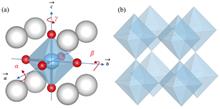
BackgroundThe oxygen octahedral rotation (OOR) in perovskite oxides is closely related to its physical properties. The recent development of synchrotron radiation three-dimensional diffraction provides opportunities for efficient characterization of the superlattice half-order peaks corresponding to OOR, but quantitative analysis is still difficult.PurposeThis study aims to provide guidance for the measurement of OOR half-order peaks and lay a foundation for their quantitative analysis through a theoretical simulation of the half-order peak intensity.MethodsFirstly, a universal calculating formula for coordinates of all the oxygen ions in an OOR super cell was provided. Then, starting from the calculation formula of structure factor of a lattice unit cell, a quantitative formula for calculating the half-order peak intensity of lattice with OOR was deduced according to the basic theory of crystal diffraction kinematics. Subsequently, the half-order peak intensity distribution patterns corresponding to the 27 rotation modes were simulated and exhibited by programming, and the appearance rules were summarized. Finally, two typical examples were used to verify the consistency between the simulation results and the measured results.Results & ConclusionsTwo typical examples show that the simulation results are in good agreement with the measured results. Based on these results, the OOR half-order peak pattern can be predicted beforehand and their origins may be verified after hand for experimental measurement of half-order peak. This work may promote the application of synchrotron radiation diffraction in the characterization of perovskite OOR.
BackgroundSynchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a powerful tool for material structure analysis, and it is commonly used in structural analysis, phase identification, etc. The X-ray diffraction data are often collected using two-dimensional detectors in Synchrotron Radiation Facility at present, but the experimental system cannot ensure the vertical geometric relationship between the X-ray and the detector area, resulting in systematic errors in the experimental data and impacting on subsequent data processing and analysis seriously. Although existing domestic and foreign software such as FIT2D, pyFAI calib2, Dioptas, SGTools, etc. provide calibration functions, there are still some shortcomings in operability and usability.PurposeThis study aims to develop and implement an user-friendly software to calibrate 2D XRD detector experimental parameters through the standard sample independently.MethodsA domestic software, named as Corona, was developed using Python and PyFAI library. The experimental geometric parameters were calibrated in Corona by making use of the Debye Scherrer ring of the standard powder sample. By comparing and testing with existing foreign software FIT2D and Dioptas, the accuracy and usability of Corona calibration parameters and data integration were verified.ResultsVerification results show that Corona can effectively achieve calibration detector parameters and data integration accurately with advantages of friendliness, convenience, and ease of user operation.ConclusionsCorona proposed in this study provides effective tools to calibration 2D X-ray diffraction detector experimental parameters and data integration, but further improvement need to be implemented for expanding application.
BackgroundSolid-state amplifiers of synchrotron radiation high-frequency cavity equipment may sustain unrecoverable damage due to the excessive reflected power resulting from load detuning, a high-power circulator is used to guide the reflected power to the absorbing load and thus protect the power source. In this case, if the reflected power suddenly increases during device operation, the temperature of the circulator cavity will be risen and the parameter characteristics of the gyromagnetic ferrite will be changed in the circulator, and eventually lead to poor absorption of the reflected power by the load.PurposeThis study aims to design and develop a circulator with a temperature compensation control unit, capable of functioning at 499.654 MHz with a 160 kW continuous wave radiofrequency power.MethodsFirstly, the circulator was simulated and optimized using the HFSS software. Thermal simulation shows that the temperature rise of ferrite sheets under 160 kW continuous wave is less than 13 °C. Then, impedance matching was performed on the circulator using tuners arranged at each of the three ports, and feedforward control was used to compensate for the temperature changes. Finally, a constant temperature water tank was employed to simulate the change in water temperature during actual operation, the reliability of temperature compensation function of the control unit was verified by the performance of the circulator restoring to the best condition.ResultsThe insertion loss is better than -29 dB under the worst case of a complete short circuit at the output port, the circulator loss is less than 0.1 dB in the bandwidth of ±5 MHz, and this loss reaches 0.06 dB at the center frequency.ConclusionsThe S parameters of the circulator meet the design requirements, and the reliability of the temperature control compensation unit of circulator is verified by constant temperature water tank simulation test in this study.
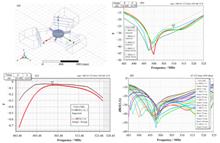
BackgroundThe Scanning Transmission X-ray Microscopy (STXM) endstation, located at the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF), stands as China's sole STXM device. It boasts the capability for high spatial resolution imaging down to a 15 nm scale. Utilizing the scanning coherent diffraction imaging method (i.e. ptychography), this station achieves an optimal resolution of 7.32 nm, necessitating utmost system stability. However, the STXM system operates within a complex environment where the impact of external vibrations on imaging quality is increasingly problematic.PurposeThis study aims to develop a closed loop control method for the vibration of STXM system to improve imaging quality.MethodsFirst of all, system vibration between the Fresnel zone plate (FZP) and the sample was analyzed in detail, so did the vibration suppression methods. Then, a software-driven closed-loop control system was developed on Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) platform by leveraging these insights, and a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) based approach was implemented to process precise (picometer-scale) and rapid (1 kHz) positional data captured by a laser interferometer. Finally, the internal sensor of motor controller was replaced by laser interferometer to realize the closed-loop control to suppress vertical vibration, and vibration data were applied to a piezo motor for effectively replacing its internal sensors to suppress system vibrations.ResultsThe optimal performance achieved by the closed-loop control scheme shows that the root mean square (RMS) value of the vibration is reduced to 4.833 nm, which is around one third of the value before.ConclusionsThe successful implementation of this closed-loop control scheme has furnished robust technical foundations for further enhancements in the imaging resolution of the STXM system.
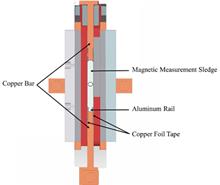
BackgroundA superconducting undulator prototype with the length of 4 m, the period length of 16 mm, and the gap of 5 mm for the Shanghai High Repetition Rate XFEL and Extreme light facility (SHINE) has been successfully integrated and delivered for acceptance test.PurposeThis study aims to propose a magnetic field measurement method tailored for small gap superconducting undulators and to optimize the phase error associated with the magnetic field.MethodsA magnetic field measurement technique based on dual Hall probes without fixed guiding rails was put forward based on the calculating formulas derived for the position of the magnetic neutral plane and the magnetic field distribution on this plane using data from the dual Hall probes. Then, a phase error optimization method based on segmented powering of the superconducting undulator magnet was proposed. These methods were applied to measuring and optimizing the magnetic field in the middle section of the prototype, which was 2 m long and divided into two 1-m sections, each powered by separate power supplies.ResultsThe measurement results show that the repeatability of the effective peak magnetic field between two measurements at 100 A excitation current is better than 1.5 Gs, and the phase error repeatability is better than 0.2°. After fine-tuning the excitation current, the phase error of the 2 m segment is reduced to 4.6°, meeting the design requirements.ConclusionsThe results confirm that the magnetic field measurement and optimization method proposed of this study is practical and effective.
BackgroundWith the increasingly strict requirements of the fourth-generation synchrotron radiation light source on the brightness and emittance of the beam, the impact of micro-vibration on the beam quality has gradually become prominent. However, there is still no unified standard for comprehensive testing and evaluating the impact of ground-based micro-vibrations, making the effective management and control of micro-vibration particularly difficult.PurposeThis study aims to evaluate the random characteristics of ground vibration and analyze the vibration sources in detail.MethodsA spectral estimation-based model was developed for vibration data processing, and a method based on probability statistics was proposed to evaluate the displacement of ground micro-vibration. Then, triaxial force feedback velocity sensor (seismometer) was employed to test the micro vibration of foundation of Wuhan Advanced Light Source (WALS) pre-research site, and the vibration root mean square (RMS) displacement was comprehensively and objectively assessed by aforementioned approach.ResultsThe results indicate that the vertical vibration average RMS displacement of the isolated foundation in the experimental hall of WALS within the pre-research zone of WALS is 8.08 nm, with a σ value of 4.55 nm. It is noted that the vertical vibration displacement (ave RMS+3σ) reaches about 21.73 nm, which satisfies the 40 nm requirement.ConclusionsThis vibration data processing method proposed in this study is appropriate for evaluating the vibrations of the original background and isolated treatment foundation, as well as for analysis of vibration sources at the component level.