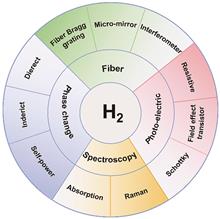
Hydrogen energy, recognized as a clean and renewable source, has progressed rapidly in recent years under the global initiative for energy conservation and emission reduction. Optical sensing has also advanced swiftly, offering high precision, fast response, low power consumption, and no arc generation issues. It has been widely applied in remote sensing, bio-detection, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. Our study focuses on optical hydrogen sensing technology. We begin by briefly elucidating the principal features of optical hydrogen sensing compared to other hydrogen sensing technologies. We then review the different mechanisms and device types within existing optical hydrogen sensing technologies. Subsequently, we analyze and discuss the developmental history, current research status, and prospects of various optical hydrogen sensing types, including spectroscopy, palladium-hydrogen phase change, optical fiber, and photo-electric composite types, as well as the challenges they face. We also explore the application requirements for different scenarios. Finally, we compare the main technical performance indicators of mainstream optical hydrogen sensors that have been reported and provide perspectives on the research directions and future development of optical hydrogen sensing technologies.
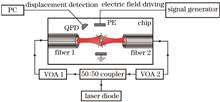
In a levitated optomechanical system, the electric charge on the captured particle affects the sensitivity of measurements for force, gravity, acceleration, mass, and electric field. In this study, we propose and design a dual-beam optical trap chip with integrated electrodes to measure the charge on trapped particles using both direct current signal-driven electric fields and alternating current signal-driven electric fields. We successfully measure the precise charge of 10 μm diameter silicon dioxide microspheres trapped in the chip using an all-fiber miniaturized system. The results show that both methods yield a charge number of 493 for the silicon dioxide microspheres, confirming the reliability of these charge measurement methods.
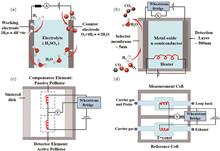
In recent years, researchers have integrated various detection mechanisms and investigated a series of optoelectronic detection technologies, aiming at online monitoring of hydrogen leakage in sealed hydrogen storage devices and hydrogen pipelines. This review categorizes direct and indirect detection methods and introduces recent advancements in detection technologies for hydrogen storage and transportation infrastructures. We conduct a comparative analysis to summarize the features and merits of each technology. Finally, we predict the prospects for the further development of optoelectronic detection technologies for the safe operation and maintenance of hydrogen storage and transportation systems.