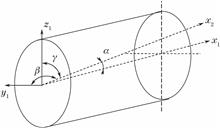
A pre-labeling method for the reconstructed image position of a diffuse reflector in the reconstructed plane is proposed. Firstly, a hologram is obtained by using the specular reflected light of a specific area on the object as object light, and the area where the +1 st-order reconstruction image is located is pre-marked. Then, without changing the position of the object, the object light emitted by the diffuse reflector on the object is holographically recorded, and weak diffuse reflection is extracted from the original pre-marked area. By changing the inclination of illumination light and combining FIMG4FFT method, the three-dimensional contour of the object at a specific viewing angle is obtained. After obtaining the three-dimensional contours at multiple viewing angles, the problem of solving non-linear equations is transformed into an optimization problem by using particle swarm optimization (PSO) to solve the stitching parameters, so as to achieve the final stitching of the three-dimensional object contours at multiple viewing angles in cylindrical coordinates. The error calibration experiment shows that the maximum relative measurement error is 5.6%. The proposed method can successfully acquire and stitch the threaded surface with multi-view and three-dimensional contours, and realize the three-dimensional holographic display of rotary parts.
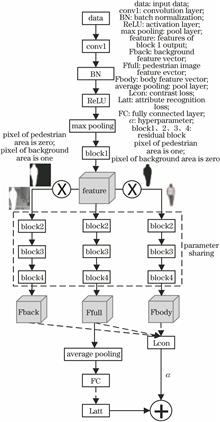
In this study, we propose a pedestrian attribute recognition method based on background suppression to solve the problems of background clutter and object occlusion associated with the monitor scene. The proposed method can reduce the impact of the background on pedestrian attribute recognition. First, three branches are generated by improving the convolutional neural network. These three branches are used to extract the features of the pedestrian images, human body regions, and background regions. Then, the regional contrast loss function and weighted cross-entropy loss function are considered to constitute the joint cost function of the network. The features learned by the neural network exhibit background clutter invariance under the constraint of the joint cost function. Therefore, the proposed method can improve the pedestrian attribute recognition accuracy. The proposed method was verified using the PETA and RAP pedestrian attribute datasets. The results denote that the proposed method exhibits improved the mean accuracy, accuracy, precision, and other performance indicators when compared with those exhibited by the remaining methods, confirming its effectiveness.
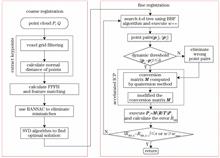
Registering highly efficient and accurate point clouds with strong noise and inhomogeneous density remains a challenging task. In this paper, we propose a point cloud registration algorithm based on keypoint extraction and the improved iterative closest point (ICP). In coarse registration, we first fused the voxel grid filtering and normal distance keypoint extraction and then computed the fast point feature histogram of keypoints for feature matching. Then the random sampling consistency (RANSAC) algorithm was estimated and optimized by correspondent relation for eliminating mismatches. In fine registration, we implemented the best bin first (BBF) algorithm to search for the nearest point of k-d tree and set the dynamic threshold to eliminate wrong point pairs. Finally, we used the improved accelerated ICP algorithm based on the “point-to-triangle plane” model to obtain the registration vector. By registering the model point cloud and building point cloud, we compared the proposed algorithm with other commonly used algorithms. The results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm is robust against noise, and in particular, the running speed and registration accuracy are enhanced.
In this study, we propose a subgraph learning method based on the Markov chain Monte Carlo framework. Further, we obtain an iterative process with respect to the subgraphs in the state space by constructing a Markov chain and optimal subgraphs for matching to effectively improve the graph matching precision and reduce the impact of the discrete values. During this process, the proposed method can effectively save the pairs of matching points under one-to-one matching constraints, avoiding the influence of the discrete and distortion values. Furthermore, the experiments are conducted with respect to the synthetic image dataset, real image dataset, and three-dimensional model dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method is superior in the graph matching process.
Based on naked-eye three-dimensional display technology with LED screen, this paper proposes a method for improving the reconstruction spatial resolution of integral stereo imaging system by using time division multiplexing technology, which solves the problem of low resolution caused by the divergence of the pixel point source of the LED screen and the excessive spacing between the adjacent pixels. By studying the illumination principle of LED display devices, we analyze the factors affecting the spatial resolution of the reconstructed image and the influence factor of reconstruction resolution of imaging system is obtained. Therefore, when the LED display array is unchanged, the time division multiplexing technique can effectively extract the pixel information around a single pixel point and finally improves the spatial resolution of the reconstructed image. The theoretical analysis and experimental verification of this method show that the proposed method effectively improves the resolution of the reconstructed image of LED display and meets the requirements of improving the resolution of integral imaging reconstruction.
The accuracy of current road extraction algorithms for high resolution remote sensing images is low. Aiming at this problem, a road extraction algorithm for remote sensing images based on the improved expectation-maximization (EM) clustering is proposed. First, the morphological preprocessing is carried out to remove the interference information from the road. Then, the improved EM clustering is applied to determine the number of segmentation regions and segment the images automatically. And the extraction of roads from remote sensing images is finally completed through the contour detection and gray histogram thresholding. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively screen the noise on the road and extract the main road information, with high accuracy of over 90% and low redundancy.
We propose a method based on nonsubsampled shearlet transform (NSST) and parameter-adaptive simplified pulse coupled neural network (SPCNN) for underwater polarization image fusion. Firstly, the degree of linear polarization and polarized light intensity images of underwater objects are acquired. Then NSST decomposition is performed on the two images to obtain their multi-scale and multi-direction subband coefficients. The high frequency direction subband coefficients of the two images are fused by the parameter adaptive SPCNN model. The low frequency subband coefficients of the two images are fused by an adaptive weighted fusion method based on regional energy. Finally, the fused image is reconstructed by inverting NSST to the high frequency direction subbands and low frequency subbands. Experimental results show that compared with other polarization image fusion methods, the proposed method can detect more details and significant features of underwater objects, and improve subjective visual perception and objective evaluation.
The quality of a depth map generated by coarse features which are predicted by convolutional neural networks (CNNs) is low. Meanwhile, strong-supervised methods strictly limit the data volume due to lack of labeling. To address these problems, an unsupervised monocular depth estimation method by fusing dilated convolutional neural network and simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is proposed. This method adopts the idea of view reconstruction to estimate depth. Photo-consistency error is utilized in the method to constrain training, expand the field of view, and concern the image details. Traditional SLAM algorithm functions to globally optimize the camera pose and incorporate it into the reconstruction framework. Finally the straight correspondence between the input monocular image and its depth map is exploited. The method is evaluated on the public KITTI dataset. The evaluation results show that, compared with the classical sfmlearner method, the error indicators, including absolute relative difference, squared relative difference, root mean squared error, and log root mean squared error, decrease by 0.032, 0.634, 1.095, and 0.026 respectively, and the accuracy indicators, δ1, δ2 and δ3, increase by 3.8%, 2.6%, and 0.9% respectively. The availability and robustness of the proposed method are verified.
In order to solve the problem of inferior recognition accuracy for small objects, a object detection algorithm guided by dual attention models is proposed. The method is based on the realization principle of single-stage detection algorithms, and introduces two attention models to improve the detection performance, especially for small objects. Specifically, a multi-scale feature cascade attention module is first introduced into the convolutional neural network, which weights the importance on different regions of the original convolutional neural network's feature map to reduce the interference of background and negative object information in the feature map, especially highlighting the small objects effectively in the shallow feature map. Besides, dense connection alleviates the problem of gradient disappearance in the process of back propagation. A salient channel self-attention module is introduced for the fused features, which focuses on the difference among different channels of the feature map so as to screen out useful channel information, thus making the feature map to be detected more representative. In addition, the experiments on COCO benchmark dataset of object detection verify the effectiveness and advancement of the proposed method.
Aiming at the existing remote sensing aircraft image detection methods based on deep learning, which require a large number of tagged data sets and a long training time, we propose a semi-supervised learning method based on generative adversarial networks (GANs). Two granularity deep-learning generative adversarial networks are used to get the edge feature and deep semantic feature information. By combining these two discriminator networks of the GANs, we design the object detection model. The experiment shows that the proposed method has a faster training speed and less labeled dataset is needed during the training process.
Because of the high missing rate and low accuracy of Tiny YOLOv3 algorithm in the detection of abnormal escalator behavior, an improved Tiny YOLOv3 network structure is proposed for the detection of abnormal escalator behavior. K-means++ algorithm is used to cluster the target boundaries in the data set. The a priori parameters of the network are optimized according to the clustering results to make the training network have a certain pertinence in abnormal behavior detection. The network structure of feature extraction is deepened by using multi-layer deep separable convolution to extract deep semantic information. A scale is added to fuse low-level semantic information to improve the structure of the prediction layer of the original algorithm. Finally, the GPU is used for multi-scale training. The optimal weight model is obtained to detect the abnormal behavior of escalators. The experimental results show that compared with Tiny YOLOv3, the optimized model improves the missed detection rate by 22.8%, the detection accuracy by 3.4%, and the detection speed by 1.7 times. It gives better consideration to the accuracy and real-time performance of the detection.
Aiming at the problems of the halo phenomenon and inaccurate selection of atmospheric light values in dark channel prior algorithm, an image dehazing method based on dark channel compensation and improvement of atmospheric light value is proposed in this paper. In order to weaken the halo effect at the edge of the image scene, a solution based on the dark channel compensation model is proposed first, the halo region is identified by the weighted channel difference method, and then the dark channel values of this region are modified by corrosion, fusion, and other treatment. It is linearly fused with the original dark channel images to compensate the dark channel. For the problem of inaccurate selection of atmospheric light value, the quadtree segmentation method is improved, with the strategy of adjacent region comparison added. Hence, the proposed method can obtain more accurate atmospheric light values, leading to more clear and natural restored images with more details. Finally, the haze-free image is restored by means of the atmospheric scattering model and the optimized transmittance. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively remove the halo effect and obtain the atmospheric light value accurately.
The difference in size between different kinds of objects will lead to the difference in summed volume region (SVR) of corresponding laser point cloud. In the first frame, object recognition is accomplished based on SVR selection and global feature matching to automatically select the interested object. The performance and execution time of four global feature descriptors are compared. After obtaining the position of the interested object in the first frame, an object tracking method based on global feature matching processing of laser point cloud is put forward for subsequent frames. The experimental results show that adding SVR selection is helpful to improve the accuracy of recognition and tracking and the overall running speed of the algorithm.
Existing hyperspectral image classification methods focus on using spatial information without considering the continuity of ground object in spatial distribution. Based on this, this paper proposes a space-spectrum weighted nearest neighbor hyperspectral image classification algorithm. By constructing the neighboring space of the test sample points, the spatial neighboring points in the neighboring space that are inconsistent with the test sample labels are filtered to further remove the interference of heterogeneous points in the neighboring space towards the classification of central pixels and improve salt and pepper effect. According to the spectral similarity between the spatial neighbors and the test pixels, different weights are assigned to the spatial neighboring points, which increases the similarity between similar pixels and the difference between the heterogeneous pixels. The distance between the training sample and the test sample neighboring space is obtained by introducing the regularization coefficient, and the training sample label with minimum distance is selected as the label of the test sample. The overall classification accuracies by this method on the Indian Pines and PaviaU hyperspectral datasets reach 96.75% and 98.54%, respectively, which are higher than those by other algorithms listed in the paper.
This paper proposes a system for eliminating the influence of fog on optical imaging of vehicle recording equipment, the visual effect of the image acquisition by the vehicle-mounted equipment is improved, and the subsequent extraction and application of information in the image can be optimized. The designed dual-mode mist dissipating system includes two parts: hardware and software, the hardware is a mechanical defogging structure based on the physical heat dissipation effect and the software is an image processing algorithm based on the atmospheric scattering model estimation. It can better ensure the clarity and details of the vehicle recorded image under different humidity conditions, and has the advantages of real-time processing and adaptive feedback, which make it suitable for commercial applications.
Aiming at solving the problems of color and contrast distortions in traditional dehazing algorithms, we propose an image dehazing algorithm based on multi-scale fusion and adversarial training. The multi-scale feature extraction block is used to extract haze-relevant features from different scales, and the residual-and-densely-connected block is used to realize the interaction of image features and avoid gradient vanishing. Because the algorithm is not based on the atmospheric scattering model and directly fuses the shallow and deep features of the image in the multi-scale manner, so it overcomes the inaccuracy of physical model. The dehazing network is trained via the generative adversarial mechanism, the generator uses the multi-scale feature extraction block and the residual-and-densely-connected block to estimate the haze-free image, and the discriminator consisting of two sub-networks with different receptive fields carries out the adversarial training. Comparison experiments on the RESIDE (Realistic single image dehazing) dataset show that the dehazed images generated by the proposed algorithm are more visually pleasant than those by other algorithms in terms of full-reference and no-reference visual quality indicators.
Aiming at the industrial images with uneven illumination interference, a local threshold segmentation method based on multi-direction grayscale wave for image is proposed in this paper. First, the image is pretreated with mean filtering. Then, one-dimensional grayscale wave curves are extracted in four-direction of horizontal, vertical, left diagonal and right diagonal. Meanwhile, one-dimension local threshold segmentation is carried out for wave peaks and troughs which satisfy the threshold condition of wave amplitude on each curve. Finally, an and operation is processed for segmented sub-images, the final segmented image is obtained. The experimental results show that this method can effectively improve the segmentation accuracy of images with uneven illumination. Compared with two-dimensional Otsu, two-dimensional Tsallis and Niblack methods, the segmentation effect of the proposed method is significantly improved.
Aiming at the characteristics of high dimensionality of the hyperspectral image data, nonlinearity of the feature and difficulty of obtaining the tag data, combined with the stack sparse automatic coding network, we propose a two-level classification algorithm based on nonlocal mode feature fusion. Compared with the traditional stack sparse automatic coding network, the spectral angle matching algorithm stacks the spectral information found most similar to the classified pixel to form new spectral information, and puts it into the SoftMax classifier for first-level classification. The pixels satisfying the condition are added to the training data set for classification training of the stack sparse coding network. Finally, the classification algorithm is modified according to the spatial neighborhood information to make the classification result more smooth. Compared with other classification algorithms, it is found that the improved classification algorithm has higher accuracy and can effectively improve the classification effect of hyperspectral image.
This paper proposes a new linear laser phase-locked thermal imaging technology for surface crack instantaneous imaging detection of semiconductor chips. The technical system consists of a linear scanning laser source, a high-speed infrared camera, and a control computer. The surface of the target chip is scanned by a linear laser beam and the thermal wave propagation is measured by an infrared camera. A new visualization algorithm without baseline crack is proposed. Because cracks can cause thermal wave blocking, they can be visualized and diagnosed automatically, which is independent of baseline data obtained from the original state of the target chip. The microcracks of the chips generated in the manufacturing process are studied. The experiments demonstrate that the visualization of cracks with a width of tens of micrometers can be realized by the laser phase-locked thermal imaging technology.
This paper presents a driving behavior recognition model based on tutor-student network. Considering that driving behavior occurs in a local area, this paper divides the task of driving behavior recognition into two sub-tasks: action location and action classification. Aiming at the task of action location, a tutor network with shallow network layer receiving high-resolution image input is designed. The tutor network weakens the action area according to the response of feature map. On the basis of action location and action classification task, a student network with deeper network layer is designed to receive the input of low-resolution action area image. High-level semantic features which are extracted from student network are used to achieve high accuracy classification. Experimental results show that the tutor-student network model can bring high recognition accuracy and strong robustness.
An improved hyperspectral unmixed initialization method (IISSF) based on non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) combining Euclidean distance and spectral information divergence is proposed. On the basis of initialization, a parallel comparison experiment is performed in combination with the standard NMF algorithm and the block NMF algorithm. The results show that, in the synthetic image experiment, the block NMF algorithm after IISSF initialization is better than other methods in the signal-to-noise ratio range from 20 dB to 50 dB. There is a minimum average spectral angular difference between the end-member spectrum obtained in the real image experiment and the reality image endmember spectra, i.e., 0.1812. The root mean square error between the reconstructed image and the real image is the smallest, i.e., 0.007.
In this study, we propose an efficient network computing method based on Johoson’s image style transformation network model to optimize the original residual network for ensuring suitable network performance. The conducted experiments prove that the proposed method can solve the following problems: high storage and calculation cost associated with the image style transformation network model; massive consumption of the computing resources; and difficulty with respect to the transplantation to a mobile terminal without reducing the image quality.
In this study, a novel image-processing algorithm to identify flame regions in the foreground based on the combination of the RGB, YcbCr, and seeded region growth (SRG) algorithms is proposed. First, the conventional YCbCr algorithm is improved by incorporating the relationship between the red (R channel) and luminance (Y channel) components. Accordingly, the interfering noise corresponding to the reflective and non-reflective images can be removed. Moreover, in the case of noise-corrupted images, the interference associated with initial image segmentation can be eliminated. By estimating the centroid weight of the connected region, the seed can be automatically determined, resulting in region growth for the color-segmented images, which can facilitate fine segmentation. By analyzing the static and dynamic characteristics of a flame, the variation coefficients of the area and perimeter and the ratio of the centroid movement distance can be calculated. On this basis, a flame region can be distinguished from non-flame regions such as road lamps and candles. The experiment results indicate that the proposed method can not only be used to mitigate deficiencies of the individual algorithms that provide low accuracy, but can also be applied to simultaneously recognize the reflective and non-reflective regions to reduce interference and prevent inaccurate recognition.
A defect detection method based on wavelet domain signal catastrophe-points capture is proposed to address the difficulty of detecting minor defects on solar cell. The method, based on one-dimensional discrete signal, captures signal catastrophe-points through catastrophe-points detection on the image column by column in the wavelet domain, and corrects it with the energy centrobaric method so as to obtain the normal background of the defect image, which is finally fused with the original image by simple algebraic algorithm to highlight the defected area. Experiments show that the method is effective for detecting various defects on the surface of solar cells.
Polarimetric dehazing methods have shown advantages of excellent detail recovery capacity and color restoration. To improve the dehazing capacity of polarimetric dehazing methods, we propose a new polarimetric dehazing method. It utilizes discrete cosine transform to construct the image pyramid and then build the Laplacian pyramid. Each level of the Laplacian pyramid is dehazed by the polarimetric dehazing method, and the dehazed image is reconstructed from the handled Laplacian pyramid. The experiment results show that compared with the traditional polarization optical dehazing method, the proposed method can achieve the comparable or better dehazing images, and shows good dehazing capacity. The proposed method is significant for the further improvement of polarimetric dehazing method.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a technique that uses the principle of scattered light coherence for imaging, with features of no destruction, fastness high resolution, and cross-sectional imaging. The identification of physical evidence requires as far as possible to extract, inspect, analyze and obtain valuable information without destroying its original state. As an optical inspection technology, OCT can meet these requirements. It can realize real-time, in-situ and non-destructive imaging without pre-processing the sample, which is of great significance in physical evidence identification. We introduce the working principle of OCT and its application in the field of physical evidence identification.
Conventional imaging systems have large thickness and high operating cost because of requiring lenses such as convex lenses. To make imaging systems with lower operating cost and better compactness, lensless imaging systems have developed rapidly, such as lensless microscopes. Here, a polarizer is used to achieve polarization information and double-sided transparent tape instead of convex lenses is used to collect object morphologic information. A lensless polarization computed imaging system is constructed and described in detail by combining computational imaging technique. The system is introduced systematically. Its functionality as a camera is demonstrated experimentally; the acquired polarized images comply with the Marius polarization law. The lensless polarization imaging system based on scattering components can reduce the camera thickness and cost, and can be applied to acquisition of polarized images.
We propose an improved convolution neural network based on LeNet-5 to address the problems of large computation and over-fitting in the full convolution neural network based method for eliminating noise of seismic data. The network of the proposed method consists of two convolution layers, two pooling layers, and one full output layer, in addition to the input layer. By using the experimental selection method of minimum error, the parameters of the first convolution layer and the pooling layer in the single-layer convolution network are determined. Then the parameters of the second convolution layer and the pooling layer are determined based on the parameters of the first layer. Finally, 12000 seismic data with size of 32×32 are used as inputs to train LeNet-5, and 1000 seismic data with the same size and signal-to-noise ratio are used for testing the system. Experiments on pre-stack and post-stack seismic data from Marousi2 model demonstrate that the proposed method has good denoising effect for horizontal and inclined in-phase axis seismic data. Compared with the singular value decomposition algorithm, BP (back propagation) algorithm, and algorithm in Ref. [9], the proposed method has better denoising effect.
The segmentation of point cloud data is an important link in the process of model reversal. The quality of segmentation affects the efficiency and accuracy of model reconstruction. The parts with complex micro-surface are composed of several small graphics side by side and cross-combined. It is difficult to simplify feature points and identify elements, which is a difficulty in point cloud data segmentation. According to the modeling characteristics of the model, the lower boundary points of the banded feature points are separated as the real feature points of the fitting feature line, and the elements belonging to the same graph are identified by the proximity of the end points of each element and the arrangement trend of the feature points near the end points. The regional growth algorithm with boundary constraints and the triangle cross product algorithm are used to segment the point clouds on the same surface. The experimental results show that this method can overcome the problems of excessive segmentation and insufficient segmentation when dealing with complex micro-surface point clouds, which lays a foundation for high-quality model reconstruction.
A laser projection system for wireless light transmission is designed and an modified YOLOv3 (you only look once, v3) network based on deep learning is proposed to detect the location of mouse images. The network first uses packet convolution to compress network parameters to increase target detection speed, and then uses channel shuffle to enhance the network's information flow capabilities. The ratio between the positive sample and the negative sample is adjusted by two hyperparameters on the cross entropy loss function to reduce the weight of the easily classified sample in the loss function, and the detection accuracy is improved. The experimental results on the PASCAL VOC2007 and the self-made mouse image datasets show that the proposed detection algorithm based on the improved YOLOv3 network has a detection accuracy of 90.3%, which is superior to the traditional network structure in terms of detection speed and detection accuracy. The laser projection system using the algorithm can detect moving mouse targets in real time and perform optogenetic experiments such as wireless light transmission.
Aiming at the problem that nonuniform cloud is difficult to remove effectively by using single algorithms for high resolution remote sensing satellite images, an optimization algorithm based on image segmentation and improved dark channel prior method is proposed. The original cloud image is segmented into a dense fog area and a thinner fog area by the image segmentation technique. The dense fog area adopts weighted multiscale Retinex algorithm to realize local enhancement and remove the fog. The thinner fog area adopts the improved dark color method, transforming the dark color image defogging model from RGB color space to HSI color space, extracting the luminance component, and obtaining accurate atmospheric optical values. The atmospheric transmittance is optimized by the tolerance mechanism, and the defogged image is obtained by enhancement of the automatic gradation method. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can restore image details and recover image color and clarity effectively.
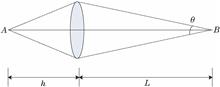
In this paper, an super-resolution imaging reconstruction algorithm based on the parametric adaptive online dictionary learning (ODL) is proposed. Under the framework of the classical sparse representation algorithm, the ODL method is used to improve the accuracy of dictionary learning. Furthermore, the regularization parameters in the sparse reconstruction stage are flexibly adjusted using the parameter adaptive method, so that the regularization parameters can be adaptively determined based on the characteristics of each image block, overcoming the disadvantages of the singularity and incompatibility of the artificially set parameters. Results show that compared with the traditional algorithm, the proposed algorithm can reduce the dependence of test images on the training image set, overcome the local blur or distortion in the reconstruction process, and improve the quality of the reconstructed image.
In terms of the problem that the traditional detection method of crowd abnormal events based on group motion state analysis does not describe the semantic information of scene adequately, the Girvan-Newman (GN) splitting up algorithm found by the community in the complex network is introduced. The pedestrians with similar motion characteristics and similar positions are divided into multiple groups, and the differences among the groups in normal and abnormal scenes are described and the occurrence of abnormal events is detected with the changes in group motion intensity and group number. Through experimental verification, the proposed algorithm can accurately detect abnormal events while enriching the semantic information of the scene.
Extraction of building boundary is a hot issue in airborne light detection and ranging (LiDAR) point cloud data feature extraction. In order to obtain high-precision building boundary, we proposed a building orthogonal boundary regularization algorithm based on directional prediction. First, the boundary points are extracted by α-shape algorithm, then the boundary key points are extracted by the improved Douglas_Peucker algorithm, the key points of angle check rules are proposed to select the right key points, the boundary are simplified by random sample consensus algorithm, and finally the regular boundary is got by the proposed direction prediction algorithm. The algorithm is verified by the Vaihingen data released, and the results show that, comparing with the popular classification forced orthogonal algorithm, the proposed algorithm reduces the maximum absolute deviation by an average of 43.1%, reduces the root mean square error by an average of 39.7%, reduces the relative error of the building area by an average of 7.02%, while increases the point cloud contribution rate by an average of 9.32%, and it can effectively reduce the error of building orthogonal boundary regularization of airborne LiDAR point cloud.
In view of the increasing demand for airborne blade measurement, an online laser detection experimental platform is established, and a laser measurement data acquisition system is developed. The collected scattered point cloud data are effectively reduced, and an incident tilt angle compensation strategy is proposed. Based on the UG platform, the grip language is used to realize the fast extraction of the theoretical contour. The basic particle swarm optimization algorithm is used to explore the optimal pose matching of the measured point set based on the local contour and the global contour. The experimental results show that the optimal solution of pose matching can be obtained by selecting the global contour. The particle swarm optimization algorithm is improved and the pose matching motion parameters are solved. The results show that, the computational accuracy is significantly improved compared with that by the basic particle swarm optimization algorithm.
Aiming at the problem of high complexity and low processing speed of heterologous image registration algorithms, a fast registration algorithm of visible light and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images is proposed. In the image preprocessing stage, the redundant information in visible light and SAR images is removed, and two different types of images are filtered respectively with Gauss low-pass filter and non-local mean filter (NLM) algorithms. Then, the multi-scale Harris method is used to detect and extract feature points, and the gradient position orientation histogram (GLOH) method is used to construct descriptors of feature points. Finally, the feature points in the original image are reconstructed based on the feedback mechanism, and the actual position of the feature points to be matched in the original image is got, so as to complete the reconstruction and matching of the feature points in the original image. The experimental results show that compared with scale invariant feature transform-modification (SIFT-M) method, this algorithm significantly reduces the running time while maintaining the average registration accuracy of more than 80%, and has important application value.
Correlated imaging has attracted noteworthy attention due to the advantages in non-local property, strong anti-interference capability, etc. And it has wide applications in three-dimensional imaging, remote sensing, biomedical technique, and national defense and military. In this paper, according to different stages of development,we introduce the development history and applications of the entangled two-photon correlated imaging, (pseudo) thermooptical correlated imaging, and computational correlated imaging, especially focusing on the improvement arising from the ICCD camera. Also, we briefly discuss the physical nature of the thermooptical correlated imaging. Finally, we give a pithy view of the practical applications.
We summarize key technologies of underwater target exploration in more details, including underwater image preprocessing, target detection and recognition, and target tracking algorithms. First, underwater image preprocessing algorithms are divided into image enhancement and restoration by judging whether they need to build a model, and then we discuss the basic ideas and characteristics of enhancement and restoration. Besides, the principles and methods of target detection and recognition, and target tracking for underwater optical images are reviewed across the board. After summarizing and analyzing the research results of the above processes, we untangle the core issues to be addressed and related difficulties existing in key technologies of underwater target exploration, and discuss the solutions and further development directions as well.
Content-based medical image retrieval method is a research hotspot in the field of computer vision in recent years, and has been widely used in the research of computer-aided diagnosis. This paper summarizes the research progress and significance of content-based medical image retrieval methods, introduces the current mainstream medical image retrieval algorithms and their advantages and disadvantages, and aims to guide researchers to quickly understand the research content in this field. The research of medical image retrieval is mainly divided into two parts: feature extraction and similarity measurement. This paper introduces the feature extraction method of medical images starting with the extraction of traditional features and the feature extraction based on deep learning emerging in recent years. The similarity measure part enumerates the Mahalanobis distance metric, vocabulary tree, and hash algorithm. Finally, the related feedback technology in the field of medical image retrieval and the commonly used image retrieval system are summarized. The possible research directions and related difficulties in medical image retrieval are discussed.