results show that the increase of outer scale will strengthen the effect of beam wander, while the change of inner scale has no significant effect on the characteristics of beam wander.
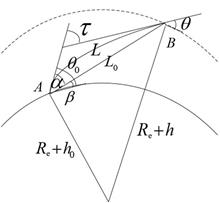
In order to analyze the location error caused by atmospheric refraction, the vertical profiles of atmospheric refractive index are deduced based on the rotation Raman lidar return signals, and then, the elevation angle error and range error at different altitude are corrected according to the error correcting theory for target positioning. The results indicate that the target elevation angle error and range error decrease as the visual angle increases at the same altitude. When the visual angle is 10o, the elevation angle error of the target at 10 km reaches 4.49' and the range error is 10.37 m. When the visual angle increases to 40o, the elevation angle error of the target at the same altitude is only 1.19' and the range error is only 2.80 m. These analysis results have a certain reference value for the correction of target positioning error.
Accurate forecast of atmospheric visibility is of great significance to air pollution control and public transportation safety. Based on the atmospheric visibility data observed by the National Meteorological Information Center from December 1, 2019 to September 23, 2020, ConvLSTM model and PredRNN model were used to forecast visibility over central and eastern China for 12 h in this work, and the forecast results of the two models were evaluated. The results show that PredRNN model performs better than the traditional ConvLSTM model in atmospheric visibility forecast, image quality evaluation index and forecast index. In addition, it is also found that compared with ConvLSTM model, PredRNN model has improved significantly in forecasting 4000 m medium-level fog area over time.
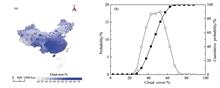
From the perspective of optical engineering application, the national cloud cover characteristics are studied, and the historical data of cloud cover in the main land areas of China in three aspects, namely, the overall average situation, the half-year change of warm and cold, and the diurnal variation, are analyzed in detail. The results show that the distribution of total cloud cover and low cloud cover in major land areas of China is basically less in the north and more in the south, and there are obvious differences in the distribution of cloud cover between the cold and warm half year, the site area where the cloud covers in the warm half year is higher than that in the cold half year is larger, and the cloud distribution difference between day and night is mainly reflected in the existence of a certaion amount of medium and high clouds in the low-value areas of low clouds during the daytime in western China.Then based on the analysis of the overall average, semi-annual and day-night variation of cloud cover, the classification of cloud cover regions in China is discussed, and it is shown that the 1 level areas suitable for optical engineering application are mainly in the north. This work is helpful to fully understand the suitable regions for optical engineering applications in whole country, and can provide support for further research on the quantitative impacts of cloud cover on optical engineering applications.
The simulation of light scattering characteristics of dust aerosol particles is mainly affected by shape models. Based on the size distribution information of dust aerosol particles provided by the Optical Properties of Aerosols and Clouds (OPAC) package, the light scattering characteristics of group dust aerosol particles are numerically simulated to study their wavelength dependency. Three incident wavelengths of 1064 nm, 532 nm and 355 nm are used for calculating the depolarization ratios of different super-ellipsoid dust particles, and the simulation results show the depolarization ratios of 0.317, 0.397 and 0.446 for each wavelength respectively. Compared with the lidar measurements, the simulation depolarization ratio at 1064 nm wavelength shows the highest consistence, followed by the simulation results at 532 nm wavelength. However, the simulation depolarization ratio at 355 nm wavelength has large bias with the lidar measurements, which may be caused by the same number of the dipoles used for all wavelengths and needs to be investigated in the future. The methodology and non-spherical models used in this study will greatly contribute to our deeper understandings on the wavelength dependence of the depolarization properties of the dust aerosol and guide the development of multi-wavelength polarization lidar. In addition, multi-wavelength polarization measurements will also provide a unique technique to study the mixing state and the evolution of the pollution aerosols.
To fully extract and fuse typical features of infrared and visible images, an image fusion algorithm based on spatial multi-scale residual network is proposed. Firstly, the source image is input into an encoder network composed of spatial multi-scale residual modules, and through the task of image reconstruction, the encoder network is trained to automatically obtain important features. Then, a feature pyramid and a channel self-attention are introduced, the output of basic layer and detail layer by the endoder are fused to reduce scale noise, and the fused image is reconstructed by the decoder. Finally, qualitative and quantitative experiments on public datasets are carried out, and it is demonstrated that the imporved algorithm outperforms the alternatives on highlighting infrared image targets and preserving visible image texture details. Compared with the DDcGAN algorithm, the standard deviation and average gradient of the proposed algorithm have been improved by 12.91% and 47.41%, respectively.
In order to study the characteristics of air quality changes and their influencing factors in Urumqi,China, during the strict prevention and control of COVID-19, the data of hourly air quality index (AQI), particulate pollutants (PM2.5, PM10) and gaseous pollutants (SO2, NO2, CO, O3) during the two strict epidemic prevention and control periods (January 26 to March 21, 2020 and July 20 to August 29, 2020) as well as before and after the two control periods in Urumqi in 2020, and in the same period of 2019, were selected for comparative analysis, the contribution of gaseous pollutants to the secondary synthesis of particulate matter was explored, and the quantitative detection of the factors affecting air quality was carried out using geographical detectors. The results show that compared with the same period in 2019, during the two epidemic prevention and control periods in Urumqi in 2020, PM2.5, PM10, SO2, NO2 and CO concentrations all show a downward trend, with a decrease of 36%, 55%, 10%, 18% and 49%, respectively. While compared with the two strict epidemic prevention and control periods, the AQI, particulate matter concentration and gaseous pollutant concentration in the pre and post epidemic periods of 2020, are generally higher. That indicates that the epidemic prevention and control measures acquired have reduced the concentration of particulate pollutants and gas pollution in Urumqi to some extent, leading to the improvement of the air quality. The single factor detection results show that CO and PM2.5 are the dominant factors in air pollution indicators, and the temperature has a relatively significant effect on air quality in meteorological factors. The interaction factor detection results show that air pollutants PM2.5 and PM10 have the most obvious effects on AQI under the interaction of the other factors, and the interaction of relative humidity with other factors in meteorological factors has a significant effect on AQI. So it is shown that the air quality of Urumqi city is the result of the interaction of multiple factors. This study provides a theoretical basis for the improvement of air quality and air pollution prevention and control in Urumqi.
Off-axis integral cavity output spectroscopy technology has the characteristics of simple experimental setup, high sensitivity and fast response time, and is widely used in various ultra-sensitive gas detection fields. As an important part of the system, the high reflectivity mirrors are one of the important factors affecting the accuracy measurement of the entire spectral system. A set of off-axis integral cavity output spectral measurement system was built with the radio frequency noise source. Firstly, the absorption spectrum line of CH4 gas at 6046.96 cm-1 was taken as the research target, and the reflectivity of the cavity mirror was calibrated under different pressures with and without noise sources. The results show that the reflectivity calibrated under two different conditions, with and without noise sources, is consistent, and the reflectivity tends to decrease with the increase of pressure. The calculated highest reflectivity of the lens is about 0.99992. Furthermore, the CH4 measurement signal at a concentration of 0.4 μmol/mol with and without noise sources was studied. It is found that after introducing noise sources, although the signal peak height is reduced, the signal-to-noise ratio is increased by about 1.3 times, and the minimum detectable concentration is 0.0045 μmol/mol, which indicates that the developed system can be effectively used for high sensitivity measurement of CH4 in atmospheric environment and industrial applications.