In order to realize the fast calculation of computer-generated holograms, a ray-tracing algorithm is proposed, which is based on the OptiX ray-tracing engine and the NVIDIA graphic processing unit (GPU). This algorithm makes full use of the ray-tracing hardware core in GPU and thus effectively increase the calculation speed of holograms. When the three-dimension model is consisted of 1.6×10 4 polygons and 4×10 4 points, the calculation speed of the proposed algorithm is 11.5 times that of the traditional point source hologram generation algorithm based on GPU.
The structure and parameters of convolutional neural network (CNN) determines the performance of image classification. Aiming at the problems of complex structure and a parameters that require a lot of manual settings in deep network, a CNN image classification algorithm based on the evolution of densely connected networks(D-ECNN) is proposed in this work. The algorithm can effectively search the network structure space, and realizes the adaptive optimization of deep network structure and parameters based on limited computing resources. The classification experiment results on the vehicle data set show that the accuracy of this algorithm can reach more than 95%, which is about 1% higher than that of the visual geometry group (VGG16) algorithm. The model file of this algorithm is smaller and the test speed is faster.
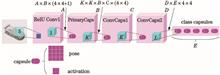
Capsule network is a new type of deep learning network, capsule structure can encode information such as posture, texture, hue, etc. of the feature, and has a good ability to express the texture feature of the image. Aiming at the problem that the primary feature extraction network of the capsule network is too simple and the feature expression ability is insufficient, a discrete wavelet capsule network (DWTCapsNet) that combines the feature expression capabilities of deep convolutional neural networks with wavelet transform multi-resolution analysis capabilities is propose in this work. First, the feasibility of the capsule network in the application of texture image classification is studied. Second, the ability of each part of DWTCapsNet on the improvement of capsule network classification performance is studied. Finally, the robustness of DWTCapsNet is analyzed through anti-rotation and anti-noise experiments. The classification accuracy is used as the standard model evaluation criteria, and the experimental results on the commonly used texture image data sets show that the classification accuracy of DWTCapsNet is higher.
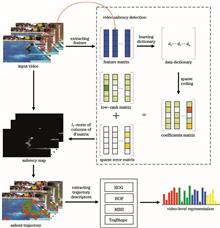
The traditional dense trajectory algorithm has achieved great success in human-body action recognition. However, the trajectories of the action and background motions are processed equally during algorithm's formation, which leads to redundant video representation and limited recognition accuracy. In this paper, the patterns of the background and behavioral motions are compared, a sparse error matrix is obtained using low-rank matrix decomposition on the basis of the sparse coefficient matrix of the feature dictionary, and a saliency map is solved. The saliency map is then used as the base for representing human-body action in only the action-related areas. The validity of this method is confirmed based on the open datasets UCF Sports and YouTube.
The target tracking algorithm based on deep learning takes the deep convolution output as the feature, which is high in accuracy but time-consuming. The target tracking algorithm based on fusion features fuses the target features according to the response value, although the tracking speed is fast, but the accuracy is reduced. In order to consider the timeliness and accuracy of the target tracking algorithm, a target tracking algorithm based on similarity feature estimation is proposed. First, sampling importance resampling filter particle is used to construct the target observation model, which includes selection of particle state, transfer system state, construction of observation model, particle weight update, and resampling process. On this basis, the statistical texture features, moving size features, moving speed, and direction features of the target are extracted, and the target feature framework is constructed by using the target features. The target positioning is estimated based on the similarity features, including describing the target model, representing the candidate model, measuring the specific similarity of the target, and the target positioning process. After the target positioning, the target tracking is realized based on real-time compression. The tracking accuracy of the proposed algorithm is above 90%, the tracking time is kept below 450ns, and the performance of this algorithm is better than that of the target tracking algorithm based on deep learning and fusion features. The proposed algorithm can track the target quickly and accurately, and has strong application advantages.
Generalized fuzzy C-means algorithm is a faster convergence algorithm than fuzzy C-means algorithm. However, it is sensitive to noise when segmenting gray images. In order to improve its robustness, a generalized fuzzy C-means algorithm based on the weighting of pixel gray value in image patch is proposed. In this algorithm, instead of a single pixel, the image patch is used to construct the objective function. The weight of each pixel in the image patch is determined by the spatial relationship between neighboring pixels and central pixel and the gray relationship of each pixel in the image patch. The expressions of membership and cluster center, in the form of image patch, are derived by using Lagrange multiplier method based on the new objective function. In this way, the neighborhood information is integrated into the clustering process, and then improves the robustness of the algorithm. Segmentation experiments are carried out with a synthetic image and several real images, and the segmentation results show that the proposed algorithm has strong robustness and good segmentation performance.
To improve the recognition performance of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image targets, multi-resolution representation and a complex domain convolutional neural network (CNN) are used in combination. Initially, the original SAR image is processed in time and frequency domain to obtain its multi-resolution representation image. Then, the complex domain CNN is used to classify the original image and its multi-resolution representation image. The classification results are weighted using a linearly weighted fusion scheme, and the test sample classification is evaluated according to the fusion result. Finally, the proposed method is tested under standard and extended operating conditions based on the MSTAR data set. The experimental results show that the proposed method is both effective and robust.
The target tracking algorithm is suffering from low accuracy and poor applicability due to the complex lighting conditions and severe changes in scale caused by the relative lens movement during panoramic video target tracking. To address this issue, we propose an algorithm for panoramic target tracking based on the improved SiameseRPN. First, the network structure of MobileNetV3 is used to extract the deep features to make the algorithm have a better adaptability to the scene defects appearing in panoramic video sequences, and the Squeeze and Excite module is used to increase the sensitivity of the network to feature selection. Then, we propose and construct a feature fusion module based on bilinear interpolation, which is used to make the output depth features of the last three layers have the same scale, and these three layers of features are fused for network prediction. Finally, we use a classification sequence to predict the positive and negative samples in the current sequence, and adopt a regression branch to predict the position information and scale information of current output targets. Thus the target position information is outputted. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has better tracking accuracy and it can effectively deal with the problems of poor local image quality and scale changes in panoramic data, while maintaining the real-time tracking performance. It shows a good adaptability to small targets, target occlusion, and multi-target cross movements in target tracking, and has good visual effects and high tracking scores.
An image processing method for accurately calculating the local fringe direction of moiré patterns was proposed that can be applied to the moiré deflectogram of a spherical progressive addition ophthalmic lens. The empirical characteristics of a collected moiré pattern were used as the basis for analyzing misalignments between assumptions and actual measurement conditions during the derivation of the measurement theory. Further investigation shows that the moiré fringe angle required for actual measurement is based chiefly on the fringe phase field rather than the intensity field. Based on this, a method using phase fitting to obtain the local angle of fringes was proposed. The method first obtained the phase of the moiré fringe by phase shifting and next fitted the phase to the Zernike polynomial to obtain the polynomial expression of the phase. The method then calculated the fringe angle of the corresponding position by solving the partial derivative of the polynomial in each of two directions. Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that this method can eliminate the influence of the uneven distribution of background light and light source amplitude, making it insensitive to fringe noise and fringe period variation. Angle calculation accuracy can reach 0.2°.
Hyperspectral unmixing aims to extract the endmember and abundance features in an image. A hyperspectral image has many mixed pixels because of the low spatial resolution. Therefore, capturing the spectral features and the corresponding spatial distribution from the mixed pixels is important. The non-negative matrix factorization(NMF)-based method for hyperspectral unmixing is regarded as an ill-posed data-fitting problem, in which the cube data must be converted into a matrix form, which leads to the loss of three-dimensional structure information. This study introduces the sparsity of the spatial features in the minimum-volume simplex to propose a novel method for hyperspectral unmixing, which not only mines the intrinsic relationship between spectral and spatial abundance features in the images, but also improves the loss of data structure information. The proximal alternating optimization and the alternating direction method of multipliers were used here to design a set of efficient solvers based on the minimum volume constraint in convex geometry and non-negative matrix decomposition. After testing the synthesized and real data sets, the experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively extract the endmember and abundance features.
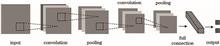
To accurately classify digital printing defects with deep learning, we propose a digital printing defect classification algorithm based on convolutional neural network (CNN). Firstly, this method performs image preprocessing of RGB color space histogram equalization, Gaussian filtering, and local mean resolution adjustment in sequence to improve the image quality of the input network. Meanwhile, the sample data set is expanded by geometrically transforming the image. Then, the topology of CNN network is designed with 2 convolutional layers, 2 pooling layers, and 2 fully connected layers, which is the optimized CNN model of digital printing defect classification. Finally, the model is verified by 600 test samples. Experimental results show that the classification accuracy of proposed algorithm for all types of digital printing defects reaches above 90.0%, and the Kappa coefficient value of multi-classification task is 0.94. The proposed method can accurately classify digital printing defects.
For the context-aware correlation filtering tracking algorithm, when extracting the background information around the target to train the filter, the time consistency of the filter is not considered. When the appearance of the target changes suddenly, the filter cannot adapt to the change of the target and background information in two consecutive frames, and the target drift is easy to occur. This paper proposes an adaptive context-aware correlation filtering tracking algorithm. First, the background information around the target is learned into the filter to enhance the filter''s ability to classify the background information and the target is added, and the time perception term is added to ensure that the filter for learning two consecutive images is as consistent as possible. Then, linear interpolation method is used to determine the target position. In the model update stage, occlusion discrimination is introduced to determine whether the target is occluded or not based on the average peak correlation energy. Finally, a large number of comparative experiments are carried out with the current mainstream algorithm on the data set OTB100. Experimental results show that the precision and success rate of the proposed algorithm on the data set OTB100 are 0.798 and 0.722, respectively. Compared with other mainstream algorithms, the proposed algorithm also has better tracking effect under complex conditions such as fast motion, occlusion, and illumination change.
Quality of images that are captured underwater typically deteriorates owing to color distortion, low visibility, and detail losses caused by absorption and scattering. To effectively handle the above-mentioned problems, a novel underwater image enhancement method using color correction and detail preservation is proposed herein. First, a Retinex-inspired method is employed to achieve color correction by adjusting the histogram distribution of each color channel. Next, a dual-interval histogram based on the average of median and mean values is applied to improve the lower and upper pixel regions, which significantly improves the contrast of the integrated image. Finally, a multiscale unsharp masking method is used to sharpen the overall image to highlight the details of the output image. The experimental results show that the proposed method both effectively eliminates the color distortion and enhances the contrast and detail of the image.
In the medical ultrasonic imaging technology, factors such as the imaging equipment, imaging mechanism, and non-uniformity of detection objects lead to problems of speckle noise and partial distortion in ultrasonic images, which not only reduce the quality of ultrasonic images, but also increase the difficulty of clinical diagnosis. In order to effectively suppress speckle noise in ultrasonic images, this paper proposes an adaptive bilateral filtering denoising method for ultrasonic images based on BP (back propagation) neural network. According to the similarity value between the local region and reference noise region predicted by BP neural network, our method can distinguish the noise regions and the tissue regions in the ultrasonic image. After that, the similarity value predicted by the BP neural network is combined with a bilateral filter to realize adaptive filtering of the ultrasonic images, and the bilateral filter can perform different filtering for different regions of the ultrasonic image. Experiments are carried out based on four ultrasonic images (the physical phantom ultrasonic image, the liver ultrasonic image 1, the liver ultrasonic image 2, and the kidney ultrasonic image). The results show that the method can better suppress speckle noise in the ultrasonic image and preserve its edge features, and can also obtain higher signal-to-noise ratio and better visual effect.
In this paper, we analyze the principle of speckle-rotation decorrelation, including the factors that influence the speckle-rotation decorrelation angle. We infer that this angle is mainly affected by the degree of speckle disorder and the size of the speckle area used in the calculation. To perform experimental tests, we change four parameters of the optical system and observe the corresponding changes in the speckle-rotation decorrelation angle. Specifically, we change the speckle area used in the calculation, change the distance between the scattering medium and the detector, shift the detector horizontally, and replace the scattering medium. The experimental results show that the larger the speckle area and the higher the degree of disorder, the smaller is the speckle-rotation decorrelation angle. In speckle imaging based on the memory effect, these research results can help both related research and applications of speckle-rotation decorrelation that have practical significance.
A multi-channel image blind restoration algorithm based on single total variation regularity can cause a ringing effect and loss high-frequency information in restored images. To solve this problem, a multi-channel image blind restoration algorithm based on total variation and dark pixels is proposed using the non-sparseness of dark pixels in blurred images. Solving the problem of total variation and dark pixel double regularization model is difficult. To address the difficult problem, the split Bregman optimization algorithm is used to ensure convergence of the results, the global problem is decomposed into independent sub-problems, and the image and point spread function are solved alternately to restore the target images. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can effectively remove image blurring, suppress ringing effects, and restore high-quality clear images. Compared to an algorithm with the total variation regular term, the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the proposed algorithm improves by 0.12 dB--5.86 dB, and the structural similarity improves by 0.014--0.125.
In this study, a protection strategy is proposed to optimize the privacy strength of the source node location for mitigating problems such as fewer hops between the phantom node and the source node, concentrated distribution areas, and insufficient diversification of the transmission paths. Using the proposed strategy, the diversity of phantom node selection can be enhanced and the visual area of an attacker can be effectively avoided. First, set the conditions for selecting phantom nodes, and the dynamic random number generated by the source nodes, and the storage location information layering in the area to select phantom nodes ensures that there is sufficient safe distance between phantom nodes and source nodes. Then, set the set of neighbor nodes with the least number of hops from the sink node and equal distances as a virtual ring. When the data packet arrives at the virtual ring, the transmission direction is randomly selected, and the dynamically generated hop value is used to transmit hop by hop, which can effectively enhance transmission the diversity of paths extends the average tracking time of the attacker. Simulation results show that compared with the traditional strategy, the proposed strategy can enhance the privacy strength of the source node location.
In this study, a power function-weighted image stitching method with fusion-improved SURF (Speeded Up Robust Feature) and Cell acceleration is proposed to resolve problems, such as the low feature point matching accuracy associated with the traditional algorithms in the image stitching process and ghosting, color difference, and stitching gaps observed during the image fusion process. First, the similarity of the feature points is verified using cosine similarity. Then, the two-way consensus algorithm and the MSAC algorithm are combined to finely match the rough matching points. Finally, the power function weights obtained via cell acceleration are used to fuse images for obtaining the image stitching. Experimental results show that compared with other algorithms, the feature point matching accuracy of the proposed algorithm increases by approximately 11%, the mean square error decreases by approximately 1.32%-1.48%, the information entropy increases by approximately 0.98%-1.70%, and the total stitching time decreases by approximately 2 s. Compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm obtains better results with respect to the matching accuracy and fusion effect; furthermore, improved image splicing quality and universality can be obtained.
Point cloud is an important three-dimensional expression, and it has a wide range of applications in computer vision and robotics. Due to occlusion and uneven sampling in real application scenarios, the shape of the target object point cloud collected by the sensor is often incomplete. To achieve the point cloud of feature extraction and shape completion, a new point cloud completion network based on the multibranch structure is proposed in this paper. The encoder is primarily responsible for extracting the global and local features from the input information, and the multibranch structure in the decoder is responsible for converting the features to point clouds to obtain the complete point cloud shape of the object. Experiments are conducted using the ShapeNet and KITTI data sets, with different incomplete proportions and geometric shapes. Results show that the method can well supplement the missing point cloud of the target and obtain a complete, intuitive, and true point cloud model.
To overcome the discontinuity of phase unwrapping caused by noise, in this paper, Canny edge detection algorithm is used to get the real edge of the reconstructed model, a second-order difference function is combined to calculate the edge reliability, and the phase is expanded region by region according to the reliability, so as to achieve the purpose of stable global phase unwrapping. The data points of any row (or column) after phase unwrapping of traditional algorithm and this algorithm are unwrapped, the standard deviations of the two algorithms relative to the original data points are 0.0562 and 0.0121, respectively. At the same time, this algorithm can solve the problem of low stability of phase unwrapping caused by excessive noise in the branch cutting method and the problem of discontinuity layer in the reconstructing model by the least square method, which overcome the noise well and carry out three-dimensional reconstruction.
To solve the problems of high-time delay and low reliability of consumer UAV video images during the transmission process, this paper proposes a video transmission algorithm suitable for consumer UAVs. With the proposed algorithm, the frames of a received real-time video image are sliced while transmitting images. Color component transform is employed to obtain Y, Cr, and Cb components, which are processed by third-level forward discrete wavelet transformation, bit plane decomposition, image coding, and parallel transmission. Additionally, the receiving process is inversed compared to the sending process. The restored complete image is stored in second-level cache, which is performed by other functions. Wavelet transform ensures image transmission reliability, image coding reduces image transmission load, and image concurrency and secondary buffer reception improve the real-time performance of images. In a WIFI environment with a communication distance of 20m, two common images (resolutions are 640×480 and 1280×720) are tested. The former's average receiving frame ratio, time delay, structural similarity (SSIM), and root mean square error (RMSE) are 47.7frame/s, 35.7ms, 0.984, and 1.61, respectively, and the latter's values are 28.8frame/s, 45.9ms, 0.978, and 2.68, respectively. The experimental results demonstrate that when a consumer UAV is shooting at ultra-low altitude, the proposed algorithm can satisfy the real-time and reliable transmission requirements of a high-definition video stream. Additionally, the proposed algorithm can be applied to other image transmission fields.
In the process of image acquisition, the image blurring problem is always inevitably caused by camera shaking or object movement. In order to solve this problem, a blind image deblurring method based on image edge determination mechanism is proposed to restore images with sharp edges. First, a PNet subnet is proposed to set blurry images as inputs, and determination learning is carried out by using a data driven method until the network is converged. The blurring image is input again to the generator of training converge in the PNet subnet, which can obtain deblurring images and the deblurring images are noted as edge-weakened images. Second, a DNet subnet is proposed, both blurry images and edge-weakened images are served as inputs for training, and the DNet generator of training convergence is image deblurring model. In addition, the edge reconstruction function and image semantic content loss function are proposed to constrain the image edge and sematic information. Finally, an object loss function for image edge determination is proposed to make the DNet subnet generator complete the true-false determination of generated images and labeled images and finish the further determination of edge-weakened images and labeled images. Therefore, the determination learning of image edge information is enhanced. Experimental results show that the proposed method can restore large-scale blurring images and blurring images caused by movement, which proves the important role of edge determination mechanism in the image edge restoring.
In order to further improve the detection accuracy of the text detector based on convolutional neural networks, first, feature extraction network with split-attention mechanism is used to replace the backbone network of the original algorithm, such as residual network, to promote information exchange between channels and maximize the activation of text features. Second, based on the original feature pyramid network, a bottom-up path is added to reduce the loss of text feature information. Experimental results show that the average accuracy of the algorithm is 78.7% and 79.0% on CTW1500 and Total-Text curve data sets, and 82.7% and 79.3% in multi-directional and multi-language data sets, respectively, which is better than other algorithms.
In this study, the Canny edge detection algorithm is proposed and applied to the image measurement field to solve the problems of image edge smoothing due to Gaussian filtering, poor self-adaptability of the threshold caused by artificially setting high and low thresholds, and poor removal effect caused by using the double threshold method to remove the false edge. First, the switching median filter instead of the Gaussian filter is used. The gray value of non-noise pixels is kept unchanged while denoising to improve the edge positioning accuracy. Next, the K-means clustering algorithm is employed to obtain the clustering center of the high and low gradient values. The OTSU algorithm is employed to acquire the gradient threshold value. The self-adaptation of the high and low threshold values could be achieved by combining the two methods. Finally, the interference edge of the image is removed by area morphology. The experimental results show that the improved algorithm has the advantages of high positioning accuracy, strong self-adaptability, and good removal effect of disturbance points.
Aiming at the problems of missed detection and low efficiency in manual classification and diagnosis of optical coherence tomography retina images, a deep learning-based convolutional network classification algorithm is proposed to construct joint multilayer features. First, retinal images are preprocessed using the mean shift and data normalization algorithm. The loss function weighting algorithm is combined to solve the data imbalance problem. Second, a lightweight deep separable convolution rather than an ordinary convolution layer is used to reduce the number of model parameters. Global average pooling replaces fully connected layers to increase spatial robustness, and different convolutional layers are used to build feature fusion layers to enhance feature circulation between layers. Finally, the SoftMax classifier is used for image classification. Experimental results show that the model can achieve 97%, 95%, and 97% in accuracy, precision, and recall, respectively, thereby reducing the recognition time. The proposed deep learning feature fusion-based method performs well in the classification and diagnosis of retinal images.
In view of the high complexity of the current facial landmark detection algorithm network model, which is not conducive to deployment on devices with limited computing resources, this paper proposes a high-precision and lightweight facial landmark detection algorithm based on the idea of knowledge distillation. This algorithm improves the Bottleneck module of residual network(ResNet50) and introduces packet deconvolution to obtain a lightweight student network. At the same time, a pixel-wise loss function and a pair-wise loss function are proposed. By aligning the output feature maps and intermediate feature maps of the teacher network and the student network, the prior knowledge of the teacher network is transferred to the student network, thereby improving the detection accuracy of the student network. Experiments show that the student network obtained by this algorithm has only 2.81M parameter amount and 10.20MB model size, the frames per second on the GTX1080 graphics card is 162frames and the normalized mean error on 300W and WFLW datasets are 3.60% and 5.50%, respectively.
A global imaging method based on the focus stack monomer data subset architecture is proposed, which it can improve the reconstruction accuracy inside the monomer and reduce the reconstruction error caused by the depth jump of the object boundary. First, the Alpha Matting algorithm is used to obtain the boundary information of the object, the focus stack is accurately divided in the (x, y) space according to the boundary information of the object, and the focus stack data is selected in the depth direction to obtain the focus stack monomer subset. Then, according to the focus measure, depth reconstruction and all-focus imaging are performed on the monomer subset, and the calculation result is optimized by the total variation regularization. Finally, the optimized reconstruction results of the monomer subset of the focus stack are globally fused to obtain the depth map and the full focus map of the global scene. Experimental results show that the proposed global imaging based on the focus stack monomer data subset architecture can improve the computational efficiency and the quality of the reconstruction results, and provide an optimized solution for the focus stack computational imaging.
Remote sensing image classification is an important part of image analysis, and post-classification accuracy assessment is the main basis for determining the effect of image classification. At present, random verification points are often used as assessment parameters in object-oriented classification, which may easily lead to inaccurate classification results. An object-oriented classification accuracy assessment method based on regular verification points is proposed in this paper. Regular and random verification points are used to evaluate the classification accuracy by using support vector machine, CART (classification and regression tree ) decision tree, and K nearest neighbor classification. Experimental results show that the proposed method has higher classification accuracy than traditional methods based on random verification points. The optimal overall classification accuracy of the three classification methods based on the regular verification points reaches 87.92%, 91.94%, and 94.63%, respectively, which are better than the accuracy assessment results of random verification points based methods.
This study proposes a multiplane activated sludge microscopic image fusion algorithm based on discrete cosine transform (DCT) to construct a clear and large-depth-of-field microscopic view of activated sludge microorganisms. First, the edge sharpening is pretreated for the microimages with the same position and different focal planes, and the transformation coefficients of the segmented images are calculated respectively. Second, the sub-block with a large coefficient variance is selected as the sub-block of the fused image, and inverse DCT is employed to perform image fusion. Finally, the two-sided filter consistency check is used to further modify the fused image. The microimages of activated sludge collected from a sewage treatment plant are studied by image fusion experiment. Experimental results reveal that the proposed algorithm has advantages in terms of image fusion clarity and computational complexity.
Aimed at the occlusion problem of target tracking in machine vision, an occlusion detection mechanism is introduced based on the original Distractor-Aware Tracking (DAT) algorithm framework, and a Detection-DAT (DDAT) algorithm is proposed. First, this mechanism extracts color characteristics of the target, calculates similarities between the target frames through color characteristics, and uses the similarity trends and the threshold values of the differences between the frames to determine whether the target has been occluded during tracking. Second, Naive Bayes and nearest neighbor classifiers are adopted to obtain the target frame in subsequent frames. Finally, similarity is applied to detect whether the target frame obtained by the two classifiers is the correct target frame. To verify the effectiveness of the algorithm, qualitative and quantitative comparisons with the DAT algorithm and other tracking algorithms were performed on the standard data set video sequence with occlusion properties.
There are many interference factors such as camera perspective, crowd overlap, and crowd occlusion in crowd-counting statistics that decrease the accuracy of crowd counting. Aiming at addressing these problems, a population-depth counting algorithm based on multiscale fusion is proposed herein. First, the proposed algorithm uses the partial structure of the VGG-16 network to extract the underlying feature information of the crowd. Second, based on the dilated convolution theory, a multiscale feature extraction module is constructed to realize multiscale context feature information extraction and reduce the model parameter amount. Finally, the model counting performance and density-map quality are improved by fusing low-level detail feature information and high-level semantic feature information. Different algorithms are tested on three public datasets. The experimental results show that compared with other crowd counting algorithms, the average absolute error and mean square error of the proposed algorithm are reduced to varying degrees, indicating that the proposed algorithm exhibits good accuracy, robustness, and good generalization.
Person re-idetntification algorithms based on global features primarily use the cross-entropy loss function and triplet loss function to supervize network learning. However, the original triplet loss function does not optimize an intraclass distance and increases an interclass distance. To solve this problem, an improved person re-idetntification algorithm based on global features is proposed. The algorithm is improved on the basis of the triple loss function, that is, an intraclass distance is introduced into the original triple loss function, so that the improved triple loss can be reduced while increasing the interclass distance intraclass distance. A number of experiments have been conducted on the Market1501, DukeMTMC-reID, and CUHK03 datasets. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm obtains discriminative features, and a model based on the global features can achieve a performance that approaches or even exceeds some local feature models.
For the convenience and applicability of distortion correction methods, a distortion correction method based on convolutional neural networks is presented in this paper. First, the self-calibration functional motion structure is used to reconstruct the image sequence taken by the real camera to estimate the camera parameters. Second, according to the functional relationship between the first and second-order radial distortion parameters, the images within the common radial distortion range are generated to solve the problem of less distorted images with the first and second-order radial distortion annotation. Finally, by using the powerful learning ability of CNN, the radial distortion features are learned to estimate the radial deformation, and the input image is mapped to the distortion coefficient to realize the image distortion correction. Experimental results show that the calibration error of this method is about 1 pixel compared with the traditional camera calibration method.
Traditional image dehazing algorithms usually appear halo phenomenon when processing regions with uneven brightness. In order to solve this problem, an adaptive bilateral filtering dehazing method based on boundary constraint is proposed. First, we use the histogram analysis method to obtain the threshold of bright region segmentation, thereby getting the global atmospheric background light. Second, a self-adaptive boundary limitation method is constructed to obtain the initial transmission image. The transmission map is optimized by an improved self-adaptive fast bilateral filtering method. Finally, the improved dark primary color theory method is used to obtain the final dehazing result. Through subjective and objective experimental analysis, we find that the proposed method is relatively superior to current dehazing methods in terms of visual effects and efficiency.
In the field of static image, deep neural networks have made breakthroughs and gradually expanded to the field of video recognition. Human action recognition is a research hotspot and difficult in the field of video recognition. Therefore, this paper proposes an improved human action recognition algorithm based on two-stream faster region convolutional neural network (Faster RCNN). First, we use RGB (Red, Green, Blue) images and optical flow data as input of the network to train the Faster RCNN separately; then, the trained network model is fused, and an improved squeeze and excitation block is introduced to process the feature channel to highlight important features; finally, we use the complete intersection-over-union loss function as the bounding box regression loss function to optimize some problems such as the inability to intersect the ground truth box with the predicted box. The experimental results show that the accuracy of the algorithm on the action recognition data set UCF101 is improved compared to the traditional Faster RCNN.
In view of the fact that the detection of moving targets in real-time video are greatly affected by weather conditions. Herein, a video sequence moving target detection algorithm that combines total variation(TV) regularization and a Rank-1 constrained robust principal component analysis (RPCA) model is proposed. Using RPCA as a tool in the framework of low-rank sparse decomposition, the Rank-1 constraint is used to describe the strong low-rank of the background layer, and the TV regularization combined with the L1 norm is used to perform the sparseness and spatial continuity of the foreground target constraints to compensate for the deficiencies of the existing RPCA model. Aiming at the proposed model, the idea of alternating iterative multiplier method combined with augmented Lagrangian multiplier method is used to optimize the objective function. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can not only accurately detect moving targets but also has a shorter running time, which provides a reference for real-time video detection. Compared with other similar algorithms, the proposed algorithm not only has better detection effect but also provides enhanced quantitative evaluation of F measurement value, recall rate, and accuracy rate.
Aiming at the phenomenon of retinopathy of diabetic patients, a diagnosis model of diabetic retinopathy based on deep learning is proposed. First, under the premise of ensuring the depth of image recognition model, the composition of Inception module is modified to reduce the model parameters and improve the convergence speed. Next, the residual module is introduced to solve the problems of gradient disappearance and gradient explosion caused by the increase of model depth. Last, by using the method of data expansion and setting the Dropout, the phenomenon that the model is over-fitting due to the insufficient data set is effectively avoided, thereby realizing the detection of the disease level of diabetic retinopathy. Experimental results show that the deep convolutional neural network DetectionNet proposed in this paper has a recognition rate of 91% for the classification of diabetic retinopathy. Compared with network models such as LeNet, AlexNet, and CompactNet, the proposed DetectionNet improves the recognition rate by more than 20%. This research is of great significance for the early prevention and treatment of diabetic patients and the avoidance of diabetic retinopathy.
Herein, a method that combines convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and improved graph search is proposed to segment seven retinal-layer boundaries in optical coherence tomography (OCT) images. First, CNN is used to extract the features of each boundary automatically and to train the corresponding classifier to obtain the probability map of each boundary as the region of interest for boundary segmentation. Second, an improved graph search method is proposed to add lateral constraints based on the vertical gradient. When encountering a vascular shadow, the segmentation line can laterally cross the shadow. The normal image is segmented using the proposed method, and the results are compared with those obtained using the graph search method and the method based on CNN. Experimental results show that the proposed method can accurately segment seven retinal-layer boundaries with an average layer boundary error of (4.31±5.87)μm.
The detection of the hole boundary of the point cloud model in reverse engineering is necessary for the hole repair, and a perfect hole contour line is conducive to improving the quality of the hole repair. Based on the definition of boundary in two-dimensinal images, the definition of hole boundary in three-dimensional point cloud was given. By analyzing the relationship between the eigenvalues of the covariance matrix of neighboring points, a boundary point detection operator was proposed to initially extract the feature points of the hole boundary, and then, the improved Kruskal minimum spanning tree algorithm was used to construct the minimum generated map of the point cloud. Subsequently, the hole boundary points were sorted and outline of the hole was extracted in the minimum generated graph. The experimental results show that the proposed boundary detection operator has simple steps and high efficiency. The hole contour line extracted by the hole contour line generation algorithm based on computer graph theory has the advantages of being smooth and continuous, and hole aggregation is completed while generating the contour line.
This study aims to investigate the impacts of plant color, surface roughness, and ranging distance on LiDAR data intensity and ranging accuracy. The multi-featured plant surface was measured using a Leica C05 laser scanner and South Total Station. The results demonstrate that the ranging error is 1-5 mm when measuring targets within 100 m. When the distance exceeds 90 m, the ranging error of the laser point cloud increases approximately 1 mm with each increase of 10 m in station distance. Color, surface roughness, and ranging distance affected the LiDAR data intensity and ranging accuracy. The white color laser had the highest intensity. There was a strong relationship between LiDAR data intensity and ranging accuracy, but no obvious relationship between surface roughness and LiDAR data intensity. The influences of plant and non-plant color on LiDAR data intensity were similar.
This research presents a novel approach for using VIS-NIR spectroscopy for soil organic matter (SOM) estimation. Soil spectrum data is collected from 89 samples retrieved from the Aibi Lake wetland. The samples are measured using a first-order differential transformation achieved through a continuous projection algorithm, a principal component analysis, and a sparse auto-encoder (SAE). The extracted data is then combined with a partial least squares regression (PLSR) and backpropagation (BP) neural network for the purpose of building a SOM estimation model. Experimental results show that the SAE method is able to effectively compress the spectrum. The BP model is shown to handle the complex and nonlinear information of the spectrum better than the PLSR model. Meanwhile, the SAE-BP method has the highest accuracy for estimating SOM. The network model is shown to significantly improve the stability and accuracy of the vis-NIR spectrum inversion of the SOM model. This model shows a robust and strong analytical power when faced with complex nonlinear problems in the spectrum.
Aiming to address the low identification accuracy of remote-sensing tree species of forests with a complex canopy and high density, a three-dimensional convolution neural network (3D-CNN) that can extract the stereoscopic features of hyper-dimensional data is introduced herein, and it can identify remote-sensing images. Furthermore, it is improved through residual network (ResNet) to build a 3D residual convolution neural network (3D-RCNN) to reduce the influence of degradation phenomenon and the inaccuracy caused by network depth. The sample set is constructed by combining GF-5 hyperspectral data (GF-5 AHIS)and GF-6 high spatial resolution data (GF-6 PMS), supplemented by forest resource data and field survey data. Then, a tree species recognition model is constructed based on the concept of 3D-RCNN. The experimental results show that compared with traditional 3D-CNN, the proposed 3D-RCNN increases the model network's density from 12 layers to 18 layers, which can deepen the network structure and alleviate network degradation. By combining GF-5 AHIS and GF-6 PMS, 3D-RCNN can effectively identify northern subtropical forest species, providing better recognition accuracy (91.72%) than traditional 3D-CNN (85.65%) and support vector machine algorithm (85.22%).
Aiming at the problem that increased difficulties in detection of ship detection in remote sensing images caused by the narrow and long shape, disorderly distribution and other characteristics, a ship target detection method based on faster region-convolution neural network (Faster R-CNN) is proposed in this paper. The method uses a two-way network to extract ship target features. In order to make the feature map fully integrate the low-level detail information and high-level semantic information, a multi-scale fusion feature pyramid network (MFPN) is used for feature fusion; in the candidate frame generation stage, an adaptive rotation region proposal network (AR-RPN) is proposed to generate a rotating anchor frame at the center of the target to efficiently obtain high-quality candidate frames. In order to improve the detection rate of the network to ship targets, the network is optimized with an improved loss function. The test results on the public ship data sets HRSC2016 and the DOTA show that the average accuracy of this method is 89.10% and 88.64%, respectively, which can well adapt to the shape and distribution characteristics of ships in remote sensing images.
Optical super-resolution microscopy, enabling to break the diffraction limit, provides a powerful observation means for research on ultra-fine structures and physiological processes. It has an important impact on studying the functions of cells and the pathogenesis of diseases, which is of great biomedical significance. As a branch of super-resolution imaging methods, single molecule localization microscopy has great scientific research value. We first introduce the research background and significance of single molecule localization microscopy. Then we describe the development process of this technology in detail. In addition, the basic principles of the existing mainstream technologies are elaborated and their corresponding advantages and disadvantages are also analyzed. Finally, we prospect the applications of the single molecule localization technology.
Optical microscopy performs an increasingly important role in clinical diagnosis and basic scientific research. With the development of novel fluorescence probes, light controllers, and detectors, super-resolution optical microscopy breaks through the diffraction limit and provides new tools for modern biomedical research. Among these techniques, structured illumination microscope (SIM) achieves super-resolution by using spatially coded structured illumination which down modulates spatial frequencies beyond the cutoff into the pass band of the microscope. SIM shows lower photo bleaching and phototoxicity, higher imaging speed, and no special requirements for fluorescent probes, which has significant advantages in application to live-cell biomedical research. In this paper, the important principles and technological progress during the development of SIM are firstly reviewed. Then we focus on the key experimental techniques and difficulties in hardware design and image reconstruction of SIM. Finally, the several applications in biological imaging are listed. It is expected that this review can provide guidance for designing and using SIM.