Subdivision of rights-based land tenure reform aims at improving the integrity and security of land right bundles. This study theoretically and empirically investigated the impacts of both integrity and security of farmland on renting activities under the “three rights separation” institutional background. Data used in the study were collected from a survey in Liaoning Province that covered 811 households. The results show that: (1) Major influencing effects of tenure integrity and security on households’ decision making of farmland transfer are the transaction cost reduction effect and the value enhancement guarantee effect. The strength of influence depends mainly on whether tenure integrity and security can be transferred from the leaser to the tenant. (2) Households’ perception of integrity of different land rights has significantly different impact on households’ decision making of farmland transfer. Specifically, households with higher level of perceived integrity are more likely to participate in land renting activities. Households with a higher level of perceived tenure integrity of mortgage right are more likely to rent in land but less likely to rent out land. In contrast, households with higher level of perceived integrity of inheritance right are more likely to rent out land but less likely to rent in land. (3) Households’ perception of tenure security of different land rights has significant positive impact on households’ decision making of farmland transfer. Specifically, households who perceive land certificate to be crucial in protecting land rights are more likely to participate in land renting activities. Households who perceive high possibilities of land adjustment in the future are less likely to engage in land renting activities. To construct a feasible synergistic property rights governance system that integrates formal state property rights governance rules and informal village governance is necessary in order to promote the development of farmland rental market within the “three rights separation” land tenure reform institutional framework. From the state’s perspective, the right division rationale of land tenure reform and construction of relevant right protection system at the legislation level should be continued. At the village level, it is crucial to take actions to guarantee the fulfillment of land rental related contracts in addition to constructing the right protection system, and to relax constraints on channels for the right bundles transfer from the leaser to the tenant.
The confirmation of agricultural land right is the institutional basis for the orderly transfer of farmland management rights, and institutional credibility of land confirmation system determines whether it can effectively work. This study constructed the analytical framework of confirmation of land right-institutional credibility of land confirmation system-farmers’willingness to transfer land, then examined the influence of the confirmation of land right on farmers’willingness to transfer land and the moderating effect of institutional credibility of land confirmation system. The results show that: First, confirmation of land right is conducive to clarifying and stabilizing farmland property rights, and the duration of confirmed land right has a significant positive impact on farmers’willingness to transfer land. At the same time, the effect of confirmation is lagging behind, the longer the time period of confirmed right, the stronger the willingness of farmers to transfer land. Second, institutional credibility has a significant moderating effect. The effective impact of the duration of confirmed agricultural land right on the willingness of farmers to transfer land is stronger in areas where the institutional credibility of land confirmation system is higher, and the weaker the converse. Therefore, we must fully consider the collective recognition of local farmers on the institutional credibility of land confirmation system. In areas with high institutional credibility, it is necessary to further strengthen the effective link between the land right confirmation system and related supporting policies, cultivate and standardize agricultural land transfer market, and consolidate and strengthen the effect of agricultural land right confirmation. In areas with low institutional credibility, we can continue to stabilize the contracting relationship of agricultural land, improve the credibility of the system, and leave a certain room for the development of the agricultural land right confirmation system.
Since most of the land transferred among land rental markets is used for grain production, the effect of grain price decline is closely related to the agricultural modernization progress and the national food security in China. As one of the three staple grain crops, the price of maize experienced a significant decline during 2014 to 2016, which had an important effect on farmers’ land rental behaviors. In this study, we specifically explored the effect of maize price decline on farmers’ land renting decisions and ratio of non-grain crops with the random logit model and fixed effect model based on the three-period panel data of 621 households from 8 counties in Henan and Shandong provinces, and we got the following results. First, maize price had a significant effect land transfer, in which maize price decline increased farmers’ willingness to rent out land and decreased farmers’ willingness to rent in land, leading to the structure change among households that participated in the land rental markets. Second, rent-in households had heterogeneous strategies in dealing with the maize price decline because market-oriented rent-in grain producers enlarged the farm size by renting in more land, while non-market-oriented rent-in grain producers had no significant change in the area of land that they rented in. Third, the maize price decline aggravates the non-grain production problem by increasing the ratio of non-grain crops among rent-in households. We reached the conclusion that maize price decline can help to achieve large-scale grain production in China, but the increasing tendency to plant non-grain crops among rent-in households can have an adverse effect on the national food security.
Voluntary principle is an important basis for the implementation of the ongoing rural residential land exit. Encouraging farmers to voluntarily exit from the rural residential land is of great significance for realizing the goal of cultivated land protection and promoting urbanization. This study used 483 samples from a survey of the Wuhan metropolitan area as an example. By investigating the relationship between farmer differentiation and their willingness to exit rural residential land, and the intermediary role of value cognition of rural residential land and generational difference in the relationship between them, this study explored the impact mechanism of farmer differentiation on the willingness to exit rural residential land. The results indicate that: (1) The effect of farmer differentiation on the willingness to exit rural residential land include direct positive effect and indirect positive effect through value cognition of rural residential land. The direct effect accounted for 48.54% of the total effect, and the indirect effect accounted for 51.46% of the total effect. (2) Generational difference had a regulating effect on the intermediary role of value cognition of rural residential land. The intermediary role of the young generation of farmers was more intense. But the intermediary role of the old-generation farmers’ value cognition was weakened and tended to be inconspicuous. Therefore, this article put forward the following suggestions to promote farmers’ willingness to exit rural residential land: improving famers’ non-agricultural employment level; guiding farmers to form a reasonable value cognition of rural residential land; and formulating targeted policies and measures for different generational farmers to promote the rural residential land paid-exit.
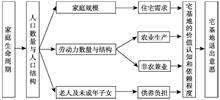
Family life cycle is an important factor that influences farming households’ behaviors and decisions. Examining the influencing factors of the willingness of farming households to exit from their rural residential land from the perspective of family life cycle is helpful to identify farming households’ different policy needs and pattern of change at different stages. This study analyzed the comprehensive impact and specific impact mechanisms of family life cycle on the willingness of farming households to withdraw from their homesteads, and conducted an empirical analysis using the survey data of farming households in typical areas of Sichuan Province. The result shows that the specific impact of family life cycle on the willingness to withdraw from a homestead is mainly reflected in three aspects: housing demand, division of labor, and support burden. There is a significant difference in farming households’ willingness to exit from rural residential land at different family life cycle stages, which appears in a N-shaped trend through the life cycle (low-high-low-high). In addition, there are differences in the key factors impacting the willingness to exit in different life cycle stages. Growing nuclear families are more concerned about children’s education and the accumulation of family capital; mature nuclear families are more inclined to migrating to an urban area, and extended families with young grandchildren are more concerned about the improvement of the ability to support the family. Therefore, under a consistent policy the government should adopt differentiated measures to respond to different farming households’ characteristics and their policy needs at different stages of the family life cycle.
In order to explore the effects of agricultural trade on land resources, this study analyzes the evolution of virtual land trade in relation to global agricultural trade, and reveals the driven factors behind the change trend by the trade gravity equation at the basis of virtual land calculation during 1986 to 2016. The results show that: the volume of global virtual land trade has increased by 1.74 times during 1986 to 2016, oil crops substitute the cereals and became the major categories of land exchange. The volume of virtual land exports increased rapidly in countries with abundant land resources, and countries with scarce land resources and rapid economic development became land importers. Population size, per capita income and trade agreements had a significant promoting effect on virtual land flow, but the impact of income varied in different economic development countries. The land and water resource endowment of the importers had a significant negative effect on the flow of virtual land, and the geographical distance between trading countries had a significant negative effect on the flow of virtual land. China has become the world’s largest importer of virtual land since 2004, and the volume of its virtual land import will continue to increase with the increase of income and shortage of agricultural resources. Thus China should take corresponding measures to ensure the sustainable supply of virtual land.
The purpose of this study was to explore the development of China’s overseas farmland investment activities. Based on the case statistics of GRAIN and Land Matrix, this study analyzed the change in spatial pattern and influencing factors of China’s overseas farmland investment development by means of literature review and spatial measurement. The results show that: (1) The overall spatial agglomeration effect of China’s overseas farmland investment began to appear after 2004, and obvious spatial differentiation has been formed locally at present. Russia and Southeast Asia have become high-high agglomeration areas; (2) The spatial variation range and degree of influence of China’s overseas farmland investment activities have undergone a process of volatile increase. The spatial variation from northwest to southeast is the most significant, and internal factors of host countries have become the key; (3) The development of China’s overseas farmland investment is significantly affected by geopolitical, geo-economic, and geo-cultural factors, including the proportion of agricultural land in the host country, the level of grain yield, the number of statements, declarations, and bulletins jointly issued with China, the number of visa-free documents of China, and the number of consular agencies in China are the six statistically significant indicators. In a situation that China’s overseas farmland investment scale has been spatially different and stable, relevant institutions should pay more attention to the protection and planning of investment for Southeast Asia and Russia.
In China’s industrial development, land elements have long been used in a disorderly, extensive, and inefficient manner. In the context of economic transformation, it is of great significance to explore the mechanism of globalization, marketization, and decentralization in the use efficiency of urban industrial land. In this study, urban industrial land use efficiency was measured by a stochastic frontier production function model for the Yangtze River Economic Belt from 2007 to 2016. Also, spatial statistical method was used to explore the spatial heterogeneity of urban industrial land use efficiency. This study analyzed the influence of economic globalization, marketization, and decentralization on the use efficiency of industrial land under the background of economic transformation. The results of the study show that: from 2007 to 2016, urban industrial land use efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt was relatively low, but showed an upward trend. The spatial distribution of urban industrial land use efficiency in the region presented a agglomeration trend, with the high is in the northeast and the low in the southwest, showing obvious spatial non-equilibrium. Industrial land use efficiency hot spots showed a significant spatial polarization phenomenon. The regression results show that under the background of economic transformation, globalization has promoted the improvement of industrial land use efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic belt through the increase of foreign investment.Through the improvement of land marketization, it also has a positive effect on the industrial land use efficiency. Decentralization has a negative effect on the industrial land use efficiency. Based on this, the following suggestions are put forward: Cities along the Yangtze River Economic belt should adjust measures to local conditions and improve the utilization efficiency of foreign investment,promote the market-oriented reform of industrial land and implement differentiated policies for the supply of industrial land.
Using the land cover data of the Tibetan Plateau in 1992, 2001, 2008, and 2015 and ArcGIS 10.5 and Fragstats 4.2 software, this research built an ecological risk index based on landscape pattern and landscape vulnerability, and used geo-statistical analysis and spatial autocorrelation analysis methods to conduct an ecological risk assessment for the Tibetan Plateau, then analyzed the spatiotemporal characteristics of landscape ecological risks. It provides a scientific basis for the prevention of land use ecological risks of the Tibetan Plateau. The results show that: (1) The distribution of landscape ecological risks on the Tibetan Plateau has an spatial aggregation effect. On the whole, the risk in the northwest is high, while it is low in the southeast. The spatial distribution of landscape ecological risks is closely related to the natural terrain of the Tibetan Plateau, which is mainly affected by the geographical conditions. (2) From 1992 to 2015, the landscape ecological risks of the Tibetan Plateau showed a downward trend, which is mainly manifested in the reduction of the high and the medium-high risk areas, and the expansion of the low and the medium-low risk areas. The main reason for this change is the influence of the warming and wetting process of the Tibetan Plateau and ecological construction on the land cover structure since the 1990s. (3) There are significant differences in the distribution and characteristics of landscape ecological risk change on the Tibetan Plateau. The regions with higher landscape ecological risk values mainly exist in the marginal areas where different terrains meet. Forest land has the highest proportion of low ecological risk areas, while barren land, glacier, and snow cover have the highest proportion of high ecological risk areas. The declining rate of barren land with high ecological risk grade was the highest, followed by grassland, which reflect that the change of barren land and grassland had the most significant impact on the landscape ecological risks of the Tibetan Plateau.
Taking China’s carbon trading policy introduced in 2011 as a natural exogenous shock, this study used the micro-enterprise data from 2010 to 2018 to construct a quasi-natural experiment. The triple difference model and multiple mediating effect models were used to examine the impact of this policy on the economic performance of highly polluting industrial enterprises, and to verify whether carbon trading policies can achieve economic dividends and its transmission mechanisms. The results show that: (1) Carbon trading policy significantly improves the economic performance of high-pollution industrial enterprises and realizes economic dividends. (2) Mechanism test shows that the carbon trading policy can indirectly affect the economic performance of highly polluting industrial enterprises through the low-carbon subsidy support effect, corporate benefit incentive effect and R&D innovation dynamic effect. Enterprise benefit incentive effect and innovation motivation effect show positive effects, while the support effect of low-carbon subsidies shows a concealing effect. (3) The heterogeneity analysis shows that, in terms of the overall effect, carbon trading policy has a better effect on the economic performance of non-state-owned enterprises and small-scale enterprises. As for the mediating effect, the whole mediation effect of carbon trading policy on the economic performance of state-owned enterprises and large-scale enterprises is obvious, and there are only some significant parallel and chain-mediated mediation effects on the economic performance of non-state-owned enterprises and small-scale enterprises. This study makes a beneficial supplement to the theoretical construction of China’s carbon market from a micro perspective, and provides data support and policy suggestions for the differentiated implementation of carbon trading policies and the design of emission reduction and efficiency enhancement mechanism for highly polluting industrial enterprises.
Using the provincial panel data from 1991 to 2017 and the stochastic frontier analysis (SFA) method, this study measured the technical efficiency of chemical fertilizer application in 28 provinces (municipalities, autonomous regions) in China. The study found that the technical efficiency of chemical fertilizer use for agricultural production in China had shown a growing trend in the study period. The average technical efficiency of chemical fertilizer application in all regions from 2015 to 2017 was significantly higher than that of 1998-2014 and 1991-1997. The technical efficiency of chemical fertilizer application in the eastern region was significantly higher than that in the western and central regions; Using Moran’s I index analysis, we also found that there is a spatial correlation between the technical efficiency of chemical fertilizer application in various provinces (municipalities, autonomous regions) in China. In addition, this spatial correlation is becoming increasingly more significant over time. Finally, we used the spatial Dubin model to analyze the influencing factors of the technical efficiency of chemical fertilizer applicationthe results show that the proportion of labor non-agricultural employment has a significant negative impact on the technical efficiency of chemical fertilizer application. The level of farmers’ income has a positive spillover effect, while the urbanization rate has a negative spillover effect. In the future, in the process of agricultural production, all regions should not only pay attention to the development within the region, but also strengthen interregional cooperation and exchanges.
Limited by the capacity of growth of agricultural production in China in recent years, reducing postharvest losses has become an important measure to increase the food supply. For a long time, farmers store grains in their households in China for household food security, but compared with developed countries, their storage skills and facilities are limited. In order to solve this problem, the Chinese government has implemented the Scientific Grain Storage Project to improve farmers’ home storage conditions and reduce the storage losses. Based on the survey data of 1202 households in 23 provinces in China, this study used the propensity score matching method to assess the impact of adopting silos and warehouses on households’ maize storage volume and storage losses. The result shows that the silos and warehouses significantly increased the households’ maize storage, and the average maize storage reached 4655.30 kg, which is 1188.87~1368.55 kg higher than non-adopters, and it alse extended the period of maize storage for 0.2 quarter. The advanced storage facilities also reduced the degree of rodent damage in the maize storage, reducing maize storage losses by 60%, and allowing farmers to save 28 to 33 kg of maize. Adopting the advanced facilities reduced the maize storage loss rate from 2.75% to 0.87%. From the policy perspective, the government should continue to implement scientific grain storage projects and encourage farmers to adopt advanced grain storage facilities.
With the development of the Chinese economy, the supply of some resources is insufficient. Therefore China’s resource enterprises hunt for natural resources by cross-border mergers and acquisitions (cross-border M&A), which occurs in many host countries with different institutional quality. Based on the perspective of host country institutional quality, this study examined the influence of political stability, government efficiency, and legal system on the location choice of Chinese resource enterprises’ cross-border M&A, with a sample of 406 cross-border M&A events for Chinese resource enterprises in 29 countries. The results show that: (1) Political stability and government efficiency have a significant positive impact on the cross-border M&A, while legal system has a significant negative impact, and resource intensity has a regulatory impact on the institutional quality; (2) The location choice of oil and gas enterprises is mainly positively influenced by political stability and negatively influenced by legal system, while the power industry is mainly positively influenced by political stability and government efficiency; (3) The three kinds of institutional quality significantly affect the location choice of state-owned resource enterprises’ cross-border M&A, while only political stability has significant effect for non-state-owned enterprises. Chinese resource enterprises could pay more attention to the institutional quality during cross-border M&A, and try to choose the target country with stable political environment and high government efficiency in the future.
The imbalanced development of China’s agricultural modernization among different regions is very disadvantageous to the comprehensive realization of China’s agricultural modernization. Therefore, it is of great significance for the coordinated development of China’s agricultural modernization to explore and study the spatiotemporal characteristics and regional imbalance of China’s agricultural modernization. In this paper, from the modernization of agricultural production, agricultural modernization management, quality of agricultural modernization, rural social economic modernization, the modernization of agriculture ecological environment five dimensions to build agricultural modernization evaluation index system, by using variation coefficient method, determining the weight to the level of agricultural modernization in China in 2004-2017 to measure and evaluation, analysis of the characteristics of space and time and the restricting factors of agricultural modernization in China. The research shows that: (1) From 2004 to 2017, the level of agricultural modernization in China and various regions has been gradually improved, but the difference between the level of development and the speed of improvement is obvious. (2) The contribution rate and driving effect of each subsystem on the overall development of agricultural modernization in different regions are significantly different at different stages, resulting in the unbalanced development of agricultural modernization in each region; (3) For the development of the regional agricultural modernization of the main factors in 2004-2017: the eastern region to the low level of modernization of agricultural production subsystem development, the central region the low level of development, modernization of agriculture ecological environment subsystem in the western region agricultural modernization quality benefit subsystem development level is low, the rural social economic modernization in northeast China subsystem development level is low. It can be seen from the temporal and spatial characteristics of China’s agricultural modernization development: from 2004 to 2017, the development level of agricultural modernization has been gradually improved, but there are obvious regional differences in the development level of agricultural modernization, leading to different regional constraints affecting the development of agricultural modernization. Finally, the paper puts forward some policy Suggestions to realize the balanced development of agricultural modernization.
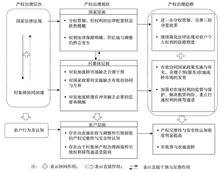
The development of a diversified ecological compensation system is an important task of China’s ecological civilization construction in the new era. Developing a market-oriented ecological compensation mechanism for tourism contributes to enriching and improving China’s ecological compensation system. Based on the literature review and an ecological-economic analysis framework, this study summarized the government-led and community-based tourism ecological compensation, and clarified the connotation, characteristics, and stakeholders of tourism market-oriented ecological compensation. We then explored the operation mechanism of tourism market-oriented ecological compensation. The results show that: tourism market-oriented ecological compensation forms an ecological tourism supply-demand docking platform, which has the characteristics of realizing the value of ecological resources through market transactions, endogenousness and feedback loops, and diversified participants. Tourists, tourism enterprises, community residents, and local governments are the main stakeholders of the platform. Its operating mechanism is that based on cooperation and investment, community residents and tourism companies convert the natural resources and ecosystem services into ecological tourism products, then tourists purchase the eco-tourism products and services to form direct and indirect compensation for the tourism enterprises, community residents, and destination ecosystem, thereby developing a sustainable market-oriented compensation path of “transaction-profit-incentive-transaction”. The prerequisite of the operating mechanism is to determine the property rights of resources, the key is to realize the ecological value of resources, the core is the interactive incentive for the transaction of ecological service functions, and government regulation is an important guarantee in the multi-party game.
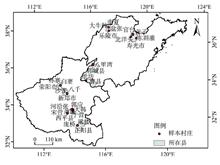
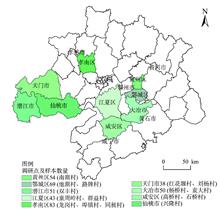
Tourism poverty alleviation is an effective way to get rid of poverty in poverty-stricken areas in rural China. As an important poverty alleviation model, The economic efficiency of scenic spots in driving surrounding farmers to participate in tourism directly affects the effect of poverty alleviation in poor areas. In this study, farmers in key poverty alleviation villages around 3A and above scenic spots in the Qinling-Daba Mountains were used as the research objects, and the data envelopment analysis (DEA)-Tobit model was used to analyze the economic efficiency and influencing factors of farming household participation in tourism under the model of tourism-led village poverty alleviation. The results show that the overall economic efficiency of farming household participation in tourism around the scenic spots is low, but it is higher than the agricultural production efficiency of farming households, and 98.3 percent of farming households is mainly restricted by scale efficiency; Farming households’ tourism management is in the stage of increasing returns to scale. Increasing the factor input of tourism operation is the main way to improve scale efficiency; the characteristic variables of farming households have the most significant impact on tourism economic efficiency, followed by the variables of individual characteristics, and the influence of community characteristics is not significant. Based on these results, this article makes specific suggestions for improving the tourism economic efficiency of farming households: (1) Extend the tourism industrial chain of “tourism-led village poverty alleviation”, and expand the scale of investment to achieve the optimal combination of factors; (2) Increase human capital investment and improve technical management level; (3) Farming households should be differentiated to promote specialized community participation.