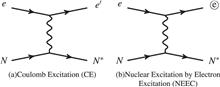
Nuclear isomers play essential roles in various fields, including stellar nucleosynthesis, nuclear clocks, nuclear batteries, clean nuclear energy, and γ-ray lasers. Recent technological advances in high-intensity lasers have made it possible to excite or de-excite nuclear isomers using table-top laser equipment. Utilizing a particle-in-cell code, we investigate the interaction of a laser with a nanowire array and calculate the production rates of the 73mGe (E1 = 13.3 keV) and 107mAg (E1 = 93.1 keV) isomers. For 73m1Ge, production by Coulomb excitation is found to contribute a peak efficiency of 1.0 × 1019 particles s-1 J-1, while nuclear excitation by electron capture (NEEC) contributes a peak of 1.65 × 1011 particles s-1 J-1. These results indicate a high isomeric production ratio, as well as demonstrating the potential for confirming the existence of NEEC, a long-expected but so far experimentally unobserved fundamental process.
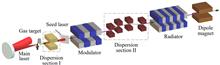
In this paper, promising but simple schemes are investigated to enhance the micro-bunching of relativistic electron beams for coherent harmonic generation (CHG) by using phase merging effects. In contrast to the standard CHG scheme, two specially designed dispersion sections (DSs) are adopted with the DS-modulator–DS configuration. The phase space of the e beam is appropriately coupled in the first DS, and the electrons within one seed wavelength can merge to the same phase with a matched second DS. Micro-bunching of the e beam can thus be enhanced by a large margin with much higher-harmonic components. Taking e beams from laser wakefield accelerators (LWFAs) as an example, start-to-end simulations are performed to show the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed schemes with several configurations. The beam current can be optimized to several tens to hundreds of kiloamperes, and the radiation power reaches hundreds of megawatts in the extreme ultraviolet regime within a 3.5 m-long beamline. The proposed schemes offer new opportunities for future compact free-electron lasers driven by LWFAs and provides prospects for truly compact and widely applicable systems.
A scheme for a quasi-monoenergetic high-flux neutron source with femtosecond duration and highly anisotropic angular distribution is proposed. This scheme is based on bulk acceleration of deuteron ions in an optical trap or density grating formed by two counter-propagating laser pulses at an intensity of ∼1016W/cm2 in a near-critical-density plasma. The deuterons are first pre-accelerated to an energy of tens of keV in the ambipolar fields formed in the optical trap. Their energy is boosted to the MeV level by another one or two laser pulses at an intensity of ∼1020W/cm2, enabling fusion reactions to be triggered with high efficiency. In contrast to previously proposed pitcher–catcher configurations, our scheme can provide spatially periodic acceleration structures and effective collisions between deuterons inside the whole target volume. Subsequently, neutrons are generated directly inside the optical trap. Our simulations show that neutron pulses with energy 2–8 MeV, yield 1018–1019n/s, and total number 106–107 in a duration ∼400 fs can be obtained with a 25 μm target. Moreover, the neutron pulses exhibit unique angularly dependent energy spectra and flux distributions, predominantly along the axis of the energy-boosting lasers. Such microsize femtosecond neutron pulses may find many applications, such as high-resolution fast neutron imaging and nuclear physics research.
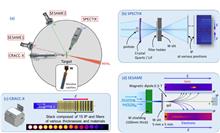
This article reports the first measurements of high-energy photons produced with the high-intensity PETawatt Aquitaine Laser (PETAL) laser. The experiments were performed during the commissioning of the laser. The laser had an energy of about 400 J, an intensity of 8 × 1018 W cm-2, and a pulse duration of 660 fs (FWHM). It was shot at a 2 mm-thick solid tungsten target. The high-energy photons were produced mainly from the bremsstrahlung process for relativistic electrons accelerated inside a plasma generated on the front side of the target. This paper reports measurements of electrons, protons and photons. Hot electrons up to ≈35 MeV with a few-MeV temperature were recorded by a spectrometer, called SESAME (Spectre ÉlectronS Angulaire Moyenne Énergie). K- and L-shells were clearly detected by a photon spectrometer called SPECTIX (Spectromètre Petal à Cristal en TransmIssion pour le rayonnnement X). High-energy photons were diagnosed by CRACC-X (Cassette de RAdiographie Centre Chambre-rayonnement X), a bremsstrahlung cannon. Bremsstrahlung cannon analysis is strongly dependent on the hypothesis adopted for the spectral shape. Different shapes can exhibit similar reproductions of the experimental data. To eliminate dependence on the shape hypothesis and to facilitate analysis of the data, simulations of the interaction were performed. To model the mechanisms involved, a simulation chain including hydrodynamic, particle-in-cell, and Monte Carlo simulations was used. The simulations model the preplasma generated at the front of the target by the PETAL laser prepulse, the acceleration of electrons inside the plasma, the generation of MeV-range photons from these electrons, and the response of the detector impacted by the energetic photon beam. All this work enabled reproduction of the experimental data. The high-energy photons produced have a large emission angle and an exponential distribution shape. In addition to the analysis of the photon spectra, positron production was also investigated. Indeed, if high-energy photons are generated inside the solid target, some positron/electron pairs may be produced by the Bethe–Heitler process. Therefore, the positron production achievable within the PETAL laser facility was quantified. To conclude the study, the possibility of creating electron/positron pairs through the linear Breit–Wheeler process with PETAL was investigated.
We present quasi-exact ab initio path integral Monte Carlo (PIMC) results for the partial static density responses and local field factors of hydrogen in the warm dense matter regime, from solid density conditions to the strongly compressed case. The full dynamic treatment of electrons and protons on the same footing allows us to rigorously quantify both electronic and ionic exchange–correlation effects in the system, and to compare the results with those of earlier incomplete models such as the archetypal uniform electron gas or electrons in a fixed ion snapshot potential that do not take into account the interplay between the two constituents. The full electronic density response is highly sensitive to electronic localization around the ions, and our results constitute unambiguous predictions for upcoming X-ray Thomson scattering experiments with hydrogen jets and fusion plasmas. All PIMC results are made freely available and can be used directly for a gamut of applications, including inertial confinement fusion calculations and the modeling of dense astrophysical objects. Moreover, they constitute invaluable benchmark data for approximate but computationally less demanding approaches such as density functional theory or PIMC within the fixed-node approximation.
Rescattering of stimulated Raman side scattering (SRSS) is observed for the first time via two-dimensional (2D) particle-in-cell (PIC) simulations. We construct a theoretical model for the rescattering process, which can predict the region of occurrence of mth-order SRSS and estimate its threshold. The rescattering process is identified by the 2D PIC simulations under typical conditions of a direct-drive inertial confinement fusion scheme. Hot electrons produced by second-order SRSS propagate nearly perpendicular to the density gradient and gain nearly the same energy as in first-order SRSS, but there is no cascade acceleration to produce superhot electrons. Parametric studies for a wide range of ignition conditions show that SRSS and associated rescatterings are robust and important processes in inertial confinement fusion.
The thermodynamic properties of boron nitride under extreme pressures and temperatures are of great interest and importance for materials science and inertial confinement fusion physics, but they are poorly understood owing to the challenges of performing experiments and realizing ab initio calculations. Here, we report the first shock Hugoniot data on hexagonal boron nitride at pressures of 5–16 Mbar, using hohlraum-driven shock waves at the SGIII-p laser facility in China. Our density functional theory molecular dynamics calculations closely match experimental data, validating the equations of state for modeling the shock response of boron nitride and filling a crucial gap in the knowledge of boron nitride properties in the region of multi-Mbar pressures and eV temperatures. The results presented here provide fundamental insights into boron nitride under the extreme conditions relevant to inertial confinement fusion, hydrogen–boron fusion, and high-energy-density physics.
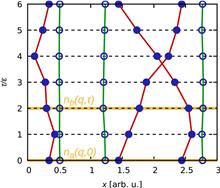
A generalized kinetic model of atomic level populations in an optically dense plasma excited by laser pulses of arbitrary duration is formulated and studied. This model is based on a nonstationary expression for the probability of excitation of an atomic transition and takes into account the effects of laser pulse penetration into an optically dense medium. A universal formula for the excitation probability as a function of time and propagation length is derived and applied to the case of a Lorentzian spectral profile of an atomic transition excited by a laser pulse with a Gaussian envelope. The features of nonstationary excitation probabilities are presented for different optical depths of the plasma, laser pulse durations, and carrier frequencies. The formulas derived here will be useful for the description of atomic populations excited by laser pulses under realistic conditions of dense plasmas.
It is of substantial scientific significance and practical value to reveal and understand the multiscale mechanical properties and intrinsic mechanisms of medium-entropy alloys (MEAs) under high strain rates and pressures. In this study, the mechanical responses and deformation mechanisms of an equiatomic CoCrNi MEA are investigated utilizing magnetically driven ramp wave compression (RWC) with a strain rate of 105 s-1. The CoCrNi MEA demonstrates excellent dynamic mechanical responses and yield strength under RWC compared with other advanced materials. Multiscale characterizations reveal that grain refinement and abundant micromechanisms, including dislocation slip, stacking faults, nanotwin network, and Lomer–Cottrell locks, collectively contribute to its excellent performance during RWC. Furthermore, dense deformation twins and shear bands intersect, forming a weave-like microstructure that can disperse deformation and enhance plasticity. On the basis of these observations, we develop a modified crystal plasticity model with coupled dislocation and twinning mechanisms, providing a relatively accurate quantitative description of the multiscale behavior under RWC. The results of simulations indicate that the activation of multilevel microstructures in CoCrNi MEA is primarily attributable to stress inhomogeneities and localized strain during RWC. Our research offers valuable insights into the dynamic mechanical responses of CoCrNi MEA, positioning it as a promising material for use under extreme dynamic conditions.
We present a novel method for investigating laser-driven dynamic fragmentation in tin using in situ X-ray diffraction. Our experimental results demonstrate the feasibility of the method for simultaneously identifying the phase and temperature of fragments through analysis of the diffraction pattern. Surprisingly, we observe a deviation from the widely accepted isentropic release assumption, with the temperature of the fragments being found to be more than 100 K higher than expected, owing to the release of plastic work during dynamic fragmentation. Our findings are further verified through extensive large-scale molecular dynamics simulations, in which strain energies are found to be transferred into thermal energies during the nucleation and growth of voids, leading to an increase in temperature. Our findings thus provide crucial insights into the impact-driven dynamic fragmentation phenomenon and reveal the significant influence of plastic work on material response during shock release.