 View fulltext
View fulltext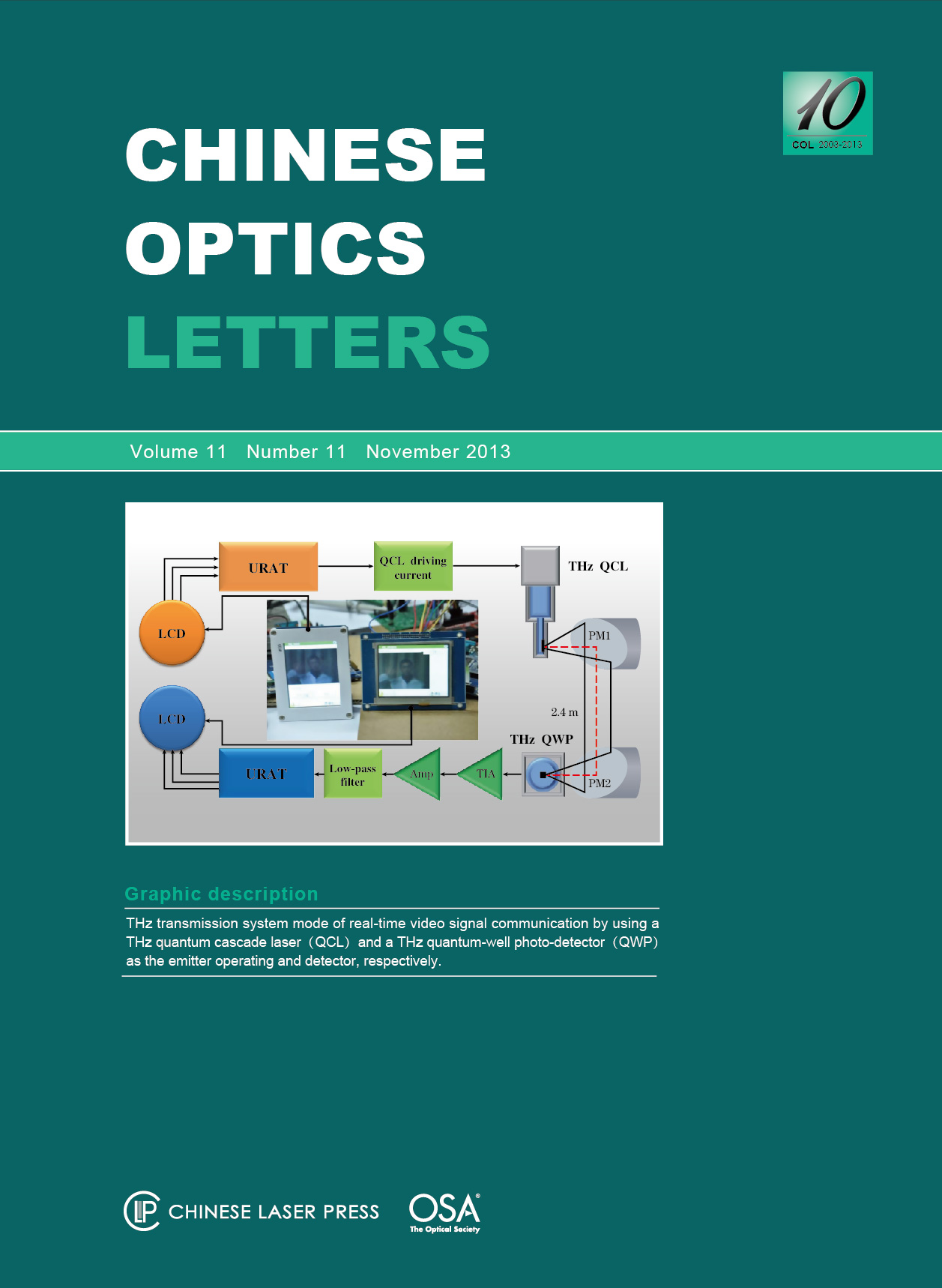
A Princeton Instruments PI-LCX 1300 charge-coupled device (CCD) camera used for X-ray spectrum measurements in laser-plasma experiments is calibrated using three radioactive sources and investigated with the Monte Carlo code Geant4. The exposure level is controlled to make the CCD work in single photon counting mode. A summation algorithm for obtaining accurate X-ray spectra is developed to reconstruct the X-ray spectra, and the results show that the developed algorithm effectively reduces the low-energy tail caused by split pixel events. The obtained CCD energy response shows good linearity. The detection efficiency curves from both Monte Carlo simulations and the manufacturer agree well with the experimental results. This consistency demonstrates that event losses in charge collection processes are negligible when the developed summation algorithm of split pixel events is employed.
In this letter, we investigate quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (QC-LDPC) codes in a 40-Gb/s nonreturn-to-zero differential phase-shift keying (NRZ-DPSK) signal transmission system based on a fiber-based optical parametric amplifier (FOPA). A constructed algorithm of QC-LDPC codes according to the optimizing set of shift values on the circulant permutation matrix (CPM) of the basis matrix is proposed. Simulation results prove that the coding gain in the encoded system can be realized at 10.2 dB under QC-LDPC codes with a code rate of 5/6 when the bit error rate (BER) is 10-9. In addition, the error-floor level originating from the uncoded system is suppressed.
Optical microfibers (OMs) are good alternatives in the field of sensing. In this letter, a simple and effective miniature temperature sensor based on OM is proposed and experimentally verified. Using pure water and fiber coating as the OM clad, an additional loss will occur due to the absorption of outer medium. The temperature of the outer environment can be estimated by monitoring the change in additional loss. In the demonstrated experiments, a series of OM with different diameters, waist lengths, and constructions are used as sensing elements. The correlation coefficients between the experimental results and the linear fittings are better than 0.99, and the temperature sensitivity obtained by the linear fittings can achieve –0.151 dB/oC (in pure water) and –0.405 dB/oC (covered by fiber coating). Moreover, higher sensitivity can be obtained by decreasing the diameter, increasing the waist length of the OM, or choosing the proper operating wavelength.
A fiber inline interferometric refractive index (RI) sensor consisting of a microchannel and a fiber taper is proposed in this letter. The microchannel is fabricated by combining femtosecond laser micromachining and arc fusion splicing. No subsequent chemical etching process is needed. Three sensors with microchannel widths of 4, 8, and 10 \mu m are prepared. The sensitivity in the RI range from 1.33 to 1.35 is up to ~361.29 nm/RIU at the microchannel width of 8 μm. The sensitivity is ~20 times greater than that of the paired taper-based MZI sensors and long period fiber grating pair MZI sensors.
All-optical 1×4 broadcast and 1×3 multicast experiments of a 40-Gb/s return-to-zero on-off keying (RZ-OOK) signal based on a periodically poled lithium niobate (PPLN) waveguide are demonstrated in this letter. Clear opened eye diagrams and error-free performance are achieved for the broadcast signals at 1541.3, 1543.7, 1548.5, and 1550.9 nm. Multicast technology uses cascaded second-harmonic generation and difference-frequency generation in a Ti:PPLN waveguide. An error-free operation with a negligible power penalty is achieved for the three wavelength-division multiplexing multicast signals at 1533, 1537, and 1541 nm.
We report on the experimental and numerical investigations of an all-optical network interface from back-bone networks to local area networks based on semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOAs). All-optical signals at 40 Gbps with return-to-zero (RZ) format in backbone networks are demultiplexed to signals at 10 Gbps with nonreturn-to-zero (NRZ) format in local area networks. SOAs and optical band-pass filters are used in the optical interface. We study the waveform, optical spectrum, and bit error rate (BER) of the interface scheme based on the experimental and numerical simulation results. The interface technique can be used in variable length and bit-rate variable optical networks.
We propose a novel scheme for optical frequency-locked multi-carrier generation based on a directly modulated laser (DML) and a phase modulator (PM) in cascade through synchronous sinusoidal radio frequency (RF) signal. The optimal operating zone for the cascaded DML and PM scheme is determined via theoretical analysis and numerical simulation. We demonstrate 16 optical subcarriers can be successfully generated based on the cascaded DML and PM scheme in the optimal zone. The generated 16 optical subcarries have frequency spacing of 12.5 GHz and power difference of less than 3 dB. These results agree well with those of the numerical simulation. We also demonstrate intensity modulation and direct detection (IM-DD) based on one of the 16 generated optical subcarriers. After 20-km single-mode fiber-28 (SMF-28) transmission, the bit-error ratio (BER) of 1 \times 10-9 can be attained for both 3.125- and 12.5-Gb/s bit rates.
We design a D-shaped fiber optic biosensor based on the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) of a metalgraphene layer and simulate this SPR using the finite element method. Using a metal-graphene layer as the sensing material, surface plasma resonance is simulated as the refractive index of the external environment ranges from 1.33 to 1.36. Simulation results show that a metal-graphene layer attached to the D-shaped optical fiber core can couple with light under a specific polarization state and excite strong plasma oscillations on the layer surface. Calculated transmission coefficients show that the resonance wavelength obviously moves toward longer wavelengths as the refractive index of the test medium increases, and a sensitivity of 5400 nm/RIU is obtained. Because of its large surface volume ratio and good biocompatibility, graphene may be utilized in many applications in the field of biosensing.
Acquiring deep-space images with high spatial resolution and sensitivity is important for space-debris surveillance and early warning. We propose a novel computational imaging (CI) method for high-sensitivity image acquisition in this letter. The proposed approach introduces CI into image formation. The proposed capturing process conducts minor modifications for cameras to encode more desirable information during capture, which is practical for hardware implementation. The latent image is reconstructed by formulating a recovery problem into an optimization problem, which is solved with iteratively reweighted least square technique. The experimental results clearly show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
This letter presents a label-free biomolecular imaging technique based on white-light interferometry and spectral detection. The method measures thickness changes caused by specific binding between biomolecules to detect the presence of certain analyte. A spectrum-shifting algorithm is developed to resolve the thickness information from the spectrum. The axial resolution of the experimental instrument can reach ~1 nm, thereby enabling detection of trace amounts (~1 ng/mm2) of proteins or DNA. This letter also presents two experiments to prove the feasibility of the method for detecting proteins and DNA without fluorescent labeling.
A pulsed current is introduced into the traditional coaxial laser cladding process to decrease the porosity of the cladding layer. The magneto contraction force caused by pulsed current exerted on the molten pool squeezes the gas out and compensates the shrinkage during molten pool solidification. As a result the porosity of the cladding layer is decreased to an extremely low degree. Simultaneously, the grain of the cladding layer is finer with the added supercooling degree with pulsed current. The microhardness of an equiaxed zone in the cross section of a cladding layer also increases.
Silicon nanocone arrays with metal silicide (Fe and Cr)-enriched apexes are fabricated on Si (100) substrate by the Ar+ ion bombardment method. The nanocone arrays show excellent field emission properties. A high current density (J) of ~0.33 mA/cm2 under a field of ~3 V/\mu m, a very low turn-on field of ~1.4 V/\mu m, and a very large enhancement factor of ~9466 are also obtained. The emission J of Si nanocone arrays remains extremely stable for long periods of time (24 h).
We theoretically investigate the classical analog of electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) and electromagnetically induced absorption (EIA) in a planar metamaterial at optical frequency, which originates from destructive and constructive interference between dark and radiative elements. The metamaterial consists of two coupled resonators with different geometries. An EIT-like transparent window with low absorption is observed and found to be strongly affected by resonant states of the resonators. The transition between the EIT and EIA is achieved by changing the split width and coupling distance. The absorption is enhanced up to 2.5 times compared with the dipolar case. The excitation of the dark mode is very important for EIT- and EIA-like responses of the proposed metamaterial. The EIT and EIA phenomena offer a potential method for manipulating electromagnetic response in metamaterial-based devices.
A weak infrared (IR) image amplifier with more than 60-dB optical gain and frequency up-conversion is developed from a picosecond (PS) 355-nm pumped gated optical parametric amplifier (OPA) in a \beta- BaB2O4 (BBO) crystal. The IR image at 1064 nm is amplified and up-converted into the visible region at 532 nm by parametric amplification and up-conversion. With the optimized optical gain, the lowest detectable energy of the image can be as low as 1.8 femto-Joule per pulse, which is three orders of magnitude lower than the detection limit of a charge-coupled device (CCD) camera. The transversal resolution of the OPA imaging is investigated, and the approaches for higher detection sensitivity and higher transversal resolution are proposed.
The nonlinear photoresponse to a 1.56-\mu m infrared continuous wave laser in semi-insulating (SI) galliumarsenide (GaAs) is examined. The double-frequency absorption (DFA) is responsible for the nonlinear photoresponse based on the quadratic dependence of the photocurrent separately on the coupled optical power and bias voltage. The electric field-induced DFA remarkably affects the native DFA in SI GaAs. The surface electric field or the surface band-bending of SI GaAs significantly affects the magnitude variation of the photocurrent and dark current.
The radio frequency magnetron sputtering method is used to prepare well-dispersed pyramidal-shaped Ge nanoislands embedded in amorphous SiO2 sublayers of various thicknesses. The estimated size and number density of Ge nanoislands in SiO2 sublayer thicknesses beyond 30 nm are approximately 15 nm and 1011 cm-2, respectively. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) reveals root mean square (RMS) roughness sensitivity as the SiO2 sublayer thickness varies from 30 to 40 nm. The formation of nanoislands with high aspect ratios is attributed to the higher rate of surface reactions between Ge adatoms and nucleated Ge islands than reactions associated with SiO2 and Ge. The Ge nanoisland polyorientation on SiO2 (50-nm thickness) is revealed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns. Photoluminescence (PL) peaks of 2.9 and 1.65 eV observed at room temperature (RT) are attributed to the radiative recombination of electrons and holes from the Ge nanoislands/SiO2 and SiO2/Si interfaces, respectively. The mean island sizes are determined by fitting the experimental Raman profile to two models, namely, the phonon confinement model and the size distribution combined with phonon confinement model. The latter model yields the best fit to the experimental data. We confirm that SiO2 matrix thickness variations play a significant role in the formation of Ge nanoislands mediated via the minimization of interfacial and strain energies.
A highly tunable optical nanoantenna element is proposed through gradual transformation from a sphere to a prolate spheroid. This new element induces field enhancement and an increase in resonance frequency. Rather than a purely metallic material, we propose the use of a metal-coated dielectric spheroid as a nanoelement because of its flexibility. We show that a spheroidal element enhances the near-field better than its rod and sphere counterparts. As such, spheroidal elements are good candidates for improving solar-cell performance.
Bessel beam propagation in scattering media is simulated using the angular spectrum method combined with slice-by-slice propagation model. Generating Bessel beams with a spatial light modulator, which provides a means to adjust flexibly the parameters of the Bessel beam, allows us to validate the simulation results experimentally. The study reveals that the self-reconstructing length changes oppositely with the axicon angle (i.e., the larger the axicon angle, the shorter the self-reconstructing length). The radius of the incident beam has little influence on the self-reconstruction of the Bessel beam central lobe.
We theoretically and experimentally study self-accelerating and self-breathing Bessel-like beams that follow arbitrary trajectories, including hyperbolic, hyperbolic secant, and three-dimensional (3D) spiraling trajectories. The beams have an overall Bessel-like profile in transverse dimensions; however, the intensity of their central main lobe breathes while traveling along a curved trajectory. Such beams can be readily generated experimentally through appropriate phase modulation of the optical wavefront. The beams contribute to the design of new families of self-accelerating beams.
A 2.4-m communication link operating at 3.9 THz based on a terahertz quantum cascade laser and a terahertz quantum well photodetector (THz QWP) are introduced. The lumped electrical models of THz QWP for small signals are presented. A discussion of the bandwidth limit of the detecting circuit is presented. Using direct on – off-keying modulation and intensity detection, the transmission of digital video signal with a data rate of 2.5 Mb/s is demonstrated. Pseudo-random binary sequences are transmitted to investigate the bit-error rate (BER) at different rates. Result shows the error free transmission when the rate is below 5 Mb/s.
A novel plasmonic waveguide filter design based on three cascaded slot cavities is proposed. The cascaded nanocavities support a united resonant (UR) mode. Light is trapped in the middle nanocavity at telecommunication wavelength (1550 nm) when the UR mode exists. This phenomenon leads to the efficient transmittance and high Q factor of the plasmonic filter. The resonant wavelength and Q factor can be easily modulated by the cavity radii and the waveguide width.
The ant colony optimization (ACO) algorithm based on the probability density function is applied for the retrieval of spherical particle size distribution (PSD). The spectral extinction data based on the Mie theory and the Lambert–Beer Law served as input for estimating five commonly use monomodal PSDs, i.e., Rosin–Rammer distribution, normal distribution, logarithmic normal distribution, modified beta distribution, and Johnson's SB distribution. The retrieval results show that the ACO algorithm has high feasibility and reliability, thus providing a new method for the retrieval of PSD.
We present a method by which to determine the bulk viscosity of water from pulse duration measurements of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS). Beginning from a common model of Brillouin scattering, the bulk viscosity is shown to play an important role in Brillouin linewidth determination. Pulse durations of SBS back-reflected optical pulses are measured over the temperature range of 5–40 oC. SBS linewidths are determined via Fourier transformation of the time-domain results, and the bulk viscosity of water is measured and derived from the obtained values. Our results show that the proposed method for measurement of pulse durations is an effective approach for determining bulk viscosity. The method can be easily extended to determine bulk viscosities of other Newtonian liquids.
A Projector-camera (Procam) system is an inexpensive, household, controllable system that can be used to eliminate inter-reflection existing in the measurement. We propose an estimation method for spectral reflectance that uses the Procam system. The method recovers reflectance from the training set constructed by a known reflectance and the corresponding 9D color-mixing matrix. Experiment results show that our method performs well with 9D response, and the local weighted training set based on Mahalanobis metric can enhance the accuracy of result efficiently.
The fastness and robustness of a control algorithm are highly important in the performance of adaptive optics systems. The proportional-integral-derivative control with arranging the transient process, which is designed using a tracking differentiator, is applied into an adaptive optics system. This control algorithm greatly improves the dynamic properties of the control system. To identify the underlying reasons for these improvements, the influence of the control algorithm is theoretically discussed. The control algorithm is verified by a simple adaptive optics system for tip/tilt correction. The experimental results demonstrate that the control algorithm is fast and robust.
Analytical expressions of the temporal power spectral models of angle of arrival (AOA) fluctuations are derived using the generalized exponential spectral model for optical waves propagating through weak non-Kolmogorov turbulence. Compared with expressions of temporal power spectral models derived from the general non-Kolmogorov spectral model, the new expressions consider the influences of the inner and outer scales of finite turbulence. Numerical calculations show that large outer scales of turbulence increase the value of the temporal power spectrum of AOA fluctuations in low-frequency regions.
Optical waveguides are fabricated in Nd3+:Y3+:SrF2 crystals by a 1-kHz femtosecond laser using the double-line approach. Waveguides with different separations (10, 15, and 20 \mm m) between two consecutive optical breakdown tracks are produced, and their optical performances are explored by end-fire coupling to 780-and 532-nm lasers. Propagation loss of the waveguide with 20-\mm m separation is estimated. The microphotoluminescence and micro-Raman spectra indicate that the original fluorescence and lattice structure of the Nd3+:Y3+:SrF2 crystals are well preserved in the waveguide. Therefore, the obtained waveguide structures are promising candidate for application in integrated waveguide lasers.
The design of a two-dimensional high-frequency electrostatic microscanner is presented, and an improved method for routing isolation trenches is investigated to increase the reliability and mechanical stability of the resulting device. A sample device is fabricated and tested using an optimized micromachining process. Measurement results indicate that the sample device oscillates at inherent frequencies of 11586 and 2047 Hz around the two rotational axes, thereby generating maximum twisting angles of +(-)7.28o and +(-)5.63o, respectively, under two square waves of 40 V. These characteristics confirm the validity of our design and satisfy the requirements of a laser projector with VGA standards.










