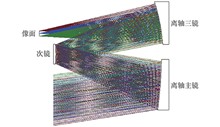
Luminous remote sensing images have been widely used in social and economic estimation, urban monitoring, ecological environment assessment and public health. Using luminous remote sensing to detect ground objects in low illumination conditions such as nighttime and twilight, it is complementary to traditional daytime remote sensing to form all-day earth observation capability. However, in low illumination environment, the image quality of remote sensing camera will decline sharply with the attenuation of camera light input, so how to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of remote sensing image is the focus of luminous remote sensing. The SNR of a remote sensing camera developed in the early stage was analyzed and modeled in detail. The functional relationship between SNR, integration time and ground radiation brightness was given in the face array staring mode. When the integration time is greater than 2 ms, the SNR is better than 10 dB, and when the integration time is greater than 15 ms, the SNR is better than 20 dB. In strip imaging mode, the relation between SNR and line frequency and TDI series was given. The results show that when the TDI series is constant, the SNR decreases with the increase of line frequency, and when the line frequency is constant, the SNR increases with the increase of TDI series, but the speed of SNR increase gradually slows down with the increase of TDI series.
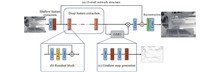
Existing image super-resolution networks are mostly designed for visible light images, with relatively fewer studies focusing on infrared image super-resolution, and most of them simply adopt methods from visible light image super-resolution. In response to the low resolution and blurred edges of infrared images, a gradient-guided infrared image super-resolution reconstruction network was proposed. The gradient information in low-resolution infrared images was fully utilized by the network, fusing the gradient map with the extracted features, thereby resulting in a high-resolution image with clearer edges and higher contrast. The experimental results of the comparative and ablation studies demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms other comparative methods in infrared image super-resolution reconstruction, generating high-resolution images of higher quality.
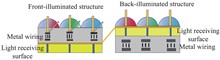
In complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) image sensors, forming a barrier with a Delta structure (delta-doping) on the surface can effectively resolve the issues of performance changes in traditional CMOS image sensors under irradiation environment. The width and height parameters of the barrier directly affect the dark current on the surface of the CMOS image sensor as well as the efficiency of surface signal detection. It was assumed that the total energy of electrons and the cross-sectional direction of tunneling satisfied the Schrodinger equation, calculating the probability of tunneling and the relationship between the tunneling height and width, and resulting in the conclusion that the minimum width of the Delta-doped barrier should be above 1 nm, thereby designing the doping structure and doping concentration. It was discussed that CMOS with Delta doping had the feature of high-efficient, stable, and uniform quantum efficiency, which enhanced low-energy electron detection and contributed to low-light imaging and space exploration.
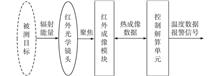
The infrared radiometer is generally used for the calibration of the infrared thermal imager testing equipment. A measurement module and method for infrared radiometer were introduced. A measurement scheme of sample and hold was designed, the sampling pulse was generated from the reference signal, and the sampling point was set at the 1/4 phase of each signal period, which could significantly improve the measurement ability of weak signals. For the black-body radiation signal at 35 ℃, the measured signal strength could be increased by 57.6% by comparing with the existing scheme. Under the condition that the background temperature of the infrared thermal imager testing equipment was 22 ℃, the measurement signal accuracy could be improved by more than 50% through the comparison test with the existing instruments.
During the continuous launching of gun, the temperature of inside wall of gun bore increases substantially, which will cause a high security risk when the temperature exceeds the ignition point of all combustible cartridge. An application and device of infrared thermal imaging technology in gun bore temperature measurement was introduced, included the composition and temperature measurement principle of the device. Combined the course of replacing ammunition during the continuous launching process, the image processing techniques such as edge detection, contour extraction, and identification judgment were used in the gun bore temperature measurement device, it could automatically analyze the effective time and the target area of temperature measurement. Based on the resolving curve calibrated by least-square method, the maximum temperature and average temperature of the target area could be determined, and the device reported the temperature data to the gun control system in real time for it to determine whether to replace ammunition or strike, which could effectively improve the safety of gun during the continuous launching process.
In the process of assembling and adjusting the infrared optical lens group, the optical center-deviation will occur. Since the infrared material is not transparent to visible light, the traditional visible light adjustment mode cannot be used, which becomes a difficulty in the assembly and adjustment of the infrared lens group. An assembly and adjustment scheme based on the OptiCentric dual-optical path center-deviation measuring instrument from TRIOPTIC company in Germany was proposed, and introduced in detail the assembly and adjustment methods of no-mirror seat centering method, the mirror seat method and the aspheric surface. The advantages and disadvantages of the no-mirror seat centering method and the mirror seat method were analyzed. In addition, it was pointed out that there were still some limitations in the centering of aspheric surfaces using the OptiCentric center-deviation measuring instrument. Finally, the optical transfer function tester was used to test the lens adjusted by the above two methods. The test results show that the lens adjusted by the center-deviation measuring instrument can meet the requirements of technical indicators.
With the development and application of infrared (IR) imaging technology, the IR imaging simulation and its validation methods have been paid more and more attention. The existing validation methods of IR imaging simulation model rarely take the impact of human vision into account, which will lead to the serious consequences. In order to solve this problem, the validation method of IR imaging simulation model based on the recognition range was proposed. With the recognition range as the accuracy evaluation factor of IR imaging simulation model, the comprehensive differences of various aspects such as gray level distribution, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) , resolution, imaging size and human vision between the simulated image and the measured image could be evaluated.