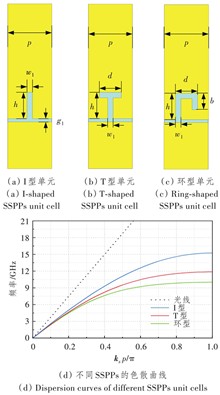
【Objective】Spoof Surface Plasmon Polaritons (SSPPs) has the characteristics of low loss, high transmission efficiency, and strong binding ability to electromagnetic waves, which has been widely used in microwave device design. In this article, an ultra wideband Bandpass Filter (BPF) is proposed based on SSPPs, which features a simple structure, ease of processing, and excellent out-of-band suppression performance.【Methods】The BPF can be divided into two parts, a Coplanar Waveguide (CPW) high pass filter loaded with a pair of Split Ring Resonators (SRR) and a ring-shaped SSPPs low pass filter. The article is based on BPF design theory and SSPPs dispersion characteristics. It adopts modular and cascaded structural design methods to model the two parts of the structure separately. The dependency relationship between key structural parameters and performance indicators is studied. The tolerance analysis, sample development, and testing are also conducted.【Results】The proposed SSPPs low pass filter is composed of ring shaped SSPPs unit cells, which have better slow wave characteristics comparing with traditional I-shaped and T-shaped SSPPs unit cells. The proposed ultra wideband BPF has a passband range of 3.3~10.3 GHz. Its upper cut off frequency can be flexibly controlled in the structural design by changing the size of the SSPPs unit structure. The return loss within the passband of this BPF is better than -13 dB, with most insertion losses better than -1 dB. The out-of-band suppression reaches -25 dB for the lower stopband and -30 dB for the upper stopband. The rectangular coefficient within -20 dB is close to 1. The test results agrees well with the simulation results.【Conclusion】The developed BPF features a simple structure, convenient and low-cost processing, wide frequency band, and good steepness of the transition band. It can effectively realize signal filtering and out-of-band harmonic suppression functions, making it suitable for the development of circuits and equipment in related fields such as ridio frequency microwave communications and instrumentation measurements.
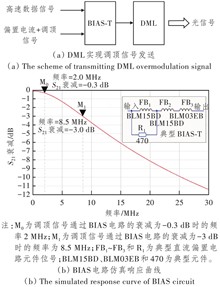
【Objective】The Auxiliary Management and Control Channel (AMCC) based on overmodulation technology is independent of the data service and has the advantage of ultra-low latency jitter, aligning with the development trend of access networks, which feature large bandwidth, low latency, and intelligence. This article aims to explore the principles, implementation methods, and technical verification of overmodulation AMCC technology in optical access networks, and provides an in-depth analysis of its novel applications in access networks. This serves as a reference for further research and development, as well as engineering applications of this technology in access networks.【Methods】Through a literature review and analysis of experimental data, the article systematically elaborates on the technical principles of overmodulation AMCC. The research focuses on exploring low-cost implementation pathways for it in optical access networks, including technologies such as direct modulation lasers and split detectors. The paper also analyzes the application of overmodulation AMCC technology in different optical network systems and its impact on network performance. It further discusses the application methods of related technologies in access network systems for multi-channel monitoring, reflection, optical power estimation, and the avoidance of Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) Passive Optical Networks (PON) silent windows.【Results】The study shows that overmodulation AMCC technology can effectively support multi-channel monitoring and management in access networks, distinguishing it from traditional methods. It is particularly applicable in The 5th Generation Mobile Communication Technology (5G) front-haul transmission, optical line reflection monitoring, and low-latency TDM PON systems. This technology supports high-speed network transmission while enabling the perception and management of optical layer channels, demonstrating significant technical potential in addressing TDM PON silent window issues.【Conclusion】The overmodulation AMCC technology can achieve low-cost, multidimensional multiplexing of high-speed data and low-speed signals in access networks to a certain extent. It has broad application prospects in optical access networks, enhancing the intelligent management level of networks while fulfilling requirements for large bandwidth and low-latency communication. Additionally, it facilitates perception at the optical layer. Implementing this technology can improve network efficiency and stability, meeting the developmental needs of The 5th Generation Fixed Network-Advanced (F5G-A) and The 6th Generation Fixed Network (F6G) in future. Further research on its application in PON structures, more modulation formats, and additional application scenarios could optimize its performance and adaptability, promoting its vigorous development.
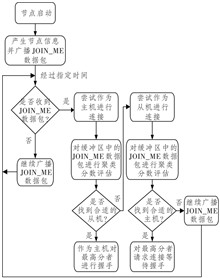
【Objective】Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a low-power, low-cost wireless communication technology, and the development of BLE Mesh further enhances the network scalability and communication range. Fruitymesh stands as the only open-source routing-based BLE Mesh networking strategy at present. However, using Fruitymesh in highly dynamic node environments leads to issues such as interruptions in tree-shaped topology network transmission links due to frequent node entries and exits, resulting lower data transmission success rates. To address this problem, this paper utilizes the networking principles of Fruitymesh and proposes a limited flooding-based routing strategy suitable for highly dynamic node scenarios.【Methods】By modifying the clustering scoring mechanism, the network topology is refined from a tree-shaped structure to a partial mesh structure, enhancing the overall reliability of the network topology. Simultaneously, a route selection mechanism is introduced, and a limited flooding routing strategy is designed.【Results】Through simulation verification, compared to Fruitymesh, the limited flooding routing strategy demonstrates a 71.4% improvement in network topology robustness. In fixed-point attacks, the overall network Packet Delivery Rate (PDR) is increased from 15.00% to 85.67%. In random attacks, the overall network PDR is increased from 53.00% to 92.29%. And the average PDR of non-neighboring nodes in the limited flooding routing algorithm is improved from 78.73% to 86.97% as compared to the flooding routing algorithm.【Conclusion】The proposed limited flooding routing strategy in this paper effectively enhances the network topology robustness, route transmission reliability, and the success rate of network communication in highly dynamic node environments.
【Objective】To meet the requirements of the engineering of high-speed Underwater Wireless Optical Communication (UWOC) technology, and to address the issue of high Bit Error Rate (BER) in underwater channels when using modulation methods such as On/Off Keying (OOK) that rely on threshold demodulation for high-speed communication, this paper conducts comparative simulation analysis of commonly used underwater optical communication modulation methods and proposes an improved modulation and demodulation algorithm that combines Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) with Manchester encoding and does not require threshold decision-making.【Methods】The paper uses sliding mean filtering to improve the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR). The frame synchronization is then achieved by parallel multi-path threshold-free decision-making on the PPM frame header, providing a time calibration basis for Manchester encoding and demodulation. Finally, high-speed communication system with low BER is realized by using Manchester encoding sub-frame headers and Reed-Solomon (RS) error-correcting codes in the data part. The algorithm is designed and implemented on a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA), and a UWOC system using this method is built to conduct BER tests under different environments and distances.【Results】The test results show that the UWOC system based on this demodulation algorithm has an BER of 10-5 in indoor clear water pools and 10-3 in nearshore lake water at a communication speed of 50 Mbit/s and a communication distance of 10 m.【Conclusion】The proposed algorithm in this paper is applied in nearshore lake water with a distance of 10 meters, compared to modulation methods such as OOK and PPM, using modified Manchester encoding modulation can achieve more reliable 50 Mbit/s communication.
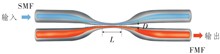
【Objective】Mode-Selected Coupler (MSC) is a key component of Mode Division Multiplexing (MDM) for optical fiber communication system. In a MDM system, MSC can realize the transmission of different signals in different modes, thus increasing the transmission capacity. However, when fabricating a MSC with low insertion loss, the fabrication difficulty of the MSC is heightened due to the very close propagation constants between the modes. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a Few-Mode Fiber (FMF) with easily separable modes to serve as a key material for the fabrication of MSCs, thereby reducing the fabrication difficulty.【Methods】In this letter, a new type of ring-core FMF is proposed and fabricated. The FMF supports three linearly polarized modes LP01, LP11 and LP21 in the C-band for fiber communication. Based on the theory of mode coupling, the article analyzes the impact of various parameters of the MSC on mode coupling and studies the coupling patterns between modes as influenced by fiber core spacing and coupling distance.【Results】The fused biconical tapering method is used to fabricate the MSCs of LP01, LP11 and LP21. The experimental results show that the insertion losses of the MSCs of LP01, LP11 and LP21 at 1 540, 1 530 and 1 550 nm are 0.10, 0.17 and 0.30 dB, respectively. The mode conversion efficiencies are 97.72%, 96.16% and 93.32%, respectively. The mode conversion bandwidths of LP01, LP11 and LP21 are 125, 120 and 35 nm, respectively.【Conclusion】This research provides a new type of ring-core FMF, which can reduce the fabrication difficulty of MSCs. The low-loss MSCs have great potential application for MDM optical fiber communication system.
【Objective】Silicon-based optoelectronic platforms have the advantages of low-cost manufacturing, high integration density, and high transmission speed. However, due to the photoelectric properties of silicon materials, it is difficult for monocrystalline silicon to directly achieve high responsivity detection in the O/C band of optical fiber communication. InP-based InGaAs material has an absorption coefficient of 1.0×10 cm-2 in the O/C band of optical fiber communication, which can be used as an active photodetector with high absorption efficiency. Therefore, the combination of InGaAs/InP active devices and silicon-based waveguides through heterogeneous integration is a feasible direction to achieve high-efficiency photodetectors based on silicon photonic platforms. The large lattice mismatch and the difference in thermal expansion coefficient make it hard to achieve large-scale integration through epitaxial growth technology. The micro-transfer printing technology in bonding integration technology can achieve integration on the micron scale, thereby enabling low-cost, high-efficiency preparation of heterogeneous integrated devices. In the existing preparation process of this technology, the scheme of separating the device from the substrate by etching the sacrificial layer requires extremely high process accumulation. The purpose of this paper is to realize the direct bonding integration of InGaAs/InP Avalanche Photodetector Device (APD) and Silicon on Insulator (SOI) Grating Coupler (GC) by micro-transfer method while retaining the original substrate of the detector.【Methods】This paper studies the basic principle of micro-transfer printing method and builds a micro-transfer printing experimental platform. The heterogeneous integration of the III-V APD sample and the GC on the SOI wafer is realized by the micro-transfer method. The feasibility of the micro-transfer method is evaluated based on the test results.【Results】The response bandwidth of the heterogeneous integrated photodetector obtained by micro-transfer integration is about 4 GHz, and the dark current is about 13 nA (@-13 V), which is basically consistent with the performance test data before the integration of the sample. Affected by the coupling loss, the responsivity of the integrated structure is 7.3×10-3 A/W (@-25 V). After eliminating the loss of the input fiber-GC, the responsivity of the integrated device is about 1.8×10-2 A/W (@-25 V).【Conclusion】The work of this paper verifies the feasibility of heterogeneous integration of III-V APD and SOI waveguide platforms based on micro-transfer method. By retaining the InP substrate, the micron-scale × micron-scale APD and SOI GC are directly bonded and integrated through the van der Waals force between the InP substrate/silicon-based photonic platform interface. In this way, we simplify the implementation process of the micro-transfer process with improved integration efficiency. It can be verified by experiments that the dark current and bandwidth performance of the devices before and after integration remain basically unchanged.
【Objective】The two functions of Energy Harvesting (EH) and Information Transmission (IT) are mutually restricted in the Simultaneous Lightwave Information and Power Transfer (SLIPT) system. In order to make the SLIPT system work more efficiently, it is necessary to regulate these two functions.【Methods】The article firstly tests the commonly used receiver circuit in SLIPT system to optimize the receiver. The receiver circuit designed in this article consists of three circuits: decoupling, energy harvesting and signal processing. The decoupling circuit consists of three branches, including Energy Harvesting Branch (EHB), Current Regulation Branch (CRB) and Information Transmission Branch (ITB), which is used to separate and regulate the output current of the optoelectronic converter. The EH circuit consists of three parts: boost circuit, energy management circuit and voltage stabilizing circuit, which is used for EH management and output. The signal processing circuit consists of a two-stage low-pass filtered non-inverting amplifier circuit and a threshold comparison circuit, which is used for signal filtering, amplifying and shaping. Finally, the receiving circuit is applied in a SLIPT system that uses Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs) and Photovoltaic cells (PV) as optical/electrical conversion devices, and a microcontroller as the processor. The constraints and control methods between the two functions of EH and IT are summarized.【Results】Experiment results show that the SLIPT system based on the as-designed circuit can be controlled to work in the EH mode, IT mode, or information-energy simultaneous transmission mode. By adjusting the parameters of the receiving circuit, the PV output current distribution can be regulated, thereby controlling the power input to the EHB and the Signal-to-Interference Ratio (SIR) of the ITB. This enables efficient energy harvesting and stable information transmission. The corresponding energy storage power and communication rate can be balanced and regulated by the decoupling circuit.【Conclusion】The receiving circuit can operate without an external power supply and features maximum power point tracking, low power consumption, and adjustable operating modes.
【Objective】Underwater Visible Light Communication (UVLC), as a cutting-edge technology replacing traditional acoustic communication, has garnered widespread attention due to its high data rates, broad bandwidth, low latency, and enhanced security. However, it also faces challenges such as the complexity of underwater channel environments, signal power attenuation, and the imperfections of optoelectronic devices leading to nonlinear effects. The signal degradation caused by these low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and nonlinear effects can make it difficult for the receiving end to correctly identify and demodulate the original signal. However, accurately identifying the signal modulation format lays the foundation for subsequent use of other algorithms, such as nonlinear compensation and frequency offset compensation, to enhance communication performance. Hence, this study aims to address the performance limitations in Modulation Format Recognition (MFR) within UVLC systems, with a special focus on improving recognition accuracy and system robustness in complex underwater environments.【Methods】To address these issues, we propose an innovative MFR algorithm that combines Bidirectional Gated Recurrent Units (BiGRU) with coordinate transformation. This algorithm leverages the advantages of BiGRU in sequential data processing and the efficiency of coordinate transformation to effectively extract the signal features, significantly enhancing the modulation format recognition accuracy in underwater environments.【Results】Experimental results demonstrate that under various transmission voltage conditions, the algorithm achieves recognition accuracy rates exceeding 96% for ten different Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) and Amplitude Phase Shift Keying (APSK) signal modulation formats, including 2QAM, 4QAM, 8QAM, 8APSK, 16QAM, 16APSK, 32QAM, 32APSK, 64QAM and 64APSK. The training speed has doubled, and robustness in low SNR and nonlinear distortion conditions is significantly improved.【Conclusion】The algorithm proposed in this study notably enhances the MFR performance in complex underwater environments for UVLC systems, holding significant application value and technological innovation. It lays the groundwork for the future development of high-speed underwater communication technologies.
【Objective】In order to solve the problem that the traditional Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) algorithm updates the same map, resulting in the inability of parallel planning, a parallel multi-objective optimization submarine cable route planning algorithm is proposed in this paper, which realizes the precise planning of local areas.【Methods】In this paper, the grid map of the target sea area is divided into multiple grid subgraphs by the idea of divide and conquer, and a parallel multi-objective optimization submarine cable route algorithm model is established, and the key parameters of the model are optimized. Then, the Parallel Ant Colony Optimization (PACO) algorithm is used to carry out the submarine cable route planning under the optimal model parameters, and the submarine cable route scheme solved by Pareto frontier is counted.【Results】The simulation results show that the parallel multi-objective optimization model obtains the best search ability and efficiency when the number of blocks is 6 and the size of ant colony is 150. The PACO algorithm can save 33.9% of the cost of submarine cable route compared with the traditional ACO algorithm under the same risk conditions, and the cost of routes is smaller than the traditional ant colony algorithm. The maximum cost of routes is also reduced by 20.6% compared with the minimum cost of the traditional ACO algorithm, and the corresponding risk is reduced by 65.8%.【Conclusion】In multi-objective submarine cable route planning, compared to the traditional ACO algorithm, the PACO algorithm not only achieves better planning results but also improves computational efficiency by at least 8 times.
【Objective】As a potential important optical device, chalcogenide high nonlinear fiber has a wide application prospect in the mid-infrared region. In order to meet the requirements of optical signal processing and transmission in infrared region, a chalcogenide high nonlinear fiber is proposed to improve the efficiency and performance of optical signal processing in the infrared region.【Methods】Using the finite element method as a design and analysis tool, combined with the selection of highly nonlinear materials and the optimization of fiber structure parameters, the fiber design with efficient nonlinear effects in the mid-infrared region is realized. The confinement loss, dispersion and nonlinear coefficient of the highly nonlinear Photonic Crystal Fiber (PCF) with spiral structure of As2Se3 material in the wavelength range of 1~7 μm are analyzed and optimized.【Results】The results show that the confinement loss can be as low as 10-8 orders of magnitude at the wavelength range of no more than 6.25 μm. It has dispersion flattening characteristics at the mid-infrared region range of 2~5 μm. There are multiple zero dispersion points in the range of 1~7 μm, and the nonlinear coefficient can be as high as 248 630 W-1·km-1.【Conclusion】The fiber can realize ultra-wideband low loss dispersion flatness and high nonlinearity in the mid-infrared region, and has potential application prospects in the field of mid-infrared optical communication and optical sensing.
Free-Space Optical (FSO) communication, as an effective transmission technology with high speed, low latency, large bandwidth, and support for rapid link deployment, has been increasingly valued in the field of wireless communication aimed at big data transmission in recent years. However, the communication performance of FSO signal link is susceptible to weather conditions and atmospheric states (especially atmospheric turbulence), resulting in degradation of signal reception and transmission quality as well as system performance. In order to enhance the reception, transmission, and overall performance of FSO communication systems, researchers have begun to apply various advanced machine learning algorithms to optimize the signal detection and channel modeling processes in FSO communication systems. In this article, the research progress of applying typical machine learning algorithms in FSO communication systems in signal detection, channel estimation, auxiliary optical compensation, and other aspects are reviewed. We compare and analyze the application characteristics of different typical machine learning algorithms, and discuss the future development trends of applying machine learning algorithms in FSO communication systems.
The integration of sensing and communication is beneficial of efficiently co-utilizing resources for optical networks. It empowers multi-dimensional sensing and ubiquitous optical communication, which is in line with the future development and evolution of optical network. The integrated optical network with sensing and communication capabilities can fully utilize existing fiber-optic network resources, enhance network quality and operational efficiency, and enable low-cost, high-efficiency, and high-reliability deployment and application of various novel fiber-optic sensing technologies. In this paper, we introduce the key technologies and technical challenges of integrated sensing and communication of optical networks. Then we elaborate and analyze several typical application scenarios. Finally, we discuss the prospective development of integrated sensing and communication of optical networks.
【Objective】This paper aims to address the challenge of predicting performance degradation (frame transmission errors) in Optical Transport Network (OTN). Frame error performance metrics in OTN rely on the detection of Bit Interleaved Parity (BIP) bytes in OTN frame overhead, which are periodically calculated by network management systems. In the vast majority of cases where the OTN network operates normally, the error-related performance values remain zero, which undoubtedly poses a challenge for both traditional methods and the Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies in predicting OTN error-related performance.【Methods】This paper proposes a creative approach to predict error probability by leveraging the correspondence between the optical and electrical layers in OTN. Firstly, deep learning techniques are used to predict the trend of Bit Error Rates (BER) in optical channels. Subsequently, based on the predicted BER in optical channels, the proposed machine learning models are employed to further predict the frame error probability in OTN.【Results】Verified through simulation experiments, the prediction accuracy of this method exceeds 90%.【Conclusion】The proposed solution meets the requirements for engineering applications, providing a new and effective method for predicting performance degradation in OTN networks. It also provides a strong basis for predictive maintenance of OTN networks.
【Objective】In order to effectively improve the transmission rate of Visible Light Communication (VLC) system and reduce the Bit Error Rate (BER) of the communication system, a multilevel Protograph Low-density Parity-check Codes (PLDPC) and iterative decoding design scheme is proposed.【Methods】First, the multilevel PLDPC code and modulation constellation structure in the VLC system based on Color Shift Keying (CSK) are thoroughly investigated, and a multilevel PLDPC-CSK transmission scheme is designed. Secondly, based on the perceived color constraints, the method of transmitting consecutive symbol sequences is introduced, and the CSK mapping scheme that minimizes the number of symbol sequences at the minimum Euclidean distance is proposed. Finally, a multi-level iterative soft decoding scheme is designed based on the multi-level PLDPC-CSK transmission system.【Results】The simulation results show that at the data rates of R=2 and 3 bits/symbol, the multilevel PLDPC-CSK design scheme for symbol sequences proposed in this paper has a performance gain of about 1.8 and 4.5 dB, respectively, compared with the standard and other same-rate CSK constellation structures.【Conclusion】In summary, the BER performance of the design scheme of the paper is significantly better than that of the comparison scheme, which improves the reliability of data transmission and optimizes the system performance of VLC.
After more than 60 years of exponential rapid development, the most advanced process node of integrated circuits has come to 1 nm. In the past decade, the development of integrated circuits has shifted, from planar proportional scaling to three-dimensional equivalent scaling, from performance-driven to power-consumption-driven, from unit integration to system integration, and the industry generally believes that it has entered the post-Moore era. At present, integrated circuits are facing three major technical challenges, which results in great difficulties in reducing size. Not only is process upgrading slowing down, but the cost exceeds 10 billion dollars. Some wafer fabs such as GLOBALFOUNDRIES have given up advancing to more advanced processes, while only a few such as Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), Samsung, Intel, and Imec continue to advance towards More Moore. This article studies the theoretical space for further utilization from the dimensions of integration and energy consumption, and briefly introduces the technology evolution roadmap of International Roadmap for Devices and Systems (IRDS) for the next 15 years. Beyond Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) is committed to finding potential devices and methods that are significantly superior to traditional CMOS through innovation in principles, materials, structures, etc., and this exploration is still in the forefront of academic research. The industry is paying more attention to More than Moore (MtM) technologies such as System-in-Package (SiP), heterogeneous integration, and chiplets. Due to the current difficulties and limitations faced by information hardware technology stemming from the physical properties of electrons, photons are highly anticipated because of its difference from electrons. Now photonics is being generalized from traditional transmission technology to Information Communications Technology (ICT) full-scale connection technology, and gradually entering complex functional domains such as computing, processing, and routing. Photonics-electronics convergence has gradually become an important development direction of information technology. Photonics-electronics convergence is mainly reflected in two dimensions, functional dimension synergy and hardware dimension integration. This article introduces the progress of these two dimensions, and points out that silicon-based heterogeneous integration and hybrid integration are the current focus of the chip-level photonics-electronics convergence, which makes the development of optoelectronics exhibit the remarkable characteristics of "microelectronization". Photonics-electronics convergence is just beginning, and in its exploration process. The article concludes three points. At first, the attention to adaptive changes should be paid at the system architecture level, not just stay at the chip level. Secondly, the convergence still requires innovation in various aspects such as new materials, new devices, new processes, new equipment, and new systems. Thirdly, photonics-electronics convergence cannot be narrowly limited to the current focus on MtM direction, but also should recognize its many possibilities in the direction of Beyond CMOS.
【Objective】In order to improve the accuracy and efficiency of temperature sensing, the application of Microwave Photonic Filter (MPF) based on One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network (1D-CNN) in Radio Frequency (RF) intensity temperature sensing is studied.【Methods】The MPF system based on Mach-Zehnder Interferometer (MZI) structure is built experimentally, and the RF spectral data of 20~70 ℃ under the condition of notch depth of 8.1 dB are collected by changing the ambient temperature. 30 sets of data are collected under each temperature condition. Then the 1D-CNN structure is designed and optimized by greedy strategy to determine the number of network layers, the size of the convolutional kernel, the size of the pooled kernel and the type of activation function. The model is trained with the training set data and validated with the test set data to optimize the model parameters for optimal performance. Its nonlinear mapping capability is used to extract features from RF spectral data to achieve high-precision demodulation of RF intensity and temperature changes. Finally, the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) is used as the evaluation index, and the performance of 1D-CNN is compared with the traditional algorithms (maximum-value method, centroid method and Gaussian fitting method) to analyze its performance under different temperature conditions.【Results】The experimental results show that the RMSE of the prediction model based on 1D-CNN reaches the order of 10-3, while the RMSE of the traditional algorithms is usually in the order of 10-1. Compared with the traditional Gaussian fitting algorithm, the demodulation speed of the 1D-CNN-based algorithm is improved by 2.72 times. 1D-CNN shows high stability and low error under different temperature conditions.【Conclusion】1D-CNN has significant advantages in dealing with complex nonlinear relationships and feature extraction, not only superior in computational efficiency and robustness, but also effective in dealing with noise and environmental interference. The research in this paper provides new ideas and methods for the application of MPF in the field of RF intensity temperature sensing.
【Objective】As video services gradually become the core pillar of broadband networks, Passive Optical Network (PON) technology has rapidly developed, expanding from the traditional field of home broadband access to a wider range of application areas such as government and enterprise, intelligent manufacturing in industry, and telemedicine. Consequently, the requirements for network bandwidth, latency, packet loss rate, and jitter in terms of service quality have become increasingly stringent. In this condition, the next-generation optical access network technology with a speed of 50 Gbit/s has emerged. The 50 Gbit/s PON is not only required to provide an access bandwidth more than four times that of the 10 Gbit/s PON, but also needs to enhance the service support capabilities, network security protection, and ensure compatibility and smooth evolution with the existing 10 Gbit/s PON technology. In the implementation process, the development of optical transmitter components is particularly crucial.【Methods】The 50 Gbit/s Combo PON Optical Line Terminal (OLT), presented in this study, leverages hybrid integrated package technology to address key challenges such as multi-channel wavelength combination, signal splitting, and crosstalk minimizing. Through meticulous optical path simulations and crosstalk analyses, the device successfully achieves a balance between performance and efficiency.【Results】By means of a meticulously designed 4-channel QSFP28 package size module, the functionality of 3 transmitters and 3 receivers within a metal hermetic tube has been realized. At the same time, thanks to advanced optimization design, the crosstalk from the transmitter to the receiver has been significantly reduced, with an improvement of 20 to 30 dB. This important breakthrough not only enhances the performance of the optical components, but also lays a solid foundation for the commercial deployment of 50 Gbit/s PON.【Conclusion】The test results indicate that the wavelength performance of the optical components proposed in the article fully complies with the requirements of the International Telecommunication Union-Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) G.9804.3 international standard. Both the operating eye diagram and sensitivity have reached the expected indicators. This means that the 50 Gbit/s Combo PON OLT optical components are already capable of being applied in actual network environments. Looking to the future, with the continuous progress of technology and the sustained growth of application demands, 50 Gbit/s PON will play an important role in promoting broadband network upgrades, enhancing service support, and improving user experience. It is expected that more innovative achievements will continue to emerge in this field, jointly promoting the prosperous development of optical network technology.