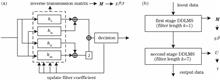
The wide use of high baudrate and high-order modulation format signals makes coherent optical communication systems more sensitive to hardware impairment in the transceiver, so there is an urgent demand for corresponding impairment estimation scheme. This paper proposes a new joint estimation scheme for transceiver impairment based on digital signal processing, which can simultaneously monitor in-phase/quadrature (IQ) amplitude, phase imbalance, and time skew caused by the hardware imperfections of the optical transmitter and optical receiver. First, the Godard timing error detector and Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization method are used to estimate and compensate for the receiver impairment. Then, the maximum likelihood-based independent component analysis method and cascaded decision-direct least mean square (DDLMS) algorithm are used to achieve polarization de-multiplexing and carrier phase recovery which are insensitive to transmitter impairment. Finally, the transmitter impairment is estimated from the tap coefficients of DDLMS algorithm. The scheme achieves wide range impairment monitoring, which is attributed to polarization de-multiplexing and carrier phase recovery that are insensitive to the IQ of the transmitter. Simulation results demonstrate that the estimation ranges of the amplitude and phase imbalances of the proposed scheme are improved by about 100% and 33% compared with that of the conventional digital signal processing scheme, respectively.
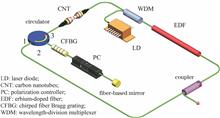
In this paper, we achieved the output of switchable multi-wavelength mode-locked pulses delivering picosecond and femtosecond solitons simultaneously by means of adding a chirped fiber Bragg grating (CFBG) into an erbium-doped mode-locked fiber laser based on carbon nanotubes. By adjusting a polarization controller, we output the switchable multi-wavelength mode-locked pulses near 1530.8 nm, 1549.5 nm, and 1556.5 nm, with the pulse duration of 833 fs, 7.43 ps, and 899 fs, respectively. In addition, the formation of the above three wavelengths could be jointly attributed to the gain spectra of the erbium-doped fibers and the filtering effect of CFBG. In conclusion, the study provides a reference for designing the multi-wavelength mode-locked fiber lasers with different pulse duration.
Based on the analysis of the characteristics of the beam splitting when a laser beam passes through a single attenuator, a pair of attenuators with V-type and parallel arrangement, methods are given for the characterization of the beam energy splitting, beam center spacing, and their overlapping parts for N-attenuators. Two effective solutions are explored, and details of the design and application methods are presented. The results show that there is an optimal incidence angle that can maximize the spacing of all levels of speckles. For common attenuating materials with a refractive index in the range of 1.4 to 1.7, the optimal incidence angle is in the range of 48° and 50°. Therefore, by making full use of the optical transmission characteristics of attenuators with V-shaped and parallel-shaped arrangement, rationally placing the attenuators, and using the beam stop scientifically, speckles at all levels can be effectively removed and an ideal single beam spot can be obtained.
Stripe non-uniformity is a relatively common fixed pattern noise in infrared focal plane array imaging systems, which has a great impact on imaging quality. It is generally believed that the non-uniformity of an image is mainly reflected in the gray level difference between pixels, that is, the gray level difference caused by the non-uniformity. In order to solve this problem, a correction method of stripe non-uniformity based on gray difference estimation is proposed. According to the spatial characteristics of the strip noise, the position of the non-uniform strip in each frame is judged. According to the gray level difference between adjacent pixels at the position of the strip, the non-uniformity is preliminarily estimated, and the estimation results of the next frame are evaluated to further improve the estimated value. Experimental results show that the proposed method can significantly reduce fringe non-uniformity and can effectively protect the edge information of the image.
Phase measurement profilometry based on Gray code has high robustness and anti-noise ability, and it is a major research hotspot in the field of three-dimensional (3D) measurement. Based on the existing measurement methods, this paper proposes a 3D shape measurement method via embedding the Gray code into the phase-shifting fringe for composite pattern projection. By moving the traditional three Gray code patterns to the right with the shift distance of half a fringe period, six Gray code patterns are obtained, which are alternately embedded into three groups of the same four step phase-shifting fringes and projected in turn combined with binary defocusing technology. After a series of deformed composite fringe patterns are captured, the information of the three groups of deformed composite patterns is synthesized and decoded along the time sequence to obtain two groups of staggered fringe levels, which can avoid the error of Gray code order edge from the source; at the same time, the corresponding truncated phase distribution is calculated by using the traditional phase-shifting algorithm, and the comprehensive decoding results on the time sequence can be used to guide the generation of truncated phase and reconstruct the 3D shape information of the object to be measured. Experimental results of 3D measurement of static and dynamic scenes verify the reliability, efficiency, and robustness of the method. This method can reconstruct a new 3D surface shape for every five more patterns recorded, which has good practicality in high-speed dynamic 3D measurement.
Different from the measurement of plane illuminance in traditional lighting, panoramic illuminance is a parameter that evaluates the overall illumination of visible objects in space. Regarding its measurement method, in addition to introducing the existing approximate estimation method based on the measurement value of a cubic meter in six dimensions, a luminance distribution spherical function decomposition method based on the high dynamic range panoramic image is proposed, and a spherical light source is used to compare the accuracy of these two measurement methods. The results show that, compared with the former method, the latter method is more robust and will promote the use of digital equipment around to measure the panoramic illuminance.
In order to quickly and accurately reconstruct the 3D shape of a complex scene, we propose a 3D shape measurement method based on speckle-embedded phase-shifting fringe patterns and wrapped phase-to-height lookup table (LUT). As an auxiliary signal, the speckle is embedded into the phase distribution of the four-step phase-shifting fringe patterns to obtain the composite fringe pattern to be projected. The phase-shifting algorithm is used to demodulate the wrapped phase and the additional speckle information. Multiple candidate heights corresponding to the wrapped phase are first obtained using the LUT, and then the height ambiguity is solved by marking the fringe period by the speckle. The correct height corresponding to the wrapped phase is uniquely determined, so as to realize the rapid reconstruction of the 3D shape of the measured object. This method directly reconstructs the 3D shape from the wrapped phase information without projecting any additional patterns and phase unwrapping. The theoretical analysis and experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve high-accuracy and robust 3D shape measurement of dynamic and static complex scenes.
The all-sky auroral imager is an important ground-based instrument for auroral observation and research. The real excitation intensity of auroras on different wavelengths can be obtained by calibrating the radiation parameter of all-sky imager, which is of great significance for quantitative study of space physics. Due to the conditions of polar observation stations, many all-sky auroral imagers cannot calibrate radiation parameters on the observation site. In this paper, a method to calibrate the radiation parameter of all-sky imager is presented which is based on stellar radiation stability. The stellar is regarded as the virtual standard light source, and the radiation parameter between radiation intensity and image value are finally determined by using the sky map obtained by the all-sky imager. Using more stellar brightness and the precipitating electrons data of aurora detected by ionospheric satellite and the auroral excitation intensity calculated by GLOW model, the radiation parameter of all-sky auroral imager is verified by two different methods. The results show that in the verification of stellar brightness, the maximum deviation is 12.22%, and the average deviation is 4.624%; in the satellite precipitating particle verification, the maximum deviation of the auroral arc peak intensity calculated by the model and all-sky imager is 11.30%, and the average deviation is 5.603%. The two verification results are similar, which shows that the proposed method is effective and credible.
In this paper, a whispering-gallery-mode (WGM) oval-shaped microcavity based on polymers was proposed, breaking the circular symmetry of traditional microcavities, and its wavelength-level notch on the boundary achieved unidirectional emission at an extremely low far-field divergence angle. In addition, the three-dimensional finite-difference time-domain method was used to investigate the WGM and unidirectional emission performances of the proposed microcavity, especially the influence of different deformation parameters on the far-field properties. With the optimal deformation parameters, the WGM near- and far-field performances of light field distribution near the wavelength of 536 nm were obtained. Besides, the effect of notch size on the output spectrum of the proposed microdisk was also analyzed. Then, extending the oval microdisk to an ovoid microsphere further reduced the beam divergence (~2.5°), with the highest unidirectional emission efficiency being 93%. Therefore, the proposed structure can function well as an excellent platform to explore the light-matter interaction, expand the research range of notched microcavities in the field of unidirectional emission, and promote the development of photonic microdevices in the fields of biomedicine and environmental detection.
In autonomous driving applications, the vision-based relative pose estimation is one of the core technologies to realize self-positioning of driverless cars. Aiming at the problems that the monocular vision system has a small field of view and the binocular vision system needs a overlapping field of view, a method for decoupling relative pose estimation of multi-camera systems with non-overlapping field of view is proposed. Use the different characteristics of the near and far points in the scene to decouple the rotation matrix and the translation vector. The relative rotation matrix is solved by the histogram voting method for the feature points of the distant scene, and the relative translation is solved by the sampling height method for the feature points of the near scene under the condition that the relative rotation matrix is known. The feasibility, robustness and accuracy of the proposed method are verified through simulation and actual experiment. Experimental results show that the relative attitude accuracy of the proposed method is better than 0.05°, and the relative translation vector direction accuracy is better than 2.5°, which has higher accuracy and better robustness.
In order to accurately extract structured light stripes from weld images in the complex noise environment, we proposed a deep learning model combining semantic segmentation with object detection to detect the weld images. In the semantic segmentation branch, the model was optimized by adding parallel downsampling modules and reducing the number of convolution kernels to increase the detection speed, and the feature extraction parts of this branch and the object detection branch shared the weights. Aiming at the problem that the proportion unbalance of structured light stripes and background pixels in the weld images caused the model segmentation results to be biased towards negative samples, we introduced a Dice coefficient into the loss function to correct the model. The experimental results show that the proposed method can achieve the extraction of structured light stripes with high accuracy on the basis of ensuring real-time performance.
The integrity of edge detection of printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) components directly affects the visual measurement accuracy of the size and gap of components obtained by assembly robots. Aiming at the problem that the edges of objects in dense areas extracted by the Canny operator have obvious edge adhesion and missing phenomena, a new method of PCBA component edge detection with high integrity is proposed. First, for the edge pixels determined by the original Canny operator based on the gradient of the pixel gray value, an adaptive threshold non-maximum suppression method with a 3×3 neighborhood window is proposed to effectively avoid the adhesion of adjacent edges in dense areas. Second, based on the gradient field of the Snake curve after parameterization by the EPGVF Snake model, combined with the edge fidelity term, a neighborhood window adaptive judgment method for determining whether the edge is broken is proposed. Finally, a pixel replacement template is used to fill the broken edge pixels to effectively retain the weak edges and avoid breaks. Experimental results show that the proposed method can avoid the adjacent edge adhesion and weak edge missing effectively in the dense area of PCBA, and the integrity of the preserved edge is improved about 15.5% compared to other methods.
The absorber based on planar metal/dielectric thin films has attracted much attention due to its superior absorption performance, simple preparation process and broad application prospects. In order to improve the absorption performance, an ultra-broadband perfect absorber with a multilayered Zr/SiO2 structure is proposed, which is based on multiple Fabry-Perot (FP) resonant absorption. The structural parameters are optimized by employing the transfer matrix method combined with the genetic algorithm and the calculation results show that as for an absorber with a 10-layered Zr/SiO2 structure (which constitutes 4 series FP cavities), the minimum absorption efficiency exceeds 96.6% and the average absorption efficiency is up to 98.6% in the wavelength range of 0.4--3.0 μm. Even as for one with only a 4-layered structure, its average absorption efficiency still reaches 91.5%. Furthermore, the absorption characteristics of the proposed structure are analyzed in other wavelength ranges and the relation of its average absorption efficiency with lay number is also calculated. Compared with other absorbers with complex structures, the proposed absorber has the characteristics of large working bandwidth, high absorption efficiency and simple structure. It has wide application prospects in the fields of solar energy collection, heat radiator, and infrared cloaking.
The absorber with broadband and high absorption is the key for the utilization of solar energy. We designed a solar absorber based on a two-dimensional photonic crystal structure including an antireflective layer, in which Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is used as the absorbing medium and filled in the tungsten (W)-based circular empty cavity of two-dimensional photonic crystal with tetragonal lattice. The finite element method is used for the simulation and calculation, and the results show that in the wavelength range of 300--2500 nm, the average absorptivity of the absorber is 92.5% and the effective absorptivity is up to 94.9%. Moreover, the effective absorptivity of the absorber is 90.13% when the incident angle is 50°. The proposed structure has the characteristics of high absorption in the full solar spectrum, polarization-insensitivity and wide-angle absorption. These research results can provide a certain reference for the high-performance solar absorber.
In order to study the degradation behavior of the related parameters of GaAs sub-cells induced by space irradiation, the proton irradiation simulation was carried out under different irradiation conditions, taking GaAs sub-cells of three-junction solar cell as the research object. The structure model of GaAs sub-cells was established and the degradation results of short-circuit current, open-circuit voltage, fill factor and maximum power induced by proton irradiation with different energies and fluences were obtained. The normalized maximum power degradation of GaAs sub-cells induced by proton irradiation versus fluence was verified by the existing experimental data. According to the maximum power degradation results of GaAs sub-cells under different irradiation conditions, the degradation equation of normalized maximum power versus displacement damage dose was obtained. The research results indicate that the irradiation defects induced by proton irradiation directly lead to the degradation of sub-cells, and the short-circuit current, open-circuit voltage, fill factor and maximum power of GaAs sub-cells degrade with the increase of proton fluence. When the proton fluence is more than 1×10 11 cm -2, the degradation degree of the normalized electrical parameters of GaAs sub-cells is directly proportional to the log value of proton fluence. Meanwhile, the degradation of the electrical parameters increases gradually with the decrease of proton irradiation energy. The degradation of the external quantum efficiency of GaAs sub-cells induced by proton irradiation in the long-wavelength range is more serious than that in the short-wavelength range.
To obtain a cleaner InGaAs material surface, the effects of chemical cleaning methods on the removal of InGaAs surface carbon contaminations and oxides are investigated using the hydrofluoric acid solution, the mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and deionized water, and the mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and isopropanol. On this basis, a method combined with ultraviolet-ozone cleaning is proposed. The InGaAs surfaces cleaned by different methods are analyzed using scanning focused X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Moreover, the micro-area characteristics of the surface are obtained with the aid of the secondary electron image produced on the sample surface, and the surface chemical element composition and surface corrosion degree are accurately detected. The analysis discloses that the hydrofluoric acid etching seriously corrodes the sample surface and destroys the surface structure and compositions, in contrast, the etching based on the mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and isopropanol etching combined with ultraviolet-ozone cleaning shows a better cleaning effect and can more effectively remove the surface carbon contaminations and oxides.
In order to study the service life of multiple fused silica lenses in the deep ultraviolet lithography system, based on the theory of laser beam spatial shaping and the principle of afocal zoom, a set of multi-lens irradiation accelerated material aging system that meets the actual working conditions is designed. The aspheric cylindrical lens group is used to shape the beam whose light intensity distribution in the vertical direction is approximately Gaussian distribution, and then the beam spot size is reduced by the variable magnification beam reduction system to increase the energy density. The maximum uniformity of the beam spot in the vertical direction of the reshaped system is 96.8%, the beam shrinkage ratio is between 0.2 and 0.5, the maximum root mean square value of wave aberration is 0.1778λ, which is all less than λ/4, and the energy density is increased by 4--25 times. The system can simulate actual working conditions and meet the irradiation acceleration requirements of multiple lenses, thereby solving the problems of long experimental cycles and high cost in current tests.
Ritchey-Chretien (RC) optical system is widely used in long-distance detection fields such as aviation and aerospace. Due to its small field of view, additional optical elements are usually used to achieve large field of view imaging, but this will lead to a complex structure, which is not good for miniaturization and lightweight of the system. In view of this, a R-C system indirect imaging method is proposed. First, the aberration characteristics of the system are analyzed. Then, the wavefront model is constructed based on the wavefront aberration theory and Zernike polynomial. Second, the PSF model is established by Fourier transform. Finally, the image is processed by combining the deconvolution algorithm. In the case that only primary and secondary mirrors are used, the R-C system can achieve large field of view imaging. The R-C optical system with a focal length of 1300 mm, a full field of view of 0.9° and an F number of 4 is simulated. The simulation results show that the MTF of the proposed method increases by about 0.25 on average at a frequency of 40 cycle/mm, and the imaging quality is significantly improved.
During the operation of fishing with light at sea, rolling motion of the fishing boat changes the illumination angle of the light-emitting diode (LED) fishing lamp, resulting in continuous changes of the sea surface illumination, which has an adverse effect on attracting and gathering phototactic fish. This article proposes a method using a free-form surface lens to realize a fan-shaped light intensity distribution, with the divergence angles on the X-Y and Y-Z planes being 110° and 10°, respectively. The similarity and error rate of the relative illuminance distribution of the target plane within the illumination angle range of -10°--10° were analyzed. The normalized cross correlation (NCC) of the simulation results and the experimental results are greater than 98.50% and 99.53% respectively, and the root mean square error (RMSE) are less than 5.56% and 4.60%, correspondingly. By comparing this design with a standard LED fishing lamp and metal halide lamp, the results show that the proposed design significantly improves the illumination stability of the LED fishing lamps when the fishing boat rolls, indicating that the free-form surface lens is able to provide stable illumination on the sea surface at different illumination angles.
The dielectric elastomer has the characteristics of compact structure, large deformation, fast response speed, and easy integration. In order to reduce the driving voltage, the dielectric elastomer is applied to the liquid lens and the separation structure of dielectric elastomer and the lens membrane are used. Mathematical models of elastic body active membrane deformation, lens membrane deformation and focal length of liquid lens are established. Simulation results show that when the initial liquid pressure is 500 Pa and the driving voltage is 1000 V, the zoom range of the liquid lens is 15.13--22.80 mm, and the focal length increase is 51%. The effects of the Young's modulus, residual stress, initial thickness and radius of the dielectric elastomer on the focal length of the liquid lens are analyzed. The results show that the initial thickness of the dielectric elastomer has the greatest influence on the focal length of the liquid lens at the same increase in magnification, followed by the residual stress, the research results can provide a reference for the optimal design of liquid lens driven by dielectric elastomer.
In visible light positioning system, the receiver needs to capture the visible light signals from different reference optical sources, and then the position coordinates of the receiver are estimated based on the position information of the reference light source and the preset visible light positioning algorithm. In the above positioning process, it is usually assumed that the light source is a Lambertian light source, that is, the light beam of the light source conforms to the Lambertian law. In order to achieve specific lighting effects, solid-state light source manufacturers often reshape the light beams by improving the subassembly process and adding secondary optical lenses to obtain diversified spatial light beams. In order to quantify the impact of actual non-Lambertian beams on the visible light positioning system, three commercial non-Lambertian beams, EdiPower Emitter, LUXEON Rebel, and Side Emitter are introduced into typical indoor scenes. The quantitative results show that, compared with the traditional Lambertian beam configuration, the maximum positioning error and the average positioning error introduced by the non-Lambertian beam are 101.7 cm and 48.8 cm, respectively. Taking into account the influence of the non-normalized radiation power of commercial non-Lambertian beams, the above positioning error will be further increased.
To explore the optical characteristics and formation mechanism of Achillidesbianor Cramer scales, the discoloration experiment of butterfly scales is carried out by filling alcohol solution and changing the incident angle. The microstructures of the forewing and hindwing scales are observed and analyzed in this paper. The bionic structure model of the scales with structure color is constructed, and the reflection spectrum characteristics of the scales film structure are simulated by using the transfer matrix method. The surfaces of the yellow-green and cyan areas on the edge of the scales of the Achillidesbianor Cramer are composed of the dark-brown base scales of the lower honeycomb grid light-trapping structure and the colored scales of the upper fold and pit-like film structure. The colored scales are formed by mixing 2 structural colors at the bottom of the surface micro-pits and the side walls, and it is sensitive to organic solution and light conditions due to the influence of the structure of natural photonic crystal film and its fine size. The unique optical characteristics of the Achillidesbianor Cramer scales can provide some reference for the field of bionic intelligent materials, such as adaptive color changing camouflage, sensor detection and so on.
On the basis of the law of energy conservation, we analyzed a diffraction integral formula for the converging light field, derived an inclination factor of the diffraction integral formula for a semi-spherical reference wave front of the diffraction source, and suggested a formula for calculating the light field distribution on the focal plane. In addition, we explained the diffraction process of the converging light field by the interference process of suppositional vector wavelets. Then, according to the wave front transformation properties of focusing objective lens satisfying the sine condition, a calculation formula for the light field in focal plane which focuses from a planar wave front by the focusing objective lens was proposed. Finally, the applications of the above formulas were discussed through the focusing characteristics of the Laguerre-Gaussian beams with simple rectangular coordinate polarization and simple cylindrical coordinate polarization.
With regard to the low segmentation accuracy of planar point sets and poor merging effect of segments in the existing multi-factor segmentation algorithms of point clouds, an improved multi-rule region growing algorithm was proposed in this paper. On one hand, the plane fitting residuals of point clouds were calculated, based on which, the seed condition was set and the segmentation of planar point sets was optimized, so as to increase the segmentation accuracy of planar factors. On the other hand, on the basis of the distance condition, the merging strategy was improved in combination with similarity and volume changes to achieve effective merging of segments. In addition, the threshold parameters involved in this algorithm were set adaptively using the median clustering, Baarda data snooping, and k-means clustering. Furthermore, three different types of point clouds were tested, and the results show that the improved algorithm can boost the segmentation accuracy of planar point sets, and enhance the veracity of segments merging. Compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm can take into account both accuracy and efficiency and has better segmentation results.
A wide-angle complementary treble-bandpass filter is prepared based on the imaging principle of wavelength-division 3D technology. Via the investigation of film materials, suitable materials are selected as the equivalent spacer layer of the Fabry-Perot filter, which improves energy dispersion and enhance the bandpass transmissivity at a large incident angle of light. With the adjustment of the amount of the reactive gas of inductive coupled plasma, the extinction coefficient of Nb2O5 material can be reduced and the film transmissivity at a short wavelength can be enhanced. The experimental test and analysis results show that the prepared complementary treble-bandpass filters process the transmissivity of larger than 92% at each bandpass when light incident at 0°--30°. Moreover, the transmitted light satisfies the color balance index and meets the design requirements.