View fulltext
View fulltext
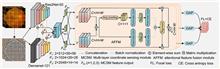
In order to meet the market demand of the optical industry, the rapid manufacturing technology of aspheric optical elements is one of the best solutions to realize low cost, mass production, and high precision production. This paper mainly introduces the rapid manufacturing technology of aspheric optical elements, including precision optical glass molding technology and precision optical plastic injection molding technology, and compares the two technologies with the manufacturing technology of other aspheric optical elements. This paper also expounds on the types of mold materials, mold processing methods, molding materials, molding process, etc. Finally, the development status of rapid manufacturing technology of aspheric optical elements in recent years is summarized, and future development has prospected.
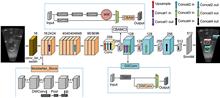
Aiming at the problems of unbalanced sample distribution and difficulty identification of the lesion area in diabetic retinopathy, we propose a retinal lesions grading algorithm that integrates coordinate perception and hybrid extraction. This algorithm first processes the retinal input image and the Gaussian filtering to enhance the difference between the image lesions and the background of the noise, and then the hybrid dual models composed of the backbone network of Res2Net-50 and Densenet-121 will be enhanced. The image is extracted layer by layer to achieve the full capture of the multi-scale feature texture, then the multi-layer coordinate perception module and the attention characteristics fusion module are integrated at the mixed dual model connection to achieve the purpose of eliminating the characteristics of the lesions and the realization of different lesions. The weight of semantics is reshaped, finally uses the combined loss function to relieve the uneven distribution of samples to further supervise the training and test of the model. This article is experimented on the IDRID and Aptos 2019 data sets, with the secondary weighted coefficients of 88.76% and 90.29%, respectively. Accuracy rates were 81.55% and 84.42%, which provides a new window for the diagnosis of retinopathy grades and intelligent auxiliary diagnosis.
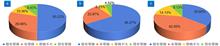
This paper first introduces the important measures of the NSFC on the reform of science fund in 2023, and then statistically analyzes the project applications and fundings of the F05 "Optics and Optoelectronics" subject, including the free category programs (general program, youth scientists fund, regional science fund), the key program, the excellent young scientists, the outstanding young scientists and other programs. It also makes a statistical analysis of the distribution of the secondary codes, supporting organizations and attributes of the four types of scientific problems of the proposals, and then introduces the pilot work situation of the review mechanism reforming of "responsibility, credibility, contribution" (RCC). Finally, combined with the project applications and funding results of this year, suggestions are given to the project applicants and the experts in the field of "Optics and optoelectronics".
To address the problems of blurring and insufficient sample size in sonar images, an improved sonar image target detection algorithm is proposed based on YOLOv5. The algorithm uses geometric filtering, vertical flipping, and other methods to enhance the sonar image dataset. The fusion attention mechanism module is added to make the algorithm better focus on the features of small targets in sonar images. At the same time, in response to the problem that most target detection algorithms currently run on the cloud and cannot achieve real-time sonar image detection, this paper uses lightweight network replacement and NCNN edge porting technology. It adopts the GSConv module in the neck network to successfully transplant the algorithm to the ZYNQ platform, realizing real-time detection of sonar images on the embedded end. After experiments, the algorithm proposed in this paper reduced the parameter quantity by 56%, increasing map50 and map50-95 by 2.2% and 2.5%, respectively. The algorithm’s performance has significantly improved, proving that the method proposed has certain feasibility and effectiveness in lightweight sonar image target detection tasks.
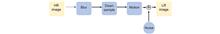
The super-resolution reconstruction algorithm is an algorithm that restores low-resolution images to high-resolution images, which is widely applied in the fields of medicine, remote sensing, military security, and face recognition. It is hard to construct datasets in some specific scenarios, such that the application of super-resolution reconstruction algorithms based on deep learning is limited. The scanning pattern of micro-scanning imaging technology is fixed, which requires high precision of the device. To address these two problems, we propose an image super-resolution reconstruction algorithm based on active displacement imaging. Specifically, we control the camera to move randomly while recording the displacement at the sampling moment and then reconstruct the high-resolution images by solving, mapping, and selecting zones, obtaining the sub-pixel information between multiple frames, and finally iteratively updating the reconstruction. The experimental results show that this algorithm outperforms the latest multi-featured super-resolution reconstruction algorithms for POCS images in terms of PSNR, SSIM, and mean gradient. What's more, the present algorithm does not require a fixed scanning pattern, which reduces the requirement of the micro-scanning technique on the device in place accuracy.
The surface defects of solar cells exhibit significant intra-class differences, minor inter-class differences, and complex background features, making high-precision identification of surface defects a challenging task. This paper proposes a Convolutional -Vision Transformer Network (CViT-Net) that combines local and global features to address this issue. First, a Ghost-Convolution two-fusion (G-C2F) module is used to extract local features of the solar cell panel defects. Then, a coordinate attention mechanism is introduced to emphasize defect features and suppress background features. Finally, a Ghost-Vision Transformer (G-ViT) module is constructed to fuse local and global features of the solar cell panel defects. Meanwhile, CViT-Net-S and CViT-Net-L network structures are provided for low-resource and high-resource environments. Experimental results show that compared to classic lightweight networks such as MobileVit, MobileNetV3, and GhostNet, CViT-Net-S improves the classification accuracy of solar cell panels by 1.4%, 2.3%, and 1.3%, respectively, and improves the mAP50 for defect detection by 2.7%, 0.3%, and 0.8% respectively. Compared to ResNet50 and RegNet, CViT-Net-L enhances the classification accuracy by 0.72% and 0.7%, respectively, and improves the mAP50 for defect detection by 3.9% and 1.3%, respectively. Compared to advanced YOLOV6, YOLOV7, and YOLOV8 detection networks, CViT-Net-S and CViT-Net-L structures, as backbone networks, still maintain good detection performance in terms of mAP and mAP50 metrics, demonstrating the application value of the proposed algorithm in the field of solar cell panel surface defect detection.
Road scene semantic segmentation is a crucial task in autonomous driving environment perception. In recent years, Transformer neural networks have been applied in the field of computer vision and have shown excellent performance. Addressing issues such as low semantic segmentation accuracy in complex scene images and insufficient recognition capabilities for small objects, this paper proposes a road scene semantic segmentation algorithm based on Swin Transformer with multiscale feature fusion. The network adopts an encoder-decoder structure, where the encoder utilizes an improved Swin Transformer feature extractor for road scene image feature extraction. The decoder consists of an attention fusion module and a feature pyramid network, effectively integrating semantic features at multiple scales. Validation tests on the Cityscapes urban road scene dataset show that, compared to various existing semantic segmentation algorithms, our approach demonstrates significant improvement in segmentation accuracy.
To solve the problems of low color saturation and edge blurring caused by viscous resistance and other factors in color EPD, this paper proposes a color e-paper edge enhancement error diffusion algorithm based on HSL space to improve the display quality. This algorithm first uses an edge detection operator to obtain edge-enhanced images from denoised images. It combines edge-enhanced image pixel neighborhood average gray level, pixel and neighborhood gray level difference, and pixel neighborhood similarity to obtain new RGB image pixel value. Then, the new RGB image is processed by a threshold process to obtain a 16-level RGB image. Finally, the 16-level RGB image is converted to HSL space, and a conversion model between HSL and RGB color spaces is established. According to the brightness and saturation of the pixel, the adjustment factor is calculated to enhance the saturation of the RGB image. Compared with the traditional error diffusion algorithm, the signal-to-noise ratio PSNR of this algorithm is improved by 3.9%~26.7%, the UCIQE is improved by 10.1%~48.2%, and the SSIM is improved by 13.2%~25.4%. The subjective evaluation refers to the ITU-R BT.500-1 standard to design experiments and calculate Z scores. Finally, the image details and colors of the image processed by this paper algorithm are closer to the original image on the color e-paper, and the overall visual effect is better.