View fulltext
View fulltext
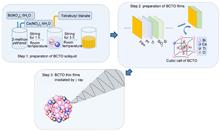
A series of ferroelectric thin films of Bi3.25Ce0.75Ti3O12 (BCTO) was deposited on a composite substrate of Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si through the sol-gel method, and the deposited films were irradiated with different doses of gamma rays. The
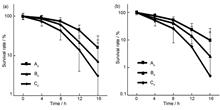
To explore the therapeutic effect of metformin combined with single high-dose radiotherapy in mice with non-small cell lung cancer and the mechanism involved. Invitro cell test: the cytotoxicity of metformin under different oxygen
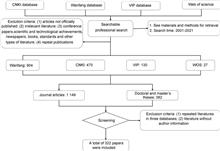
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is applied in various forms, such as decoction pieces, raw powder, extract, and patent Chinese medicine, etc. Controlling exogenous microbial contamination, ensuring the safety and effectiveness
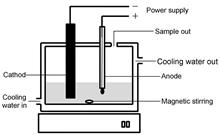
Mucormycosis infected by Actinomucor elegans is relatively serious in the population, so it is urgent need to inactivate Actinomucorelegans. In order to investigate the sterilization effect and mechanisms of contact glow discharge
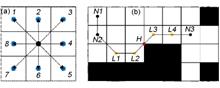
In order to enhance the path planning application of the transfer robot in a nuclear radiation environment, this paper addresses the problem of lack of influence from the surrounding environment on the path by the traditional A* a
To study the representative dose coefficients near nuclear facilities in the arid regions of Northwest China, a simplified anatomical model of Sphingonotus insects using computed tomography (CT) scanning is proposed. In addition,
The S-band electron linear accelerator developed for nondestructive testing is primarily used to inspect pressure vessels, petrochemical parts, and other industrial components. The X-band electron linear accelerator has been devel