View fulltext
View fulltext
Glucose molecules are of great significance being one of the most important molecules in metabolic chain. However, due to the small Raman scattering cross-section and weak/non-adsorption on bare metals, accurately obtaining their "fingerprint information" remains a huge obstacle. Herein, we developed a tip-enhanced Raman scattering (TERS) technique to address this challenge. Adopting an optical fiber radial vector mode internally illuminates the plasmonic fiber tip to effectively suppress the background noise while generating a strong electric-field enhanced tip hotspot. Furthermore, the tip hotspot approaching the glucose molecules was manipulated via the shear-force feedback to provide more freedom for selecting substrates. Consequently, our TERS technique achieves the visualization of all Raman modes of glucose molecules within spectral window of 400–3200 cm?1, which is not achievable through the far-field/surface-enhanced Raman, or the existing TERS techniques. Our TERS technique offers a powerful tool for accurately identifying Raman scattering of molecules, paving the way for biomolecular analysis.
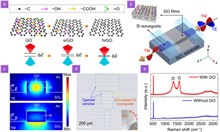
Optical polarizers, which allow the transmission of specific polarization states, are essential components in modern optical systems. Here, we experimentally demonstrate integrated photonic polarizers incorporating reduced graphene oxide (rGO) films. 2D graphene oxide (GO) films are integrated onto silicon waveguides and microring resonators (MRRs) with precise control over their thicknesses and sizes, followed by GO reduction via two different methods including uniform thermal reduction and localized photothermal reduction. We measure devices with various lengths, thicknesses, and reduction degrees of GO films. The results show that the devices with rGO exhibit better performance than those with GO, achieving a polarization-dependent loss of ~47 dB and a polarization extinction ratio of ~16 dB for the hybrid waveguides and MRRs with rGO, respectively. By fitting the experimental results with theory, it is found that rGO exhibits more significant anisotropy in loss, with an anisotropy ratio over 4 times that of GO. In addition, rGO shows higher thermal stability and greater robustness to photothermal reduction than GO. These results highlight the strong potential of rGO films for implementing high-performance polarization selective devices in integrated photonic platforms.