With the strong demand of lightweight, structural and functional integration, high strength Al-alloy complicated precision parts are widely used in aerospace and other fields. But due to its poor welding and casting performance, it is difficult to be prepared by conventional techniques. Selective laser melting (SLM) is the most promising method to achieve the high demand requirements for producing such parts. High strength Al-alloy has many disadvantages such as low absorption rate of laser, high thermal conductivity, easy oxidation, containing abundant easy burning loss of alloy elements, which has a strong hot cracking tendency. It is hard to be formed, so its SLM forming technology lags far behind other materials. Despite all that, SLM-processing of high strength Al-alloy is developing rapidly in recent years because of its broad application prospect. This paper summarizes the research status, development trend and the main problems of high strength Al-alloy SLM at home and abroad.
The recent application of 3D printing technology in orthopedic field is summarized. We explore the applied levels in orthopedics health of 3D printing, the first level is that 3D printing makes out models for preoperative simulation, which eliminates the need for intra-operative steps, reduces the time of surgery, meets the requirements of patients, and reduces the labor intensity of doctors. The next one is that 3D printing produces surgical guide based on computer-aided design to achieve the precision of the tailor-made implant operation, which shows how to use the guide to ensure the accuracy of surgical position, direction and angle, and improve the safety and predictability of surgery. The third one is 3D printed implants encounter the clinical policy challenge, but personalized 3D printed implants can better meet the needs of the patient. Compared with foreign technology, there is still a gap in the 3D printing in the orthopedics in China, which reveals the countermeasures need to be focused on by China. Finally, the future of applications of 3D printing in orthopedics is prospected.
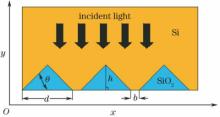
In the community of green energy utilization, it has been a key issue to effectively enhance the light conversion of thin film silicon solar cells. A rear surface reflector structure of thin film silicon solar cells based on triangular one-dimensional diffraction gratings is designed, which can effectively enhance the light utilization efficiency of the solar cells. With a variety of grating structure types, inclination angles, grating periods and grating separations, the light reflectance of the rear surface of thin film silicon solar cells are respectively studied via the finite difference time domain (FDTD) method. The results indicate that the one-dimensional grating structure consist of isosceles right triangles gives rise to an optimal rear surface reflectance, and the reasonable increase of the grating period can also enhance the light reflectance of rear surface of the silicon solar cells. Besides, the study in this work also shows that there appears a resonance peak in the reflectance curve when the light wavelength matches the grating period of the gratings. Based on this diffraction characteristics, the one-dimensional grating structures proposed in this work can also be utilized as a wavelength selector in future designs.
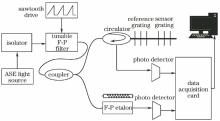
In order to establish a stable fiber grating sensor wavelength demodulation system, we use narrow band filter characteristic of tunable Fabry-Perot filter to make a linear scan of broadband light source, and use a high-precision reference grating placed in a thermostat to calibrate Fabry-Perot etalon, and to provide multiple wavelength reference points with the same interval and stable amplitude. The original data sequence is modified by the improved wavelet threshold denoising algorithm(using a new threshold function and a new threshold). We gain raw peak sequence by the core idea of the Gaussian fitting algorithm, and then do the secondary treatment, remove some invalid peaks, modify location of part peaks, and build a fiber grating displacement sensor real-time monitoring and demodulation system. Compared with spiral micrometer, accuracy of this system is about 0.25 mm.
According to the basic principle of laser communication and common aperture technology, the parameters of the optical system of common aperture free space laser communication are analyzed, and an off-axis common aperture laser communication optical system is designed. With an off-axis two-mirror structure, the optical antenna of the system has an effective aperture of 160 mm and the beam compression ratio is 10∶1. Tracking and pointing system adopts non-focus telescope structure. The maximum tracking field of view is ±1 mrad, and the best tracking accuracy is 2 μrad. Based on Zemax software, the ray tracing and performance analysis are given. The results show that the wavefront error of the system is better than 0.1λ (λ=632.8 nm), so the performance of the system is excellent. The system is of the compact structure, the reasonable tolerance and the simple assembly. The system can meet the needs of practical application and has certain engineering significance for the realization of medium earth orbit (MEO) free space laser communication.
In the study of diffraction field calculation of spatial curved surface light source, it is a popular algorithm that considering the curved surface light source as a set of small triangle surface light sources. The analytic expressions of arbitrary triangular surface light spectrum and special frequency point is derived based on coordinate affine transformation. The problem of partial triangular spectrum loss in the traditional method is solved and the quality of the reconstructed image of the hologram is improved. Through rigorous theoretical analysis and calculation, the analytical expressions of two-dimensional and three-dimensional arbitrary triangular spectrum is solved accurately. The analytical expression of three-dimensional primitive triangular spectrum is simplified. A fast calculation method of 3D objects computing holograms using surface element division is obtained. Theoretical simulation and experimental results verify the validity of this method.
To preserve defined edges of the fused multi-focus image while enriching the detail features of the image, a novel algorithm based on the fast finite shearlet transform (FFST) and the guided filter is proposed. Firstly, the original images are decomposed into low frequency subband coefficients and bandpass direction subband coefficients by using FFST. Then, in the fusion of the low frequency coefficient, a novel Sum-Modified-Laplacian (NSML) is defined, and a selection scheme of low frequency coefficients is designed based on regional NSML. Due to the rich detail information of high frequency coefficient, we present a regional weighting energy fusion algorithm based on the guided filter. Finally, the final fused image is produced by inverse FFST. Comparison experiments are performed on different image sets, and experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm performs better in both subjective and objective qualities.
The traditional facial expression recognition (FER) methods only extract single expression feature. Meanwhile, the choice of expression classifiers has limitations. To solve these problems, we propose a FER method based on the fusion of local features and deep belief network (DBN). Firstly, the eyebrows and eyes part and mouth part with rich expression information are extracted as local expression images. In order to attain more effective expression features, the Log-Gabor features with texture information and second-order histogram of gradient direction features with shape information are extracted and fused from local expression images. DBN model is trained with fusion features. The trained DBN model is used to recognize the facial expression. The experimental results show that the recognition rates of the proposed method on three databases are 96.30%, 97.39% and 95.73%. The proposed method effectively improves the recognition rate of facial expression.
In view of the holding unsatisfactory effects of the traditional non-local means algorithm for texture details, an improved non-local means denoising algorithm combined with fuzzy edge complement (FEC) is proposed. The edge texture feature image is detected by the FEC algorithm. The similarity weight parameter is chosen adaptively according to the edge texture feature, and the edge texture region and the flat region are smoothed for different degrees pertinently, which prevents the edge texture information from being lost. The similarity weights of non-local image blocks are improved using the structural similarity of edges. The effects of pixels in the same area are increased, and those in different areas are reduced. Thus, the better texture hold effects can be achieved. Experimental result indicates that the image denosing can be effectively achieved by this method. Meanwhile, the more texture detail features and geometrical structural features are persevered.
Due to the image noise and boundary uncertainty, the noise resistance and accuracy of image segmentation algorithm is a challenging task. Two improvement fuzzy clustering algorithms for image segmentation are proposed. The proposed algorithms for image segmentation act as the following two steps. The first step is detecting the probability of every central pixel being a noise point adaptively based on the grey levels in its local information. The detecting results, playing the roles of denoising and detail information, are used to construct a new image, and then two novel segmentation algorithms based on fuzzy clustering are proposed. The second step is detecting the potentially misclassified pixels and refining the segmentation results by correcting the errors of clustering for improving the segmentation accuracy and visual effects. The obtained segmentation algorithms are carried out on synthetic image, Berkeley images and other real images in different noise levels. The results show that the proposed algorithm has advantages of segmentation accuracy and adjusted rand index compared with the others fuzzy clustering algorithms, and the segmentation results have clear contour and better visual effects.
Aiming at the problems of scale change, illumination change and noise interference in the uppers matching, a shoe upper matching detection method based on the speeded-up robust features-object request broker (SURF-ORB) algorithm combined with random sample consensus (RANSAC) algorithm is presented. The feature points of the uppers image are extracted by SURF. The descriptors are obtained and the feature points are described by the ORB algorithm. In order to obtain more accurate matching points, the initial matching is completed by using the Hamming distance, and then by combining the RANSAC algorithm, the mismatching points generated by noise interference and illumination changes are eliminated. The experimental results show that the algorithm can effectively match and has strong robustness when there are scale change, illumination change and noise interference in the shoe uppers image.
With the development of content-sharing networks, the on-line video data have grown dramatically and a large number of illegal copies have been appeared. To reduce any copyright infringement disputes, it is necessary to detect illegal copies on-line internet. Video fingerprint, which can express the video perceptual content as a compact description, is a key technology for copy detection. The video fingerprint algorithm based on spatio-temporal deep neural network is designed by the use of the excellent robustness of denoising auto-encoder (DAE) and building a deep neural network to extract features on frame level through greedily training DAE. Consequently, a long short-term memory network is adopted to extract each frame features of the deep network, and the training algorithm is designed on the basis of the theory of slow-feature analysis. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can reveal a high accuracy in video copy detection and outperform a number of the comparative algorithms.
For the skew correction of complex scanned electronic documents with text, images, tables and formulas, a new skew detection method is proposed based on Shearlet transform and multi-scale analysis. Based on the localization and directionality of Shearlet transform, energy in all directions can be obtained. The two components with the highest energy can correspond to the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. According to these two directions, the direction of the text line in the scanned document can be accurately detected and the skew angle of document image can be further determined. The experimental results show that the proposed method can avoid the interference of images, tables, and so on in scanned documents, and has a good anti-noise ability. The proposed method is of higher detection accuracy for document images with complex content.
In order to reduce the influence of different scales of noise on the reconstruction of three-dimensional point cloud models, a denoising and simplification algorithm based on the method library of the passthrough filter, statistical filter, radius filter, improved bilateral filter and voxel grid filter is proposed. Firstly, the object is extracted by the passthrough filter. Then according to the distance between the noise points and the model body, the noise points are divided into the small scale noise and the large scale noise. The large scale noise is removed by the statistical filter and the radius filter, and the small scale noise is removed by the improved bilateral filter. Finally, the three-dimensional point cloud is simplified by the voxel grid filter to reduce the space complexity and the accuracy of the proposed algorithm is shown via the triangular mesh reconstruction. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively remove different scales of noise existing in the point cloud model and ensure the uniformity of point cloud simplification under the precondition of not destroying the geometrical structure of the point cloud. In addition, this algorithm runs quickly and has high reconstruction efficiency.
The color feature can effectively characterize the color distribution of images. However, most of the existing algorithms are based on a single color space, and the color moment is the most commonly used as global color feature vector, thus the lack of color spatial information lead to retrieval errors. Aiming at the problems, a block color feature extraction algorithm based on the mixed color space is proposed. The extracted color feature and texture feature are combined for classification and recognition of image. Experimental results show that the precision and recall of the color feature extraction algorithm in the mixed color space are improved in the process of classification and identification for Chinese painting and general image, when it compared with the single color space feature extraction algorithm. And they are further enhanced after image segmentation.
In order to solve the problem of high probability of misclassification for similar samples of the collaborative representation classifier (CRC), we propose a discriminative CRC (DCRC), which takes the effect of all training samples and each class of training samples on the collaborative representation coefficient into account. The coefficient obtained has strong discrimination and can improve the discriminability of the similar samples. Human action recognition is conducted based on DCRC. We first extract the features of depth action sequence via depth motion maps (DMMs). Then, we use DCRC to encode the DMMs features and perform classification and recognition by new classification rules. Experimental results on the human action recognition datasets show that the DCRC has certain discriminative properties for similar actions, and the recognition accuracy is superior to some existed methods.
In order to improve the correlation of the fusion coefficients in multi-focus image fusion technology and enhance regional information abundance, we propose a method based on the entropy rate segmentation and multi-scale decomposition on multi-focus image fusion. After multi-scale decomposition, the edge and detail information are stored in the high frequency subband. We can better preserve the details of the image through model value and comparison consistency check. At the same time, the similar information coefficients of image are assigned to the same area, combined with low frequency subband and entropy rate segmentation. Then the image is fused according to the regional spatial frequency and energy, the correlation of the coefficients is improved, and the fusion image edge transition is more natural. Finally, the inverse transformation is carried out on the images to get the fusion results. Experimental results show that the proposed method has better performance in both subjective and objective evaluation, and achieves better fusion effect with high applicability.
Aiming at the halo artifacts caused by traditional hogging image enhancement algorithm, a fractional image enhancement algorithm combining fractional differential and multi-scale Retinex is proposed. The proposed algorithm first processes the original image with a fractional order differential algorithm to preserve its low frequency information, and converts the processed image from the RGB color space to the HSI color space. Then, the Gaussian filter in the multi-scale Retinex algorithm is replaced with a leading filter to extract the luminance component and the reflected component, and the sum of the two components is used as the new luminance layer, and the Gamma correction function is used for the saturation layer. Finally, the HSI image is converted back to RGB image. An objective evaluation method is used to evaluate the effectiveness of the algorithm. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has high efficiency and no halo artifacts present in the processed image.
High-precision decoding is a key problem of DeBruijn color structured light three-dimensional measurement. We proposed a DeBruijn color structured light decoding algorithm based on color transfer technology. Firstly, the color information of the structured light-coded image is used as priori knowledge, and the color structured light projection image is enhanced and de-illuminated by the color transfer method to restore its stripe color information. Secondly, the central coordinates of fringe are extracted accurately based on the proposed dual-step sub-pixel extraction algorithm for stripe center point positioning of color structured light projection image . Finally, the matching of feature points is performed based on the dynamic programming algorithm. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively improve the decoding accuracy, and has strong robustness under the condition that the texture of the illumination and the surface texture of the measured object lead to the degradation of the structure light projection image quality.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-destructive, high-resolution,and fast tomographic imaging technique. Electrical tape is an important physical evidence in the forensic science. A self-built frequency-domain OCT system is employed to obtain two-dimensional (2D) cross-sectional OCT images of electrical tapes from ten different brands. The optical path, the scattering intensity ratio, the number of signal peaks, and the attenuation coefficient are extracted from the 2D cross-sectional OCT images of electrical tapes. Statistically significant differences of the parameters are compared in those different samples. Meanwhile, three-dimensional (3D) OCT image reconstruction of the electrical tapes is also implemented to create transverse sectional images beneath the surface. The experiments demonstrate that OCT provides a series of new features to effectively distinguish different brands of electrical tapes. OCT provides in-situ, non-destructive, high-resolution, and easily operated real-time examination, and it is a promising method for electrical tape examination in the forensic science.
In the distributed aperture synthesis imaging system based on digital holography, the errors of detector rotation and the pupil magnification among the sub-apertures are studied, and the correction methods based on the sub-aperture image registration is proposed. The scale-invariant feature transform algorithm, the nearest neighbor search method based on Euclidean distance and the M-estimator sample consensus algorithm are carried out to realize the image registration of sub-aperture, so that the errors of relative rotation angle and magnification among the sub-apertures are calculated. Then the complex amplitude of object light is processed to correct the rotation and magnification errors. The experimental results show that the calculated relative error values are less than 0.01, and the sharpness value of synthetic aperture image is significantly improved after correction.
The synthetic aperture (SA) beam forming can realize bidirectional dynamic focusing in both transmission and receiving, so it improves the imaging resolution effectively and will be widely used in the multi-element phased array ultrasonic endoscope system. However, because of the low transmission energy of the single element, the echo signals are weak and could be influenced by noise easily, thus the signal-noise ratio (SNR) of the image is relatively poor. A new imaging algorithm is proposed, which combines the Barker coded excitation using the linear frequency modulated carrier with the synthetic aperture beam forming (LFM Barker SA). The broadband of linear frequency modulated signal and the autocorrelation of Barker can remedy the SNR of synthetic aperture beam forming, and the proposed algorithm improves the imaging resolution further. The simulation results with FieldⅡ software show that the LFM Barker SA algorithm improves the SNR about 10 dB and increases the axial resolution from 0.60 mm to 0.38 mm, compared with the Pulse SA algorithm. The experimental result verifies the feasibility of this algorithm.
Aiming at the wide application of the visual coordinate measurement of the handheld target, an on-site two-step calibration method for the probe tip center of the planar target is proposed. The conversion relationship between the target coordinate system and the camera coordinate system is established by two sets of target images in different positions. Based on the position invariant principle, the object optimal function is established according to the image information of the first set target parallel to imaging plane with different angles. The Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm is employed to solve the optimal corrected value of the probe tip center along x and y directions in target coordinate. The error of the probe tip center along z direction is solved by using the image information of the second set target relative to the imaging plane of the camera with different angles. The correctness of the method is verified by simulation and experiment. The experiment results show that the repeatability accuracy of the probe tip center coordinates in x, y and z direction can reach 0.077 mm, 0.035 mm and 0.140 mm, respectively, which can effectively solve the problem of on-site calibration of the probe tip center of the handheld planar target.
Under the environment affected by non-gravitational external force, the pose measurement of a 6D laser target becomes invalid. In order to solve this problem, a pose measurement method based on laser target combined with strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS) is proposed. By deriving the Kalman filtering state equation and observation equation, Kalman filtering model of combined measurement system is established. The pose error and the random error of the inertial measurement unit (IMU) are both corrected by the Kalman filtering. The fault detection method is introduced into the Kalman filtering model, so that the combined system achieves the ability of self-monitoring. When the pose data of the laser target become invalid, the system can only use the corrected SINS data to ensure the reliability of the system. Finally, the method is verified by the simulation experiment. The simulation results show that this method can effectively solve the invalid problem of pose angle measurement of the laser target and improve the anti-interference and dynamic performance of the system.
According to digital level barcode''s common characteristics of black and white alternation with different widths, a fast adaptive correlation matching barcode location method is proposed, which is based on equal stripe number and equal width between the matched image and the template image. The barcode grayscale image to be matched is obtained by preprocessing of graying, cutting and correcting of the proposed method. And every time the scale factor of the matched image is obtained according to the assumption of equal strip number and equal width between the matched image and the template image. The image to be matched is transformed to matched image with equal width as the template image using bilinear interpolation method. The matching and precise positioning of barcode are achieved after shift-related operation between the measured image of adaptive scaling and the template image. Leveling measurement experiment results show that this method makes full use of the whole information of barcode image, which has the characteristics of strong anti-interference ability, independence of coding rules, high algorithm efficiency and high precision,which can be widely used for height measurement of barcode level with different coding rules.
A controllable polarization analyzer based on waveguide structures is one of core components in integrated photonic systems, whose output polarization state can be dynamically manipulated, and it has an important application value in integrated photonic systems. A novel controllable polarization analyzer based on deflection ridge waveguide is proposed. With the anisotropy and large birefringence of the liquid crystal material, the controllable output of transverse electric wave and transverse magnetic wave can be realized based on the electro-optical effect. The optical performance of the proposed device is numerically demonstrated by beam propagation method. The results show that the extinction ratio of the proposed system is 29.8 dB and the optical loss is only 0.002 dB, and the proposed device is insensitive to wavelength and fabrication error. The proposed device has the advantages such as simple dynamic control, easy design and fabrication and simple structure, which has wide applications in integrated photonic systems.
The selective laser melting (SLM) is a metal additive manufacturing (AM) technique in which a high-energy laser beam is used to melt the metal alloy powder on the designed two-dimensional cross-sections and solid parts are printed layer by layer from bottom to top. It has the advantages of high dimensional accuracy, good surface quality, high density and little material waste, and has been developed into one of the key AM technologies in the metal part forming field. The principle and research status of the SLM technology are introduced, and its applications in aerospace, medicine, automobile, mold and other aspects are summarized. In addition, its future development trend is prospected.
As an additive manufacturing technology to fabricate metallic components directly, the selective laser melting (SLM) can be used to fabricate complex structures with a high precision. The development status and principle of SLM technology are introduced, and the research and application status of SLM technology of titanium and titanium alloys at home and abroad are discussed from several aspects, which include material systems, forming processes, microstructures and mechanical properties. Furthermore, the problems and future trend of SLM technology for titanium and titanium alloys are summarized and prospected, respectively.
The research progress on the technologies related to the additive manufacturing of aluminum alloys is introduced. The advantages and development prospects of the selective laser melting, wire-arc additive manufacturing and laser-arc hybrid additive manufacturing in the field of additive manufacturing of aluminum alloys are focused. The results show that the study of selective laser melting is mainly focused on the improvement of the efficiency of space filling of formed parts, the control of microstructure and the improvement of mechanical properties. The present efficiency of space filling of formed parts is close to 100%, the microstructure and mechanical properties are better than those of the casting parts, but worse than those of the forging parts. The research on the wire arc additive manufacturing is mainly focused on the size control of large scale structures, but the improvement of performance is limited by the relatively large heat input. As for the laser-arc hybrid additive manufacturing, the related research is few, and it is the future prospect to improve the corresponding process technique and the laser-arc coupling behavior.
The recent applications of the additive manufacturing technology in the fields of personalized ophthalmology, precision ophthalmology, mobile ophthalmology, optometry and ophthalmic bionic, and its future prospects are reviewed. With the advantages of high efficiency and convenient of customization, the laser additive manufacturing is expected to help patients to obtain more humanistic, more targeted and more widespread ophthalmic medical services.
With the improvement of the quality and performance of laser additive manufacturing metal components, the metal powder material has become a restraining factor for the application of metal laser additive manufacturing technology. Therefore, the special metal powder for laser additive manufacturing has recently become one of the research hotspots in the recent years. The research current status of steel powders used for laser additive manufacturing is reviewed from various aspects such as materials design, powder fabrication, powder evaluation and sample cases. Also, the main problems and research directions are put forward for the research and application of laser additive manufacturing steel powders.
The application of laser in the additive manufacturing technique has enriched the additive manufacturing technique category and broadened the precision range and application fields. The category, principle and characteristics of the laser additive manufacturing (LAM) techniques of ceramic materials are summarized and its applications and research status are introduced. In addition, the existing problems of the above techniques are analyzed, the future development of LAM of ceramic materials is prospected.
Principles of 3D printing techniques are briefly introduced. Based on the digital model file, the object is constructed by means of adhesive material, which is printed layer by layer. Then the research status of 3D printing glass is highlighted, including 3D printing glass with or without laser. Problems existing in the study of 3D printed glass are described. We further deepens the cognition of laser 3D printing glass technology through the detailed introduction of principle and application. Finally, we make a summary and future prospect about the emerging technique.
Devices in a diversity of application scopes are now evolving towards miniaturization, functionalization and integration. Finely-patterned 3D micro-nanostructures are in great demand as core components in more and more devices. This keeps challenging the current micro-nanofabrication techniques. 3D femtosecond laser nanoprinting (FsLNP) is an outstanding mask-free three-dimensional additive fabrication technique with both powerful designability and high accuracy far beyond the optical diffraction limit. Based on the unique two-photon photopolymerization mechanism of 3D FsLNP, a series of highly efficient and well-functioned micro-nanodevices can be fabricated when suitable photopolymerization scheme and structure arrangement are given. In this review, we briefly introduce the technical essentials and physical fundamentals of 3D FsLNP, as well as several typical application examples.
The stereolithography, selective laser sintering and two-photon polymerization are typical laser micro-nano three-dimensional (3D) printing techniques, where because the feature size of two-photon polymerization can be beyond the diffraction limit, it is possible to fabricate micro-optical elements precisely at sub-wavelength scales. These three laser micro-nano 3D printing techniques are reviewed.
The microstructure and stress state of the additive parts are improved by the combination of laser shock peening (LSP) and wire-arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) technologies. The microstructures, microhardness and residual stress distributions in the depth direction of 2319 aluminum alloys fabricated by WAAM before and after LSP are investigated. The research results show that LSP can significantly refine the grain size and improve the residual stress distribution of 2319 aluminum alloys fabricated by WAAM. After LSP, the average grain diameter of additive parts decreases from 68.86 μm before LSP to 34.32 μm, and the microhardness increases from 67.8 HV before LSP to 100.6 HV. The maximum residual compressive stress is about 90 MPa and the influence depth is 0.65 mm.
A new structural method of laser additive manufacturing (LAM) with four-wavelength laser, multi-tube dusting, and quasi-six-degree-of-freedom numerical control motion is proposed. The overall system architecture is analyzed in terms of linear space and Lie subgroup function. A linear and spatial mathematical model for this system is established. The components of Nd-Fe-B rare earth permanent magnets are sprayed quantitatively by using the multi-dusting mechanism. In addition, by the control of the powers and angles of four laser beams, the selective and directional laser irradiation is conducted, and the LAM of heterogeneous permanent magnetic parts is realized with forming accuracy of 20 μm, minimum width of less than 80 μm, and magnetic energy product of 474 kJ·m 3.
A cylindrical lens working in the terahertz (THz) frequency range is designed and its sample is also fabricated by using the three-dimensional (3D) printing technique. A test on this sample is conducted. The comparison among the testing results, the simulation results, and the testing results of the commercial THz lenses is made. The results show that the focal lengths of two kinds of lenses are both about 100 mm, which matches with the simulation results. Moreover, under different propagation distances, the full widths at half maximum of spots for the printed lenses are very close to those for the commercial lenses, which proves that the 3D printing technique can be used in the fabrication of THz optical devices, such as cylindrical lenses.
As a rapid dieless production method, 3D printing is promising to avoid the high cost of mold manufacturing and maintenance in the preparation of sealing glass preforms. Glass preforms are prepared by selective laser sintering (SLS) with granule and curing agent as main ingredients. The experimental results show that sealing glass powder granule can be applied to SLS process by powder laying, while polyethylene glycol (PEG) is used as binder to form granule, and polystyrene (PS) with a proper mass fraction of 20% is used as curing agent for laser sintering. Preforms with regular size can be obtained by selective laser sintering the homogeneous mixture of curing agent and granule. After laser sintering, preforms have to be heated to expel the organic agent, and then it becomes the sealing glass preforms meeting the strength requirement. The technology can be applied to the rapid dieless manufacturing of sealing glass preforms.
A new method to fabricate the filled-type conductive composites is proposed. Based on the selective laser sintering technology, the honeycomb-like porous graphite skeleton body is fast fabricated. After the immersion, drying and carbonization treatments for the body, the preform is obtained. The new conductive composite is prepared with the combination of the preform and the phenolic resin powder. The research results show that, when the number of honeycombs is 18, the conductivity of Y-type conductive composites can approach 0.104 S·cm -1, while the bending strength is 20.61 MPa. The electrical and mechanical properties of the filled-type conductive composites can be adjusted and controlled with the different porous graphite skeleton structures and the different post-treatment processes.
In order to apply the image processing technique to the surface defects online-detecting of stamping parts, a real-time fast detection system is designed. Multi-pattern matching algorithm is used to locate the stamping parts in the image, then the region of interest is built. The shading correction algorithm based on the Laplace-Gaussian (LoG) operator is proposed to enhance the defect parts of workpieces. The Otsu algorithm and morphology are used to extract the defect parts. The system adopts MATLAB to realize the filtering algorithm based on LoG operator, the rest of the algorithm are implemented by LabVIEW and the MATLAB script node is called by LabVIEW, the multithreading technology is used to accelerate the computation. According to the experiment results, the proposed system can detect each stamping parts on the production line and detect the defectives. The whole process takes less than 100 ms, which can satisfy the demand of online detection.
The machine vision technique is introduced to recognize the Empoasca flavescens automatically on the yellow sticky traps in natural scenes in order to realize the accurate and timely forecast of Empoasca flavescens in tea garden. The superpixel segmentation algorithm and DBSCAN (density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise) cluster algorithm are employed to separate the interesting target regions from background, which ensures the accuracy and completeness of the target area. Then, six classification features, including mean value of L, a, and b and their standard deviation, are extracted from the marked area in target image. Last, LSSVM (least squares support vector machine) is developed to identify Empoasca flavescens from other insects that are captured by sticky traps. As the imbalanced sample number between Empoasca flavescens and other insects results in the low classification accuracy, the improved SMOTE (synthetic minority over-sampling technique) algorithm and KS (Kennard-Stone) algorithm are used to improve recognition accuracy of Emposace flavescens. The proposed algorithm achieves 99.03% of the overall recognition accuracy, and the identification accuracy of Empoasca flavescens reaches 91.76%. The proposed algorithm can provide an effective way for real-time detection of Empoasca flavescens.
The structure of dielectric ring-shaped photonic crystals based on the checkerboard complex lattice is constructed. By the plane wave expansion method, the complete bandgap width of this structure and the structural parameters are optimized. The study results show that, under the optimal parameters, the maximum value of the complete bandgap width is 0.160, and the bandgap ratio is 30.59%. The proposed structure has a good stability.
With the help of Mathematica symbol calculation software, we extend the F/G expansion method improved by the G''/G expansion method and obtain exact solutions of a series of high dimensional nonlinear evolution equations by combining the variable separation method. Taking a (2+1)-dimensional dispersive long wave equation as an example, constructing the exact solutions by F/G expansion method is to extend the original traveling wave transform to any function transform, in which the traveling wave transform is only a special case of this any function transform. Then the non-traveling wave solutions of the (2+1)-dimensional dispersive long wave equation are obtained. By choosing the appropriate function, we can construct (2+1)-dimensional bright dromion solution and periodic solitary wave solution of the dispersion long wave equation. Then we study the propagation of the bright dromion solution with time and the evolution of the periodic solitary wave solution over time further.
In order to improve the grayscale level and resolution of the micro display on silicon, and maintain pixel grayscale linearity at the same time, the study of digital and analog hybrid scan strategy is proposed with the advantages of analog amplitude modulation and digital pulse width modulation. The subspace weight-bit scan algorithm and its effect of improving the scanning efficiency are introduced. Then, the bit and grayscale modulation of the digital and analog hybrid scan strategy are introduced, and a 256-level grayscale case is deduced. The result shows that the method can reduce the data transfer frequency effectively and this advantage becomes more obvious with the increasing of the grayscale and resolution. In the case of 256 grayscale and 1920 pixel×1080 pixel resolution, the required data transfer frequency can be reduced to 52.49 MHz, the scanning efficiency is 92.58% and the linearity keeps at 100%. This method reduces the required data transfer frequency and the requirement of the display device.
A graphene-based band-stop filter structure for the surface plasmonic polariton in the mid-infrared wave band is proposed, which consists of a periodic array of single-layered graphene. The numerical simulation results show that the slight variation of the chemical potential of the graphene nanoribbon results in the shift of resonance wavelength. This structure possesses a sensitivity of 1100 nm/RIU and a figure of merit of 138 in the mid-infrared spectrum range, which can be used as a highly sensitive refractive index sensor.
With the successive operation of the creation operator combination of two-mode (a, b) and the two-mode squeezing operator on a two-mode vacuum state, a two-mode squeezed vacuum state excited by combination operators is constructed. By the numerical calculation method, the influences of two-mode squeezing parameter and combination coefficient on the quantum properties such as the squeezing effect of mode b, the anti-bunching effect, the Q parameter and the two-mode entanglement degree are discussed. The study results show that the mode b does not display the squeezing effect while the anti-bunching effect and the sub-Poissonian distribution property of mode b are both weakened with the increase of the squeezing parameter or the combination coefficient u. The entanglement degree between the two modes becomes larger with the increase of the squeezing parameter. And there exists a non-linear relationship between the two-mode entanglement degree and the operator combination coefficient.
For the interference problem of outliers on the point set registration, a robust affine point set registration method based on Bayesian student′s t mixture model (SMM) is proposed. Under Bayesian framework, the point set registration problem is formularized as the probability density estimation problem by using the SMM. By introducing the approximate variational posterior distribution, the objective function is converted to maximize the variational lower bound of complete data log-likelihood, and the variational Bayesian expectation maximization (VBEM) method is used to estimate the variational posterior distribution of model parameters iteratively. The free degree of student t distribution is estimated by maximizing the complete data log-likelihood, and it is approximated by using the Stirling formula. Registration experiments on simulated point sets and optical remote sensing images verify the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method.
The moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) images from 2014 to 2016 are collected in the Strait of Gibraltar (SOG). The temporal and spatial characteristics of internal waves are analyzed statistically based on MODIS images. The optical remote sensing images show that internal waves generate at the east of Camarinal sill, and concentrate at the western Mediterranean. The eastward propagation internal waves have arc-like shape. The temporal distribution of internal waves shows that the majority of internal waves are observed in the second and third quarters. The generation and propagation characteristics of internal waves in the SOG are further studied by Massachusetts Institute of Technology general circulation model (MITgcm). Through the change of surface elevations and isotherms, the interaction between barotropic tide and the sill of the SOG is analyzed. The arc-like eastward internal waves are generated nearby the jaw. The amplitude decreases with the increase of water depth and the strengthening of dispersion effect. The east propagating internal waves disintegrate into a train of rank-ordered internal waves packets in the process of propagation. In addition, the width between the crest lines and the radius of the arc-like crest line increase. The number of inertial wave in the wave packet increases. The simulation results are consistent with the results observed by optical remote sensors.
During the scanning process of airborne laser radar (LiDAR), ground edge line in the back of the building is always shaded, edge point data of building surface are usually hard to be obtained accurately, so a digital surface model (DSM) with low precision is obtained by three dimensional reconstruction with these low accurate LiDAR point cloud data. In order to improve the DSM accuracy, we propose an edge line automatic extraction algorithm. This approach initially extracts local point cloud of building surface edge to fit local trend surface. Then two neighborhood trend surfaces are used to compute the intersection''s equation and add edge point cloud data. Finally, using the laser point cloud of the building with the additional extracted edge points, we rebuilt the DSM of the building, and the accuracy of the reconstructed DSM with adding the edge points is compared with that of the DSM without adding the edge points. Simulated results show that the accuracy of the DSM reconstructed by this method can be improved significantly.
The rapid estimation of soil moisture content (SMC) is of great significance to precision agriculture in arid and semi-arid areas. Using Organ River-Kuqa River delta oasis as research area, we adopt wavelet transform to realize 1-8 layer wavelet decomposition for reflectance spectrum. The maximum number of decomposition layers is determined by correlation analysis, nine routine mathematical transformation methods are used for conducting characteristic spectrum of each layer from original reflectance to maximum number of decomposition layers, and the correlation analysis between reflectance of soil and SMC is carried out. Waveband with maximum correlation coefficient is taken as sensitive waveband filtrated from all kinds of transformation of characteristic spectrum of each layer. Optimum waveband combination is filtrated by grey relational analysis (GRA). SMC prediction model is developed and analyzed by partial least squares regression. The results show that, with the increase of the number of decomposed layers, the correlation between soil reflectance and SMC increases and then decreases, and L6 is the most significant band at 0.01 level. In general, the characteristic spectrum of L6 can maximally preserve the spectral details while denoising, so the maximum decomposition order of the wavelet is 6 order decomposition; In general, it is shown that the combination of wavelet transform and differential transform can deepen the spectral potential information and improve the correlation between reflectance of soil and SMC. Comparing the predictive effects of SMC estimating models, the model based on L-GRA is much better than others, and it has better performance in predicting SMC in the study area (root mean square error of calibration is 0.026, determination coefficient is 0.710, root mean square error of prediction is 0.030, determination coefficient is 0.965,and residual predictive deviation is 2.800). It is shown that the combination of wavelet transform and GRA makes it possible to lose the spectral details as little as possible and remove the noise more completely when the model is established, at the same time, it can effectively remove the non-information variables.
Each substance has its own unique spectral information, so it is possible to identify substances based on spectral information. An identification method of spectral information divergence pigment based on statistical manifold is studied. The Riemann metric on the statistical manifold is used as a new metric in the information divergence. The spectral matching for four commonly used mineral pigments is carried out withutilization of the proposed method and traditional method, and the matching results are compared. The experimental results show that the method of spectral information divergence based on statistical manifold can solve the problem of geometric measurement of probability variation, and the accuracy of spectral information matching recognition is improved obviously.
Powder density, as a very important physical parameter, has a huge influence on the fluidity of powder, therefore, studying the characteristic of powder density is of great significance to powder processing, packaging, transportation, storage and so on. The hyperspectral scattering technique combined with moment method in hyperspectral scattering image feature extraction is used for non-destructive detection of bulk density of wheat flour. Hyperspectral scattering images of 474 wheat flour samples are acquired at the wavelength of 500-1000 nm. Images are pretreated to eliminate the noises, and the zeroth-order moment (ZOM) and the first-order moment (FOM) of scatter images are extracted. Finally, the ZOM, FOM, and their combination (Z-FOM) are used for developing bulk density prediction models using partial least squares (PLS) algorithm. The results demonstrate that the prediction model developed by Z-FOM achieved the optimal performance compared with ZOM or FOM. The PLS model using Z-FOM obtained 0.968 of the predicted correlation coefficient RP, and 3.95 of the residual prediction deviation. Experiments show that the moment method is an effective method for extracting features of the hyperspectral scattering images and can be used for high-accuracy detection of bulk density of wheat flour.
Parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) and alternating residual tri-linearization (ART) algorithms are used to measure and identify petroleum pollutants. The differences between the two algorithms in oil identification are emphatically compared and analyzed. The CCl4 solutions of No. 95 gasoline, No. 0 diesel and kerosene are used as the research objects. We take petroleum mixed solutions with different concentrations as samples to measure the three-dimensional fluorescence data of each sample by F-7000 fluorescence spectrometer. When PARAFAC algorithm is applied and the component number is set to 3, the recovery rates of diesel, gasoline and kerosene are (95.60±3.60)%, (94.67±3.66)% and (95.49±4.49)%, respectively. ART algorithm does not require a preset component number, and the recovery rates of diesel, gasoline and kerosene are (96.58±2.17)%, (95.17±9.17)% and (95.90±8.90)%, respectively. The results show that the two algorithms can be used for the measurement and identification of three kinds of petroleum pollutants, and high recovery rates can be obtained. ART algorithm does not require presetting component number, so it has more advantages.
Collinear double pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (DP-LIBS) is applied to quickly and quantificationally detect the content of heavy metal chromium (Cr) in edible vegetable oil. LIBS spectra of samples are collected by a two-channel high precision spectrometer, and then several spectral lines such as three atomic lines of Cr (Cr I 425.39 nm, Cr I 427.43 nm, Cr I 428.87 nm), CN molecular line (CN 421.49 nm) and Ca atomic line (Ca II 422.64 nm) are determined at wavelength range of 420-430 nm. Then, competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS) method is used to select characteristic and related variables of Cr, and least squares support vector machine (LSSVM) method is used to establish calibration model using selected variables. The results show that the number of variables reduces from 132 to 10 after CARS variable selection, and the variable compression rate is 92.42%. The correlation coefficient, root mean square error of calibration (RMSEC) and root mean square error of prediction (RMSEP) in CARS-LSSVM calibration model are 0.9926, 5.287×10 -6 and 5.860×10 -6, respectively, and the relative error of prediction samples is 8.55%. The performance of CARS-LSSVM calibration model is superior to that of univariate calibration model and LSSVM calibration model with five variables. So it can be concluded that DP-LIBS technique is feasible to detect the content of Cr in edible vegetable oil, and CARS method can select characteristic and related variables of Cr effectively, eliminate redundant and noise variables, thus reduce the influence of matrix effect on analytical element and improve prediction accuracy of LIBS analysis.
In order to establish a more accurate and efficient identification model of tobacco origin, a random forest pruning algorithm based on adaptive genetic algorithm (AGARFP) is proposed. According to evolution degree of groups, the proposed algorithm can adapt to different selection operators; then, by utilizing the improved adaptive genetic algorithm, random forest pruning can be conducted. The samples of five producing areas are selected to build an identification model for tobacco origin, the precision of origin identification is used as the standard to weigh the pros and cons of the algorithm. Experimental results show that the classification precision of AGARFP can be as high as 94.67%, the classification effects of AGARFP are superior to that of the comparative methods, thus the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is demonstrated.
In order to study the degradation of indigo carmine, we establish the indigo carmine photo degration rate model by the UV-vis absorption spectroscopy. The absorbance at 611 nm of the absorption spectra of indigo carmine solution declines with the increase of illumination time and up to 0 after 8 hours. Based on the absorption spectra of the indigo carmine solutions with different mass concentrations, we established an absorbance-mass concentration prediction model at 611 nm and a peak area-mass concentration prediction model within 500-700 nm by exponential fitting. The results show that the peak area-mass concentration prediction model is more accurate than the former. Taking the completely degraded indigo carmine as interferent, we mixed it with the newly-prepared indigo carmine solutions to verify the peak area-mass concentration prediction model, and the model''s average relative deviation is 2.7%. Combining the absorption spectra area of the indigo carmine solutions (within 500-700 nm) at different illumination durations with the peak area-mass concentration prediction model, we obtain the content of indigo carmine and degradation rate, and obtain an exponential function between the degradation ratio of indigo carmine and the illumination time. The degradation rate model established in this paper has high measurement accuracy, and it can easily test the degradation rate of indigo carmine.
Blue needle-like dumortierite can be regarded as the rare mineral inclusions in crystal. Gem microscope, micro-X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, micro-Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) and micro-confocal Raman spectrometer are used to test and analyze the blue needle-like dumortierite in crystal as well as the morphology and color distribution of blue inclusions in dyed crystal. The corresponding spectral and morphological features can be used for analysis and identification of crystals and internal blue needle-like inclusions.
Traffic accidents, security incidents and crime affairs have a high incidence from evening to early morning due to low illumination. A thermal imaging camera suitable for low illumination environment is installed on the mobile platform to realize the expansion of surveillance area. Pedestrian and background regions in thermal imaging pictures are framed firstly, and then the brightness feature and oriented center symmetric-local binary patterns texture feature are extracted for the training and classification of random ferns classifier. The detected targets are used to extend training sample database, the posterior probability distribution of the classifier is updated, and the online automatic learning of the classifier is realized. Through simulation test, the computing speed of the algorithm for vehicle video is 242.18 s and the false detection rate is 9.53%. For unmanned aerial vehicle video, the computing speed is 14.93 s, and the false detection rate is 4.52%. This algorithm has low false detection rate, fast classification speed and transplant easily. It is suitable for applications with high real-time requirements, and it has certain practical engineering significance.