The link transmission performance of the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) retro-modulating optical communication system under the weak turbulence condition is studied and verified by simulation. The influence of pointing error on the system is considered, and the Gauss-Hermite integral method is used to derive the bidirectional channel fading probability density function and the closed expression of its cumulative distribution function for this system. The closed expressions of system average bit error rate and the outage probability are further derived. The research results show that under the joint influences of weak turbulence and pointing error, and the incident angle, modulation order and refractive index of the corner cube retro-reflector have great influences on the error performance of this system. When the divergence angle is 3-10 μrad, the system error rate reaches an optimal value. When the divergence angles are 6, 8 and 10 μrad, respectively, the outage probability is reduced to 10 -9 orders of magnitude under the condition of relatively high signal-to-noise ratio threshold.
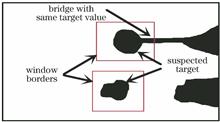
In order to detect dim the small infrared targets more effectively, a small infrared target detection algorithm based on statistical features and bridge method is proposed by analyzing the difference between the small dim infrared targets in infrared images and their neighborhood backgrounds. The mean value, variance and other characteristics of pixel values are extracted in the sliding window range. According to these statistical characteristics and the bridge method, whether there are small infrared targets in the window range is determined. If there is a small target, its location is recorded, and then the small target area is screened twice. The research results show that the false alarm rate of the proposed algorithm is 58% lower than that of the classical algorithm.
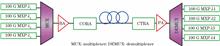
An unrepeated transmission system of 4×100 Gbit·s-1 over a span loss of 68.85 dB is realized by the bi-directionally pumped Raman amplifier (BDPRA) scheme. The optical signal to noise ratio, transmission margin, and bit error ratio of this system are tested. The power evolution of this BDPRA in the 4×100 Gbit·s-1 transmission system is simulated. The research results show that the signal input power, forward/backward Raman gain distribution and cost should be comprehensively considered in the applications of the BDPRA scheme.
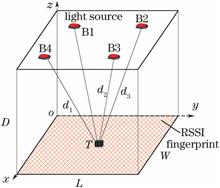
A range-assisted visible light fingerprint localization (RAFL) method is proposed. Based on the ranging method, the position range of the positioning target is preliminarily determined according to the multiple sets of light sources. Then the bilinear interpolation algorithm is used to construct the localized area fingerprint and the fingerprint matching is carried out within the target range. The actual location of the target is finally obtained. The research results show that the proposed method has a strong anti-interference ability and can effectively improve the positioning accuracy.
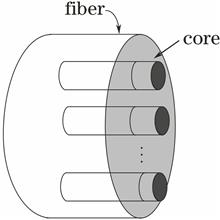
The problems of routing and fiber-core assignment in the elastic optical networks (EONs) with multi-cores are investigated. Since the exchange of cores has an effect on the performance of the network, a global constrained optimization model is established which minimizes the blocking ratio. Taking the length and spectral availability of path into account, the candidate path set is selected for each connection request. Based on this, to solve the model effectively, an efficient genetic algorithm with high efficient encoding scheme, tailor-made crossover, mutation and local search operators is designed. The simulation experiments are conducted on different network topographies, and the experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can be used to obtain a small blocking ratio under the same scene.
In order to solve the problem that the traditional bridge crack detection algorithm cannot extract cracks accurately, a bridge crack detection algorithm is proposed based on image processing, which is suitable for complex scenes. According to the principle of the deep convolutional generative adversarial network, the bridge crack image generative model is proposed and used to amplify the dataset. For the characteristics of bridge cracks, a bridge crack image segmentation model is constructed based on semantic segmentation. The bridge crack image segmentation model is used to extract the bridge cracks from the high-resolution crack images. The research results show that the proposed algorithm has a better detection effect and a stronger generalization ability in the complex road scenes compared with the existing algorithms.
To effectively distinguish the handwritten and printed texts, a discrimination method is proposed based on the hidden layer frame features of a convolutional neural network. The hidden layer frame feature is extracted by the convolutional neural network. The Gaussian mixture model is first combined with the hidden Markov model to model the features, and then the Viterbi decoding algorithm is used to determine the category of each frame feature. Based on the recognition results of the frame features, the recognition results are post-processed in combination with the image information. The final handwritten and printed text areas are determined. For the signature document line images, relative to the baseline, the discrimination accuracy of handwritten and printed texts by the proposed method increases by 10.8% and 27.57%, respectively. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified with the natural scenes, tables and noisy documents.
In order to solve the problem of low accuracy rate caused by the equal length segmentation of the attention curve in the traditional methods, a scheme is proposed, in which the key video segments are extracted based on the image quality curve. The frame with the highest attention value is selected from each segment as the key frame. On the local database, the precision and F-measure are 52.94% and 62.77%, 5.23% and 2.65% higher than those by the Muhammad method, respectively.
In order to accurately measure the size of nanoparticles, an automatic particle segmentation method based on U-Net convolutional neural network is proposed according to the nanoparticle images captured by the transmission electron microscopy. Combined with the Batch Normalization (BN) layer, it reduces the dependence of networks on initialization and thus speeds up training. The nanoparticle image is filtered by the semi-implicit partial differential equation to enhance the image edge information. The improved U-Net network is used to train the nanoparticle individual segmentation model and the segmentation result is obtained. The research results show that the proposed method can accurately segment the nanoparticles in the image, and the segmentation effect is especially obvious for the nanoparticles with edge blurs and uneven intensities.
It is difficult to search the spectrum line in handwritten music spectrum, so in order to improve the robustness of the handwritten music spectral line deletion algorithm, a method based on multidimensional local binary pattern recognition and XGBoost model is proposed. The local binary pattern operator is designed and improved based on the characteristics of music score image, and from which the multidimension local binary pattern feature operator is extracted. Therefore, a high-dimensional feature vector is formed and the optimal XGBoost model is selected to identify the music spectral line location, then the line is deleted. The research results show that F-measure of this method is 97.19% on the test data, which illustrates that the method has a high accuracy and recall rate. F-measure is 96.43%, 98.36% and 96.79% respectively on three different test subsets, which shows that it has good robustness. Compared with existing lightweight spectrum line deletion algorithm, the F-measure of this method is relatively improved.
An algorithm called gradient clustering based area proposal method (APM) is proposed to solve the problem that the existing methods are slow to detect objects, which is based on a large number of edges of artificial objects in aerial images. Then the extracted regions of interest are detected by the object detection method. The real-time performance and precision rate of this method are evaluated on the DOTA (Dataset for Object Detection in Aerial Images). The research results show that the proposed method greatly improves the detection speed of large-size, target-dense aerial images by the object detection algorithm, and still keeps a high recall rate.
A quality assessment method of remote sensing images is proposed based on deep learning and the human visual characteristics. The convolutional neural network and the back propagation neural network classifiers are used for the simultaneous feature learning and grade classification of blur and noise intensity for the remote sensing images. The masking effect and the corrected assessment model of the perceptual weighting factors are used to obtain the quality assessment results of remote sensing images, which are more in line with the human visual characteristics. The research results show that the proposed method can effectively solve the difficulty in the quality assessment of remote sensing images with both blur and noise. Moreover, the quality of remote sensing images can be effectively and accurately evaluated, and the results are well in good agreement with both the subjective evaluation results and the human visual experiences.
With the help of the resonance effect of graphene nanoribbon arrays, a three-layer graphene nanoribbon array is proposed. The influences of the various parameters of this array on the multi-frequency filtering characteristics of the composite structure are investigated. With the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method, the influences of Fermi level, graphene bandwidth ratio, and external refractive index on filter frequency are discussed. The research results show that the increase of Fermi level can make the resonant frequency blue shift, in contrast, the increase of graphene bandwidth ratio and external refractive index can both make the resonant frequency red shift. When Fermi level is changed by 0.1 eV, the resonant frequency can be changed by an amount of more than 5 THz.
A passively Q-switched solid state monolithic laser based on the composite Nd∶YAG/Cr∶YAG crystal is studied. A Cr∶YAG saturable absorber is taken as the passively Q-switched unit and the component integration design is adopted. A laser with output energy of 3.5 mJ, pulse width of 2.1 ns and peak power of 1.67 MW is obtained. The performance factors reach the same level in the world. The key parameters of this monolithic laser are calculated based on the passively Q-switched rate equation, and the theoretical pulse energy value is basically consistent with the experimental value. A prototype of the Nd∶YAG/Cr∶YAG monolithic laser is obtained based on the integration and assembly of the components of a composite monolithic laser, which can successfully breakdown the air near the target and induce plasma. The preliminary requirement as a laser plug is satisfied.
In the markerless augmented reality, an improved registration method which combines oriented FAST and rotated BRIEF (ORB) feature and sequential sampling consistency is proposed based on visual simultaneous localization and mapping (VSLAM). The difference between pairs of matching samples is measured through the similarity function, and the samples are extracted from the data subset of the highest quality function. So that the better matching point pairs are obtained and the plane detection is completed in the three-dimensional map reconstruction process. The direction and position of the virtual object is represented by SVD. The registration of the virtual object is completed with the use of pose estimation of cameras. The experimental results show that the proposed method makes the average registration efficiency increases by 34.5%.
Based on the high dynamic range (HDR) image technology, a calculation method for obtaining the luminance parameters is investigated. In this method, according to the photographic characteristics and the imaging principle of digital cameras, a set of low dynamic range time series images is synthesized into a HDR image using the Photosphere software. The gray value of this image is calculated and fitted with the tristimulus value of R, G, B data obtained by linear transformation. And thus the luminance is obtained. The luminance of each color block in the standard color plate is calculated under three background luminance and it is found that the average luminance error is less than 9.22%. Moreover, the luminance errors of all color block targets and coloured targets are reduced with the decrease of background luminance, and the luminance error of the gray targets reaches a minimum when the background luminance is within an appropriate scope.
Aiming to avoid the local epitaxial growth of amorphous silicon films in the pyramidal valleys of the textured silicon wafers, a chemical polishing mixture named CP133 is used to polish the textured crystalline silicon (c-Si) surfaces. The research results show that the morphologies of the pyramidal valleys change from V shape to U shape, which clearly improves the passivation effect at the hydrogenated amorphous silicon/crystalline silicon interface. When the temperature is lower than 30 ℃, the solution is difficult to react with the crystalline silicon. However, the problem can be solved by the increase of the solution temperature up to 35 ℃. The performance of the solar cells is relatively good when the polishing time is 30 s and the NaOH texturing solution has a mass fraction of 1%.
Based on Moiré measurement technology, a method of measuring grating constant with simple setup and higher measurement precision is presented. The standard gratings with grating constants of 0.05 mm and 0.02 mm as well as corresponding grating to be measured are selected for experiments. In the experiment, three levels of Moiré fringes with high light intensity and high contrast are obtained, namely -1 level, 0 level and +1 level. The grating constant and its error of the grating to be measured are calculated. Results show that the error tends to increase with the increase of the angle between the standard grating and the grating be to measured.
A new method for detecting the nerve growth factors (NGF) is proposed based on the fluorescence quenching effect of carboxyl quantum dots. The research results show that in the pH7.5 buffer solution, the NGF antigen specifically binds to the carboxyl quantum dot-labeled NGF antibody, which can quench the fluorescence of the carboxyl quantum dots. The fluorescence quenching degree and the NGF antigen mass concentration has a good linear relationship in the range of 1-20 ng/mL, and the linear correlation coefficient is 0.9696 with the detection limit of 1 ng/mL. This proposed method has good anti-interference characteristics and has great potential applications in diagnosis and detection.
To remove the large-scale and dense noise from the terrestrial laser scanning data and keep the edge features of buildings, a filtering method fusing intensity with density of points is proposed based on the varied distance of the points to the scanning stations. The spatial distribution of noise and the intensity distribution of point clouds are analyzed comprehensively. The spatial quadtree index is established based on the horizontal and vertical angles. The fast clustering of local points and the removal of isolated points are realized based on the account of the distance before and after points in the leaf nodes, and the large-scale and dense noise is filtered out according to the ratio among different types of intensity point numbers in the same point set. The research results show that the proposed method can be used to effectively filter out the large-scale and dense noise involved in the terrestrial laser scanning data with an accuracy of above 90%.
To improve the filtering effects of point clouds in abrupt terrains, a filtering algorithm is proposed based on dynamic thresholds. This algorithm can be divided into two stages. The first filtering aims at obtaining the more accurate ground points, while the second filtering aims at obtaining the elevation difference thresholds in different regions based on the ground points obtained by the first filtering. Subsequently the original point clouds are filtered according to the above thresholds. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can be used to obtain the smaller Type Ⅰ error and total error, comparing with the other classic algorithms. Moreover, this algorithm can be used to filter the ground objects and simultaneously protect the terrain details effectively.
A method for the extraction of feature lines is proposed. This method includes the extraction of boundary and fold. The extraction of boundary mainly relies on the included angle of adjacent vectors calculated by the neighboring points. In contrast, the extraction of fold is realized mainly by means of the cluster of adjacent vectors. The point cloud data of different types of targets are collected to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
In order to improve the sorting accuracy of radar modulated signals in the electronic countermeasure environment, based on the partial connection fuzzy C-means (PCFCM) algorithm and the teaching-learning random forest (TLRF) algorithm, a radar modulated signal sorting model PCFCM-TLRF is proposed. In this model, we introduce the partial connection number (PCN) to improve the K-means clustering algorithm and optimize the fuzzy C-means (FCM) algorithm. Then the signal sample is pre-processed with the improved FCM algorithm. The teaching-learning-based optimization (TLBO) algorithm is used to optimize the random forest (RF) algorithm, so that the optimized RF algorithm can form a better classifier with much lower complexity. The pre-processed sample is used as the training sample in the TLRF algorithm to realize the sorting of radar signals. The research results show that the sorting accuracy of the PCFCM-TLRF model is higher than those of other sorting models. This model can realize the effective sorting of radar modulated signals.
Currently, the external quantum efficiency (EQE) for deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (DUV LEDs) with emission wavelengths shorter than 360 nm is generally lower than 10%. On one hand, the transverse-magnetic (TM) polarized light dominates the light emission from the AlN-rich AlGaN based quantum wells, which strongly reduces the light-extraction efficiency (LEE) for DUV LEDs. On the other hand, limited by the current hetero-epitaxial growth technologies for AlGaN materials, the crystal quality for DUV LEDs is still poor, which increases the non-radiative recombination rate in the active region, thereby causing the reduction of the internal quantum efficiency (IQE) for DUV LEDs. Besides, the carrier injection efficiency, especially the hole injection efficiency, also strongly influences the IQE for DUV LEDs. Thus, the researchers have made extensive efforts to increase the hole injection efficiency and thus improve the EQE for DUV LEDs. The recently proposed approaches for the improvement of the hole injection efficiency for DUV LEDs are reviewed and discussed. Moreover, the underlying physical mechanisms are disclosed in the in-depth level. These are important for the improvement of the device performances for DUV LEDs.
As the transmission capacity and distance increase, Kerr nonlinearity becomes more and more obvious, which is currently becoming a major factor limiting the fiber transmission performances. The basic principles of some techniques for fiber Kerr nonlinearity compensation in fiber communications are introduced in detail, such as the digital backward propagation algorithm and the perturbation-based nonlinear compensation method. The development status of these technologies is reviewed. The advantages and disadvantages of each algorithm are also presented. Furthermore, the trend and potential applications of these technologies are prospected.
Compared with traditional Fabry-Perot (F-P) cavity semiconductor lasers, the edge-emitting semiconductor lasers with distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) gratings exhibit excellent characteristics in terms of narrow linewidth and stable output wavelength. They have huge application requirements in the fields of laser communication, optical interconnection and nonlinear frequency conversion. The DBR semiconductor laser can achieve laser narrow linewidth, dual wavelength output and wavelength tunability by properly designing the DBR grating and device structure. The DBR tapered semiconductor laser can simultaneously combine high power, narrow linewidth and high beam quality owing to the built-in DBR grating structure. In this paper, the structural design, fabrication process and performance advantages of these types of lasers are discussed, and the present situation of research and development at home and abroad are summarized. Based on this, the research work and development trend of DBR semiconductor lasers are further discussed and prospected.
The important role and major achievements of a wireless laser and radio frequency (RF) complementary communication system are introduced, and the superiority and importance of the wireless laser and RF complementary communication technologies are explained. And the basic working principle of the wireless laser and RF complementary communication system is expounded, and the feasibility of the wireless laser and RF complementary communication system is illustrated. Combining with the latest research results of the complementary communication systems in foreign countries in recent years, the key problems encountered are mainly analyzed. The challenges faced by the complementary communication systems at present are presented. The key technologies to solve these challenges are put forward. The application prospect and development trend of the complementary communication are pointed out.
The process of petroleum extraction is often accompanied by the production of corrosive gases, metal particles and minerals, resulting in the serious corrosion and wear of petroleum machinery and equipment. Laser surface treatment technology can improve the material properties, such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance and fatigue resistance of parts and workpieces. The applications of laser surface treatment technologies in the petroleum machinery are summarized. The laser quenching, laser cladding and laser alloying are introduced in detail. The other laser surface treatment technologies and their applications are also summarized. The application status and exiting problems of laser surface treatment technologies in the petroleum machinery are analyzed and their development prospects are also put forward.
In order to solve the geometric distortion caused by filter change in the imaging process of multi-channel spectral data, a multi-channel spectral image registration method based on speed up robust features (SURF) and maximum submatrix is investigated. The features of the multi-channel spectral images are extracted by the SURF algorithm, and the preliminary registration images are obtained through perspective transformation. In addition, aiming at the problem that there exists the invalid regions with zero pixel value on the image edge after registration, a method for detecting the largest inner rectangle in images by maximum submatrix is proposed to remove the invalid edge regions and maximize the retention of valid area information. The multi-channel imaging data of the murals are tested. The results show that the proposed method has better robustness to image scale and brightness variation, and can avoid the influence of invalid regions on the subsequent spectral reconstruction and color restoration occurred in the other registration methods. It also has better performance in registration accuracy, information maximization retention, and time efficiency.
The ultrafast transient absorption spectroscopy of interband excitation is utilized to evaluate the ultrafast carrier recombination dynamics in the conductive (n-type) nitrogen (N)-doped and semi-insulating (SI) vanadium (V)-doped 6H-SiC wafers. The carrier relaxation of n-type 6H-SiC with carrier lifetime more than 10 ns is dominated by indirect recombination through N impurities and/or inherent defects. Compared with the n-type 6H-SiC, the V-doped one has a pronounced modulation of transient absorption, resulting from an additional carrier recombination process caused by the carrier trapping of V deep levels. The carrier-trapping with a lifetime of about 160 ps is more than two orders of magnitude faster than the indirect recombination. With a simplified energy level model and the global analysis, the carrier recombination mechanism is investigated and the carrier lifetime of 6H-SiC is determined accurately.
Aiming at the influence of the complicated deep-space communication environment on the anti-noise performance of X-ray communication system, a bit error rate optimization model is proposed based on quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM). The mathematical expression of the primary noise source is derived through analyzing the noise source in actual communication scenario combined with an existing X-ray communication link model. On the basis of Poison distribution model, the calculation model of the communication error rate in intensity modulation direct detection (IM/DD) system is established under the QAM mode, and its effectiveness is verified by simulation. The simulation result shows that the bit error rate of QAM system can be reduced to 10-6 orders of magnitude.When the same amount of photons are received, the proposed method launched less photons compared with the existing binary on-off keying (OOK) and pulse position modulation (PPM) methods. Furthermore, this proposed method is suitable for the modulation of the space X-ray communication system when it is deployed in the environment with an unstable noise intensity.
Based on the high-frequency emphasis filtering and adaptive histogram algorithm, the digital image enhancement technology is introduced into the X-ray images of the cultural relics with reference to the medical X-ray image processing method. After image enhancement, the edges and details of the X-ray image of an artifact are enhanced, the contrast is stretched, and the useful information is clear. The results show that the proposed method not only facilitates the image analysis, but also simplifies the entire inspection process.