View fulltext
View fulltext
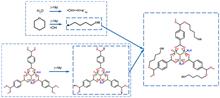
Researching of adsorbent materials is a hot topic in the fields of uranium mining, processing and treatment of uranium-containing wastewater from spent fuel reprocessing and uranium extraction from seawater. The binding of adsorbent materials to uranium is mainly via the coordination of functional groups, among which the amidoxime groups exhibit excellent adsorption selectivity due to their specific interaction with uranium. In this paper, we summarize the preparation methods of amidoxime groups, especially the cyano-hydroxylamine method is introduced in detail. The progress of the present research on the mono-functional adsorption materials of amidoxime is elaborated from the perspective of the morphology and function of adsorbent materials, while the bifunctional synergistic adsorption of -NH2 and -AO or -COOH and -AO is introduced, and the coordination mechanism of amidoxime groups with uranium is briefly analyzed, and finally, trends are prospected in view of the selection of substrate materials, preparation methods and special functionalities of amidoxime-based adsorbent materials.
The specific surface area and surface hydrophilicity of metal-organic frameworks can be tailored by changing their central metal ions and organic ligands. In this study, the surface of the metal-organic framework MIL-101(Cr) was modified in an aqueous solution of tetrahydropyran via the radiolytic method. A large number of hydroxyl groups were introduced to the surface of MIL-101(Cr), thereby effectively improving its surface hydrophilicity and substantially increasing its specific surface area without changing its central metal ion and organic ligand. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy demonstrated that the irradiation products of tetrahydropyran were bound to the surface of MIL-101(Cr) through covalent bonding. X-ray diffractometry demonstrated that the crystal structure of the material was retained after irradiation. The specific surface area of MIL-101(Cr) significantly increased, and water contact angle tests indicated that the surface changed from hydrophobic to hydrophilic after modification. These results show that the irradiation reaction of MIL-101(Cr) with tetrahydropyran significantly improves its specific surface area and hydrophilicity. This study provides guidance on the application of the irradiation method to prepare metal-organic frameworks with various properties by simple and rapid modification.
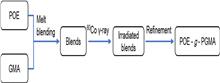
Epoxy-functionalized ethylene-octene copolymer (POE-g-PGMA) was prepared by 60Co γ-ray radiation, and polyamide 6/polyethylene-octene blend (PA6/POE) containing POE-g-PGMA was prepared by twin-screw melt extrusion. In this study, the mechanical properties, thermal properties, surface morphology, interfacial compatibility, and water absorption properties of PA6/POE blends with added POE-g-PGMA were investigated. The results showed that GMA was successfully grafted on POE by γ-ray radiation. The morphological analysis showed that the addition of POE-g-PGMA enhanced the dispersion of POE particles in the PA6 matrix. In particular, it demonstrated that with the addition of POE-g-PGMA, pure PA6 has good interfacial compatibility with POE. The results of the Molau test confirmed the compatibilization reactions between POE-g-PGMA and PA6. The thermal analysis showed that the addition of POE and POE-g-PGMA in the dispersed phase had negligible effect on the melting behavior of PA6; however, the crystallization temperature of PA6 improved by approximately 18 °C during the cooling crystallization process, and the crystallinity increased by approximately 4.5%. Furthermore, the impact strength of the compatibilized PA6/POE blend was significantly higher than that of the PA6/POE blend, with the highest value of impact strength obtained at a POE-g-PGMA content of 3% being approximately 2.75 times greater than that of pure PA6 under the experimental conditions.
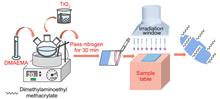
TiO2-doped polymethacrylate N, N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA) (TiO2-g-PDMAEMA) was successfully synthesized by the co-radiation grafting method with titanium dioxide (TiO2) and DMAEMA as the base and the monomer, respectively. Meanwhile, the effects of monomer concentration and absorbed dose on the adsorption of heavy metal ion were investigated. A series of characterizations, including X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and contact angle, confirmed that DMAEMA monomer was successfully grafted onto TiO2 surface by electron beam co-radiation grafting method. When the absorbed dose was 60 kGy and the monomer concentration was 20%, TiO2-g-PDMAEMA exhibited excellent adsorption capacity for Cr (VI, 10 mg/L), up to 10.75 mg/g. In addition, the TiO2-g-PDMAEMA prepared at 60 kGy absorption dose and 10% monomer concentration displayed the optimal adsorption-photocatalytic reduction ability under visible-light irradiation, and the removal rate of Cr (VI, 10 mg/L) reached 85.56%. In conclusion, the adsorption-photocatalytic synergistic effect of this new photocatalyst could meet the requirement of removing Cr (VI) from water.
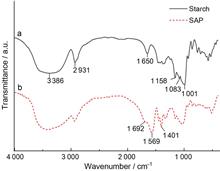
A super absorbent polymer (SAP) was prepared using starch and acrylic acid under exposure to 60Co γ-rays irradiation. The chemical structure of the SAP was characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy Scanning electron micrographs showed that the surface of the SAP contained numerous mesoporous structures. Thermogravimetric analysis indicated improved thermal stability of the SAP compared to that of the original starch. The absorbed dose and feed ratio of the acrylic acid and starch significantly affected the water absorption performance of the SAP. The water absorption capacity of the SAP was 532 g/g at the optimal conditions (absorbed dose: 20 kGy, crosslinking agent: 80 mg/L, feed ratio of starch to acrylic acid: 1/2). The SAP efficiently released the loaded KNO3 or Na3PO4; the release rates were 82% for K+ and 80% for PO43-.
To investigate the effects of 5G mobile phone radiofrequency radiation (RFR) on sperm quality and sex hormone level of adult male mice, 24 healthy adult male C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into two groups, the sham-exposure group (Sham) and 4.9 GHz-exposure group (4.9 GHz RFR), with 12 mice in each group. The mice in the exposure group were exposed to RFR with a power density of 50 W/m2 and frequency of 4.9 GHz for 21 consecutive days, for 1 h a day. After exposure, the sperm quality was evaluated by detecting the sperm quantity and abnormality rate; Histomorphology of the testis was determined using Hematoxylin Eosin (HE) staining; the levels of testosterone (T), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), glial derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), and stem cell factor (SCF) were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); A western blot was used to detect the levels of GDNF, SCF and tight junction related proteins (ZO-1 and Occludin) of the blood-testis barrier (BTB) in testis tissue. Compared with the Sham group, no significant change in testicular morphology, sperm count, and sperm abnormality rate was observed in the 4.9 GHz RFR group; The content of FSH and LH in serum showed no significant differences; and the levels of GDNF, SCF, ZO-1 and Occludin in the testis showed no significant differences. However, the concentration of T and GnRH in serum decreased significantly. The results showed that under the experimental conditions, 4.9 GHz RFR had no significant effect on the sperm quality of mice, but could lead to changes in sex hormone levels.
In this study, the biological electromagnetic dose variations and uncertainty caused by body weight differences in experimental animals were evaluated. An electromagnetic dose simulation environment of experimental rats under plane wave excitation was established using bio-electromagnetic simulation software and a three-dimensional digital model. The study frequency band was 0.1-6 GHz. The results showed that there was a linear relationship between the body weight of experimental rats and the whole-body average specific absorption rate under conditions of body weight disturbance. Below the resonant frequency point, the linear relationship was positive, whereas above the resonant frequency point, the linear relationship was negative. In the 1-6 GHz region, the degree of the linear fit was close to 1. The dose uncertainty for the experimental rats was investigated and a fitting calculation method was proposed. Combined with the experimental design case, the calculation process, calculation amount, and evaluation accuracy of the fitting calculation evaluation method were compared. The evaluation method had high accuracy and a low modeling calculation amount. The results of this study have certain guiding significance for the experimental design and dose evaluation of bioelectromagnetics.
In order to discuss the accuracy of iterative cone-beam computed tomography (iCBCT) image used for pelvic tumor dose calculation, thirty cases were selected from a hospital that use a Halcyon accelerator for radiotherapy. The volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) plan was redesigned using Eclipse 15.6 planning system, and the setup iCBCT image acquired for the first time was registered with the planning CT image (pCT). The VMAT plan (pCT plan) of each case was transplanted to the iCBCT image, and the dose was calculated again based on the CT-relative electron density curve calibrated using the iCBCT image to generate a new treatment plan (iCBCT plan). The dosimetric parameters of the two plans were analyzed using SPSS 26.0 software to perform t-tests. The results of D2, D98, Dmean, conformity index (CI), and homogeneity index (HI) in the planning target volume dosimetry parameters of the iCBCT plan were similar to those of the pCT plan. The average differences were 0.71%, 0.53%, 0.97%, 0.25%, and 0.95%, respectively, with no statistical significance (p>0.05). Among the organs at risk, the average difference of Dmean, D5, V20, V30, and V40 between the left and right femoral head, rectum, and bladder was small, with no statistical significance (p>0.05). The parameter with the largest average difference (1.71%) was Dmean of the bladder. Compared with that of the pCT plan, the gamma pass rate of the iCBCT plan was 1%/1 mm standard (88.1±1.1)% and 2%/2 mm standard (97.8±1.2)%. Compared with the measured values, the mean difference between the isocenter dose of the two plans was 0.98% and 0.81%, respectively, with no statistical significance (p>0.05). The results show that in most pelvic cases, the results of the iCBCT images used for radiotherapy planning dose calculation are accurate and reliable, and the accuracy meets the requirements of clinical application.
Forty-eight mice were randomly divided into eight groups of six mice each. Group 1 was the control group, groups 2, 3, and 4 were the Potentilla anserina L drug groups, group 5 was the irradiation group, and groups 6, 7, and 8 were the irradiated Potentilla anserina L drug groups. The control group was administered distilled water by gavage for 5 d without irradiation; the irradiation groups were irradiated with 5 Gy 60Co γ rays. In the drug groups, the mice were gavaged with distilled water and Potentilla anserina L polysaccharide within 30-60 min after irradiation for 5 d and euthanized on the sixth day. The effects of different doses of Potentilla anserina L polysaccharide on the blood routine, organ index, DNA content in bone marrow, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), lymphocyte subpopulation ratio, and malondialdehyde (MDA) content in the mouse livers were determined. The results showed that Potentilla anserina L polysaccharide increased the erythrocyte and leukocyte counts, hemoglobin content, and erythrocyte-specific volume as well as the spleen index, liver T-AOC, SOD activity, and lymphocyte count and decreased the MDA content. The DNA coefficient of irradiated mice was improved to some extent. Potentilla anserina L polysaccharide exert good therapeutic effect on the hematopoietic and antioxidant systems and can mitigate the DNA damage of bone marrow cells in radiation-injured mice.
In order to promote the germination of Lycium barbarum seeds, the Lycium barbarum seeds were treated by contact glow discharge plasma (CGDP), the effects of CGDP on germination were explored under different treatment time, voltages, and electrolyte conditions. The seed treatment process was optimized by response surface optimization design based on seed germination rate and vigor indexes. The effects of CGDP on the structure and properties of the seed coat were preliminarily studied through the detecting changes in the morphology and the contact angle of the seed coat. The results showed that the optimized conditions for seed treatment were 15 min, voltage 550 V, Na2SO4 electrolyte, and the highest seed germination rate was 95.56%. After treatment, the seed coat becomes flat, the texture is blurred, and the hydrophilicity of the seeds is enhanced; the chlorophyll content in the leaves of seedlings increases. Therefore, glow discharge plasma treatment can promote the germination and growth of Lycium barbarum seeds.
To explore the effects of absorbed dose and particle size on enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of reed straws (Phragmites australias), the straws were irradiated with γ-ray irradiation at different doses (0-500 kGy) and then passed through different aperture sieves after mechanical grinding. The effects of absorbed doses and sieving aperture size on particle size distribution, comminution energy, main component content, enzymatic hydrolysis conversion rate, and ethanol conversion rate of cellulose were examined, and the optimal respective sieving aperture for reed straws with different absorbed doses were determined. The results showed that with decreasing sieve aperture size, reed straw quality decreased significantly and was negatively correlated with the absorbed dose; the comminution energy of reed straws decreased with increasing absorbed doses. With respect to consistent quality of sieved reed straws, the comminution energy increased significantly with decreasing sieving particle size. In reed straws with the same absorbed dose, the enzymatic hydrolysis conversion rate and ethanol conversion rate of cellulose increased with decreasing sieving aperture size. Compared with reed straws with particle size r ? 0.850 mm, the cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis conversion rates in reed straws with particle size r ? 0.180 mm increased by 129.20%, 85.98%, and 106.63% at absorbed doses of 0 kGy, 206 kGy, and 404 kGy, respectively, and cellulose ethanol conversion increased by 136.04%, 21.75%, and 4.39%, respectively. By compre- hensively comparing the increased ratios of comminution energy, cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis conversion rate, and cellulose ethanol conversion rate, the optimal sieving aperture of non-irradiated (0 kGy) reed straws was deter-mined to be 0.850 mm, and that of reed straws irradiated with 206 kGy or 404 kGy was determined to be 0.425 mm.
Owing to its electrical and thermal conductivities and ductility, copper metal is extensively used in daily life and conventional industrial production. Moreover, it plays an essential role in the new energy revolution. However, copper materials are highly susceptible to oxidation and various types of corrosion during application, which inevitably lead to performance degradation and severe economic losses. This study reports a novel strategy for preparing antioxidant copper materials by coordinating photo-induced carbon dioxide anion radicals (CO2?-), which are generated by ultraviolet (UV), visible, electron beam, and high-energy γ-rays, with metallic copper surfaces to construct an anti-corrosive binding layer. This novel anti-corrosion technique maintains the electrical and thermal conductivities of copper, while introducing anti-corrosive properties in diverse environments. Compared with conventional anti-corrosion strategies, this technique does not require a high temperature and pressure, and significantly reduces power consumption and environmental pollution. Additionally, the technique is applicable to various sizes and shapes of copper materials and enables the rapid, large-scale preparation of anti-corrosive copper using industrial electron beams.