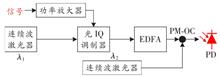
【Objective】E/W band millimeter-wave frequency covers 60~110 GHz, with abundant frequency band resources and potential for high-capacity transmission. Compared with lasers, E/W band millimeter-wave beam is wider, with advantages of directionality, anti-interference and ease of alignment, making it a promising frequency band for long-distance wireless communication at sea. However, the characteristics of near-sea surface channels such as atmospheric absorption and multipath at the sea surface limit the transmission distance of E/W-band millimeter waves, resulting in bottlenecks in E/W-band millimeter wave transmission near-sea surface. This paper focuses on the direction of long-distance millimeter-wave wireless transmission at sea, using microwave photonics technology to propose an ultra-wideband millimeter-wave modulation and demodulation system architecture to improve the millimeter-wave frequency conversion and modulation performance. We then study the optimal high-order modulation format in near-sea surface long-distance transmission systems to achieve high-capacity long-distance transmission.【Methods】The power amplifier in long-distance communication systems can introduce nonlinear distortion to the signal. It analyzes the factors affecting the performance of high-order modulation formats such as Amplitude Phase Shift Keying (APSK) and Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) due to the nonlinear characteristics of solid-state power amplifiers. The optimal distribution, Euclidean distance and inner and outer radius ratio of 16APSK signals have been studied. By the equivalent power experiments, the nonlinear resistance of 16QAM and 16APSK signals are compared and analyzed.【Results】The millimeter-wave long-distance transmission experiment is carried out for performance investigation. It proves that the APSK modulation format is more suitable for long-distance transmission system than QAM format.【Conclusion】Based on the 16APSK modulation format, the performance of 16 Gbit/s, equivalent 34 km long-distance transmission are achieved in the experiment, providing high-value technical means for long-distance high-capacity transmission at sea.
【Objective】To improve the linear fit between the reflected spectral center wavelength and external environmental variables in Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) sensing system, this paper proposes to use particle swarm optimization of Gaussian process regression model to the field of FBG stress sensing.【Methods】For the reflectance spectral characteristics of the FBG, the paper studies the impact of the linear fit in the spectral fitting of FBG sensing system. The particle swarm algorithm is used to search for the optimal hyperparameters in the Gaussian process regression model in order to enhance the predictive performance of the reflectance spectral wavelength of the center. A FBG stress sensing experimental platform was built, and the FBG was laid on the strength beam. Different weights were applied to one end of the equal strength beam to produce axial strain on the FBG, and the reflectance spectral data were collected by the spectrometer and analyzed by linear fitting with the studied model. The results obtained by the unoptimized Gaussian process regression model, the maximum value method, the Gaussian fitting method, and the center of mass method were used as the control group.【Results】The results show that under the conditions of erbium-doped fiber amplifier output power of 10 dBm, transmission fiber distance of 50 m, and the number of sampling points of the spectrometer of 501, the linear fit between the reflected spectral center wavelength and the mass of the weights is better than that of the control group. The linear fit of the studied model can reach up to 0.951 9, which is improved compared with that of the control group. Under the conditions of 501, 251, 167 and 126 spectral sampling points, the studied model can improve the linear fit of the system to 0.990 0, which is a maximum improvement of 0.258 7 compared with the maximum value method.【Conclusion】The analysis results show that the Gaussian process regression model optimized by the particle swarm is able to effectively improve the linear fit of the FBG stress sensing system.
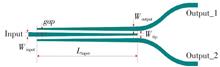
【Objective】In order to solve the problem of the limited bandwidth of polarization insensitive optical power splitter, an ultra-broadband polarization insensitive optical power splitter based on Silicon Nitride (Si3N4) waveguide is proposed.【Methods】The ultra-broadband polarization insensitive optical power splitter is designed based on adiabatic coupling Si3N4 waveguide.Optical bandwidth of 300 nm (from 1 400 ~ 1 700 nm) is demonstrated for both Transverse Electric (TE) and Transverse Magnetic (TM) modes.【Results】Over the entire optical bandwidth, the losses for TE and TM mode are less than 0.10 and 0.15 dB, respectively.The footprint of the proposed ultra-broadband polarization insensitive optical power splitter is only 60.00 μm×2.75 μm, which means that the optical power splitter can be used for large-scale integration.Furthermore, the relationship between the performance and the structure parameters of the proposed optical power splitter is studied.【Conclusions】The results show that the performance of the optical power splitter maintains almost unchanged by varying the structure parameters with ±50 nm.In other words, the optical power splitter possesses large fabrication tolerance which can be easily fabricated.
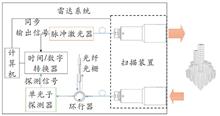
【Objective】Single-photon detection and single-photon ranging systems have widespread applications in three-dimensional imaging and long-distance spatial remote sensing. However, device limitations and background noise from the sun light limit the application to only nighttime conditions.【Methods】We have improved traditional laser radar systems by implementing all-fiber optics systems with ultra-narrowband fiber optic filtering, leading to significantly improved system stability. By implementing mechanical motion control, we are able to attain single-photon imaging systems with ultra-wide scanning and ultra-high resolution. The systems can operate in optical environments that are typically challenging, such as daytime or foggy weather. Moreover, the laser radar system is designed based on the 1 550 nm wavelength which has good atmospheric penetration and low transmission loss, enhancing its ability to work in foggy and rainy conditions.【Results】In a foggy condition with a visibility of about 500 m, the system achieves three-dimensional imaging of objects 1.6 km away, which is a distance 3 times longer than the visibility at the time. The distance resolution can be significantly enhanced by optimizing the intensity and distance information of the histogram using the minimized negative logarithmic likelihood function, with the assistance of a high-resolution time/digital converter and the model constructed by the system response function of the laser radar. Compared to the maximum value method with a distance resolution of 0.05 m, this system achieves a distance resolution of 0.006 m via the minimized negative logarithmic likelihood function method. Additionally, the image normalization processing is performed to suppress fluctuations in photon technology and eliminate noise in the image. The 1 550 nm all-fiber laser radar system has strong mechanical stability and can work in adverse weather conditions.【Conclusion】It has significant application value in remote sensing and mapping, ground and vehicle-mounted laser radar, and other fields.
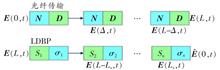
【Objective】In long-distance optical communication systems, compensating fiber nonlinear impairment through traditional Digital Signal Processing (DSP) is difficult due to intractable interactions between Kerr nonlinearity, chromatic dispersion and amplified spontaneous emission noise. Machine learning algorithm can be used to further process signals on the basis of traditional DSP to mitigate fiber nonlinear impairment and improve long-distance transmission performance.【Methods】In this paper, the traditional Digital Back Propagation (DBP) algorithm is combined with Deep Neural Network (DNN), where the linear step size and nonlinear step size in DBP are taken as one neuron. It means that the linear step size is taken as the weight matrix of DNN, the nonlinear step size is taken as the activation function, and DSP is taken as the static layer of DNN. A DNN-based Learned Digital Back Propagation (LDBP) algorithm is proposed.【Results】In order to verify the feasibility of the proposed LDBP algorithm, the simulation was carried out in a single-channel polarization division multiplexing 16-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) optical transmission system. The numerical simulation results demonstrate that the 1-step-per-span LDBP algorithm improves the optimal launched power from -2 dBm to 1 dBm in compared to linear equalization. Meanwhile, compared with DBP with the same computational complexity, the proposed algorithm improves Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) by 0.82 dB at the transmission distance of 1 200 km. In addition, compared with DBP with the same computational complexity and linear equalization, the SNR of the transmission system corresponding to LDBP method decreases more slowly with the increase of transmission distance, and the algorithm can work without knowing the link parameters, showing the characteristic of universality and robustness.【Conclusion】The proposed LDBP algorithm is more suitable for practical long-distance coherent optical communication system than the traditional DBP algorithm.
【Objective】The optical communication system working at the traditional telecommunication band is faced with "capacity crunch" with the rapidly development of optical communication technology. The acceptable loss of 0.2 dB/km (@2 μm) from the hollow-core photonic bandgap fibers as well as the high optical amplification gains (30 dB@2 μm) of thulium-doped fiber amplifiers (CTFA type) provides the potential for the 2 μm wavelength band to alleviate the communication "capacity crunch". As a result, the needs of the 2 μm silicon-based photodetectors is also raised due to its mature and convenient manufacture process. The main solutions of the silicon-based photodetectors include the usage of Ⅲ-Ⅴ compounds with tunable band gap, the introduction of low band gap width materials as absorption regions, the use of new absorption mechanism in optical absorbed material at the 2 μm wavelength band and so on. The Ge material has a high Two Photon Absorption (TPA) coefficient (1 225 GW/cm@2 μm). And the Ge-on-Silicon-On-Insulator (SOI) photodetector is an excellent method to realize 2 μm optical signal detection, which is compatible with the standard silicon photonics device manufacturing process that has the advantages of low production difficulty and cost. The purpose of this paper is to verify the feasibility of the Ge-on-SOI photodetector to achieve 2 μm wavelength band photoelectric detection by using the special optical absorption mechanism of TPA.【Methods】In this paper, the photoelectric detection at the 2 μm wavelength band based on the physical absorption mechanism of current generated from high TPA of Ge material is realized. The quantification of the photocurrent generated by Ge material through TPA effect is analyzed and discussed in this paper. In the experimental test, we first apply a high power 2 μm wavelength band input light source magnified by thulium-doped fiber amplifiers to the input port (grating coupler) of the commercial waveguide-type Ge-on-SOI photodetector in the on-chip active silicon photonics device test system. Then we adjust the alignment of the optical fiber with the grating coupler and the input light polarization to reduce the optical transmission loss from the input optical fiber to the Ge absorption region. Finally, the TPA photocurrent of the on-chip photodetector is obtained by a probe.【Results】A net photogenerated current up to 651 nA and an estimated value of responsivity greater than 10 mA/W is obtained experimentally under a 2 μm wavelength optical input power of 21.9 dBm.【Conclusion】The work of this paper verifies the scientific feasibility of 2 μm waveband photodetector through the TPA effect of Ge material, and provides experimentally support for the design of the 2 μm wavelength band Ge-on-SOI photodetector based on TPA.
【Objective】In this paper, machine learning method is applied to 30 Tbit/s (60 × 500 Gbit/s) Nyquist Dual Polarization-16 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (DP-16QAM) system after 6 300 km transmission in G. 654E optical fiber. Nonlinear channel equalization is used to reduce the transmission Bit Error Rate (BER).【Methods】Referring to the "receptive field" mechanism of convolution neural network, the size of "convolution core" is designed, and the data set is constructed according to the divided sampling data. The artificial neural network is constructed by optimizing the parameters. The one-to-one data corresponding to the transmission and reception of different wavelengths, different optical signal-to-noise ratios, and different fiber input powers in the C-band are collected. Refer to the classic full-connection neural network structure, the neural network is constructed according to the data structure of the data set. The network fitting is carried out for the real part and the imaginary part respectively. After training stage, the test data is sent into the network, and the performances are compared with the traditional methods.【Results】Two kinds of neural networks are used to fit the transmission BER under 60 different wavelength transmission conditions of C band frequency from 191.562 5 to 195.987 5 THz. Compared with Maximum Likelihood Sequence Estimation (MLSE), Network 1 has an average reduction of 23% in BER, and Network 2 has an average reduction of 41% in BER. A frequency of 193.812 5 THz is then selected for the calculation of the fiber input power ranging from 14 to 19 dBm. The average improvement in network 1 and network 2 are 32% and 52%, respectively. Under different optical signal-to-noise ratios, Network 1 has an average improvement of 30%, and Network 2 has an average improvement of 57%.【Conclusion】The two neural networks have excellent performance in nonlinear equalization of coherent transmission systems. At the same time, the number of network layers and nodes will jointly affect the fitting results. Increasing the number of layers and nodes can obtain better fitting results, but the corresponding parameters, training time and the required space will also increase. Therefore, in the application, the actual situation should be considered to choose between the fitting performances and the model attributes.
【Objective】The baseline drift of the Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) spectral signal is usually one of the main problems, caused by the complex external environment. A spectral baseline correction method based on the improved Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) model is proposed in this paper.【Methods】Compared with LSTM model, the improved LSTM model extracts feature information of FBG spectral signal by the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The improved LSTM model is composed of CNN, full connection, and LSTM network. In this paper, the improved LSTM model is trained by artificial datasets and measured datasets. The artificial datasets are made up of feature noise, baseline, and FBG spectroscopy. Five methods including wavelet soft threshold method, penalty least square method, Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), LSTM, and the improved LSTM model are used as baseline correction. Identification signal probability and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) are used to evaluate correction results by the five methods.【Results】The artificial datasets of FBG signal are corrected by the improved LSTM model, and the identification signal probability is increased by 60.8%. The improved LSTM model with training by artificial datasets and measured datasets shows better correction results, compared with training by measured datasets. The mean of the RMSE for FBG spectrum decreases by 10.95%. The standard deviation of RMSE decreases by 4%. The measured datasets of FBG signal are corrected by the improved LSTM model, and the identification signal probability is increased by 50.5%. Compared with wavelet soft threshold method, penalty least square method, RNN and LSTM, the improved LSTM model shows best correction results. The mean values of RMSE and the standard deviation of RMSE are 0.012 2 and 0.002 4, respectively. The RMSE value of the demodulated central wavelength is 0.036 pm. And the baseline correction process takes only 9.68 ms.【Conclusion】The improved LSTM model is an effective method to achieve baseline correction, and has wide range of application prospects in complex external environment.
【Objective】The light source of fiber grating sensing system provides energy for the system. The stable and continuous light source is crucial for the application of the whole demodulation system. When the Modulated Grating Y-branch (MG-Y) laser is used as the light source of the fiber grating demodulation system, it is necessary to solve the problem that it is difficult for the MG-Y laser to quickly obtain the stable and continuous tuning within the required specific wavelength range.【Methods】In order to obtain the stable and continuous wavelengths quickly for MG-Y lasers, the K-Means (KMeans) clustering model is proposed and applied to obtain high-quality current-wavelength Look Up Table (LUT) for MG-Y lasers.【Results】By combining the tuning characteristics of the MG-Y laser with the KMeans clustering model method, the centroid of the optimal tuning parameter curve in the phase tuning region of the LUT can be quickly obtained with time of about 18.26 s. Then, according to the tuning characteristics of the left, right and phase of the MG-Y laser itself, the fine tuning of the MG-Y laser wavelength can be achieved by uniform interpolation method. The LUT with the full tuning range is obtained from the KMeans clustering model, and the target LUT is selected at a certain interval. According to the output wavelength issued by the laser according to the target LUT, the mean value of the measured wavelength and the absolute value of the error of the target wavelength is 0.18 pm. The standard deviation of the absolute value of the error is 0.52 pm. Therefore, the MG-Y laser can be used as a stable light source for the fiber grating sensing system.【Conclusion】It is verified by experiments that the traditional manual search for each phase tuning region needs at least 30 min to find the centroid point. The same operation can be completed by KMeans clustering model method, which can greatly shorten the time to find the centroid point. Based on this method, the stable wavelength of quasi-continuous tuning can be achieved by controlling the MG-Y laser.
【Objective】The symbol decomposition technique aims to decompose Optical Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (O-OFDM) symbols into multiple symbols with a small Peak to Average Power Ratio (PAPR) to mitigate the non-linear effects of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). However, O-OFDM generates more decomposed symbols with a higher PAPR, thereby reducing the information rate and degrading the Bit Error Rate (BER) performance.【Methods】The proposed design of Precoding O-OFDM Adaptive Symbol Decomposition with Serial Transmission (PCO-OFDM-ASDST) system uses precoding scheme to reduce the PAPR of O-OFDM symbols. The proposed method can reduce the average number of symbol decompositions for adaptive symbol decomposition. The theoretical Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) expressions are derived for multipath channels, and the performance of PAPR, BER, and information rate is analyzed using Monte Carlo BER simulations.【Results】The results demonstrate that under 4 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) modulation in Asymmetrically Clipped Optical Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (ACO-OFDM) systems, the symbol power required for PCO-OFDM-ASDST is 7 dB less than that of Adaptive Symbol Decomposition with Serial Transmission (ASDST) when the BER is 10-4. Moreover, under 64QAM, the information rate can be increased by 10 Mbit/s when the symbol power is 20 dBm.【Conclusion】The results indicate that the PCO-OFDM-ASDST outperforms ASDST systems in terms of BER and information transmission rate.
【Objective】In the production test process of 50 Gbit/s Small Form Pluggable (SFP) 56 optical module, the number of instruments and equipment to be matched for the test is large. Therefore, the test instruments are used in isolation, and the test process is complex. These issues make the optical module test longer, and the test efficiency is relatively low. It brings a lot of inconvenience to the test personnel, and can not guarantee the consistency of the test products. The purpose of this paper is to enhance debugging and testing efficiency while alleviating testers' workload.【Methods】Python language and its robust third-party libraries, including the VISA and pyserial libraries, are utilized to develop an automatic testing system for SFP56 optical modules compatible with the Windows operating system.【Results】The system can debug and test the optical module automatically. The test instruments can be used in parallel, reducing the waste of time and resources. According to the test requirements, the optical module can also be tested step by step, which greatly improves the efficiency of the debugging and testing of the optical module in the production line. It can also reduce the requirements of the tester. The verification shows that compared with the traditional optical module test, the test time of each optical module is saved by about 70 s, which greatly improves the test efficiency of the optical module. In the optical module test, the result deviation caused by human operation is avoided, and the product consistency can be guaranteed.【Conclusion】In comparison to Labview-based automatic optical module testing systems, which are currently prevalent in the market, the system designed in this study is more scalable and convenient for upgrades and maintenance. Moreover, it can be expanded to support optical module testing at speeds of 100, 200, 400, and 800 Gbit/s, thus laying a technical foundation for future high-speed optical module testing.
【Objective】In order to solve the problem of cross sensitivity of temperature and strain in Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) sensing, the response characteristics of temperature and strain in each mode of Few Mode Fiber (FMF)-FBG were studied in this paper. A four-mode FBG temperature and strain dual parameter sensor was also proposed.【Methods】The basic mode and a few higher modes can be transmitted simultaneously in the low-mode fiber, taking into account the advantages of low mode dispersion of Single Mode Fiber (SMF) and low nonlinearity of multi-mode fiber, which can be used for sensing multiple physical quantities at the same time. By analyzing the different optical power sensitivity of the LP01 mode in the FMF-FBG at different temperatures, and considering the good linearity of wavelength, temperature and strain under this mode. Thus, the temperature and strain dual parameter sensing of FMF-FBG is realized.【Results】The results show that the sensor can better solve the problem of cross sensitivity of temperature and strain.【Conclusion】Compared with SMF-FBG, the FMF-FBG has several reflection peaks of different modes at the same time, which can not only solve the cross-sensitivity problem of temperature and strain, but also greatly improve the accuracy and stability of sensing, which may have a good application prospect in the field of new type of sensing.
【Objective】In order to solve the problem that it is difficult to make the temperature sensor of the Photonic Crystal Fiber (PCF) with Surface Plasma Resonance (SPR), a D-structure PCF temperature sensor is proposed. The micro-structure and arrangement of the air hole are also designed. The method of coating the polishing surface of the optical fiber with gold layer is used to stimulate the SPR of the optical fiber.【Methods】Ethanol is used as a temperature-sensitive material, and the temperature-sensitive effect is used as the temperature sensing mechanism to achieve the effect of temperature sensing. The finite element analysis method is used to simulate the thickness of the gold layer and the size of the elliptical air hole of the fiber respectively. The coupling characteristics between the core mode and the surface plasma mode are analyzed under different conditions, and the structure of the sensor is optimized.【Results】The temperature characteristics of the sensor are simulated. In the range of -80~80 ℃, the sensitivity of the sensor is 3.4 nm /℃, and the linearity is better than 0.969 63.【Conclusion】The temperature sensor designed in this paper has a wide temperature detection range, satisfactory sensitivity, and linearity, which can be used for real-time temperature monitoring in industrial, agricultural, and medical fields.
【Objective】The use of random mapping and traditional constellations in Optical-Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (O-OFDM) - Index Modulation (IM) system cannot reach the optimal Bit Error Rate (BER) performance. Therefore, a step-by-step optimal signal mapping method is proposed based on the optimal selection of active sub-carriers and the optimal rotation of constellation to improve the BER performance of O-OFDM-IM system.【Methods】At the transmitter side, the method firstly selects the optimal combination of active subcarriers based on the channel state information and the channel norm maximization criterion. Then considering ?=0.5° as the step size, an exhaustive search algorithm is used to obtain the optimal constellation by using the channel state information. Next, the optimal constellation graph obtained by rotation is loaded on the active sub-carrier for signal transmission. At last, the Maximum Likelihood (ML) detection algorithm is used to recover the original signal at the receiver to minimize the system error probability.【Results】The results show that at the condition of BER=10-4 and strong turbulence, the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) is improved by about 1.45 dB when the modulation order is 16 in (4, 2) system. In addition, with the increase of turbulence intensity, the improvement of BER performance is more obvious. For example, when the BER=10-4 the SNR of the (4, 2) system at 8 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) is improved by about 1.35 dB in strong turbulence and 1.2 dB in weak turbulence.【Conclusion】Based on the known channel state information, a step-by-step optimal signal mapping method for O-OFDM-IM is proposed in this paper, which can effectively improve the BER performance of the system in strong turbulence channels.
【Objective】There is a problem that traditional unrepeatered transmission system need to use disturbed Raman amplifier and remote optical pump amplifier, while both of these two amplifiers need to use high power pump laser which will increase the complexity of fiber link in unrepeatered transmission system. In this paper, we propose a new structure of unrepeatered transmission system using Erbium Doped Optical Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) to replace the forward disturbed Raman amplifier.【Methods】We analyze and compare the performance of the proposed unrepeatered transmission system, and realize a real-time unrepeatered transmission experiment with the proposed structure.【Results】The results show that the gain effect of forward Raman pump in traditional unrepeatered communication system can be achieved by using high power amplifier to increase the signal launch power, and the new structure of unrepeatered transmission system is more suitable to achieve higher bitrate with the help of Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology. We confirm the unrepeatered transmission system can achieve 500 km span distance at 10 Gbit/s bit rate in single channel communication transmission, and 500 km span distance at 4×10 Gbit/s bit rate in the WDM technology.【Conclusion】The proposed unrepeatered transmission system can simplify the traditional unrepeatered transmission system, and increase the bit rate by using multi-channel WDM system with EDFA. It has important practical significance to simplify the structure and improve the bit rate in future unrepeatered transmission system.
【Objective】With the continuous emergence of information-based bandwidth-consuming services such as 5th Generation Mobile Communication Technology (5G), the Internet of Things, and cloud computing, people’s demand for high-speed information transmission has increased dramatically. However, due to the inherent nonlinear effects, the transmission capacity of single-mode optical fiber has approached the Shannon limit, and it will no longer be able to meet people’s needs for ultra-high-speed and large-capacity transmission. Solving the transmission capacity problem has become a top priority. In order to solve the needs of large-capacity communication systems and long-distance high-speed transmission problems, we have built a two-mode single-channel C-band Few Mode Fiber (FMF) transmission system.【Methods】At the transmitting end, an arbitrary waveform generator is used to convert the digital signal into an electrical signal and drive the In-phase and Quadrature (IQ) modulator to modulate the optical carrier. The modulated signal is transmitted simultaneously using two multiplexing technologies: Mode Division Multiplexing (MDM) and Polarization Division Multiplexing (PDM). In order to achieve long-distance transmission of dual-mode signals of 1 000 km, we construct a dual-circulation loop system. Each time the signal passes through the loop, it will pass through a 50 km FMF. After being transmitted to the target distance, the coupler outputs the signal to the demultiplexing module, and the coherent optical receiver performs homodyne detection on the demultiplexed modulated signal. Finally, the transmitted signal is stored in an oscilloscope for offline Digital Signal Processing (DSP). The signal is sequentially subjected to frequency domain dispersion compensation, downsampling, clock recovery, and least mean square algorithm to restore the original signal.【Results】It was found that within the range of Optical Signal-to-Noise Ratio (OSNR) of each channel in the experiment, the Bit Error Rate (BER) under low Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) is close to the theoretical channel result. Under high SNR condition, the BER is 1×10-2, which is 2.5 dB away from the theoretical value. We test the BER of LP11a and LP11b modes at Back-To-Back (BTB) and 250, 500, 750 and 1 000 km transmission cases respectively. The BER at all distances are lower than the Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) soft decision threshold with 28% redundancy (5.2×10-2 Soft Decision - Forward Error Correction (SD-FEC)). The BER after 1 000 km transmission in the two modes are 1.7×10-2 and 1.8×10-2 respectively, and the total net transmission rate is 400 Gbit/s.【Conclusion】This article demonstrates the transmission of a 32 Gbaud MDM-PDM-16 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) C-band signal in a 1 000 km two-mode single-channel FMF system. At the receiving end, the advanced Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO)-DSP algorithm is used for channel equalization, and the obtained two-mode BER of 1.7×10-2 and 1.8×10-2 are both lower than the LDPC SD-FEC threshold with 28% redundancy. The result reachs a domestic record of 400 Gbit/s net transmission rate based on FMF transmission, and highlight the potential of FMF in large-capacity long-distance transmission.
【Objective】Aiming at the limited transmission distance of ultra-long distance optical transmission system using remote pump technology, this paper proposes a single span repeaterless transmission system with mixed transmission of 100 and 200 Gbit/s service. The experiment tests the maximum span loss of the system by adjusting the input power of the system and the position of the remote pump gain unit in the system without considering the influence of other factors such as dispersion.【Methods】The key amplification technologies in the experiment mainly include remote pump amplification technology, Erbium-doped optical fiber amplification technology and Raman amplification technology. In the transmission, Erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, Raman amplifier and remote pump gain unit are used to carry out non-relay amplification of optical signals in the system, and the relay transmission distance is further improved by adjusting the position of remote pump gain unit. The remote pump bypass access method which can improve the amplification gain of remote pump is used in the experiment.【Results】Three different modules were used in the experiment, with a total of 9 service waves. The modulation formats of 200 Gbit/s Polarization Multiplexed - Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (PM-QPSK), 100 Gbit/s PM-QPSK and 200 Gbit/s Polarization Multiplexed -16 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (PM-16QAM) were used respectively. The transmission experiments were constructed by G. 654b ultra-low loss optical fiber with a loss of 0.17 dB/km. Finally, the single-span ultra-long distance transmission with a total capacity of 1.5 Tbit/s and a cross-segment loss of 75 dB is realized.【Conclusion】The results show that the transmission distance of the system can be improved by setting the optimal fiber input power and adjusting the position of the gain unit of the remote pump. The experimental results provide reference value for the construction of the ultra-long distance optical transmission system based on the remote pump technology, and provide reference data for the development of the repeaterless transmission based on the remote pump technology.
【Objective】Light Emitting Diode (LED) is an important nonlinear optical signal generating device in Visible Light Communication (VLC) systems. The static nonlinearity of LED and the dynamic nonlinear memory effect caused by frequency response can lead to signal distortion and degrade the system performance.【Methods】The nonlinearity of LED can usually be compensated by estimating a pre-distortion model, and the wireless VLC is usually intensity modulated/directly detected.【Results】Therefore, the LED nonlinearity modeling is investigated, and an adaptive pre-distortion device based on Amplitude Factorization Polynomial (AFP) is proposed to compensate LED nonlinearity in this paper. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme exhibits good Bit Error Rate (BER), Amplitude Modulation/Amplitude Modulation (AM/AM) correction and constellation diagram performance with higher modeling accuracy.【Conclusion】The normalized mean square error performance improvement of more than 15 dB compared with the traditional memory polynomial is achieved.
【Objective】It is always difficult to timely locate the location of the network attack and achieve rapid deployment of defense strategies when the smart grid is attacked by the network.【Methods】In order to solve this problem, this article proposes a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model that integrates Convolutional Block Attention Modules (CBAM) (CNN-CBAM) to detect False Data Injection Attack (FDIA) positions. The attack identification problem of FDIA is modeled as a multi label classification problem, where CNN is used to extract spatial features of the data. The CBAM module can be directly integrated into the convolution operation of the CNN module, which not only focuses on important parameter information from the perspective of spatial domain, but also considers feature relationships in the channel domain, and allocates attention to the input data from two dimensions to improve the performance of the model.【Results】The performance of the proposed CNN-CBAM network FDIA position detection model is verified on Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 14 and IEEE118 node systems. The experimental results show that the FDIA position detection rates of CNN-CBAM on IEEE14 and IEEE118 node systems are 98.25%and 96.72%, respectively.【Conclusion】Compared with other methods, the CNN-CBAM network model proposed in this paper can effectively extract the spatiotemporal characteristics between data, with improved existence of FDIA. It also im-proves the accuracy of attack location identification with better robustness.
【Objective】Replenishing the power supply system of an underwater communication system is usually very expensive and impractical. The underwater Simultaneous Light-wave Information and Power Transmission (SLIPT) communication systems based on solar cells are powerful solutions. However, the communication bandwidth of the silicon solar cell receiver is very limited, and it is easy to have the phenomenon of deep fading of the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) due to the underwater light attenuation effect.【Methods】For these problems, this manuscript employs a negative-biased solar cell light receiver scheme that increases the-3 dB bandwidth of silicon solar cells from 420 kHz to 768 kHz. Aiming at the deep fading of SNR caused by various degradation effects in the water environment, a Discrete Fourier Transfor (DFT) extended Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) modulation scheme with a low peak-average power ratio is adopted to offset the deep fading phenomenon in the system.【Results】The performance of DFT Spread OFDM (DFT-S-OFDM) and OFDM modulation systems in water environments with different turbidity (absorption and scattering characteristics) is compared. It is shown that the DFT-S-OFDM modulation and demodulation system is more robust.【Conclusion】Finally, experiments have shown that the total battery power efficiency of the energy harvesting system can be increased by 1.87 times under continuous illumination of white LEDs for 3 h, realizing synchronized energy harvesting in the communication process.
【Objective】Traditional Free Space Optical (FSO) communication requires both ends of the communication to be installed at the same time, including the laser transmitting system, laser receiving system and acquisition, tracking and aiming system. It results in the problems of weight, volume, power consumption, and equipment complexity, thus limiting the development of FSO communication. Using the passive modulation technology constructed by asymmetric space laser communication link, the design of small volume, light weight and low power consumption of the communication terminal is successfully realized, which provides convenience for the application of small and medium-sized space laser communication technology.【Methods】In this paper, the research status of passive modulation at home and abroad is reviewed, which is mainly summarized abroad. In addition, the composition of the reverse modulation system and the working principle of the reverse modulator are described. Common Modulated Retro-Reflector (MRR) such as angle reflector reverse modulator and cat’s eye reverse modulator are analyzed. The selection of wavelength and the size of optical receiver aperture are discussed.【Results】This paper summarizes the different implementation types and characteristics of passive modulation, summarizes the application of passive modulation in FSO communication, and looks forward to the future development direction and prospect of this technology.【Conclusion】In the future, passive modulation can be developed along the direction of high speed, focal plane pixelation, two-way communication, coherent detection, and there is a lot of room for development. This paper can provide a reference direction for the research of passive modulation and a new idea for the research of FSO communication.
【Objective】The objective of this study is to investigate the resource allocation problem in Optical Wireless Communication (OWC) systems using Rate Splitting Multiple Access (RSMA) technique. We propose a joint precoding matrix and rate allocation algorithm based on linear approximation to enhance the system reliability and performance.【Methods】We employ variable transformation and linear approximation techniques to convert the non-convex fractional functions into convex ones. By using the joint precoding matrix and rate allocation algorithm, system resources can be effectively allocated to improve system performance. The optimization problem is solved using a continuous iterative algorithm to obtain the optimal solution.【Results】Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed joint optimization scheme significantly reduces the system outage probability and exhibits a fast convergence rate. This indicates that the proposed method can provide more reliable and efficient communication performance in the RSMA-OWC system, which is based on rate splitting access.【Conclusion】This study provides an effective resource allocation method for RSMA technology in OWC systems, enhancing system reliability and performance. Further research should focus on the challenge of system outage probability in RSMA-OWC systems, as well as resource allocation, precoding design, and application scalability. This study offers valuable insights to promote the application and development of RSMA technology in the field of OWC.
【Objective】This paper discusses full lifecycle energy efficiency of optical communication systems in the purpose of energy conservation and carbon reduction. It aims to establish a universal model for description of energy efficiency, which covers all stages of system lifecycle, and it is not limited to specific technologies or network structures. It also analyzes the key influencing factors for improvement of energy efficiency of optical communication systems.【Methods】This paper explores the useful work and energy consumption of optical communication systems, to establish a universal model for energy efficiency. In the expression of useful work, in addition to the commonly used factor data rate, distance factor is introduced as an important factor. The paper recommends that the value generated by data transmissions which meet specific quality requirements and maintaining network connectivity in specific scenario applications should be considered in the description of the useful efficacy. The description method is named as comprehensive useful efficacy. In the discussion of energy consumption, the system lifecycle is decomposed into four stages: manufacturing, installation and construction, operation and maintenance, and waste recycling. Main influencing factors of energy efficiency improvement are discussed based on the established model.【Results】Main results of the research include: (1) Distance factor can be one of the main factors for evaluating the useful work of a system, and distance factors affect energy consumption at various stages of the system's lifecycle; (2) For new scenarios and applications, setting weights for data transmissions which meet specific quality requirements and assigning values for maintaining connectivities status in description of the system useful work could reflect the value brought by the energy cost of the system to meet the needs of scenario applications; (3) Energy consumption factors of each stage of the life cycle should be considered in evaluation of energy consumption of the full lifecycle, and the energy consumption of each stage should be converted into unit time based on the system operating life for accumulation; (4) Optimized network topology and routing design, reduction of line losses, as well as evolution of optical transmission technology and equipment/facility energy saving technologies, are important means to reduce energy consumptions throughout the entire lifecycle of the system and improve the energy efficiency.【Conclusion】This paper discusses the comprehensive useful work and full life cycle energy consumption of optical communication systems, and establishes a universal model to describe the full life cycle energy efficiency of the system. This model takes distance as an important influencing factor in the expression of the useful efficiency and also energy consumption of the system, which corresponds the value of the optical communication system based on communication distance with the energy consumption in the life-cycle caused by distances. It also suggests considering the value generated by data transmissions which meet specific quality requirements and maintaining network connectivity in the evaluation of the useful efficiency. This model could comprehensively evaluate the energy efficiency of optical communication systems, for improvements of system energy efficiency, and could adapt and promote applications of optical communication systems in new scenarios.
【Objective】The non-linear characteristics of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) contribute to the degradation of Bit Error Rate (BER) performance in Visible Light Communication (VLC) systems, particularly in Optical Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (O-OFDM) systems with high Peak-to-Average Power Ratio (PAPR). A single-stage equalizer based on the Volterra series can handle the high-order non-linear distortions of LEDs with low latency. However, solving the traditional Volterra series necessitates multiple integration operations, resulting in the high implementation complexity of the Volterra-based equalizer. Additionally, the single-stage equalizer accumulates errors with limited performance improvements.【Methods】Firstly, to address the issue of high computational complexity in the traditional calculations of the Volterra series, a proposition is made to retain only the high-order power series terms of the various nonlinear terms and kernel coefficients within the Volterra series. This approach, known as the Memory Polynomial-based Volterra Series (MPVS), not only reduces the computational complexity compared to the traditional Volterra series but also enhances the accuracy of nonlinear system modeling by considering all input signals at the current moment. Subsequently, the design of channel equalizer considers the Memory Polynomial-based Volterra (MPV) equalizer and the Memory Polynomial-based Volterra Decision Feedback Equalizer (MPV-DFE). For a single-stage MPV-DFE, if an error occurs in the decision part leading to an incorrect symbol decoding, this error tends to manifest as a consecutive series of errors, thereby impacting the entire symbol sequence. To mitigate this, a proposal is made to cascade the two non-linear equalizers, MPV and MPV-DFE, forming a hybrid equalizer called MPV+MPV-DFE. The MPV equalizer performs a primary equalization on the LED's nonlinear distortion signal, effectively suppressing a portion of the non-linear distortions and thereby reducing symbol decoding errors in the MPV-DFE. Subsequently, a secondary equalization is carried out by the MPV-DFE, leading to improved suppression of residual nonlinear distortions.【Results】Finally, the effectiveness of the system design was validated using Monte Carlo simulation to analyze the BER. The results demonstrate that compared to the single-stage MPV equalizer and the linear-cascade nonlinear hybrid equalizer (LMS+MPV-DFE), the proposed hybrid equalizer achieves approximately 7 dB and 2 dB Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) gains, respectively, in a 4 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) -modulated Asymmetrically Clipped Optical OFDM (ACO-OFDM) system at a BER of 10-4.【Conclusion】In conclusion, the implementation of the MPV equalizer is straightforward, and the cascaded design of the two-stage nonlinear equalizers as a hybrid equalizer enables better mitigation of the LED’s nonlinearity.
【Objective】With the development of the sixth generation mobile communication technology, the inter-carrier interference in the traditional Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system makes the channel estimation performance insufficient to provide highly reliable communication, and Orthogonal Time-Frequency Space (OTFS) system can effectively solve the problem of communication system reliability degradation caused by fast time variability and Doppler effect, which has received wide attention in recent years.【Methods】In order to effectively meet the channel estimation performance requirements of OTFS systems, this paper uses an Optimized Generalized Complex Exponential (OGCE) Basis Expansion Model (BEM) to calculate the channel impulse response as a time-invariant basis function with basis function coefficients, which can effectively fit fast time-varying channels in high-speed mobile communication scenarios. The OGCE-BEM improves the spectral leakage by more intensive sampling and reduces the error of the high-frequency basis model by adding correction coefficients to reduce the error of the HF-based model.【Results】The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm is suitable for high-speed mobile communication scenarios with more reasonable design of the basis function. The estimation method has lower mean square error than the fixed forgetting factor, and the channel estimation results are more accurate. Compared with Least Square (LS), BEM-LS and BEM-Linear Minimum Mean Square Error (LMMSE) channel estimation methods, the performance of mean square error is significantly improved.【Conclusion】It can be seen that the channel estimation algorithm based on OGCE-BEM can effectively reduce the number of unknown parameters to be estimated and improve the accuracy of channel estimation.
【Objective】Aiming at the problems of low spectral efficiency and limited system throughput in Optical Quadrature Spatial Modulation (OQSM), a Signed Optical Quadrature Spatial Modulation (SOQSM) scheme is proposed in Free Space Optical Communication (FSOC) in this paper. In addition, in view of the fact that the channel used in the performance analysis of OQSM is not suitable for all turbulence, this paper also adopts the Málaga channel, which is suitable for all turbulence intensities to analyze the bit error performance of the system.【Methods】First, the scheme divides the input binary bit stream into five parts at the sending end. The first part is used for constellation symbol mapping, and the last four parts are used for laser mapping. Then, the constellation symbol mapping is used to transmit the real and imaginary parts of the constellation symbol and its inverse symbol. The laser mapping is divided into two parts, the in-phase phase and the quadrature phase, which are used to activate the laser sequence mapping. Finally, after transmitting through the channel, the signal received and processed at the receiving end.【Results】Compared with OQSM, SOQSM carries an additional2log2Nt bits of information in the space domain within a transmission period. The upper bound of the average bit error rate is then calculated in the symbol domain and the space domain respectively. Finally, the upper bound of the average bit error rate of the SOQSM scheme is obtained, and the method of calculating the upper bound of the average bit error rate has good convergence. This solution greatly improves the spectral efficiency and transmission rate of the system, and has good bit error rate performance.【Conclusion】The Monte Carlo simulation results show that compared with Optical Spatial Modulation (OSM) and OQSM, the bit error performance of the SOQSM scheme is better when the spectral efficiency is the same. The bit error rate can reach 10-6 when the signal-to-noise ratio is 16dB. When the modulation order is the same, the bit error performance of SOQSM is better, especially when the signal-to-noise ratio is high. It is also shown that the simulation and theory fit well. In the Málaga channel, the bit error rate performance of the weak turbulence is better. In addition, different turbulence intensities have little influence on the trend of the bit error rate performance of the SOQSM scheme. However, with the increase of the signal-to-noise ratio, the influence will gradually increase. Therefore, SOQSM has better bit error rate performance than OQSM and OSM.
【Objective】Undersea optical cable plays a leading role in international communication. In the planning of undersea optical cable communication system, several groups of possible schemes are often determined according to experience. The scheme with relatively better transmission performance and investment cost is then selected. However, with the development of communication equipment and communication technology, the number of optional modulation formats and optical fibers keeps are increasing. The number of alternative schemes is too large to quickly determine the optimal scheme. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a cost optimization model of undersea optical cable communication system to solve the cost optimal scheme.【Methods】Aiming at the problem of system planning and configuration in the undersea optical cable communication system, a cost optimization model considering the parameters of transmission performance, transmission capacity and supply voltage is established by taking the span length, optical fiber type, number of optical fiber pairs, repeater output power, modulation format and number of practical channels as the variables. The cascaded-lexicographic method is used to solve the cost optimization model.【Results】The results show that the difference between the planning results of the proposed optimization algorithm and full traversal algorithm are no more than 0.34%. However, the number of operations of the optimization algorithm proposed in this paper is far less than that of the full traversal algorithm, with only 1/100 of that of the full traversal algorithm. Secondly, the number of operations of the cascade genelexicography method is less affected by the range of variables than that of the total traversal method. Finally, by comparing the optimal cost of the undersea cable communication system under different span length, it is found that the planning results have no regularity.【Conclusion】The variables always influence each other. The optimal cost design of the system cannot be obtained according to experience, so it needs to establish a model. The algorithm used in this paper is not only accurate, but also uses fewer operation times.
【Objective】When analyzing the nonlinear mutation frequency interference problem in all optical communication networks, interference detection mainly relies on estimating channel covariance directly, without expanding network communication signal transformation processing, resulting in low F1-score values of the detection results. Therefore, a nonlinear abrupt frequency interference detection algorithm based on finite difference time domain is proposed for all-optical communication networks.【Methods】We collect all optical communication network traffic data by combining packet capturing and mirroring methods, followed by cleaning, conversion, and protocol processing. Relying on the working principle of finite difference time-domain method, we first describe the time width and bandwidth of the signal in time-domain and frequency-domain space. Then we apply derivative and Fourier transform algorithm to transform the real-time collected network communication signal. Next, we use the transformed signal to analyze the nonlinear abrupt frequency interference. Finally the transformed signal is detected and analyzed. With the aid of the time-frequency joint feature analysis method, the time-domain and frequency-domain features of the interference signal are extracted. Relying on the back propagation algorithm and the minimization of the loss function, the detection process of nonlinear abrupt frequency interference is simplified. The characteristic distance function is used to replace the network loss function, and it is input into the interference recognition model based on the twin network to obtain the detection results of nonlinear abrupt frequency interference.【Results】The experimental results show that under different noise conditions, the F1-score value of the proposed algorithm's nonlinear mutation frequency interference detection results remains above 0.95. The detection time is less than 40 ms.【Conclusion】The new detection method using the finite difference time-domain method can more accurately reflect the interference situation of the current communication network. It ensures the normal operation of the communication network, and meets the interference detection requirements of all-optical communication network.
【Objective】In Free Space Optical (FSO) communication, atmospheric turbulence can cause a decrease in communication link performance.【Methods】In this paper, a polar coding channel coding scheme is proposed for this problem, and Monte Carlo algorithm is used to construct polar codes for Gamma-Gamma distribution atmospheric turbulence channels commonly used in FSO communication. By comparing the Block Error Rates (BER) of the proposed polar coding scheme, uncoded transmission, and Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes with similar code lengths under Gamma-Gamma distribution atmospheric turbulence channels.【Results】The simulation results show that when the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) is greater than 6.7 dB in weak turbulence, 10.3 dB in moderate turbulence, and 11.5 dB in strong turbulence, the proposed polar coding scheme performs better than uncoded transmission. Compared with LDPC codes, under weak turbulence conditions, when the SNR is greater than 7.1 dB, the overall performance of the proposed polar coding scheme is better than that of LDPC codes. Under moderate turbulence conditions, when the SNR is greater than 10.6 dB, the overall performance of the proposed polar coding scheme is better than that of LDPC codes. Under strong turbulence conditions, when the SNR is greater than 12 dB, the overall performance of the proposed polar coding scheme is better than that of LDPC codes. In addition, it is found that when the code length is short, the code rate is low, and the decoding width is small, the proposed polar coding scheme has better performance.【Conclusion】The use of the proposed polar coding scheme effectively improves the atmospheric turbulence effect in FSO communication systems. Moreover, in the harsh atmospheric turbulence channel environment of moderate and high turbulence intensities, the proposed polar coding scheme exhibits more obvious advantages than LDPC codes. This indicates that polar codes have good development prospects in FSO communication.
【Objective】In Space Division Multiplexing (SDM) system, in order to achieve mode demultiplexing, it is necessary to adopt Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) equalization scheme at the receiving end. As the number of transmission modes or transmission capacity increases, the computational complexity of MIMO increases significantly, resulting in high power consumption. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the computational complexity of MIMO equalization.【Methods】We propose a frequency-domain joint equalization technique based on Cyclic Prefix (CP) to reduce the complexity compared with a traditional frequency-domain independent equalization and a separate dispersion compensation module in few-mode fiber short-range transmission systems.【Results】Based on the few-mode fiber model in VPI simulation platform, we build a 6×6 few-mode fiber transmission system to verify the advantage of computational complexity reduction of the proposed technology. The simulation results show that, the performance and computational complexity reduction of different CP ratios are also different. Under the same simulation conditions, when the proportion of CP is larger, the reduction of computational complexity is also larger, vice versa. With the same performance, the computational complexity of the frequency-domain equalization scheme with CP accounting for 11.11%is only 15.29%of that of the traditional frequency-domain equalization scheme based on block convolution.【Conclusion】Compared with the traditional frequency-domain equalization combined with a separate dispersion compensation module, the proposed frequency-domain equalization with CP has lower computational complexity.
【Objective】In the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite Internet of Things (IoT) scenario, the time delay and power consumption requirements of Narrowband (NB) -IoT terminal in wide coverage area vary due to different business scenarios. However, the ground NB-IoT terminal with a single business scenario adopts a fixed working state timer parameter configuration method, which cannot meet the needs of time delay and power consumption for multi-scenario terminals in large geographical areas of LEO satellite IoT.【Methods】In response to the wide coverage characteristics of LEO satellite IoT, the problem of different delay and power consumption requirements for terminal multi-scenario application services in LEO satellite IoT scenarios, this article proposes a method based on a simplified interaction process and Markov chain model for terminal work state switching. The method uses system downlink delay and terminal power consumption as Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithms-Ⅱobjective functions to obtain a set of Pareto optimal solutions for multiple scenario frontiers. Furthermore, it selects working state timer parameters from the Pareto frontier to configure terminals online that meet different scenario delay and power consumption requirements.【Results】The simulation results show that the multi-objective optimization method proposed in this paper can globally optimize the timing parameters of the working state timer, and overcome the shortcomings of traditional methods such as exhaustive search falling into local optima. Additionally, it has been verified that simplifying the random access interaction process can effectively reduce terminal delay and power consumption.【Conclusion】The multi-objective optimization method proposed in this paper can obtain the working state timer parameters of the terminal in various scenarios of LEO satellite IoT.
In recent years, high quality factor echo wall mode optical microcavities have developed rapidly and become a hot research topic in the fields of optics and physics. Optical microcavity is a kind of micro optical element. Due to its small size and high-quality factor, it can enhance the interaction between light and matter, enabling long-time light stays. Echo wall mode resonators are one of the typical representatives of optical microcavities, with advantages of small size, high sensitivity, and long life. Currently, applications based on echo wall mode resonators are mainly concentrated in various fields such as sensors, lasers, filters, and so on. However, current research on echo wall mode resonators has not yet achieved large-scale production, and is only in the laboratory research stage. Industrial production still has shortcomings such as high cost and manufacturing process difficulties. This article focuses on the research progress of echo wall mode resonators, expounds the impact of echo wall materials on Q values, and discusses the applications of echo wall mode resonators in the fields of sensors, lasers, and filters in recent years. It also proposes the challenges and further research directions of echo wall mode resonators in the future, which may realize all-optical networks. For further research directions, we believe that it is necessary to reduce costs, shorten time, and improve the accuracy and efficiency of the preparation process. It is also necessary to solve the coupling problem between the microcavity and the optical device, improving the coupling efficiency and the anti-interference ability. It should also address the sensitivity of the cavity to the environment to ensure that the microcavity has good stability when preparing devices such as filters.
【Objective】With the continuous development of satellite technology, the application of satellites to low coverage areas of ground information networks for personnel search and rescue is becoming increasingly popular. As an effective means of indicating the location of personnel and facilities, satellite search and rescue positioning technology is widely used in maritime, aviation, and personal distress rescue operations. Therefore, in the continuous development and research of global satellite search and res-cue systems, achieving high-precision and rapid positioning of search and rescue sources is the main goal.【Methods】In view of the sudden characteristics of satellite search and rescue signals, dual-satellite Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) and Frequency Difference of Arrival (FDOA) positioning are adopted as the satellite search and rescue positioning methods. The estimation of the required TDOA and FDOA parameters is the key to improve the positioning accuracy. In order to improve the parameter estimation performance and positioning accuracy of dual-satellite TDOA and FDOA positioning technology, this paper proposes a search and rescue positioning technology scheme based on time-frequency difference estimation of windowed Cross Ambiguity Function (CAF). The method of filtering redundant noise by adding windows in time domain is introduced, and the accuracy of time-frequency difference estimation is improved by adding windows in time domain and CAF. The estimated value is substituted into dual-satellite TDOA and FDOA positioning equations to calculate the location of the search and rescue signal source. It means that the purpose of improving the positioning accuracy is to efficiently and accurately find the search/rescue source by improving the estimation accuracy of TDOA/FDOA parameters.【Results】The simulation results show that the method of estimating the TDOA/FDOA parameters of CAF with windows can be applied to search and rescue positioning, and the accurate time-frequency difference estimation value can be obtained through this method. The method proposed in this paper can effectively improve the accuracy of time-frequency difference parameter estimation, and add Fourier transform to reduce the time of parameter estimation, thus optimizing the positioning performance. When the TDOA error is controlled within 4 μs and the FDOA error is controlled within 0.2 Hz, the positioning accuracy can reach the kilometers.【Conclusion】The time-domain windowed time-frequency difference parameter estimation scheme proposed in this paper has improved the positioning performance after being incorporated into the satellite search and rescue positioning technology, which can support the application of the satellite search and rescue positioning technology in the satellite search and rescue system. The algorithm has the advantages of simple structure, low complexity and practical feasibility.
【Objective】With the development of the space-ground integrated information network, the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite communication system is ushering in a development boom. The Paired Carrier Multiple Access (PCMA) technology is gradually developing to the low-orbit satellite communication due to its advantages of saving bandwidth resources. However, traditional PCMA technology is mostly used in high-orbit satellites, and cannot adapt to the highly dynamic fading channel character-istics of low-orbit satellite channels, which greatly degrades the bit error performance of the PCMA receiver. The bottleneck lies in the channel estimation and equalization technologies for overlapping signals.【Methods】Aiming at the channel characteristics of LEO satellites, this paper proposes a channel estimation scheme that combines training sequence estimation and Autoregressive (AR) model prediction. Based on the idea of superimposed training sequence channel estimation, an iterative method suitable for PCMA mixed signal channel estimation is introduced to improve the accuracy of training sequence channel estimation through iteration. The AR model is used to predict the Channel State Information (CSI) of the data sequence in real time. The use of AR model can also reduce the frequency of channel estimation in training sequences, so as to adapt to the dynamics of LEO satellite channels.【Results】The simulation results show that the idea of superimposed training sequence channel estimation can be applied to the PCMA signals, and accurate channel estimation can be obtained after iterations. The method proposed in this paper can effectively improve the accuracy of channel estimation. After signal separation and demodulation, the bit error rate can reach the order of 10-3when the signal-to-noise ratio is greater than 9 dB.【Conclusion】A channel estimation method for PCMA signal is proposed in this paper. The simulation results show that the bit error rate loss is within an acceptable range, which can support the application of PCMA technology in low-orbit satellite communication. The proposed algorithm has the advantages of simple structure, low complexity, and high practical value.
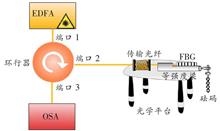
Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) pressure sensor has the advantages of underwater passive, corrosion resistance, light weight, low cost and anti-electromagnetic interference, which has been widely used. This paper first briefly introduces the basic principle of FBG pressure sensing. It then summarizes the development status of FBG writing technology, pressure sensing and sensitizing technology, and temperature compensation technology. Next, it summarizes the application progress of FBG pressure sensor in the fields of ocean depth, lake level measurement, oil and gas pipeline pressure measurement, and rock and soil pressure monitoring in recent years. Finally, the FBG pressure sensing technology is prospected.
【Objective】With the continuous advancements in satellite and communication technologies, the integration of space laser communication and ranging technology becomes more mature. As deep space exploration, satellite navigation, and other fields continue to develop, there is a growing demand for higher communication capacity and ranging accuracy between satellites. Thus, the need to achieve laser satellite high-speed communication while completing ranging and further improving ranging accuracy, under the premise of considering satellite payload and power consumption, has become an urgent issue.【Methods】This article designs and implements a coherent communication and ranging integrated system that supports both QPSK and BPSK, based on the principle of dual one way ranging. To further improve the ranging performance, the differential time sampling method is used to obtain the frequency difference and phase difference between the sending clock and the receiving clock through frequency and phase discrimination, thereby achieving higher clock accuracy and correcting the ranging value.【Results】The system can operate stably in an environment where the received optical power is greater than-48 dBm. Different rates can be set for different application requirements, with a maximum rate of 5 Gbit/s in QPSK mode and rates of 2.5 Gbit/s, 1.25 Gbit/s, and 625 Mbit/s in BPSK mode. The theoretical ranging accuracy of the system can reach a minimum of 53 ps. In normal communication, using Matlab and Vivado to calculate and process ranging data, the ranging accuracy of the system is verified to be less than 0.1 ns. Furthermore, using the differential time sampling method under simulation conditions, the ranging accuracy can be improved to the order of 10-3 of the symbol width, reaching±0.36 cm.【Conclusion】The proposed communication and ranging integrated system can achieve high-precision ranging while achieving high-speed communication, which is of practical significance for future applications of laser satellites.
【Objective】In this paper, an ultra-low power consumption optical transmitter is developed to broaden the application of optical communication in short-reach interconnection such as board level and backplane level. The basic principle of the scheme is that the Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser (VCSEL) laser generates an optical pulse signal after loading a bias current and a modulation signal through a Bias-T circuit.【Methods】In this work, the feasibility of the scheme is verified by means of simulation. It is also found that the main factors affecting the increase of the transmission rate are the parasitic parameters of the laser device and the impedance matching of the drive circuit. The two electrical transmission distances of 200 and 10 mm are studied by experiments. And the law of eye diagram quality and bit error rate as a function of driving voltage and bias current is studied through experiments under two electrical transmission distances.【Results】The results show that a larger effective extinction ratio ranging from 0.84 to 6.69 dB can be obtained by shortening the electrical transmission distance to 10 mm with the minimum differential driving voltage of 200 mV, the minimum bias current of 15 mA, and the power consumption of 1.2 mW/Gbit/s. Compared with traditional optical modules, the power consumption of optical transmission is reduced by about 80%.【Conclusion】This optical transmitter solution can be applied to intra-data center. Combined with low-power optical receivers, the overall power consumption of the data center can be significantly reduced.
【Objective】Due to its comb filter characteristics, Sampled optical Fiber Bragg Grating (SFBG) has attracted wide-spread attention and become a new focus in the research of optical fiber grating technology. The research work on designing optical filters with high channel numbers, flat tops, and narrow pass bands is of great importance in practical situation. Consequently, an Multi-Phase Shift Interpolated Sampling optical Fiber Grating (MPS-ISFBG) filter is proposed.【Methods】ISFBG has a large number of reflection channels and can introduce multiple flat top narrow transmission channels by inserting multi-phase shift. By optimizing the location of the two π phase-shift distributions of the inserted ISFBGs, an optical filters with 41 transmission channels was designed which covers the C-band with a channel interval of 100 GHz. Each channel has a flat-top response, a narrow 3 dB bandwidth (<1 GHz) and a small shape factor (<3.2). With structure parameters unchanged, three π phase shifts are inserted, which can further reduce the shape factor, thus improving the rectangular shape of the transmission channel. Finally, doubling the number of channels with half of the channel interval is achieved by introducing the MPS technique and inserting three π phase shifts into the ISFBG.【Results】The filter with 81 channels flat-top narrow bandwidth covering the C-bands with 50 GHz channel spacing is demonstrated. The 3-dB bandwidths of the multiple channels are 900.5 MHz and the shape factors are close to 2.17. Meanwhile, the effect of the magnitude of the multiphase shift, the location and the equivalent length of the fiber on the actual fabrication is discussed.【Conclusion】The designed filter has a large number of channels. Each channel has a flat-top response and narrow bandwidth, in line with the design purpose. Such filters have potential applications in multi-wavelength lasers and multi-wave microwave signal processing systems.
【Objective】Coherent optical communication is a high-speed, high-quality, and highly secure communication method, and coherent detection plays an extremely important role in coherent optical communication. High sensitivity coherent detection systems can significantly increase the distance of coherent optical communication. By studying the factors that affect the sensitivity of coherent detection, targeted corrections can be made to improve the detection sensitivity.【Methods】This paper first briefly describes the principle of the coherence detection, and summarizes the research progress in this field at home and abroad. Then the paper analyzes the influence of thermal noise, shot noise, wavefront distortion, polarization loss, spot size deviation, optical axis deflection, coupling efficiency, detector performance, preamplifier and other aspects on coherence detection sensitivity of wireless optical coherence detection system.【Results】The results show that the influence of the thermal noise and shot noise of the system on the detection sensitivity can be minimized by controlling the local oscillator power. The wavefront distortion of signal light can be suppressed by adding an adaptive correction system. The polarization control compensation device can be used to compensate the polarization mismatch between signal light and local oscillator light. The deviation of spot size and optical axis deviation requires improving the processing level of hardware to reduce this error. The use of new detectors can improve the performance of detectors to a certain extent. The pre-amplifier can amplify weak signal light, which is crucial for improving detection sensitivity.【Conclusion】This article analyzes the factors that affect the sensitivity of wireless optical coherent detection, and summarizes the methods used by domestic and foreign scholars to improve detection sensitivity in recent years. It provides theoretical reference for improving the sensitivity of detection systems in practice, which has important significance for improving the performance of coherent optical communication systems.
Ultraviolet technology has a wide range of applications in military and civilian fields, such as space detection, ultraviolet light guidance, ultraviolet interference, corona discharge detection and military communications. Starting from the single and multiple scattering of ultraviolet light, this paper first introduces the progress of ultraviolet optical communication at home and abroad. Then it analyzes the different links in ultraviolet optical communication. Next, it discusses the pulse broadening effect and atmospheric turbulence of ultraviolet communication in non-direct link ultraviolet communication. Finally, the paper summarizes the ultraviolet Ad Hoc network, and shows the trend of the development of ultraviolet optical communication.
【Objective】To meet the diverse application demands for high-performance Optical Frequency Comb (OFC), especially in terms of independently adjustable parameters like bandwidth, flatness, central wavelength, and spectral line spacing, a method based on secondary coupled Radio Frequency (RF) signals to drive a single Dual Drive Mach-Zehnder Modulator (DDMZM) for OFC generation is proposed.【Methods】Utilizing a single multiplier to generate the secondary RF coupled signals not only increases the number of comb lines produced by the OFC but also offers the advantages of a simple structure and low cost. Additionally, to further enhance the optimization efficiency and performance of the OFC, a deep learning-based inverse design and analysis approach is adopted.【Results】The study shows that the inverse design based on the constructed cascaded network can identify the corresponding parameters for the target OFC in less than one second. This rapid parameter determination method enables programmability of the number of comb lines, OFC power, and line spacing. It can also generate a 13-line OFC with a flatness of 1.769 dB. This efficient design method provides robust support for the rapid preparation and application of OFCs.【Conclusion】The proposed solution in this study demonstrates significant advantages in OFC generation technology, particularly in performance, flexibility, and optimization efficiency. The method of generating OFC through DDMZM driven by secondary coupled RF signals not only simplifies the system structure and reduces costs but also significantly improves design efficiency through the reverse design approach of deep learning. These characteristics make this solution suitable for a wide range of applications, especially in scenarios requiring quick, efficient, and flexible adjustment of OFC parameters.
【Objective】In order to realize intelligent cloud-light integration and to solve the problem of slow deploying optical transport network, the article provides a fast deployment method for end-to-end business of cross-domain and cross-vendor.【Methods】By analyzing current status of cross-domain and cross-vendor service deployment on the live network, we find and solve the problems of intelligent optical business integration of Software Defined Network (SDN) control system of the device manufacturer with Abstraction and Control of Traffic Engineered Networks (ACTN) and Software Defined Optical Transport Network (SDOTN) standards. The paper also proposes the methods and directions to improve the SDN management and control system of device manufacturers.【Results】Verified by testing, by optimizing and improving the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) management and control system of device manufacturers, the efficiency of enabling end-to-end services within a domain can be improved. The intelligent one-click deployment of cross-domain end-to-end services can be implemented.【Conclusion】Proved by the test results, Optimizing and improving the SDN management and control system of equipment manufacturers is conducive to the service opening of intelligent cloud-light integration.
【Objective】This paper studies numerical characteristics and characteristic matrix of attenuation spectrum of G.652.D single-mode optical fibres, and considers the attenuation factor to optimize the mathematical expression of optical fibre attenuation spectrum model. The study aims to improve the digital modeling ability of optical fibre attenuation spectrum for research and manufacturing of optical fibre and development of optical system.【Methods】ITU-T G.650.1(2020) provides an example matrix for use in the "spectral attenuation modelling" method to calculate attenuation spectrum of G.652.D single-mode optical fibres. This paper analyzes and demonstrates that the spectral attenuation model method could approximately obtain optical fibre attenuation spectrum with low error by characteristic matrix corresponds to four wavelengths. An optimized attenuation spectrum characteristic matrix is given by considering sources of attenuation, and the effect of the new matrix is verified with attenuation spectrum test data of 1000 fibre samples.【Results】Main research results of this paper include: (1) When there is a good correspondence between the wavelengths corresponding to the fibre attenuation spectrum characteristic matrix and main attenuation sources of G.652.D fibre, the spectral attenuation model method is able to approximate the fibre attenuation spectrum with small errors; (2) An attenuation spectrum characteristic matrix of G.652.D single mode fibre is calculated based on attenuation sources of the fibre, and this matrix is able to reflect mechanism of fibre attenuation better, compared to the characteristic matrix calculated solely from data; (3) Verification with test data of optical fibre samples shows that the new matrix could calculate the attenuation spectrum of optical fibre samples with comparable small errors.【Conclusion】This paper studies and concludes that the reason why the spectral attenuation model method is able to approximate the optical fibre attenuation spectrum is that the corresponding wavelengths of the characteristic matrix has a good correspondence with main attenuation sources of the optical fibre. Combining with the attenuation sources, optimized characteristic matrix can be calculated. The new matrix could reflect the mechanism of the optical fibre attenuation and also effectively calculate the attenuation spectrum of the optical fibre samples with small errors.
【Objective】For the problem of limited sensing distance of distributed optical fiber sensing system, a Phase-Sensitive Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (φOTDR)distributed optical fiber sensing system based on Remote Optically Pumped Amplifier (ROPA) technology was proposed.【Methods】Adopting polarization diversity reception technology to obtain orthogonal polarization signals to solve the problem of polarization mismatch, Frequency division band processing suppresses coherent fading and polarization fading. Applying high-order Raman pumping technology and cascaded ROPA technology, three remote gain units are selected with appropriate gain medium lengths. Introduced at the appropriate positions in the transmission link, the pump light and signal light are coupled and sent by the remote pumping unit to excite erbium ionst for unrepeatered amplification, realizing ultra long single span vibration signal sensing and solving the problem of insufficient single-span sensing distance of existing φOTDR.【Results】The experimental results show that In-phase and Quadrate (IQ) demodulation algorithm can be used to achieve linear recovery of Piezoelectric Transducer (PZT) disturbed 100 Hz signal.【Conclusion】The results show that this system can achieve vibration signal sensing of 176.6 km ultra long single span, breaking the existing φOTDR single span sensing distance recording. The vibration curve of the first 176 km is stable and the amplitude is below 0.4 rad. The undisturbed position in the three-Dimensional (3D) map is relatively stable, and the disturbance signal added by PZT at the end of the link can be accurately perceived. After Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) transformation processing, the signal-to-noise ratio of the 100 Hz disturbance signal is 8.9 dB. The experimental results are crucial for building ultra long single-span φOTDR sensing system and provides a certain reference value for the development of unrepeatered ultra long-distance sensing in OTDR systems.
With the development of the social informatization, the demand for optical fiber communication system capacity continues to grow. Channel impairment has always been the key factor limiting the capacity in optical fiber communication system. As the basic function and key technology in optical fiber communication system, channel impairment compensation is constantly improved. Applying deep learning technology in channel impairment compensation of optical fiber communication has attracted the attention of many researchers. This paper introduces the common deep learning models used and the development of deep learning technology for impairments compensation of optical fiber communication systems in recent years.
Liquid Crystal-Spatial Light Modulators (LC-SLM) control the optical path by modulating the refractive index of liquid crystal, and play an important role in adaptive optics. This paper sorts out the development status of LC-SLM at home and abroad, and introduces the working principle and phase calibration principle of LC-SLM in detail. Aiming at the application of LC-SLM in adaptive optics, the research status of key technologies of LC-SLM at home and abroad is discussed. The experimental research in this field of Xi'an University of Technology is analyzed and summarized. Finally, the application status of LC-SLM is prospected.
【Objective】In response to the needs of Ultra High Voltage (UHV) site infrastructure control and intelligent transportation and inspection, 5th Generation Mobile Communication Technology (5G) is applied to the construction phase of UHV converter station for the first time in China.【Methods】On the basis of realizing 5G full coverage of Henan southern converter station, 5G virtual private network of converter station is built and the Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) cloud platform is deployed. Fully considering the needs of early infrastructure and late operation, the intelligent infrastructure site is connected with the intelligent converter station in the later stage. Relying on the advantages of 5G and integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and other technologies, various types of data on the construction site of UHV infrastructure can be collected in real-time and unified, providing multi-functional 5G solutions for remote video monitoring of UHV infrastructure, engineering monitoring and early warning, panoramic presentation of infrastructure site, identification of safety hazards, and expert remote assistance guidance. 5G applications such as smart construction site, intelligent inspection and intelligent control are organized and 5G network adaptation test is carried out.【Results】Providing a flexible, large-bandwidth and high-speed communication methods of 5G for the business application of Henan southern converter station. It effectively enables various business requirements in the UHV converter station, verifying the carrying capacity of 5G for UHV construction and inspection services. It also improves the management efficiency, and reduces the operation and maintenance cost.【Conclusion】The successful application of 5G in the Henan southern UHV converter substation provides a typical UHV substation solution of 5G+ energy Internet, which verifies the feasibility of 5G in the power industry and also promotes the application of 5G in power scenarios.
【Objective】With the development of domestic optical network construction, the management of fiber optic cable routing resources increasingly attract the attention of operators, especially the problem of low efficiency in fiber optic cable survey. There is an urgent need for a feasible fiber optic cable survey method and plan to solve the current problems. The effectiveness and practicality of fiber optic cable routing survey methods are also important indicators that determine the improvement of network construction and maintenance indicators in the region.【Methods】The article investigates and analyzes the existing survey methods and laws of a large number of complex environmental optical cable routes. It also compares and analyzes the detection principles, application scenarios, and existing problems from multiple dimensions. The article focuses on evaluating efficiency improvement, operability, and cost. Combining with actual case situations, it analyzes the actual survey effects of different schemes in a targeted manner.【Results】The article innovatively proposes the research concept of a new fiber optic cable survey method and its application in multiple types of scenarios. The focus is on the practical application of cable identification instruments and cable knocking survey instruments that can be used for full process identification. They have advantages in efficiency and cost, and can solve the pain points of pipeline resource management for operators, providing ideas for the informational development and innovation of pipeline resources for domestic operators.【Conclusion】The method of fiber optic cable routing survey are important breakthroughs in effectively solving practical problems such as cable laying, cable inspection, and cable repair, which are important links in the construction of high-quality optical networks.
【Objective】Natural disasters such as earthquakes have the characteristics of persistence and wide range. During the occurrence of disasters, the link resources of the optical network will be continuously damaged, resulting in the constant change of the link risk. In the face of constantly changing link risks, improper service recovery planning may cause service failures. From a service perspective, repeated faults will interrupt data transmission many times, and the subsequent link status damage may be aggravated after a disaster occurs. From the perspective of network management and control, repeated recovery wastes route calculation resources and occupies the recovery resources of other services. At the same time, different services have different requirements for transmission reliability because of the importance of the data to be transmitted. When a fault occurs, the high-importance services should be recovered first. Therefore, in the scenario of a large-scale persistent disaster, it is a problem worth studying to comprehensively consider the sustained impact of the disaster on link risk and the difference in path reliability requirements of different services for service recovery. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a link risk-aware service recovery algorithm-Dynamic Link Risk Reroute Algorithm (DLRRA) under persistent disasters.【Methods】Firstly, according to the service importance and link risk, we establish the service importance evaluation model and link risk evaluation model. Then we propose the optimization target route reliability. The DLRRA, combined with the optimization objective, fully considers the change of link risk degree caused by the impact of disasters on the continuity of links. By preferentially allocating low-risk recovery resources to the fault services of high importance, the risk of secondary failure of the same high-importance services is avoided during the continuous occurrence of disasters.【Results】The simulation results show that the second failure probability of DLRRA recovery is reduced by 11% compared with the traditional algorithm, and the average importance of DLRRA recovery under the high load is increased by 10%.【Conclusion】Therefore, the algorithm effectively avoids the loss caused by multiple service interruptions caused, and ensures the continuous and stable operation of important services in the disaster environment.
【Objective】Deformable Mirror(DM) is a key device in adaptive optics system for wavefront correction, and its performance directly determines the wavefront correction capability of the system. By studying DM and their control algorithm, the wavefront correction capability of adaptive optics system can be continuously improved. On one hand, the accuracy and response speed of DM can be enhanced to better correct various complex wavefront distortions. On the other hand, the control algorithm can be improved to increase the efficiency and accuracy of the correction. These studies will directly affect the imaging quality and performance of adaptive optics system. Therefore, investigating the DM and their control algorithm is of great significance for improving the wavefront correction capability, expanding application fields, and enhancing imaging quality and performance of adaptive optics system.【Methods】The article aims to summarize the research progress on DM and their control algorithm both domestically and internationally, as well as analyze the correction accuracy of different control algorithm for wavefront distortion, establishing the groundwork for the advancement of adaptive optics. Firstly, several typical DMs are used as examples to model the DM and provide detailed introductions to the structures and working principles of separate actuator DM, splicer DM, thin film DM, dual piezoelectric DM, Micro Electromechanical System (MEMS) DM and voice coil DM. Then, several control algorithms such as the Prandtl-Ishlinskii (PI) hysteresis model-based control algorithm, decoupled control algorithm, and sparse sampling control algorithm are analyzed.【Results】Summarized the work done by Xi'an Technological University in this field, and finally pointed out the future technological breakthroughs and improvement directions in this field.【Conclusion】The research progress on DM and their control algorithm lays the foundation for the development of adaptive optics, enabling its application in more fields and further improving the performance of adaptive optics system. This will help improve imaging quality and drive the development of adaptive optics technology.
【Objective】Power Line Carrier(PLC)communication adopts the frame burst transmission mode. Due to the carrier frequency offset between transceivers, various noise and time-varying characteristics of PLC channel and the system has no dedicated reference signal. The traditional channel estimation has no tracking and prediction ability for the channel, which leads to the deterioration of the PLC system performance.【Methods】Aiming at the existing problems, this paper proposes a Denoising Long Short Term Memory (DnLSTM) neural network based on Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) neural network and Denoising Convolutional Neural Network (DnCNN), which is used for PLC channel estimation. First, offline training is performed on DnLSTM and the parameters are saved after training. Then the trained parameters are deployed in PLC system. After loading parameters, online prediction is performed to obtain the predicted PLC system channel estimation. In the simulation of PLC system, this paper uses Least Squares (LS) algorithm, Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE) algorithm and DnLSTM to estimate the channel response, and gives the simulation results under the conditions of Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN), combined noise, impulsive noise and colored noise. Meanwhile, simulations for different number of preamble symbols for channel estimation are performed.【Results】The results show that there is a relationship between the accuracy of DnLSTM channel estimation and the number of preamble symbols. Using four preamble symbols for channel estimation, its estimation accuracy is better than LS and close to MMSE algorithm. DnLSTM has a good ability to resist carrier frequency offset and channel time-varying. When the number of preamble symbols for channel estimation increases, PLC system performance with low Singnal to Noise Ratio (SNR) gets better and PLC system performance is similar with high SNR.【Conclusion】According to simulation results above, it can be concluded that DnLSTM, which is based on DnCNN and LSTM, can predict PLC system channel response with frequency offset very well and it can track the varying PLC system channel response in real time.
【Objective】In order to improve the confidentiality and performance of the mixed Radio Frequency (RF)/Free Space Optical (FSO) communication systems, it is necessary to study the security performance of the Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)-assisted mixed RF/FSO system to obtain the relationship between system security performance and parameters such as RIS deployment location and the degree of correlation between different antennas branches.【Methods】In the article, a single eavesdropper is considered to eavesdrop against RF links and FSO links respectively, with RF links obeying an arbitrarily correlated Nakagami-m distribution and FSO links obeying a Gamma-Gamma distribution. Closed expressions for the Security Outage Probability (SOP) and Strictly Positive Security Capacity (SPSC) probability of the communication system for the two eavesdropping scenarios are derived using the decode-and-forward protocol, and the SOP is analyzed asymptotically. Simulation experiments are also conducted using the Matlab software to verify the accuracy of the derived formulas through Monte Carlo simulation.【Results】Simulation results show that deploying the RIS close to the receiver reduces the security outage probability of the system. It is also shown that an increase in the degree of antenna correlation increases the SOP of the system when the channel quality of the RF main channel is better compared to the eavesdropping channel.【Conclusion】The RIS-assisted FSO link has better security compared to the RF link. Although the multi-antenna diversity technique can effectively improve the security performance of the system, antenna correlation, similar to the fading caused by pointing error and atmospheric turbulence, can also damage the security performance of the system. It is also shown that the security of the system can be effectively improved by reducing the degree of antenna correlation.
【Objective】High-frequency microwave carriers (GHz) with tunable capability have a wide range of applications in 5th Generation Mobile Communication Technology (5G)/ 6th Generation Mobile Communication Technology (6G) wireless networks, radar systems, and satellite communications. Due to the relatively simple structure of the system, the large bandwidth and the low loss, the technical scheme of generating high-frequency tunable microwave carriers based on photonic technology has attracted extensive attention from domestic and international research teams. Current photogenerated microwave experiments are mostly conducted in C-band wavelengths because of the mature commercial devices. Meanwhile, the Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)-Radio Over Fiber (ROF) technology integrates the WDM technology with the ROF technology so as to flexibly realize the combining/splitting of microwave bands with the help of the combining/splitting of WDM system in the optical frequency domain. The ROF part of the system employs photogenerated microwave technology to simplify the base station configuration. Constrained by the limited bandwidth resources in the C-band wavelengths(35 nm, 1 530~1 565 nm), there is a drive for the generation of microwave to expand to wider spectral ranges. The U-band wavelengths can also provide channel bandwidths as wide as 50 nm (1 625~1 675 nm) to alleviate the channel utilization pressure in the C-band wavelengths; In the U-band wavelengths, Standard Single Mode Fibers(SSMFs) have achieved optical power loss as low as 0.195 dB/km (@1 625 nm); In particular, thulium-doped fiber amplifiers have also demonstrated a large bandwidth gain of 18.7 dB (@1 655 nm). These advantages attract SSMFs-based WDM systems to expand into the U-band, which leads to the extension of WDM-ROF technology into long wavelengths, and in turn leads to the expansion of photogenerated microwave technology. Therefore, this paper studies the photogenerated microwave technology in the U-band.【Methods】From the mathematical model, the commonly used photogenerated microwave carriers technologies are transparent to the applied optical carrier bands, and can be used to generate microwave carriers at arbitrary bands by selecting photonics devices corresponding to the operating bands. In principle, C-band wavelengths photonics devices (such as polarization controllers, Phase Modulator (PM), Fiber Phase Shifter (FPS), etc.) can work in the U-band, and the process technology of these devices is mature. Therefore, in this paper, photonics devices such as C-band wavelengths PM, FPS and optocouplers are used to build a photogenerated microwave carrier system based on U-band optical carriers.【Results】Finally, tunable microwave carrier with a tuning range of 7.5~12.0 GHz and a spurious rejection ratio of 29.6~35.2 dB is ultimately generated based on this system.【Conclusion】Through formula principle analysis and experimental verification, this paper extends the working band wavelengths of the photogenerated microwave carrier to the U-band wavelengths.
【Objective】In this paper, the objective of the research is to improve the performance of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)-Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) optical fiber communication system. a Quadrature Grouped Subcarrier Amplitude Shaping (QGSAS) dual-Phase Conjugate Twin Waves (dual-PCTW) scheme is proposed, which can suppress the nonlinear effect of the systems. In addition, the simulation systems under different conditions are built to explore the performance of the scheme. The specific experimental methods are as follows.【Methods】With the mixed programming of Optisystem and Matlab, a QGSAS dual-PCTW OFDM system is simulated based on 16-ary and 64-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) formats. Two kinds of QGSAS (sinusoidal amplitude shaping, rectangular amplitude shaping) and three dimensions dual-PCTW (time domain, polarization domain, sub-carrier domain) are adopted for the system to form 12 different combinations.【Results】The simulation results show that the QGSAS dual-PCTW scheme can effectively suppress the nonlinear effects in the system. In several combination schemes discussed, the 16QAM dual-PCTW scheme in time domain has the best performance. When the QGSAS technology is used, the scheme of rectangular amplitude shaping is better than the sinusoidal amplitude shaping.【Conclusion】Therefore, it can be concluded that in the scheme studied in this paper, the rectangular amplitude shaping scheme combined with the time domain scheme dual-PCTW technology under 16QAM can effectively suppress the nonlinear effect of OFDM-WDM system.
In the field of optical communication, laser and its modulation bandwidth and modulation rate are very important for optical wireless communication. There are two main modulation modes for semiconductor laser signal: internal modulation and external modulation. These two modulation technologies have their own characteristics and are suitable for different fields of optical fiber communication. Internal modulation laser, also known as direct modulation laser, has become a cost-effective light source for the Fifth Generation Mobile Communication Technology (5G) fronthaul and data center because of its high-speed transmission and low cost. There is no additional Chirp of light source in external modulation laser, so the Composite Second Beat (CSB) distortion caused by fiber dispersion can be effectively overcomed. On the basis of reviewing the development history of communication laser and its modulation technology, this paper introduces the work and main progress made by Xi’an University of Technology in this field. This paper discusses the internal and external factors of nonlinear distortion of semiconductor laser, simulates the effects of various parameters of response characteristics, linearization compensation method and power control system on the output light source of light emitting device, and analyzes the influence of temperature fluctuation on the output power of laser and modulation device. Based on the basic theory of refractive index ellipsoid and numerical analysis, the variation trend of emitted light intensity with temperature is discussed under the longitudinal and transverse modulation, respectively. The results show that the variation trend of outgoing light intensity with temperature under longitudinal modulation is only related to the refractive index of Lithium Niobate (LN) crystal. Under transverse modulation, the variation trend of outgoing light intensity with temperature is affected not only by the refractive index of the crystal, but also by the crystal size and its expansion coefficient. Therefore, the special size crystal can be used to improve the temperature stability of the electro-optic modulator.
Passive Optical Network (PON) is considered a crucial networking technology for the next-generation industrial Internet due to its advantages of high bandwidth, cost-effectiveness and resistance to electromagnetic interference. However, the technical development of conventional PON is based on the principle of "bandwidth enhancement",making its transmission scheduling mechanism difficult to meet the transmission requirements of "time-sensitive" industrial services. This poses a significant challenge to the network transmission capability of conventional PON, necessitating the incorporation of determinism as a new characteristic. This paper mainly focuses on the Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)-PON. Firstly, it illustrates the service characteristics and transmission requirements of industrial Internet, and analyzes the two major technical challenges faced by conventional TDM-PON in industrial Internet scenarios: one being uncertain delays caused by the traditional bandwidth allocation scheme; and the other being uncertain delays caused by the inflexible scheduling mechanism. Addressing these challenges, this paper summarizes the key technologies to enhance the deterministic transmission capability of TDM-PON, such as collaborative transmission interfaces, multi-bursts per frame, and Deterministic Bandwidth Allocation (DetBA). Furthermore, this paper proposes a network calculus-based delay boundary modeling method as a theoretical model for designing and evaluating the performance of deterministic industrial PON systems. Finally, potential technologies and directions for deterministic industrial PON are discussed, including the service layer, the Media Access Control (MAC) layer, the physical layer, and the control and management plane.
The standards for 50 Gbit/s Passive Optical Network (PON) are nearly complete, but the standards for the post-50 Gbit/s PON era are still blank. It is necessary to carry out relevant research to guide the industry’s strategic planning in system, optical module and chips. Experts predict that single-wavelength 200 Gbit/s rate and coherent technology will be the two key features of the next-generation PON system after 50 Gbit/s PON. Firstly, the single-wavelength 200 Gbit/s rate is particularly attractive to operators. However, Intensity Modulation and Direct Detection (IM/DD) technology struggles to meet the Class C+ power budget requirements at this speed. Therefore, it is necessary to use a coherent technology which is more sensitive than IM/DD technology. However, some technical challenges need to be overcome if coherent technology is applied to PON. As the PON system shows a typical Point-to-MultiPoint (P2MP) topology, key challenges include the architecture reconstruction of PON Media Access Control (MAC) chips and system equipment, the Bi-Di technology and the burst-mode technology of coherent PON optical modules, and the wavelength management in PON system. Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) remains the best way to achieve P2MP transmission. New multiplexing dimensions, such as Sub-Carrier Multiplexing (SCM) can enhance this method. The introduction of new multiplexing dimension adds flexibility but also complicates the design, potentially overhauling the entire PON system architecture. With SCM, digital interfaces are no longer used to connect optical modules. Instead, optical modules will need to use highly linear driver and modulator. The user-side optical modules need the ability to switch instantly to avoid interference with other users, necessitating the development of new coherent optical chips with burst-mode control functionality. Considering the uplink P2MP burst-mode coherent reception, it is necessary to control the wavelength of multiple lasers at the system level to avoid errors from frequency offset estimation, caused by rapid wavelength switching among users. In summary, applying coherent technology to PON is a completely new and complex task, which cannot directly inherit the existing coherent system architecture. It needs to match the requirement of P2MP system application, through technological innovation in chips, modules, and equipment.
Compared to the traditional Intensity Modulation and Direct Detection (IM/DD) system, the coherent system offers higher capacity and power budget, better meeting the needs of high-capacity Passive Optical Network (PON). In recent years, the application of coherent technology in PON to better support future high-bandwidth services has become a hot research topic. This article summarizes the research progress in coherent PON technology from four aspects: system architecture, coherent simplification, uplink burst-mode detection, and flexible PON. In addition, it proposes laser-shared uplink and downlink Filter Bank Multi-Carrier (FBMC)-PON and Semiconductor Optical Amplifier (SOA) current-adjusted flexible PON schemes.
The deep integration of optical fiber communications and high-capacity, high-frequency wireless communications is a core technology for the future 6th Generation Mobile Communication (6G). It is crucial for establishing typical 6G scenarios such as immersive communications, ubiquitous connectivity, and integrated communications Artificial Intelligence (AI). This paper reviews mainstream technologies and solutions for optimizing the architecture and improving the spectral efficiency of fiber-wireless integrated transmission systems. It also summarizes the progress made by our team in these areas. Firstly, to meet the high-capacity needs of next-generation of immersive communications, a novel architecture for seamless "fiber-wireless-fiber" integrated transmission system is proposed using commercial Digital Coherent Optics (DCO). It marks a pioneering achievement in real-time wireless transmission at 100/200/400 GbE with photonics, achieving a maximum line rate of 2×240.558 Gbit/s. Secondly, for application scenarios requiring broad coverage and flexible deployment, the Digital Sub Carrier Multiplexing (DSCM) technology is incorporated into the optical fiber-wireless convergence access system. It results in a coherent Passive Optical Network (PON) supporting up to 32 channels of fixed broadband and 32 channels of W-band millimeter-wave wireless access. This coherent PON could reach a rate of 100 Gbit/s and is adaptable for flexible rate adjustments and future upgrades. Finally, addressing the demand for communication AI integration, a likelihood-aware Vector-Quantization (VQ) Variational Auto Encoder (VAE) is proposed based on AI technology for end-to-end optimization of fiber-wireless integrated communication systems. Without the need for terahertz power amplifiers, we successfully demonstrate the wireless transmission of Dual-Polarization (DP) terahertz signal at a net rate of 366.4 Gbit/s over 6.5 m 2×2 Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) wireless link and 20 km Standard Single Mode Fiber (SSMF) link. These technologies exhibit tremendous potential for future 6G applications. Moreover, we briefly explored the possibilities for beyond 100 Gbit/s fiber-wireless integrated transmission technology, focusing on high capacity, long distance, integration and intelligentization.
To meet the growing demand for communication capacity, new multi-carrier fiber optical communication technology has become the focus of scientific researchers' attention. The paper reviews the development of traditional Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) in the field of fiber optical communication over the past 20 years and summarizes relevant research on Filter Bank Multi Carrier (FBMC) and Universal Filter Multi Carrier (UFMC) in recent years. Since 2016, scholars worldwide have been addressing the drawbacks of OFDM in optical communication, such as high out-of-band leakage, reliance on Cyclic Prefixes (CP), high Peak-to-Average Power Ratio (PAPR) values, and stringent system synchronization requirements. They have initiated research using new multi-carrier systems as a breakthrough point. FBMC optical communication is characterized by minimal sidelobe power and high spectral efficiency, but due to the use of Offset Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (OQAM), the corresponding Digital Signal Processing (DSP) algorithm needs to be redesigned for virtual part interference. UFMC optical communication has a strong tolerance for time synchronization deviation, and it is less sensitive to frequency offsets. Moreover, it can reuse the DSP algorithms of OFDM. However, challenges remain in further suppressing out-of-band power and reducing computational complexity. Finally, based on the current research status, the paper proposes research directions and suggestions for advancing the next-generation fiber optical communication system.
【Objective】In order to meet the growing demand for ultra-gigabit, from gigabit to 10-gigabit, from The 5th Generation Fixed networks (F5G) to F5G-Advanced (F5.5G), 50 Gbit/s Passive Optical Network (PON) is considered to be an important part of F5.5G. This paper conducts a thorough study of 50 Gbit/s PON technology, reflecting the latest advancements in access networks.【Methods】This paper initially addresses the difficulties in achieving high sensitivity in 50 Gbit/s PON, and proposes a solution. 50 Gbit/s Non-Return-to-Zero (NRZ) signals pass through Avalanche Photodiode (APD) detectors to form macroscopic currents that can be detected under strong electric fields. These currents are then amplified by a Transresistance Amplifier (TIA) and converted into voltage outputs. After balancing, the Feed Forward Equalizer (FFE) and Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE) of optical Digital Signal Processing (oDSP) chip are used to compensate the trailing phenomenon of pulse signal, and the influence of intersymbol interference is minimized by DFE. Then the paper analyses the key technologies such as APD, TIA and oDSP, comparing the reception performance between 25 Gbit/s and 50 Gbit/s APDs.【Results】Experimental test results show that the 25 Gbit/s APD maintains error-free signal reception at -8.48 dBm over 4 minutes, and reaches -26.61 dBm at a Bit Error Rate(BER) of 2.78e-2. The 50 Gbit/s APD exhibits no bit errors at -8.97 dBm and achieves -27.05 dBm at the same BER, with the second 50 Gbit/s APD set demonstrating similar results.【Conclusion】The 50 Gbit/s APD has superior receiving sensitivity and performance, making it highly suitable for 50 Gbit/s PON optical modules to help achieve high receiver sensitivity. The paper suggests a feasible approach for cost reduction in future implementations, focusing on the balance technology and APD.
In 2021, the International Telecommunication Union Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) developed the standards of 50 Gbit/s Passive Optical Network (PON). Currently, the equipment manufacturers and operators have completed prototype verification. ITU-T has established the Beyond 50 Gbit/s PON discussion group to explore future PON-related technical solutions. As a result, beyond 50 Gbit/s PON has become a research hotspot in the field of optical communication. According to the evolutionary pattern of previous PON standards, it is anticipated that the data rate of beyond 50 Gbit/s PON will exceed 100 Gbit/s. This article analyzes the problems and challenges faced by beyond 100 Gbit/s PON, focusing on two potential technological paths: flexible-rate PON and coherent PON architecture, along with their key technical solutions. This study provides references for future research and standardization of beyond100 Gbit/s PON.
【Objective】In recent years, data communication traffic has experienced explosive growth. To meet the demands for high-speed, high-capacity data transmission and the diverse network application scenarios, hybrid network beyond 100 Gbit/s (B100 Gbit/s) using Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) has increasingly been recognized as an effective solution. This paper analyzes the requirements, key technologies, and practical case studies of such networks, providing technical support and guidance for building high-capacity and efficient communication networks.【Methods】This paper first outlines the requirements for developing B100 Gbit/s DWDM hybrid networks, including network capacity expansion and support for complex network architectures. Next, it details the key technologies for these networks, including constellation shaping, spectrum shaping, and flexible grid technologies. To support bitrate design in hybrid networking, a method for calculating Optical Signal-to-Noise Ratio (OSNR) in cascaded Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA) communication systems is presented, using parameters such as channel configuration information, transmitted signal optical power, and EDFA gain and noise parameters, to calculate the output OSNR for each wavelength across the link. Finally, by integrating a foreign network case study and based on actual OSNR evaluation, a rational hybrid rate network design is performed, demonstrating the application effectiveness of B100 Gbit/s DWDM hybrid networking in engineering projects.【Results】Implementing B100 Gbit/s DWDM hybrid network, after flexibly configuring transmission rates and bandwidths based on OSNR evaluations, achieves hybrid rate networks deployment at 200, 600 and 800 Gbit/s. This approach fulfills the high-capacity requirements of core sites while accommodating the long-distance, extensive span requirements of edge sites. Furthermore, network upgrades and expansion are smoothly accomplished within a three-year period.【Conclusion】Practice demonstrates that B100 Gbit/s DWDM networking effectively enhances network capacity, flexibility, and spectrum resource utilization. It also provides room for the continuous network evolution, playing a crucial role in advancing the development of high-capacity optical transmission networks.
【Objective】Optical fiber dispersion, nonlinear impairments, and bandwidth limitation in high-speed passive optical access networks result in significant power budget loss with traditional intensity modulation and direct detection schemes, failing to meet the requirements of high-speed passive optical access networks.【Methods】In order to enhance the rate and performance of the intensity modulation and direct detection optical access system, this study explores the channel equalization method of VDFE-RLS based on Recursive Least Squares (RLS) algorithm, building upon the Volterra Decision Feedback Equalizer (VDFE), This equalizer uses RLS algorithm to update its tap coefficients. It includes a three-order Volterra series, allowing it to compensate for both linear and nonlinear impairments. VDFE-RLS is applied to the downlink optical access system with a single wavelength of 200 Gbit/s based on O-band intensity modulation and direct detection scheme after 20 km transmission.【Results】The experimental results show that the RLS outperforms the conventional Least Mean Square (LMS) algorithm in the equalization process. Moreover, VDFE-RLS achieves a power budget greater than 29 dB. When the length of the equalizer is the same, VDFE-RLS can increase the power budget by 2.2 dB compared with the conventional Volterra Feed Forward Equalization (VFFE)-RLS equalizer. When the length of VDFE-RLS equalizer is half that of VFFE-RLS, the VDFE-RLS can increase the power budget by 0.5 dB compared with the VFFE-RLS equalizer.【Conclusion】Compared with other traditional methods, the proposed method can shorten the length of the equalizer and increase the power budget of the system, ultimately restoring signals with better performance.
【Objective】The commonly used max-log-map algorithm reduces the complexity of soft information computation compared to the log-map algorithm. However, it still consumes significant resources for high-order Orthogonal Amplitude Modulation (QAM), such as 8QAM, 16QAM Probability Shaping (PS), and 64QAM PS.【Methods】8QAM adopts the method of constellation region division, and the soft information is represented by the distance information from the received symbol to the perpendicular between the nearest bit 0 and bit 1. The distance information is simplified and calculated using angle rotation and regional symmetry. For 16QAM PS and 64QAM PS with non Maxwell Boltzmann (MB) distribution, the central boundary between the edges of the bit 1 region and the central boundary between bit 0 on both sides of the bit 1 region no longer coincide. Region merging approximation is used to handle the region ownership between the two boundaries, and the max-log-map expression is factorized to simplify the distance difference to calculate the soft information. The soft information of 16QAM PS and 64QAM PS based on MB distribution can be obtained by simplifying the soft information expression of non-MB distribution.【Results】The simplification reduced the multiplication and addition/subtraction operations in 8QAM soft information calculation from 48 and 75 times to 12 and 16 times respectively. with a degradation of only about 0.05 dB. For MB-distributed 16QAM PS, operations reduce from 192 multiplications and 260 additions/subtractions to 2 and 4, respectively, also with a degradation of only about 0.05 dB. The reduction is even greater for 64QAM PS, decreasing from 1 152 multiplications and 1 542 additions/subtractions to 3 and 6, respectively.【Conclusion】This article proposes a soft information computation method suitable for 8QAM and MB-distributed 16QAM PS, MB-distributed 64QAM PS, non MB-distributed16QAM PS, and non MB-distributed 64QAM PS. When probabilities align with the MB distribution, the non MB methods can transform into the MB methods. When the shaping factor is 0, the expression based on the MB distribution can be converted into a uniformly distributed soft information calculation formula. The soft information calculation for non-MB distribution, MB distribution, and uniform distribution can be uniformly designed on the same circuit, improving circuit reuse rate and reducing the hardware resource consumption.
【Objective】With the advent of new internet services and the broader application of Passive Optical Network (PON) in the industry, PON, as the core technology of the 5th Generation Fixed Networks (F5G), needs to evolve and upgrade continuously to meet the needs of the future network. The latency of PON networks is a key network performance indicator that urgently needs improvement. This article conducts in-depth research on the low latency technologies in the PON networks.【Methods】This article first summarizes the challenges faced by current PON networks in terms of low latency. It identifies two main reasons for high latency: the inherent uplink delay introduced by the Optical Network Unit (ONU) bandwidth allocation mechanism and the random uplink delay introduced by the ONU registration/ranging mechanism. To address these issues, this article proposes two ultra-low latency solutions based on single frame multi burst technology and an independent registration channel, followed by experimental verification and analysis.【Results】Analysis shows that the single-frame multi-burst approach optimally balances latency and bandwidth utilization in a quarter scheduling cycle, albeit at the expense of some bandwidth. This method is ideal for latency-sensitive, bandwidth-tolerant services. The independent registration channel solution, by dedicating an extra wavelength for ONU registration/ranging, eliminates the extra delay and jitter from silent periods in standard service channels.【Conclusion】The ultra-low latency solution for PON discussed in this article can effectively reduce network latency, and help promote the large-scale commercialization of emerging applications such as Virtual Reality (VR) and accelerate the growth of industrial internet.
【Objective】The rapid development of data center networks necessitates intensive research into high-speed and high-capacity data center optical transmission systems. Single carrier 400 or 600 Gbit/s transmission will gradually become the mainstream transmission rate in the next generation of communication network. While the application of 400 Gbit/s transmission is well-studied in data center networks, detailed research on 600 Gbit/s transmission systems is less common.【Methods】This study is based on a single carrier 600 Gbit/s next-generation data center Elastic Optical Network (EON) transmission system, and conducts detailed theoretical analysis and experimental research on factors affecting transmission distance and spectrum utilization efficiency.【Results】The analysis shows that the maximum transmission distance is determined by the single carrier's peak input optical power, while the spectrum utilization efficiency is related to the bandwidth of the transmission channel. Experimental investigation is conducted on a single carrier 600 Gbit/s EON transmission system. By comparing the relationships between different fiber input optical powers, the system’s Q factor and the pre correction bit error rate, as well as the relationships between 3 dB channel filtering bandwidth and system’s Q factor for different channel numbers, it is confirmed that the system’s transmission distance and spectrum utilization efficiency are related to the optimal fiber input optical power and filtering bandwidth, respectively. Furthermore, the experiment shows that the optimal single-wave input optical power and optimal filtering bandwidth of the 600 Gbit/s transmission system are + 4 dBm and 77 GHz, respectively. Under these settings, the system achieves the longest transmission distance and the highest spectral efficiency. Under these experimental conditions, the 600 Gbit/s transmission system achieves long-term stable operation without error for 48 hours, indicating that this fiber input power and bandwidth can effectively extend and improve the transmission distance and spectrum utilization of the 600 Gbit/s communication system.【Conclusion】The 600 Gbit/s EON system has an optimal input power and filter bandwidth that maximizes bandwidth utilization and transmission distance without significant fiber nonlinear effects or channel interference. The findings have significant values for the engineering construction of 600 Gbit/s transmission systems.
In the vehicle to infrastructure communication, the millimeter wave beam width is narrow and user equipment mobility is high. Therefore, effective millimeter wave beam selection is a key and challenging task. Aiming at the problem of high overhead in the beam search process, this paper proposes a millimeter-wave beam selection algorithm based on radar and location information. The proposed algorithm trains a neural network structure on the lidar and beam tracking channel datasets using the Top-k classification metric. It also predicts the best beam pair using the Global Context Net (GCNet) model. The simulation results show that the performance of the proposed algorithm is significantly improved in the classification and recognition accuracy. At the same time, it only needs to search 5 beams to approach the performance of the exhaustive search, which greatly reduces the beam search overhead.
In recent years, with the continuous promotion of the " Ocean Power" strategy, Underwater Wireless Optical Communication (UWOC) has played an important role in marine military, underwater environment monitoring, submarine oil exploration and marine science research due to its advantages in large bandwidth, fast rate, low power consumption and high security. UWOC has become a new feasible underwater communication technology. The positioning technology is now regarded as the basis of UWOC applications and one of the key techniques in underwater target detection & moving object tracking, which has been favored by researchers. In this paper, the development of UWOC and related research results are introduced in detail, with diverse UWOC localization methods being analyzed. Besides, the research status, the challenges and the development prospects for UWOC localization technology are also discussed.
【Objective】For the implementation of Trans Impedance Amplifier (TIA) in 400 Gbit/s Dual Polarization (DP)– 16 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) coherent receiver.【Methods】A 64 GBaud dual channels differential linear TIA in advanced Silicon Germanium Bipolar Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Heterojunction Bipolar Transistor (SiGe BiCMOS HBT) process is proposed. The chip consists of two identical signal amplifying paths for the I and Q signals of Coherent Receiver. The path utilities full differential shunt-shunt feedback structure as TIA stage, and consequent two Variable Gain Amplifier (VGA) stages in series to amplify further, and Current Mode Logic (CML) buffer with single-end 50 Ω output impedance as the output stage. The chip integrates two independent Direct Current Restore (DCR) loops to remove the input direct current component and direct current offset at the core output node, and integrates Direct Current Offset Cancellation (DCOC) loop to remove the output direct current offsets due to the differential pairs mismatch along the VGA and buffer stages. An Automatic Gain Control (AGC) loop is built in to adjust automatically the trans-impedance gain of TIA stage and gain of VGA stages based on input amplitude detecting, which is aimed to avoid saturation distortion. To optimize output impedance matching and reduce the impact of parasitic capacitance of Electrical Static Discharge (ESD) diodes, a three ports bridge-T network inductive peaking technique is inserted in the output node to optimize the output return loss and improve the bandwidth. The chip is designed and manufactured in advanced SiGe BiCMOS HBT process. The die size is 1.6 mm×1.8 mm, and the channel pitch is 625 μm. The chip is assembled with Photodiode (PD), junction capacitance Cpd=50 fF and other coherent optical components into Integrated Coherent Receiver (ICR) for testing.【Results】The test results show that, the differential gain is 5 kΩ, and the 3 dB bandwidth is 32 GHz. The Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) is less than 2%, and the overload optical input is 3 dBm. The chip is powered by a single 3.3 V supply, and the static power dissipation is only 250 mW.【Conclusion】The chip can be applied in 64 GBaud coherent receiver, and implement 400 Gbit/s per lambda transmission with DP-16QAM modulation.
【Objective】Focusing on the strategic goal of building an internationally leading energy Internet enterprise with Chinese characteristics, in accordance with the promotion of the deep integration and application of advanced information and communication technologies and advanced energy technologies, and focusing on the overall requirements of improving the power communication network to support and guarantee the safe operation of the power grid, Suzhou Electric Power launched the construction of a 220 kV protection private communication network since 2019. There exist problems with the 220 kV relay protection channel in Suzhou, such as long repair time, high occupancy of communication cabinet resources, and mixed networking of protection and communication services, which pose hidden dangers to the safe operation of the power grid.【Methods】This paper analyzes the current status and existing problems of Suzhou 220 kV relay protection channel. Combined with the actual situation of optical communication network in Suzhou, this paper proposes using 2 Mbit/s optical interface to directly connect protection equipment for carrying the relay protection channel of B port, and refines the power transformation plan, networking mode, protection business bearing mode, and network management bearing mode.【Results】Utilizing the respective characteristics of the direct channels with fiber optic and the multiplexing channels with protection private communication network, Suzhou Electric Power has built a protection private communication network which covers all transformer substations owning 220 kV outlets by customizing the small private communication transmission equipment that matches relay protection services.【Conclusion】The protection private communication network accessing to the centralized transmission equipment network management could monitor relay protection channels and achieve the observability and testability of the relay protection channels. It has advantages such as rapid failure positioning, failure isolation, and channel detour and comprehensively improves the reliability, independence, flexibility, and operation convenience of the relay protection channels. The protection private communication network has achieved significant application results and innovative results, which is also a beneficial exploration for the application of " 3 routes" for the protect channels.
【Objective】The scale of Software Defined Network (SDN) equipment is increasing, and more services are carried. Aiming at the problem that the traditional Optical Transport Network (OTN) devices cannot meet the requirements of large-scale and high-performance network management by using Simple Network Manager Protocol (SNMP) to collect performance data, this paper proposes an OTN device performance acquisition system based on Telemetry architecture.【Methods】By designing a distributed data model conversion and data coding architecture, the efficiency of data conversion and coding and the scale of the acquisition system are improved. At the same time, the computing power of the equipment is balanced. The equipment regularly collects and reports performance data to the collector in seconds.【Results】This paper compares and analyzes the performance collection capability of the device using SNMP and the device deploying Telemetry.【Conclusion】The results show that the system has more advantages in data model conversion and coding, data transmission efficiency, timeliness of data acquisition and flexibility of data acquisition, which may meet the requirements of SDN for intelligent operation and maintenance.
【Objective】Optical Cross Connect (OXC) technology has solved some problems of insufficient electric crossover capacity of Optical Transport Network (OTN) system, as well as complex manual fiber connection and inflexible scheduling between Fixed Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer (FOADM)/Reconfigurable Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer (ROADM) boards. This paper studies how to introduce OXC technology into OTN Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) to improve the flexibility of the network and solve some network security problems caused by the over concentration of OXC.【Methods】This paper introduces the advantages of OXC technology, and summarizes the architecture of the OTN system in the existing network, as well as the security configuration mode of the bearer service. By establishing various OXC application models, the paper compares and analyzes the flexibility and security of various models.【Results】After testing in the existing network, the paper summarizes various model evaluation indicators, and finds the optimal application scheme.【Conclusion】In this paper, an all-optical MAN construction model based on OXC is innovatively proposed to promote the application and development of OXC technology, strengthen the scheduling capability between computing forces, and form a new infrastructure of computing network integration. It finally provides users with low latency, highly reliable, end-to-end computing connections.
【Objective】Aiming at the problem that BitString can not represent all Bit-Forwarding Routers (BFRs) in large-scale Software Defined Networking (SDN) multicast based on Bit Index Explicit Replication (BIER) due to the limited length, this study designs a Hierarchical Domain (HD)-BIER model and devises its construction algorithm.【Methods】The HD-BIER model is a multi-layer BIER network composed of multiple small-scale Sub Domains (SD), which enables BIER to support a number of devices exceeding the capacity of the BitString representation in large-scale networks. The proposed HD-BIER construction algorithm takes into account the BitString Length (BSL) limitation, link lengths between nodes, and network connectivity. It leverages the concept of community partition algorithms and introduces a modularity function based on node similarity as an evaluation metric for BIER SD partitioning. The construction follows a bottom-up approach to dynamically build the HD-BIER network.【Results】The simulation results show that the HD-BIER construction algorithm can effectively construct HD-BIER networks that exceed the BSL limit in either simple networks or the complex networks with a large number of nodes. Additionally, the resulting HD-BIER model not only ensures normal transmission of multicast service data flows through the gradual encapsulation and decapsulation of BitString layers but also maintains SDN multicast communication performance throughout this process.【Conclusion】The simulation results validate that the proposed HD-BIER model presents an effective multicast service support solution for even larger-scale networks.
Metasurface is a thin layer that composed of periodic subwavelength artificial structures. By vibrating together with the incident electromagnetic waves, it introduces the phase jump, which breaks the traditional dependence on spatial optical path accumulation and exhibits unique electromagnetic characteristics. Metasurface has attracted great interest during the past ten years due to its ultra-thin thickness, ultrashort modulation distance and manipulation of light with ultrahigh resolution, superior to traditional optical elements. As the two-dimensional counterpart of metamaterials, it is easier to manufacture and integrate into the devices with operating wavelength ranging from microwaves to visible. The manufacturing processes commonly used for metasurfaces include ultraviolet lithography, electron beam lithography, focused ion beam lithography and nanoimprinting. However, the mass application still faces contradictions between processing accuracy and mass manufacturing and processing costs. Two-photon 3-Dimensional (3D) printing technology which is based on femtosecond pulse laser and two-photon polymerization reaction can fabricate metasurface with high precision and complex 3D structure by only one-step lithography without mask. It has the merits of processing convenience and flexibility, and has the potential of large-scale manufacturing. Therefore, it is widely used in the study and fabrication of metasurface. The paper reviews recent researches on metasurface optical devices fabricated by two-photon 3D printing technologies. An introduction to the concept, advantages and processing methods of metasurface is presented firstly, followed by the principle, development, and technological advantages of two-photon 3D printing. Recent study on metasurface devices ranging from plasmonic metasurfaces, metalens, metasurfaces for nano-display and holography, and metasurfaces integrated into fiber facet are reviewed respectively. Finally, the discussion and comments on metasurface devices based on two-photon 3D printing are given.
Microelectronics technology has enabled electronic devices from discrete to integrated, bringing exponential improvements in cost, reliability, power consumption, volume and other aspects for decades, which is the key to the wide application of electronic information technology. Currently, electronic information technology is facing bottlenecks such as bandwidth and energy consumption, and Moore’s Law is struggling. As another major carrier of information, photons have characteristics such as high bandwidth, high speed, low power consumption, and high parallelism. The continued progress of information technology must rely more on photons. However, the cost, reliability, and scale productivity of photonic devices lag behind the electronic devices. Therefore, based on the historical experience of the development of electronic devices, we propose the " microelectronization" of optoelectronics, emphasizing that optoelectronics take " integration" as the development track and " photoelectric fusion" as the development direction.Taking integration as the development track is to emphasize that optoelectronics should learn from microelectronics in order to meet the requirements of modern information systems for devices. The integrated development of optoelectronics has three main characteristics: the chip platform basing on silicon; the steady increase in integration scale; and the evolution of production mode towards fabless.Taking photoelectric integration as the development direction, it emphasizes the necessity of the combination of optoelectronics and microelectronics, and jointly solve the challenges of bandwidth, rate, power consumption and other challenges currently faced by information technology through device integration and function integration of the two, so as to meet the requirements of digital twins, metaverse and other applications. Photoelectronic fusion mainly has two levels: chip and system, involving monolithic optoelectronic integration, Co Packaged Optics (CPO), hybrid optoelectronic integration, device disaggregation, photoelectric hybrid computing, etc.The " microelectronization" of optoelectronics is not only a technological development guide, but also will have a significant impact on the information optoelectronics industry. The article have conducted open-minded thinking from the perspectives of market, competition, enterprises, products, etc., and pointed out that it may lead to industry reshaping.The " microelectronization" of the development of information optoelectronics is an objective requirement for the continued advancement of information technology. On the one hand, photons are being generalized from transmission technology to ubiquitous connection technology in the entire Information Communications Technology (ICT) domain, from the ground to the ocean and space at the macroscale, and from the shelf and board to the package, and chip at the microscale. On the other hand, photons will be generalized from bandwidth providing technology to a basic hardware technology for the entire ICT domain, from transmission and connection to complex functional domains such as computation, processing, and routing. The " microelectronization" of optoelectronics will enable photons not only have the potential but also the ability to fully utilize their advantages to support the continued progress of the information technology.
Aiming at the problem of the application of the integrated photonic filter in the 3~5 μm atmospheric window banda mid-infrared add-drop filter based on the apodized grating-assisted contra-directional coupler (contra-DC) is studied and designed. The complementary lateral-misalignment method is used for phase modulation to achieve spectral sidelobe suppression and eliminate spectral distortion and broadening caused by the conventional lateral-misalignment modulation method. Simulation results show that the device can achieve a high Sidelobe Suppression Ratio (SLSR) of 22 dB, bandpass filter spectrum is flat at the top and the filtering spectrum is close to the box shape. The device has low insertion loss of about 0.4 dB through port and 0.45 dB drop port.
To improve transmission line load capacity and prevent power grid accidents, an online sag monitoring system for overhead transmission lines based on spontaneous Brillouin scattering is designed using the principles of Brillouin scattering and coherent detection. Brillouin Optical Time Domain Reflection (BOTDR) technology is used to collect the strain signal distributed along the optical fiber in real time, extract the key features of strain sensing, and realize the accurate positioning and early warning of sag anomaly points. Laboratory data and substation test results show that the system can detect and accurately locate strain change information in real time. The strain monitoring system is simple in single-end measurement and can accurately locate the strain mutation point. It can realize the early warning of cable sag abnormalities, and can timely detect and deal with potential faults to ensure the safe and stable operation of the transmission line.
In view of the defects of high energy consumption and pollution in the traditional optical fiber preform manufacturing process, this paper proposes a green and environmentally friendly cladding manufacturing process with quartz sand as raw material. Through the selection and analysis of quartz sand raw materials, it is shown that natural quartz sand is suitable for the manufacture of optical fiber preforms. Through the research on the key control points of the natural quartz sand preform making process, the quartz sand is filled into the prefabricated assembly consisting of a core rod and a thin-walled quartz tube. A large-size G.652.D optical fiber preform with an average outer diameter of 155 mm is then successfully prepared by high-temperature melting and shrinking. After fiber drawing and testing, the optical parameters can meet the low water peak optical fiber standard. There is no exhaust gas emission in the process raw material of quartz sand can be completely converted, which is more low-carbon and environmentally friendly than traditional optical fiber preform manufacturing process.
In order to accurately measure the Dissolved Oxygen (DO) concentration, and enhance the sensitivity and stability of sensor head, two fluorinated dry gel oxygen sensitive materials 3, 3, 3-Trifluoropropyltrimethoxy/Tetraethyl Orthosilicate (TFP-TriMOS/TEOS) and 3, 3, 3-Trifluoropropyltrimethoxy/1, 2-Bis (triethoxysilyl) Ethane (TFP-TriMOS/BTESE) fluorinated hybrid dry gel dope with Ruthenium (Ru) complex were developed by improved sol-gel technology. Oxygen sensing head was made by dip coating plastic optical fiber into the above prepared sol-gel. Its oxygen sensing performance was studied under different precursor ratios. Experimental results show that all the fabricated DO sensing heads have good oxygen sensing performance, and the detection limits are 0.135 and 0.118 mg/L, respectively. Compared with the fiber optic oxygen sensing head coated with a single precursor (TEOS, BTESE and TFP-TriMOS), the fiber optic oxygen sensing head based on fluorinated dry gel shows higher linearity and lower detection lower limit. The stability of the fluorinated DO sensing head and the influence of pH the intensity of fluorescence signal was studied. The results show that the two kinds of fiber optic dissolved oxygen sensing head have good stability and anti-interference ability.
Single Side Band (SSB) direct detection system is considered as an attractive solution for 80 km Data Center Interconnects (DCI), due to its characteristics of low-cost, simple system architecture, and high robustness to chromatic dispersion. However, Signal to Signal Beating Interference (SSBI) is the major problem in SSB direct detection system. In order to address the SSBI in the SSB direct detection systems, the SSB modulation realized by IQ modulator and Dual Drive Mach Zehnder Modulator (DDMZM) is investigated. A SSB signal reconstruction algorithm based on time domain iteration and an SSBI-free direct detection scheme based on DDMZM are proposed respectively for these two SSB direct detection systems. The implementation principle and simulation or experimental setup are introduced in detail. According to the simulation and experimental results, the effectiveness and feasibility of the two schemes in SSBI elimination are discussed.
Aiming at the problems of the existing Optical Transport Network (OTN) dedicated line bearer network, such as poor delay performance, low service opening efficiency, and low network intelligence, the paper proposes the networking strategy of the new generation government enterprise dedicated line bearer network. It gives the application suggestions of 100/200 Gbit/s, packet enhanced OTN, OTN cluster, Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer (ROADM)/Optical Cross-Connect (OXC) and other new transmission technologies. The relevant results are also applied to the commercial deployment of an operator's government enterprise dedicated line bearer network. The results show that the construction of the new generation government enterprise special line bearer network has significant economic and social benefits. The delay of the operator's network in the key financial direction has reached the leading level in the industry. The opening time of the private line service has been shortened from the previous average of 60 days to 15 days. At the same time, the operator has the ability to automatically open the end-to-end service.
With the new concept of computing force network being put forward, how to manage, cooperate and deploy after the integration of computing power and network has become an urgent problem for telecom operators. To better solve the problems of unified management, perceptual dispatch, and collaborative arrangement of multi-dimensional resources such as network, computing, and storage, we study from the direction of computing force network management and control. Then we investigate the overall architecture design of computing force network management and control system, the core capabilities, and the evolution of underlying network technology. Based on the principle of "the network changes with the computing force, and the network strengthens the computing force", the collaborative mode of "horizontal connection and vertical dispatch" of the computing force network is formed with the help of the management and control system capabilities. Eventually, we believe it will effectively support the development demands of computing force network business and help the development of the national "Eastern Data and Western Computing" project.
At present, the performance demand of power communication service for bearer network is constantly increasing. Software Defined Optical Network (SDON) technology drives the integration of power communication and SDON technology with its advantages of openness and softwareization. The index system and evaluation method established based on traditional optical transmission network cannot reflect the characteristics of SDON architecture and its influence on bearer performance of power communication network service. In this paper, a new index system is constructed based on the performance requirements, influencing factors and the influence of different SDON architectures on the service performance of power communication business. The decision matrix was determined according to the contribution degree of the index to each attribute. The Ordered Weighted Average-Extended-Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (OWA-E-TOPSIS) multi-attribute decision making method was proposed to realize the index screening. The weight distribution of the selected indicators is carried out by Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), and the examples are collected. After the pretreatment by utility function method, the index value aggregation is carried out. By comparing the evaluation results of each instance, the feasibility of the index system and evaluation method are verified, which provided a basis for the application of new technology and new business support of electric power communication network.
Free Space Optical (FSO) communication systems are easily affected by atmospheric turbulence effects. In order to reduce the Bit Error Rate (BER) of the system under saturated turbulence condition, and considering the requirement of maximum diversity gain under limited Signal Noise Ratio (SNR) in practical engineering, it is necessary to study the diversity performance of the system to obtain the relationship between diversity gain and parameters such as SNR and system link number. This article uses Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output (MIMO) technology to design a MIMO-FSO system based on Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM). The performance of the system in a negative exponential distribution channel model is analyzed, and the BER calculation formula and closed form expressions of diversity gain related parameters (such as Diversity Order (DO), Incremental Diversity Order (IDO), and speed of convergence (SOC)) are derived. Simulation experiments are conducted using mathematical software such as Matlab to verify the accuracy of the derived formula through Monte Carlo simulation. The simulation results show that MIMO the technology can significantly reduce the BER of FSO systems without increasing the transmission power and receiving aperture area. Moreover, in saturated turbulent channels, when the number of system links increases or the turbulence intensity decreases, the diversity order increases to the theoretical maximum with the SNR at a faster rate. The MIMO technology effectively suppresses the negative impact of atmospheric turbulence on the system and significantly improves system performance. When conditions are satisfied, using more transmitters and receivers can achieve higher diversity gain in the system under limited SNR. However, it is also necessary to consider the deployment cost and installation difficulty in actual engineering to choose the appropriate number of links.
Multi-carrier modulation technology is an advanced modulation method commonly used in broadband communication systems. However, multi-carrier signals will produce a very large Peak to Average Power Ratio (PAPR) in the time domain, which will lead to non-linear damage and seriously affects the performance of system. In this paper, a joint PAPR reduction technology enabled by neural network-based coding and companding is proposed. The frequency-domain coding is implemented by a fully connected layer, which greatly reduces the complexity and difficulty of network training. A small proportion of spread spectrum is introduced to provide coding gain, and the time-domain companding network uses a nonlinear convolutional neural network to reduce PAPR. The effect of the scheme is shown through simulation under various parameter conditions, and compared with various schemes. The simulation results show that the scheme can reduce PAPR by 5 dB while introducing rare distortion. Finally, the scheme is experimentally verified. The experimental results show that the Bit Error Ratio (BER) is reduced by 75% compared with the clipping scheme when the PAPR is reduced by 5 dB, which verifies the feasibility of the scheme.
To simplify the structure of real-time coherent Free-Space Optical (FSO) / wireless systems and reduce costs, this paper implements a low-cost FSO system based on bandpass Delta-Sigma Modulation (DSM) technology. A 256-ary Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (256-QAM) signal with a bandwidth of 400 MHz and a rate of 1.6 Gbit/s is generated to realize a 10 Gbit/s Polarization Division Multiplexed-Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (PDM-QPSK) signal after DSM. The real-time transmission in a 50 m FSO link with a sensitivity of -46.2 dBm is achieved. The experimental results indicate that the combination of coherent detection and DSM is a promising technology for future optical wireless scenarios.
Visible Light Communication (VLC) has become an effective underwater communication technology due to its advantages such as fast transmission speed and strong confidentiality. When light propagates underwater, it is prone to scattering, resulting in a decrease in the energy of light propagation with the increase of transmission distance. Therefore, improving the responsiveness of the receiving end is the key technology to achieve underwater VLC. This article first designs a new holographic waveguide focusing system for the front end of the detector, which can effectively improve the signal-to-noise ratio of underwater detectors. Then, we construct a low-cost antimony sulfide thin film detector with weak light detection capability. Based on the built VLC system, the experimental results show that the dark current of the receiver detector is only 10-7 A/cm2, with a 3 dB bandwidth of 220 kHz, a response of 0.2 A/W, and an external quantum efficiency of over 70% in the blue green light band. Therefore, the new antimony sulfide thin film detector combined with a holographic waveguide focusing system can achieve weak light detection of visible light, making it a very effective underwater visible light receiving system.
Non-Line-of-Sight (NLOS) Underwater Wireless Optical Communication (UWOC) is mainly realized through the air-seawater interface reflection or the scattering of light by particles in seawater. It can effectively solve the link alignment issues of Line-of-Sight (LOS) underwater wireless optical communication. This paper summarizes the research progress of NLOS UWOC technology in the aspects of channel model, simulation and experiment. At present, scholars mainly explore the effects of water quality, wave, turbulence, modulation technology, receiving and sending terminal configuration on the performance of NLOS UWOC link. Few scholars have studied the effects of complex hydrodynamic and water quality factors, non-linearity of light source, non-linearity, sensitivity and noise of detector on the performance of NLOS UWOC and effective solutions. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out more in-depth channel model, simulation and experimental research in the future, so as to promote the development of NLOS UWOC technology.
In underwater mobile visible light communication systems, the received optical power varies significantly when the transmission distance changes due to the large intrinsic absorption of water. This paper proposes an underwater mobile visible light communication technology based on Gain Feedback Control (GFC), which expands the dynamic range of both communication distance and Field of View (FOV). At a moving speed of 0.13 m/s, we achieved real-time duplex video transmission with adjustable communication distances between 0.9~5.2 m, data rates of 5.0 Mbit/s, video pixels of 800×600, and Frames Per Second (FPS) greater than zero. Compared with the system without GFC, the dynamic range of communication distance and receiving FOV angle has expanded to 5.3 and 2.8 times, respectively. In order to further verify the performance of the system, we measured the average scintillation index, data transmission outage probability, and Bit Error Rate (BER) of the system at different moving speeds. Within the dynamic range of communication distance, as the moving speed increases, the average scintillation index and BER correspondingly increase. However, even when the moving speed reaches 0.83 m/s, which is the maximum speed of the system, communication remains uninterrupted. Our results indicate that the system has good robustness and has good potential underwater mobile communication applications.
In underwater optical communication systems, timely acquisition of distance information with the receiving end and high-speed communication are required. This paper proposes to integrate the monocular ranging function into the underwater blue-green laser communication system to realize the underwater optical communication ranging by integrating short-distance visual ranging and long-distance laser ranging. Using Monte Carlo method simulation, an underwater laser signal channel transmission model is established to simulate underwater laser spot images under different target sizes, distances and water qualities. We analyze the influence of these three factors on the accuracy of underwater monocular ranging. Considering the influence of spot diffusion and contrast reduction in simulated images on ranging accuracy, a monocular ranging algorithm is proposed that combines image enhancement and Zernike moments subpixel edge detection for small-sized underwater light source targets to improve the accuracy of the monocular ranging algorithm. Laboratory pool experiments were conducted to verify that the algorithm accuracy can meet the requirements.
The transmission characteristics of laser in four types of harbor water were studied using Monte Carlo method simulations for the characteristics of strong absorption and high scattering of water in marine harbors. The effects of water quality parameters and transmission distance on the optical signal power, impulse response and spot quality were quantified and analyzed at certain optical wavelengths, optical energies and divergence angles. The analysis shows that the attenuation characteristics of laser remain consistent as the attenuation length increases when the optical signal is transmitted in the four types of harbor waters. The rate of attenuation of the optical power also does not conform to the linear relationship described by Beer's law. Under the same water quality conditions, the width of the optical pulse, the size of the light spot increases with the attenuation length. However, when the attenuation length is transmitted from 20 to 30, the width of the optical pulse is almost unchanged, and the change in the amount of light pulse spreading is less than 1 ns with the size of the light spot increases continuously. In addition, at the same attenuation length, the light pulse and the spreading amount of light spot with the water quality attenuation coefficient increases and decreases.
Underwater Wireless Optical Communications (UWOC) is an emerging high-speed underwater communication technology that has gradually attracted widespread attention in academia and industry due to its advantages of high transmission bandwidth, electromagnetic interference resistance, low power consumption, and small size. Although light has a larger attenuation in underwater transmission than acoustic wave, its transmission distance can still reach hundreds of meters, which is sufficient to meet the requirements for sensor data transmission. However, UWOC technology is still in an early stage of development, with most experiments being conducted only in laboratory water tanks. Therefore, unified performance testing models and methodologies are required due to different testing methods for UWOC. In order to objectively evaluate the performance of a UWOC system, this article attempts to propose the general testing method, model and evaluation indicators for UWOC systems, to promote the development of UWOC technology.
A dual-wavelength transceiver separation method is proposed for the problem of self-interference limiting the system communication performance in Full-Duplex Underwater Wireless Optical Communication (FD-UWOC) systems. Based on the Monte Carlo numerical simulation, the effects of self-interference on the performance of 450 nm single-wavelength, 525 nm single-wavelength and dual-wavelength FD-UWOC systems are analyzed under three typical water qualities of Jerlov I, Jerlov IB and Jerlov II. The simulation results show that the poorer the water quality, the stronger the self-interference. It is also shown that the enhancement of self-interference will significantly reduce the Optical Signal to Noise Ratio (OSNR) of FD-UWOC, which limits the longest transmission distance of the system. The FD-UWOC system using the dual-wavelength transceiver separation method can bring about 60 dB improvement in OSNR compared with the single-wavelength FD-UWOC system, which can achieve a longer transmission distance. An 80 m improvement in Jerlov II water quality, and an effective transmission distance of more than 100 m in Jerlov I and Jerlov IB water quality are achieved. These results provide some reference significance to the design of FD-UWOC system.
Underwater Visible Light Communication (UVLC) has great advantages of high transmission rate, large capacity, low latency, and low cost, which has become a feasible and attractive alternative in the field of underwater communication, with broad application prospects. However, UVLC performance is limited by bottleneck issues such as bandwidth limitations and various linear or nonlinear effects. In order to alleviate these problems, we studied geometrically-shaping based Amplitude Phase Shift Keying (APSK) modulation and coding mapping. A waveform-stage post equalizer based on Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network (BRNN) is also proposed. In addition, a waveform-to-symbol receiver based on Deep Neural Network (DNN) is proposed to replace the traditional matching filtering, down-sampling, post-equalization and other operations. Compared with traditional receiver, the dynamic range of voltage using BRNN based post equalizer is improved by 170 mV(69%) and it is improved by 245 mV(100%) using waveform-to-symbol receiver based on DNN. In the paper, a waveform-stage post equalizer based on BRNN and a waveform-to-symbol receiver based on DNN are experimentally verified to be promising schemes in future UVLC.
High-speed Underwater Optical Wireless Communication (UWOC) can achieve Gbit/s signal transmission rate, which is of great significance for modern underwater applications. This paper first describes the development process of UWOC, and then compares different kinds of UWOC. Finally, we summarize the research status of high speed UWOC system, and discuss three parts of high speed UWOC: light source, receiver and signal processing. It is expected that this paper can bring help to the research and development of high-speed UWOC in the future.
Aiming at the problem of spectrum scarcity faced by Vehicle to Everything (V2X) communication, a deep reinforcement learning method is proposed to manage V2X spectrum resources. Firstly, the V2X communication model of a single vehicle to infrastructure link is established. Combined with the constraints such as frequency spectrum subband and transmission power, the optimization problem is constructed to maximize the comprehensive efficiency of V2X communication network. Secondly, considering the non-convexity of the optimization problem, the communication model can be regarded as a Markov decision process. Then, the Dueling-Deep Q Network (Dueling-DQN) algorithm is introduced to obtain the optimal spectrum subband selection and transmission power allocation strategy to maximize the comprehensive efficiency of V2X communication network. Finally, the simulation is carried out on tensorflow software platform to verify the performance of the proposed method. The simulation results show that Dueling-DQN algorithm can obtain higher link performance and V2X communication network efficiency compared with other algorithm.
The transmission line forms of the power divider mainly include microstrip line, stripline, waveguide structure, etc, among which the connection between stripline structure and other transmission lines is a challenge. In response to this challenge, this paper proposes a hybrid transmission line one-to-four power divider with a stripline opening and directly connected to microstrip line. Through the analysis of the basic principles of the power divider via electromagnetic simulation software, the power divider is modeled and simulated, and the design method is verified by physical verification. The power divider has an input and output reflection coefficient of less than-10 dB and the isolation of 15 dB in the frequency range of 2~6 GHz, which achieves a good design effect. The bending design of the power divider meets the design requirements of miniaturization. This paper provides certain reference value and significance in the future research.
The effective and efficient refractive index of a multilayer optical waveguide is computed by taking into account the various order modes of the waveguide, such as the Quasi-Transverse Electric/Transverse Magnetic (Quasi-TE/TM) mode. According to the effective refractive index method, the effective refractive index of the Quasi-TE/TM mode is calculated from the electromagnetic field curve distribution calculated for each mode in the 6-layer loss optical waveguide compute the effective refractive index each order of TE/TM mdes. Further, we analyze the dependence of the waveguide properties on the structure. We conclude that the mode effective refractive index and mode order do not decrease monotonicallythe lossy waveguide mode is more prevalent. The research work in this paper can be used as the theoretical basis for the design, fabrication and application of practical optical waveguide devices.
The accurate evaluation of the communication quality of the interconnection link of the data center is an important basis to realize the coordination in the data network. In this paper, a hybrid amplification model for all-optical data center interconnection networks based on wavelength selective switches is established, which can quickly evaluate indicators such as optical signal-to-noise ratio and bit error rate in the interconnected links. In this paper, the data center interconnection link under the condition of no repeater amplification is discussed. The amplifier selection schemes under different interconnection distances are given. Through the simulation, the influence of different path selection on the communication quality of the interconnection link is compared under the conditions of the same interconnection distance and optical power gain. According to the corresponding theoretical model and algorithm, the optimal routing of the data center Internet can be established.
For the problem of inhomogeneity of the output optical power of multiple output ports, the paper designs a 1×4 Multimode Interference (MMI) coupler based on Silicon-On-Insulator (SOI) and proposes a new method to optimize its homogeneity. A tapered waveguide is used at the input/output of the coupler. To improve the uniformity of the MMI coupler, an unequal-width design is used for the tapered waveguide at the output. After optimization, the uniformity of the four output ports is as high as 0.007 4 dB, while the total insertion loss is only 0.058 dB. According to this method, the transmission constant of the output, avoid crosstalk between waveguides, and achieve an improvement in the uniformity of the output port of the MMI coupler.
Aiming at the problem of low accuracy and sensitivity of outer strand breakage monitoring of optical cable, a high-precision monitoring method of outer strand breakage of optical cable based on optical fiber temperature sensing is designed. The high-speed data acquisition circuit, signal amplification and photoelectric conversion circuit of optical fiber temperature sensor are analyzed to obtain the optimal monitoring mode. The optical fiber temperature sensor is arranged on the optical cable to collect the outer strand breaking temperature data. Wavelet de-noising method is introduced to construct the signal model of optical cable outer temperature data, separate the effective signal and noise, and realize the high-precision monitoring of optical cable strand breakage. Taking 24B1-45 and 24B1-08 Optical Fiber Composite Overhead Ground Wire (OPGW) optical cables as examples, the experimental results show that the signal-to-noise ratio of optical fiber temperature sensor can reach 152 and 157 dB, and the response frequency can reach 6 230 and 6 310 times/s. After the application of this method, it can ensure that it is not subject to too much interference with high monitoring accuracy, and meet the requirements of high-precision monitoring. Therefore, it can effectively detect the broken strand of the outer layer of the optical cable through the temperature, which provide a reliable guarantee for the fault monitoring of the outer layer of the optical cable in remote areas.
As an important part of the power Internet of things, the distribution field area network is the "last mile" infrastructure of the power Internet of things. It can solve the communication problem of the last mile of the power Internet of things. In order to meet the high real-time and high reliability requirements of distribution field area network control services and improve the coverage and reliability of the network, a highly reliable and fast routing optimization algorithm based on Dijkstra algorithm is proposed. The field high-speed power line carrier and radio frequency communication methods of the field area network have complementary advantages. The nodes select the most reliable communication link to transmit data through the hybrid routing table, and consider the reliability and real-time constraints at the same time. The simulation results show that the high-reliability routing optimization algorithm of the distribution field area network can effectively increase the coverage capacity, the number of successfully transmitted services and the average routing reliability.
In the era of 5th Generation Mobile Communication Technology (5G) communication, hardware products such as optical modems and routers are updated iteratively. As one of the key technologies of passive optical network, Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) constantly optimizes its own performance. The functional complexity of the chip is increasing, and the verification of its logic function is particularly important. This paper presents an architecture of DBA module verification platform in passive optical networks. Based on the verification methodology framework of Universal Verification Methodology (UVM), the platform calls the System Verilog (SV) reference model. It can cover a large number of scenarios with a few test cases, and realize the verification and self checking of DBA traffic requirements and authorized function points. The coverage rate of Register Transfer Level (RTL) code can reach more than 95%. The simulation results shows that the verification platform can support the system level verification of DBA, and the framework reusing and automatic data comparison. The proposed architecture can meet the requirements of verification, and provide an efficient and comprehensive verification environment for the performance test of DBA, and greatly improve the verification efficiency.
As one of the main applications of quantum cryptography, Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) is a promising secure key transmission method. Compared with traditional communication methods, QKD protocols based on the basic principles of quantum mechanics have unconditional security in theory. In general, the preparation and transmission of quantum states during QKD require the encoding, transmission, and measurement of photons. In recent years, QKD has made great progress in theory and engineering applications, and has also promoted the deployment of QKD networks all over the world. This paper focuses on several recent works on hybrid continuous-discrete variable QKD protocols. Combined with the coding method of discrete variable QKD and the detection method of continuous variable QKD, the advantages and disadvantages of building a QKD channel in practice are analyzed. Given the current stage of hybrid continuous-discrete variable QKD, we summarized its potential research priorities and difficulties in the future.
With the continuous development of Internet technology and the continuous expansion of network scale, new network services emerge in an endless stream. In order to ensure the quality of user service, accurate and rapid classification of application traffic is the focus of current research. The traditional service identification method is based on protocol or specific service classification, which is suffered from low applicability. Combining traffic characteristics and machine learning methods, this paper proposes a traffic identification method based on the fusion of Generative Adversative Network (GAN) and Extreme Gradient Lift Boosting (XGBoost). Firstly, the traffic characteristics representing service resource requirements. Then GAN algorithm was improved to expand a few class samples to solve the problem of low model accuracy caused by the unbalanced distribution of data sets in the process of application identification. Finally, the random forest algorithm was used to select the feature, and the XGBoost algorithm was used to complete the model training. The results show that the accuracy of this method is 97.32%.
Recently, Radio over Fiber (RoF) technology has become a hot research topic in the broadband communication access network field and has attracted much attention in the industry. This is mainly because the technology makes full use of the massive bandwidth of optical fiber transmission and the application advantages of flexible coverage of wireless communication. In the evolution and development of RoF technology, multi-dimensional multi-order modulation has important scientific research significance and practical value because it can improve the system bandwidth utilization and reduce the signal transmission and receiving cost. This paper summarizes the research progress of traditional amplitude modulation, typical multi-dimensional multi-order modulation and some representative new multi-dimensional multi-order modulation technologies. We also briefly analyzes the application prospect of multi-dimensional multi-order modulation technology in RoF system.
Industrial IoT (IIoT) infrastructure for smart manufacturing refers to common facilities based on IoT that support smart manufacturing in industries or sectors. It is independent from the products and production process in specific factories. This article provides requirements and framework of IIoT infrastructure for smart manufacturing to help service providers implementing their system according to the needs of smart manufacturing, and merge existing and newly developed IIoT infrastructures, in order to give the stakeholders of smart manufacturing guidance for their applications.
Due to it is irreplaceable physical characteristics, Hollow core optical fiber has become a precious basic research topic for scientific research institutions. However, the industry has been keeping a wait-and-see attitude because of its overall performance and supporting applications are not mature. In recent years, with the continuous optimization of the loss performance, and the successful promotion of several industrial application cases, hollow core fiber has gradually been paid more attention by the industry side. In this paper, three types of hollow core fibers: hollow core bragg layered fiber, hollow core photonic bandgap fiber and hollow core antiresonant fiber, are reviewed. The paper is mainly focused on their optical principles and testing methods, and combined with the application of communication, laser power delivery and sensing fields to analyze the advantages of hollow core fiber. Finally, the future technology development trend of hollow core fiber is prospected.
In order to solve the problem of response speed and improve the far-field divergence angle characteristics of the traditional Selective Area Growth-Duble Stack Active Laser-Electro-absorption Modulated Laser (SAG-DSAL-EML) in a high-frequency modulation environment, this paper uses the iron-doped buried technology to the Elector-absorption Modulated Laser (EML) structure was optimized, and the SAG-DSAL-EML with a 1 310 nm iron-doped buried structure of InGaAsP/InP material designed and a sample chip fabricated. The active area of the new SAG-DSAL-EML a mesa structure, and the two layers of the SAG-DSAL-EML epitaxially grown InP layer. At the same time, the laser part and modulator part of the designed iron-doped buried structure EML are numerically and simulated by Advanced Laser Diode Simulator (ALDS), and High Frequency Structure Simulator (HFSS). The results show that compared with the traditional multiple quantum well structure, the threshold current of the SAG-DSAL structure laser is reduced by 13% ompared with the traditional ridge waveguide structure, the lateral confinement capability of the iron-doped buried structure is improved by 52%. The difference is reduced by 40% and has a smaller far-field divergence angle ompared with the traditional PNPN buried structure, the response bandwidth of the modulator with the iron-doped buried structure at -3 dB is increased by about 24%. The sample chip is tested, and the test shows that the threshold current of the laser is 14.5 mA, the Side-Mode Suppression Ratio(SMSR) is 45.64 dB response bandwidth of the electro-absorption modulator -3 dB is 43 GHz under the injection current of 70 mA, which meets the basic requirements of high-speed laser communication.
Due to the lack of domestic 980 nm pump laser design experience and production process, the key technology of high power 980 nm pumped laser to break through. In this paper, a 980 nm pump laser with 400 mW output power has been successfully developed by using a domestic solution, including the design and implementation of chips, gratings and coupling fibers. By using the all metallized package directly coupled with wedge-shaped fiber and selecting the double grating structure for wavelength locking, the wavelength stability of the 980 nm pumped laser with 400 mW output power in the operating temperature range of -50~75 ℃ can reach 0.01 nm/ ℃. Moreover the 980 nm pump laser has passed the 800 mA charge aging at 75 ℃ for more than 5 000 h. This has laid a foundation for the research of domestic pump lasers with high reliability.
High speed directly modulated semiconductor laser offers high speed transmission rate with high reliability and low cost, making it a cost-effective light source choice for 5th Generation Mobile Communication Technology (5G) fronthaul and data center applications.There have been many researches on the performance improvement of high-speed directly modulated semiconductor lasers.This paper reviews the development of high-speed semiconductor lasers from the aspects of uncooled wide-temperature operation research and ultra-high-speed bandwidth improvement.We also briefly introduce our work in this area.
Submarine optical fiber composite cables are widely used in cross-ocean information and energy interconnection projects play a key role in the national marine strategy. the environment condition is complex, different types of mechanical damage will directly affect the safety of the submarine cable. The finite element simulation analysis provides a low-cost and high-efficiency theoretical method for the safety monitoring through the simulation of different working conditions. In order to summarize the existing technology and evaluate the future development direction, this paper the finite element simulation analysis of submarine cables under tensile, torsion and bending load summarize the research results of submarine cable mechanical damage from anchor and natural ocean current, which can provide reference for monitoring technology such as optical fiber sensing. Finally, the simulation technology is summarized and prospected.
The strain sensitivity of bare fiber grating under the action of acoustic wave is too low, which is difficult to detect the effective reflection wavelength change. In this paper, the longitudinal sensing of fiber grating is used as a model, and a layer of thickness far exceeding the inner diameter of the fiber is coated around the grating. Low Young's modulus cylindrical coating is used to increase the strain sensitivity of the fiber grating. We also use the linear region of the reflection spectrum of the phase-shift grating as the edge of the edge filtering method to improve the sensitivity of laser detection. Transmission matrix method is then applied in the simulation to analysis the reflection spectrum of grating and reflectance curve of laser. The simulation results show that the strain sensitivity of the longitudinal sensing model of acoustic wave is better than that of the transverse sensing model. The coating layer with low Young's modulus can significantly improve the strain sensitivity of the grating. Under the action of acoustic wave with frequency lower than 1.7 kHz.The longitudinal sensing sensitivity of the fiber grating coated with polyurethane coating reaches 6.1 nm/MPa, which is 381 times higher than that of the bare fiber grating. Combined with the phase-shift grating reflection spectrum linear region, the comprehensive sensitivity is improved by 2 203.6 times, effectively improving the acoustic wave detection sensitivity of the grating.
In view of the problems in transmission capacity of illumination guidance system, this paper presents a high speed of 2.5 Gbit/s optical system based on gigabit transceiver. The system takes gigabit transceiver as the core device. It is used to achieve a series of processing with multiple data types and multiple interface in optical fiber transmission and Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA). It ultimately achieves the high-speed optical fiber transmission of serial data. The results show that the system can increase the processing rate of the data from guidance array to ground console. It also reduces the number of equipment in illumination guidance system, which breaks through the limit of transmission distance between guidance array and ground console.
In the process of anti-interception of information, due to the weak control ability of data nodes, data is easily lost and information security is not high. An anti-interception method of optical fiber communication physical layer based on chaotic mapping is studied. The existence of the intercepted signal is determined by optical fiber signal detection and identification, and the ciphertext matrix is constructed based on the chaotic map encrypted image. The physical layer communication code is jointly transmitted to realize the information exchange between the receiver side and the transmitter side. We establish the anti-interception model of the communication physical layer to achieve the goal of anti-interception of the optical fiber communication physical layer. In the constructure of optical fiber communication network, a set of images with practical significance are selected as test samples. The proposed method and the traditional method are used for comparison. The experimental results show that the image data can be fully encrypted based on the proposed method. It has strong anti-interception performance, and the data information in the image can be retained in the image transmission, However, the traditional method loses 15 groups and 12 groups respectively, indicating that the proposed method has better performances.
The Guided Acoustic Wave Brillouin Scattering (GAWBS) in fibers will be excited at a low optical power level, which can cause large impairments on high-capacity spatial division multiplexing optical fiber communication, digital coherent transmission and optical quantum transmission. For spatial division multiplexing optical fiber communication system, we theoretically and experimentally investigate the characteristics of GAWBS in the self-made uncoupled seven-core four-mode fiber. The results indicate that, the cores exhibit the significant differences of GAWBS characteristics depending on their distances from the fiber center. In future, the disparate GAWBS noise compensation method for each core can be utilized to achieve a high signal-to-noise ratio for spatial division multiplexing transmission with low error rate.
Multi Core Fiber (MCF) is an important transmission medium of Space Division Multiplexing (SDM) technology, which can significantly enhance the communication capacity of existing optical fiber. However, MCF has the problems of high structural complexity, difficult to test, and no test standard for parameters. According to the structural characteristics, combined with the technical experience in the development, this paper standardize the splicing method and the parameters testing method of MCF, which lays the foundation for the large-scale commercialization of MCF in the future.
The scientific research of Hollow Core Anti Resonant Optical Fiber (HCARF) has made a great breakthrough progress, which is expected to break through some inherent limitations of traditional optical fibers. The HCARF guides the light beam in the air core, which has incomparable advantages in transmission and application compared with traditional optical fibers. Therefore, HCARF has become a hot research topic in the field of optical fiber communication area. In this paper, the light guiding mechanism of HCARF is introduced. The capacity advantage of hollow fiber in optical fiber communication system is analyzed. The development opportunities and challenges of HCARF are elaborated. It is beneficial to provide some reference value for the next generation of large capacity ultra-wideband long-distance transmission optical fiber in China.
In order to solve the problem of all-optical communication network capacity and spectral efficiency, a two-cavity six-channel Wavelength Division Multiplexer (WDM) based on the coupling characteristics of point-defect cavity and line-defect waveguide of Two-Dimensional (2-D) photonic crystal is proposed in this paper. 2-D finite-difference time-domain method is used to analyze the performance parameters. Considering the influence of relative refractive index, the coupling mode of double resonators and single straight waveguide is selected to achieve the wavelength division multiplexing of 1 451, 1 487, 1 557, 1 658, 1 440 and 1 604 nm. The results show that the multiplexer has a spectral coverage of up to 218 nm, transmission efficiency of each channel higher than 91%, the insertion loss less than 0.43 dB, the cross-talk between channels less than -9.2 dB, and the size of only 13.56 μm×19.21 μm. It is very useful for coarse wavelength division multiplexing in optical communication systems, which also has reference significance for dense wavelength division multiplexing.
Nowadays, it is in an important stage of the development and construction of the 5th Generation Mobile Communication Technology (5G) network, and the problems such as large bandwidth demand, high cost of optical modules and difficulty in laying in the construction of fronthaul networks need to be solved urgently. Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable (QSFP) packages are known to have four channels, while traditional QSFP28 50 Gbit/s optical module designs use only two of them. In this study, a Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) package smaller than the QSFP package is used to make a 50 Gbit/s optical module, which reduced the bottom area by 40.5%, the volume by 52.2%, the power consumption by 42.1%, and the cost of transmitting the same distance optical module by 73.4%. 4 Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM4) technology enables 25 Gbit/s optical devices to transmit signals at 50 Gbit/s, doubling the single wavelength rate. Through the comparative test, the room temperature Transmitter Dispersion Eye Closure Quaternary (TDECQ) is reduced by 20.5%, the sensitivity is increased by 0.6 dB, and the remaining parameters meet the relevant requirements of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.3cd 50 GE Ethernet, which can stably transmit distance of 40 km.
In order to solve the problem of Catastrophic Optical Damage (COD) caused by the rapid rise of the cavity surface temperature during the long-term high temperature operation of the laser, it is proposed that the addition of Al2O3 coating and the thermal insulation structure together at the semi-conductor laser surface, it can reduce the temperature of laser cavity surface and prevent the generation of COD. First, a simplified semi-conductor laser model is established to analyze solid heat transfer. Then, the cavity surface temperature of the laser model is simulated at 550 K when there is no coating and no insulation structure, coating and no insulation structure, no coating and insulation structure, and when the coating and insulation structure act together, the ceramic heat insulation is used in the heat insulation structure, GaAs is used in the cavity surface material, Cu is used in the heat sink and AlGaAs is used in the contact layer. The results of 4 groups of contrast experiments show that the temperature of the cavity surface can be controlled below 393.15 K when the coating and the thermal insulation structure act together. 550 K high temperature in the laser cavity surface coating and thermal insulation structure under the dual protection, can effectively prevent the generation of COD, so that the life of the laser can be improved.
Optical filters are widely used in many applications, including optical communication, spectroscopy, electronics and optical sensors. The Microwave Photonic Filter (MPF) based on Stimulated Brillouin Scattering (SBS) effect not only has the advantages of low threshold and high gain, but also has the characteristics of reconfiguration and tunability. In this paper, we apply MPF to spectral analysis. Using the tunability of the filter, the spectrum of the whole signal can be measured. And the different frequency components of the signal can be extracted by time-sharing. By setting the center frequency of the swept laser in the pump branch of the filter, the output power of the filter is measured by the optical spectrum analyzer after SBS effect generating by the pump excitation, so as to analyze the spectrum of the signal light. The results show that with the increase of pump power, the filter gain and Out of Band Rejection Ratio (OOBR) first increase and then decrease. The inflection point is about 5 dBm and the dynamic range of the filter is from -35 to -20 dBm.
During daily operation of Substation, if Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS)equipment breaks down, it will lead to the suspension of substation power supply, and national production and life cannot be guaranteed. This paper discusses how to locate the breakdown of GIS efficiently and effectively. The Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) system described in this paper is combined with Support Vector Machines (SVM) in machine learning method, which can realize fault location and facilitate fault elimination. At the same time, it is of great significance to restore the power supply of substation in time.
Recent research results show that great progress has been made in improving the generation rate of physical random numbers. However, there are still some defects such as complex generation process and large volume. To solve these problems, this paper theoretically proposes a scheme for generating random numbers using mode hopping of Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VCSEL) with optical feedback. The VCSEL is perturbed by the optical feedback to generate the mode hopping. The square wave signal then modulates the injection current, periodically restarts the VCSEL to switch from the non-emitting state to the mode hopping state, and finally outputs a random pulse sequence to realize the random number generation. The results of this paper show that unbiased random numbers with verified randomness can be generated continuously at a rate of the order of Gbit/s. Our scheme eliminates the need for optoelectronic conversion and post-processing operations, simplifing the current random number generation structure, which has the potential to realize a low-cost photonic integrated random number generator.
In advanced high-speed fiber optic communication systems, due to the introduction of dense wavelength division multiplexing technology, the signal spectral interval is getting narrower and narrower, and the traditional out-of-band Optical Signal-to-Noise Ratio (OSNR) monitoring technology is no longer accurate. Therefore, further study is required in the low-cost in-band OSNR monitoring scheme. A Deep Neural Network (DNN) link OSNR monitoring scheme for Intensity-Modulation and Direct Detection (IMDD) system is proposed. We used a 5-layer DNN trained from 550 000 datasets to successfully estimate the OSNR of the 2 GBaud On-Off Key (OOK) signal in the range of 5 to 15 dB, and the Mean Absolute Error (MAE) is less than 0.8 dB.
With the rapid development of satellite internet, the shortage of bandwidth and spectrum resources has become increasingly prominent.Satellite laser communication has the characteristics of large bandwidth and no spectrum constraints, which makes it an effective means to alleviate the shortage of radio frequency resources and improve the communication bandwidth.Through the investigation of the development of satellite laser communication at home and abroad, this paper summarizes the future technical development trend in this field.The key technologies such as network reconstruction and efficient coding are studied via simulation, which provide theoretical and technical reference for the research of satellite laser communication in China.
The development of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) discipline promotes the progress of information processing technology. At present, the Spiking Neural Network (SNN) known as the third generation ANN is widely attracted more attention in the industry because of its advantages of behaving more biologically interpretable and more suitable for the implementation of ANN hardware, and it has been successfully applied to pattern recognition, medical imaging, intelligent control and other fields. Constrained by the fact that electronic chip manufacturing process is constantly approaching the limit in the " Post-Moore Era" and the performance bottleneck brought by the " separation of storage and computing" in the von Neumann system, photonic computing solutions with low latency, low energy consumption, high bandwidth, and high parallelism applicated to the hardware implementation of SNN has become a hot topic of multi-disciplinary integration in the field of information processing. This paper introduces the origin of the photonic SNN, the research process and various implementation schemes that use the characteristics of optical devices to realize the behavior of spiking neuron and synaptic connection strength thus realizing the SNN, and summarizes the current bottlenecks and challenges of the photonic SNN. And the future development trend of photonic SNN is also prospected.
With the explosive growth of global network traffic and the consequent increase in bandwidth and energy consumption required for data transmission, traditional electronic interconnection architectures are no longer able to meet the requirement of the growing bandwidth and energy conservation. Silicon-based photonics featured as high bandwidth, low energy consumption, and more importantly, compatibility with Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) technologies enables the large-scale Photonic Integrated Circuits (PIC) and Electronic Integrated Circuits (EIC) to be integrated in a single substrate, hence it is regarded as one of the most promising solutions to address these challenges. However, with the increasing frequency of signals and the increasing number of integrated photonics and electronic devices, parasitic effects are becoming more prominent, leading to a significant degradation in the integration density, bandwidth density, and energy efficiency of the chip. 2.5D/3D integration technologies can effectively reduce the electrical interconnect length and chip size, thus reducing parasitic effects and power consumption, as well as increasing integration density. This paper presents different schemes of silicon based optoelectronic integration and its recent advances, and looks forward to the application prospects of 2.5D/3D integration technologies in data communication, Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), biochemical sensing, and optical computing, et al.
In order to meet the communication needs of the new era, the new generation communication network should have the characteristics of faster speed, larger capacity and wider coverage. By mixing different modulation formats in communication networks, the requirements of new generation communication networks can be satisfied. Facing the situation that multiple modulation formats are mixed and variable in future communication networks, the correct identification of signal modulation formats can provide the basis for the subsequent use of digital technique to improve the performance. Machine learning has obvious advantages over traditional methods in feature extraction and classification. The application of machine learning techniques to realize modulation format identification has become a hot topic nowadays. This paper introduces several machine learning methods applied to feature extraction-based classification schemes, and try to summarize the field by analyzing and comparing their applications.
There are problems of interference between Devices-to-Devices (D2D) communication users and cellular users, mutual interference between D2D communication users, and environmental interference caused by the existence of environmental obstacles in the D2D communication system assisted by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS). In order to solve the problems, an optimization algorithm aiming at maximizing the total rate of the system is proposed to maintain the high quality of services among cellular users and D2D communication. Simulation experiments show that the total system speed under the tabu search-successive convex approximation algorithm is improved by 56% compared with the phase shift optimization algorithm. The total system speed under the tabu search-successive convex approximation algorithm is improved by 21.2% compared with the power allocation algorithm.
Faster-than-Nyquist (FTN) technology can improve the spectral efficiency of Optical Wireless Communications (OWC). However, it is affected by the artificially introduced Inter-Symbol Interference (ISI) and atmospheric turbulence, which leads to the degradation of Bit Error Rate (BER) performance. To deal with this issue, a PAM modulated Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO)-FTN-OWC system is proposed, and MIMO technology is utilized to suppress the influence of atmospheric turbulence. Furthermore, the theoretical BER in log-normal fading channel is deduced, and the influence of channel correlation on the BER performance is analyzed. The simulation results show that the BER performance of 2×2 MIMO-FTN system is 9.5 dB higher than that of Single-Input Single-Output (SISO)-FTN system when BER is 10-4. In addition, the MIMO-FTN system has better BER performance than that of SISO-FTN system when the channel spatial correlation coefficient is lower than 0.6.
Generally, an optical switch is only suitable for a narrow and particular field. In this paper, a microfluidic matrix optical switch based on the electrowetting-on-dielectric driving technology is proposed, which can be applied in a wide range of optical communication and optoelectronic systems. It has the advantages of simple structure, convenient operation, polarization independence and easy integration of large matrix switches. Here the structure and working principle of this matrix optical switch are given, and the matrix driving circuit is designed. The operating voltage of the optical switch is 58V. The results show that the response time is 120 ms from "on" to "off" and is 100 ms from "off" to "on". The insertion loss is 0.26 dB, which is much lower than that of general matrix optical switches, and the extinction ratio is 139.7 dB. Moreover, two application schemes are given, namely, a photoelectricity display and a multi-beam array switch. Our work can provide a new idea for large-scale integrated matrix switches and promote the application of optofluidics in optoelectronic systems.
To solve the polarization-ralated losses and polarization mode dispersion problems of silicon on insulator platforms and to improve the efficiency of polarization diversity systems, this paper proposed a polarization beam splitting-rotation-multiplexing integrated device based on Asymmetric Directional Coupler (ADC) and Subwavelength Gratings (SWG) with a thick silicon core layer is proposed, which can convert any input light into a output light of Fundamental Transverse Electric (TE0) Mode. The integrated device consists of three parts: polarization beam splitter, polarization rotator and wave combiner. The Three-Dimensional Finite Difference Time Domain (3D-FDTD) method is used for simulation analysis, and the structural parameters are optimized. The size of the device is 4.5 ●x03BC;m×56.0 ●x03BC;m. At the input wavelength of 1.55 ●x03BC;m, it has a high polarization extinction ratio of 45 dB, and an insertion loss of 0.53 dB. A bandwidth of 75 nm is achieved when the polarization extinction ratio is greater than 30 dB and the insertion loss is less than 1 dB. Therefore, the operating frequency range of the device can cover the entire C-band. Finally, the influence of process error on device performance is analyzed. The integrated device has a compact structure and a higher polarization extinction ratio, which can meet the requirements of modern optical communication and optical integrated systems.
When the data distribution of optical fiber link changes, machine learning can be used to evaluate the transmission quality of link, which needs to recollect data and retrain. This process is time-consuming and complex. Transfer learning directly applies the previously learned knowledge to the current task, which requires less data. Therefore, it is proposed to use two transfer learning methods to realize multi classifier based on machine learning in the correlated optical communication system. The simulation results show that the multi classifier of machine learning combined with transfer learning and fine-tuning technology improves the multi classification index score by more than 0.25 compared with the direct transfer machine learning multi classifier. It is also shown that the impact of sample imbalance is reduced, and each category has high performance. It is proved that the machine learning multi classifier combined with transfer learning and fine-tuning technology can reduce the size of data set, reduce the cost of collecting data set, and improve the efficiency of transmission quality evaluation process in optical fiber link.
This paper proposes a novel Non-linear Camera Assisted-Received Signal Strength (nCA-RSS) algorithm. The basic idea of nCA-RSS is to simultaneously utilize camera and Photo-Diode (PD) to capture visual information and signal strength information to achieve both high coverage and accurate positioning. First, based on single-view geometry theorem, nCA-RSS algorithm estimates incidence angle of visible light based on visual information. Then, based on the estimated incidence angle, nCA-RSS algorithm utilizes signal strength to determine the location of the receiver. Due to the use of visual information, nCA-RSS no longer has orientation limitations. Based on Levenberg-Marquardt, nCA-RSS can use three Light Emitting Diode (LED) to achieve precise 3-Dimensional (3D) positioning. Therefore, compared with perspective n point algorithm, nCA-RSS can achieve high coverage. Simulation results show that nCA-RSS can achieve 80th percentile accuracies of less than 2.5 cm for positioning regardless of the orientation of the receiver.
In order to mitigate the effect of nonlinear noise nonlinear Channel Equalizer (CE) based on Gaussian Processes for Regression (GPR) is proposed and experimentally demonstrated in an intensity modulation and direct detection fiber link. In this scheme, the GPR model is used to estimate the transmitted symbols or the corresponding nonlinear noise after pre-processing. The experimental results show that the nonlinear CE based on GPR has better performance than conventional linear and nonlinear filter-based CE. In addition, it is shown that the GPR model in the nonlinear channel equalization process can be understood as an optimized single-layer neural network model with infinite width.
Aiming at the problem that the current Quantum Random Number Generator (QRNG) cannot simultaneously meet the high-speed and real-time requirements of random number generation in quantum key distribution communication, this paper improves the QRNG scheme based on pulse laser as light source to extract phase information. The random phase information is converted into light intensity information by single-mode Michelson interferometer, and then converted into electrical signal by high-speed Photo Detector (PD). Finally, the real-time quantum random number generation rate of 1.1 Gbit/s is obtained by using 16 bit Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) with 250 MHz sampling rate and 50% extraction rate. A high-speed, real-time and integrated QRNG equipment is realized. At the same time, the advantages of this scheme and continuous laser as light source in principle and system design are compared. QRNG based on pulsed laser light source has passed various tests of China Academy of Information and Communications. The random number output by the product in the process of stable operation can pass 15 test standards specified in the State Cryptography Administration randomness test document GB/T 32915-2016 and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) test standards.
In order to maintain the stability of the transmitter to ensure the quality of the output signal, we propose a novel technique of automatic bias control based on the pilot signal that can be used in high-order modulation formats. The proposed scheme requires loading a pair of orthogonal pilot signals to the modulator and tapping the frequency-shifted local oscillation light with the signal light output from the modulator to achieve coherent detection. The control of the bias voltage is achieved by means of correlation operation and monitoring the value of the correlation coefficient. This scheme combines coherent detection and correlation detection techniques, which can effectively improve the sensitivity and control accuracy of the system. The feasibility of this scheme in high-order modulation systems and the improvement of sensitivity are also fully verified by simulation.
With the development of big data, cloud services, and artificial intelligence, the optical network is developing towards scale and complexity, which suffers from larger probability of network failure. It is necessary to provide dedicated-path protection for each connection request to reduce the loss caused by the network failures. Therefore, in order to guarantee the network survivability, we propose a dedicated-path protection optimization method to improve the network resource efficiency in elastic optical networks with data centers. The simulation results show that the proposed dedicated-path protection optimization method can effectively reduce the blocking probability, improve the network resource utilization, and solve the survivability problem of elastic optical networks in data centers.
With the rapid development of mobile services, big data, cloud services, and artificial intelligence, traditional network services cannot no longer meet the requirements of current network development and solve the problems of the resource allocation and scheduling ossification in the current network. Therefore, by using network virtualization technologies, we can provide the flexible network resource configuration information for users to reduce network cost and improve network resource efficiency. The required bandwidth resources of each virtual link are divided into different transmission line rate by employing mixed line rate splitting. We propose an optimized cost approach for Virtual Optical Network (VON) mapping based on mixed line rate. Simulation results show that the proposed optimized cost approach of VON mapping based on mixed line rate can achieve better optimization and balance in terms of the network cost, frequency slot occupation, the configuration of optical transponders, and optical regenerators.
In response of the comprehensive popularization of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.11 in recent years, the rapid increase of Internet of Things (IoT) data has brought about problems such as high network transmission pressure, difficult data management, and high data security risks. Based on years of experience in WiFi wireless Access Point (AP) management and data warehouse implementation, this article expounds a construction method of wireless AP data warehouse based on anomaly identification and lossy compression. The results show that the abnormal identification and lossy compression of data with high repeatability of wireless AP can effectively solve the problems of high storage pressure and communication congestion in distributed data warehouses which caused by the excessive amount of repeated data of network equipment, and greatly reduce the overall cost when the company implement the data warehouse with IoT datas.
In this paper, we study the deployment problem of distributed dedicated protection services in mobile edge computing. To minimize the total delay, we develop an Integer Linear Programming (ILP) model and efficient polling based heuristic algorithms. Simulation results show that the proposed double polling based algorithm can effectively reduce the total delay of all services and balance loads of the Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) servers.
With the development of 5th Generation Mobile Communication Technology (5G) and the evolution of network architecture, the analysis and optimization of network coverage need to consider comprehensive factors, including not only the link budget of the base station antenna system, but also the geographical conditions and time characteristics of the area covered by the base station. Therefore, a more accurate network coverage optimization plan should be designed. This paper proposes an adaptive network coverage optimization algorithm based on Q-learning. The method first adopts a cellular network coverage prediction model based on data mining, which can predict the coverage situation of the access terminal through the configuration of the antenna of the cell, and verify the accuracy of the prediction based on real data. Then, a network coverage optimization algorithm based on Q-learning is proposed which modifies the action selection strategy of the agent in reinforcement learning process. According to the coverage of each cell, different optimization priorities are set. Combined with the greedy strategy, a cell and its antenna parameters are decided by the agent in each iteration. This method effectively reduces the probability of falling into a local optimum during the iteration process, and the method also has a good performance in reducing the convergence time of the optimization process. The simulation result shows that the algorithm can increase the network coverage by up to 20%.
This paper develops an adaptive and extensible remote monitoring system for seafloor observatory network in the Laizhou Bay marine ranch to realize long-term, continuous and on-line monitoring for marine ranch environment. According to the demand of seafloor observatory network, the control model of the remote monitoring system is established in this paper. And this paper creatively designs the communication mechanism, standardized communication protocol and dynamic management algorithm convenient for the plug and play of a large number of devices in the seafloor observatory network. The algorithm of data quality control is also improved. The application demonstration data of the marine ranch in Laizhou Bay shows that the package loss rate of the system is only 1%, and the success rate of instruction execution is as high as 98%. When adding, deleting and modifying seafloor devices, the system can complete the mapping and analysis data within 2 minutes. At the same time, the data quality control algorithm can effectively eliminate outliers and reduce the error rate to 0.000 81%. The successful application example of Laizhou Bay Marine ranch proves the performance and applicability of the system. It shows that the relevant algorithms in this paper can also be used in other similar systems with adaptive requirements.
In order to further strengthen the operation protection measures of the optical cable and realize real-time monitoring of the hidden danger of external force damage in the optical cable line area, this paper uses the principle of Rayleigh backscattering and coherent detection to design and construct an optical cable external damage event monitoring based on distributed optical fiber vibration sensing early warning system. Using Phase Sensitive Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (Φ-OTDR) technology, the optical fiber vibration signal is collected in real time. The key characteristics of vibration sensing are extracted, and the type of hidden danger is sent to the operation and maintenance staff to locate and warn the hidden danger of external force damage in real time. Field verification results show that the system can simultaneously detect and locate multiple vibration sources along the sensing fiber, and can identify various types of disturbance signals. The monitoring and early warning system has a complete system and a simple structure. The recognition rate of various construction signals is as high as 95%. It realizes double early warning of the type of external breakage and precise location, which can effectively prevent and stop external damage events and improve the work efficiency of anti-external breakage of optical cables.
The optical network has become the most important way to carry power communications. To ensure its high reliability, operators need to detect the cables of the network periodically, which need to enter the substations. However, the large number and scattered location of substations bring challenges to the optical cable detection for the power communication optical network. This paper studies such multi-period optical cable detection problem of optical network in the context of power communication. With the objective of minimizing the total number of entered substations, we developed an Integer Linear Programming (ILP) model and a corresponding heuristic algorithm is also proposed. The simulation results show that the proposed heuristic algorithm can effectively reduce the total number of entered substations and perform close to the results of ILP model.
The traditional Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (OTDR) technology uses back Rayleigh scattering power for fiber detection. In transmission lines with optical amplifier, Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers (EDFA) are mostly used to compensate for the loss of signal light and extend the transmission distance of the signal light. Since the EDFA amplifies the signal, it will generate spontaneous radiation noise, and the continuous accumulation of noise will rapidly decrease the signal-to-noise ratio measured by the OTDR. The paper mainly expounds the principle of Coherent Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (C-OTDR) technology. The detected signal optical power is concentrated to the intermediate frequency by the coherent detection method, and most of the noise can be filtered out by band-pass filtering the frequency signal. It can continuously extend the detection distance through the EDFA. We also propose to use the frequency shift keying method to eliminate the optical surge problem caused by the cascade of multi-stage repeaters in long-distance transmission of submarine cables. Through the development of self-developed coherent optical time domain reflectmeter, the actual test of C-OTDR technology in the simulated submarine cable multi-span transmission system has reached 3 000 km, which fully meets practical conditions.
The visible light positioning system is the hot spot of current indoor positioning technology research. Aiming at the problem of inaccurate azimuth angle acquisition in single-lamp positioning system, this paper proposes a single Light Emitting Diode (LED) indoor positioning system based on marked LED. The scheme uses a single LED light with a non-flickering lamp bead as the transmitter to transmit information while realizing the lighting function. The smartphone acts as the receiver to capture images with bright and dark stripes, and obtain the azimuth angle by combining the geometric features of the projection and processing the algorithm. Then the position of the receiver is obtained by further calculation. The results show that in the actual application scenario, when the experimental heights are 1.75 and 1.45 m. The system can achieve average positioning errors of 6.9 and 6.5 cm, which verifies the feasibility and effectiveness of the scheme.
As the single photon detection greatly improves the sensitivity of a traditional detector, it has enormous potentiality in distance measuring. Photon-counting laser ranging is able to extract the target's trajectory from large amounts of echo information in the case where prior information is unknown. This paper first provided the simulation of echo information produced by photon-counting laser ranging system, and then extracted the trajectory of the target through image processing. Comparing with the theoretical moving trajectory, the error is less than 5 m. Considering its advantages in short distance ranging, the photon-counting laser ranging system can be applied to the Beidou navigation system and solve its accuracy defects caused by environmental factors while cable patrolling.
In order to mitigate the performance fading of Free-Space Optical (FSO) communication system caused by atmospheric turbulence, a multi-aperture receiving scheme based on digital coherent beam combining is used. Digital coherent beam combining relies on the digital phase alignment algorithm to align the different versions of signals in phase. In this paper, the statistical model of combining efficiency for digital phase alignment is derived in multi-aperture FSO receivers by considering the phase alignment errors at each receiving aperture. It can be expressed as a linear function of chi-square distribution by Satterthwaite approximation. Based on this statistical model, we derive the exact expressions of the mean, variance, and probability density function of the combining efficiency. The simulation results show that this model is valuable under the condition of the different number of aperture and signal-to-noise ratio combinations. Combining efficiency is also compared for Equal Gain Combining (EGC) diversity FSO systems with or without considering aperture selection.
Aiming at the modulation problem of high energy efficiency and high sensitivity in the space laser communication system, the Differential Pulse Position Modulation (DPPM) format is studied and applied to the coherent optical communication system. The balance point is found in the system considering power consumption, Bit Error Ratio (BER) performance and bandwidth occupation through simulation and experiment. The experimental results show that in the direct modulation direct detection and coherent optical communication transmission systems, the optical power of the signal path required to reach the hard line is-36.5 and-60.0 dBm respectively when the same transmission channel and the same transmission rate of 1.25 Gbit/s DPPM signal is applied. The optical power margin of the coherent transmission system is increased by about 24 dB compared with the direct detection transmission system. In order to achieve the transmission goal of the hard judgment line, the optical power of the receiver for transmitting the DPPM signal at the rate of 3、6、12、24 Gbit/s needs to be about-49、-47、-42、-36 dBm respectively. It is demonstrated that higher sensitivity and lower BER can be obtained by using DPPM format/coherent detection.
Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) detection algorithm is used to compensate the Mode Dependent Loss (MDL) in Mode Division Multiplexing (MDM) optical fiber channel. The problem of MIMO detection algorithm is that the computational complexity is too high and the performance is degraded with a large number of modes. This paper proposes to apply Massive-MIMO detection algorithms to the fiber channel, The algorithms include Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE), Conjugate Gradient (CG), Gauss Seidel (GS), and Alternating Direction Method of multipliers based Infinity-Norm (ADMIN), and Optimized Coordinate Descent based BOX constraint (OCDBOX) . The result shows that the OCDBOX has the best Bit Error Rate (BER) performance in MDL-impaired MDM optical fiber communication system while higher complexity. The ADMIN has the second best BER performance and lower computational complexity. Therefore, the ADMIN detection algorithm can represent a good candidate in the MDM system with MDL.
The optical transmission system based on all-band is considered to be one of the methods to effectively improve the transmission capacity of optical communication. In addition of the C and L bands, the using of other bands for transmission can fully tap the transmission potential of the existing optical fiber network and solve the bottleneck problem of large capacity communication network. The realization of its key technologies and systems is conducive to promoting the industrialization process of related technologies, which has broad economic benefits. This paper analyzes and discusses the current research status of multi-band optical transmission technology. And then as the focus, the performance difference of S、C and L band is studied by experiments. Based on the devices designed for C and L bands, the experiment of 40 km transmission system covering on S、C and L band is completed by using Polarization Division Multiplexed 16 Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (PDM-16QAM) modulation format, and the transmission capacity can reach 122.4 Tbit/s. The multi-band transmission capability of G. 652.D optical fiber is verified, which provicles an experimental basis for further research on multi-band optical transmission technology.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) devices, as one of the core components of 5G fronthaul network, have developed rapidly in recent years. The fronthaul network has proposed new requirements for WDM devices, components and products. However, the technical requirements and test method standards of WDM devices for 5G fronthaul network are not clear. Through in-depth analysis of the problems encountered in the test of WDM devices, we propose a test method of 5G fronthaul WDM devices, and build the corresponding test system, which is compared with the manual test method. The results show that the proposed test method has 10 times more efficient than manual test method with good consistency.
In view of insufficient security in the next generation passive optical network, an electro-optic hybrid encryption scheme based on MD5 message digest algorithm check is proposed in this paper. In the scheme, Baker scrambling algorithm and 256 bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption algorithm are used to encrypt the picture data. The Low Density Parity Check Code (LDPC) error correction and MD5 check are combined to perform the error correcting coding and check the consistency of the encrypted picture data. In order to strengthen the security of key and MD5 digest distribution, Super Structure Fiber Bragg Grating (SSFBG) is also used to encode them so that they are hidden under the system noise. The simulation results show that after SSFBG coding, the power of the coded signal is as low as-50 dBm, which can achieve the effect of data hidden transmission over the optical fiber channel. Due to the fact that the MD5 check of the received data is added in the scheme, the information changes caused by malicious access attacks cannot be decoded by AES, which improves the security and saves Central Processing Unit (CPU) resources at the same time. Finally, Error rate curve analysis results show that the receiver sensitivity can be effectively reduced by adding LDPC error correction.
Aiming at the problem that the two-dimensional uniformity of the frequency hopping pattern in differential frequency hopping communication is poor, and the frequency hopping frequency is easy to be eavesdropped, this paper designs an encryption scheme based on the pseudo-random sequence of logistic chaotic map to randomly scramble the frequency hopping pattern. After verification, the differential frequency hopping pattern after encryption and scramble is compared with the original frequency hopping pattern. Although the performance of the system is reduced, the correlation between frequencies is reduced, and the two-dimensional uniformity is improved, which has strong anti-deciphering ability.
A hybrid integrated 89 GHz sub-harmonic mixer based on Schottky diode was proposed for meteorological monitoring radiometer. In this paper, based on the theory of millimeter wave mixing technology, a three-dimensional electromagnetic model of diode is established in the field simulation software, and a W-band 89 GHz sub-harmonic mixer is designed based on the three-dimensional electromagnetic model. The simulation and test results show that when the Local Oscillator (LO) is fixed at 45 GHz, the conversion loss is better than 14 dB from 84 to 94 GHz, and the minimum conversion loss is 9 dB. The measured results are consistent with the simulation results.
Distributed Raman Fiber Amplifier (DRFA) is widely used in modern communication systems because it has a series of excellent features. Considering the existing problems of DRFA gain control, this paper studies and improves a method of Automatic Gain Control (AGC) of DRFA by Amplifying Spontaneous Emission (ASE) out of band. In view of the fact that DRFA gain is greatly affected by the performance of optical fiber link, this paper firstly theoretically analyzes the influence of the joint loss at the position 0 away from the pump source in the optical fiber link on the Raman gain control. Then the splice loss at different positions from the pump source is set to be equivalent to the splice loss at position 0. The relationship between Raman gain and out-of-band ASE power is modified so that the AGC of DRFA can be realized more accurately. The Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR) function is integrated in the DRFA module to detect the distance between the joint loss and the pump source and the loss value in the engineering optical fiber link. Experimental results show that the proposed AGC method can control the influence of joint loss on DRFA gain within 0.2 dB.
In recent years, 200/400 Gbit/s transceiver in the form of Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable-Double Density (QSFP-DD) is favored by the market due to their relatively low power consumption and small size for high-density deployment. However, the deterioration of heat dissipation caused by high speed and small size limits the application of QSFP-DD optical modules. In this paper, the finite element method is used to conduct thermal modeling and simulation of QSFP-DD module, and the internal temperature field of 200 Gbit/s QSFP-DD Long Range 4(LR4) optical module in high temperature environment is studied. The effect of thermal pad on improving the internal heat dissipation of the module is verified. The performance of the module in high temperature environment is measured. It provides a reference for the design and application of QSFP-DD transceiver module.
In order to realize tunable multichannel high sensitivity refractive index sensing, a square resonator connected with a Rectangular Groove (RG) is proposed to couple with the highly compact Metal-Dielectric-Metal (MDM) waveguide containing double metal baffles. The transmission spectrums of the proposed waveguide structure have been calculated by the finite element method, which exhibits four sharp, asymmetric transmittance peaks and the magnetic field patterns. Based on the coupling interference between the broadband reflection mode generated by the double baffles and the narrow resonance modes occurred in the composite cavity, the generation mechanism of quadruple Fano resonance is explained. Moreover, the structural parameters of the square cavity and the rectangular groove are changed to study the tunability of the wavelengths of the quadruple transmittance peaks. When the composite cavity is filled with different dielectric media, the calculated sensitivity corresponding to four transmittance peaks are 960, 1 120, 1 320 and 1 560 nm/RIU, respectively. It provides an effective theoretical reference for the design of multi-channel and high sensitivity refractive index sensor.
Aiming at the problem of the interference of camouflage information to the carrier, this paper proposes an information hiding method based on audio technology, and forms a scheme of jointly shaping the camouflage information in the frequency domain and the time domain by the side information. In terms of limiting the interference of the carrier to the camouflaged information, this paper expands the embedding method of the improved spread spectrum modulation when the receiving and sending sequences do not match. The experimental results show that the proposed scheme has a good information hiding effect.
As the optical network structure becomes larger and more complex, optical network faults are more likely to occur. After a network fault occurs, due to the derivative characteristics of network alarms, the root cause alarms will generate multiple derivative alarms. Therefore, after network faults occur, the network management system will receive alarm storms. Due to the complex relationship between faults and alarms, the difficulty of locating network faults, especially multiple faults, has also risen sharply. In response to this problem, the knowledge graph technology that is good at managing massive amounts of information and revealing the characteristics of data is introduced into optical networks. The alarm knowledge graph contains rich relationships between alarms, which can be completed by combining Graph Neural Network (GNN) technology. The knowledge-guided automatic reasoning of the root cause of network faults is in line with the fault location ideas of the operation and maintenance personnel in the operation and maintenance process. Further, the network topology information is added in the fault location process, and the knowledge dimension of the knowledge graph is improved. The limitation of the single-fault scenario is lifted, and a high accuracy rate is obtained in the multi-fault location scenario.
In the Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) space optical communication channel estimation based on photon detection, two schemes for the estimation of signal photon average and background photon average are proposed. Scheme 1 is based on the characteristic of M-order PPM, where only one of the M slots has a signal optical slot. The signal photon average and the background photon average are roughly estimated by comparing the number of photons in each slot in each symbol counted by the photon detector and by counting the total number of photons in each slot in the error correction frame. The proposed method in scheme 2 is based on that in scheme 1. The signal optical slot position is re-determined by decision feedback in the Serially Concatenated Pulse Position Modulation (SCPPM) system. Since the existence of SCPPM accumulator leads to error propagation, the soft information output by decoding is first interleaved, and then mapped from bit to PPM symbols after hard decision and accumulation. Finally, the position of signal optical slot is re-determined to obtain more accurate signal photon average and background photon average.
In recent years, the emerging Deep Learning (DL) technology has made progress in the field of decoding. Current polar code neural network decoder has faster convergence speed and better Bit Error Rate (BER) performance than Belief Propagation (BP) decoding. However, it still has the problem of high computational complexity. Therefore, in order to improve this problem, this paper adopts the idea of improving information update in the iterative process, and proposes a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) Offset Min-Sum (OMS) BP decoding algorithm that improves Left information update (RNN-OMSBP-L) . The simulation results show that, compared with the Deep Neural Network (DNN) BP(DNN-BP) decoding algorithm, this algorithm replaces all multiplications with a cost of 6.25% addition. Compared with the current optimized RNN OMS and approximate BP(RNN-OMS-BP) decoding algorithm, the decoding algorithm in this paper uses improved information to reduce 25% of the addition operations with almost no loss in BER performance, while saving part of the storage space overhead. Under the same BER performance, it reduces the number of iterations by 37.5%.
Aiming at the application research of polar code in optical communication system, this paper proposes the combination of polar coding modulation and optical fiber Module Division Multiplexing (MDM) system. We construct an MDM system based on bit interleaved polar coding modulation, and study the performance of Maximum Likelihood (ML) detection algorithm. The simulation results show that the addition of polar code greatly improves the system performance. Compared with the MDM system without coding, the MDM system with bit interleaved polar coding modulation improves the system performance by about 8 dB under the same Mode Dependent Loss (MDL) . The paper also shows the performance of ML detection algorithm and Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE) detection algorithm in MDM system. The impact of different mode loss on system performance is also studied. Compared with MMSE detection algorithm, ML detection algorithm improves the bit error performance by about 3 dB.
This paper defines the connotation of Digital China. Based on the concept of"Five-in-one"put forward by the Party Central Committee, this paper summarizes the construction logic of Digital China Index System from the three levels of macro objectives, strategy quantification and measurement, and puts forward five core indicators, nine main indicators and four sub item index systems of Digital China. At the same time, various types of efficacy functions, weighted factor analysis and cluster analysis are used to carry out dimensionless processing, weighted calculation and data statistical analysis of the basic data of Digital China index system. Finally, we propose some policy suggestions for the construction of Digital China in the future.