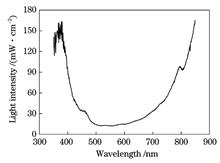
ConclusionsTo summarize, a facile zirconium oxide precursor and annealing process are developed. First, the poor formation of zirconia film is resolved by introducing a new ligand, oleic acid. Second, UV/IR irradiation is used to anneal the zirconium salt. Compared with the traditional thermal annealing, the novel annealing method via UV/IR irradiation can make the zirconium salt with oleic acid undergo decomposition, reduction, and oxidation, forming high-quality ZrOx films. The prepared ZrOx films are characterized and compared with those synthesized via thermal annealing process using UV spectrometer, AFM, and XPS. The results show that ZrOx films with UV/IR light annealing at low temperature (x films with UV/IR light annealing are better than those of the ZrOx films treated with thermal annealing. Our study demonstrates that the ZrOx film fabricated by our facile precursor and UV/IR annealing can potentially be used in the fields of flexible electronic and optoelectronic devices.
ConclusionsThis paper proposes a road marking extraction algorithm based on a vehicle-mounted laser point cloud. Based on the ground attributes of road markings, CSF algorithm is used to obtain ground point clouds, eliminating the influence of nonground point clouds on the extraction of markings; according to the difference of normal vectors on both sides of the road, the area growth method is used to segment and extract road points from the ground point cloud, eliminating the interference of curbs and ground objects on both sides of the road; to speed up the processing efficiency of the algorithm, the pavement point cloud is projected to generate intensity feature images; for the uneven intensity distribution in the extraction of markings, the intensity feature images are divided into multiple subimage to reduce the incident angle and range of the image. To avoid misclassifying subimages that are all roads or markings, the proposed algorithm use the largest interclass variance to classify the subimages and select different thresholds based on the subimage category. Dynamic threshold segmentation is used by the calculation method. Finally, three actual road sections’ point cloud data are chosen for experimental verification in this paper. The results show that the recall rate, accuracy rate, and comprehensive evaluation index of road marking extraction are 92.8%, 96.8%, and 94.8%, respectively, suggesting that the algorithm in this paper is effective and feasible, has some practical application value, and supports the production of high-precision maps in unmanned driving.
ConclusionsOn haze days, the aerosol extinction coefficient decreased as the height increased, whereas the change in extinction coefficient with height was not apparent on clear days. Weather circumstances had an effect on the vertical distribution of aerosols in the Taiyuan Basin. The aerosol extinction effect in the Taiyuan Basin was strongest at 200-300 m above ground, where it was influenced by northwest or westward airflow and regulated by low-level warm advection. Under static and steady weather conditions, low-level warm advection resulted in the production of an inversion layer, with the aerosol extinction effect being strongest at a height of 360 m above the ground. On the ground, the Taiyuan Basin was ahead of the bottom of the high pressure, with quite strong ground winds. The cold advection at 700-850 hPa brought pollutants from high-latitudes to the Taiyuan Basin. The aerosol extinction effect was strongest during the transmission of such pollutants at a height of 1200 m above the ground. Due to the complexity of the influence of meteorological components on the vertical distribution of aerosols, we intend to perform additional research in the future.
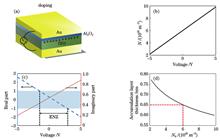
ConclusionsIn this study, a phase modulating metasurface based on ITO film is designed. The combination of the ENZ characteristics of ITO and the plasma resonance effect of the upper metal electrode significantly enhances the light-matter interaction. By designing the metal-insulator-metal (MIM) capacitor structure, a phase modulation range of >330° is achieved under the gate voltage -2-5 V. Consequently, the optical phase array and tunable focal length lens are successfully realized. The designed phase modulating metasurface is significant for applications, such as optical detection, imaging, and communication.
ConclusionsIn this paper, we propose a scheme for optical generation and application of chirp polarity-modulated LFM signal. Furthermore, we generate an LFM signal with quadrupled carrier frequency and bandwidth, whose chirp polarity is controlled by input binary sequqence. The simulation results verify the feasibility of the scheme in frequency-multiplied signal generation, measurement of Doppler frequency shift, and wireless communication. Additionally, we input 4-6 GHz, 5-6.5 GHz, 8-9 GHz LFM signals, generating 16-24 GHz, 20-26 GHz, and 32-36 GHz triangular frequency-modulated signals, respectively, whereas the time-bandwidth product is expanded seven times. Also, the generated signal realizes the speed measurement of a moving target at a speed of 800 m/s. The ambiguity function is used to analyze the performance of the signal on solving the range-Doppler coupling problem. Besides, for wireless communication, the matching filter at the receiving end successfully recovers the 10-bit binary sequence with a code rate of 0.1 Gbit/s. This scheme combines chirp polarity modulation and optical microwave frequency multiplication, thereby generating a triangular wave frequency modulation signal for the joint measurement of radar speed and distance, improving radar detection resolution, and enlarging the chirp modulation usage scope to realize the integrated application of radar communication.
ConclusionsTandem pumping is one of the main technical approaches to realize high power fiber lasers. By combining the improved chemical vapor deposition method with the solution doping technique, we have fabricated an Yb-doped double-cladding fiber. Through the design of fiber core components and the optimization of the rod making process, the uniformity of the refractive index of the highly doped fiber core is improved. The laser performance of the fiber is demonstrated by an all-fiber master oscillator power amplifying laser system. As for the 1081 nm fiber laser based on tandem pumping, a 20.88 kW laser output at 1080 nm with a high stimulated Raman scattering rejection ratio has been achieved with an 82.7% slope efficiency. This is the highest power achieved for the domestic fiber based on tandem pumping.
ConclusionsIn this research, a polymorphic modulation method is proposed to suppress crosstalk by establishing a general formula adapted to different modulation depths; the optimal modulation method is determined by different modulation depths to eliminate the dead zone. According to the National Military test standard, the performance tests of the four-state and polymorphic modulations are carried out under modulation depths of π/2, 2π/3, 3π/4, 4π/5, 5π/6, and 7π/8. The dead zone thresholds corresponding to these depths are about 0.453, 0.741, 0.340, 0.623, 0.539, and 0.432 (°)/h. The zero offset stability corresponding to the use of polymorphism modulation is 0.0893, 0.0701, 0.0491, 0.0429, 0.0397, and 0.0365 (°)/h, respectively. The corresponding angular random walk coefficients are 0.0031, 0.0027, 0.0021, 0.0019, 0.0015, and 0.0012 (°)/h, respectively. Using the polymorphic modulation method derived from the general formula, the good performance of the fiber optic gyroscope can be maintained, and the obvious dead zone cannot be observed. Results show that the polymorphic square wave modulation has a significant advantage in eliminating the dead zone problem caused by crosstalk, which provides an important step for the realization of high-performance fiber optic gyroscopes.
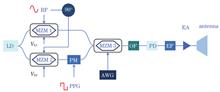
ConclusionsIn this study, we design a transmitter compatible with five modulation formats based on dual IQ modulators. We develop a schematic of a multimodulation format compatible transmission system in the simulation software. The simulation results show that this system is compatible with OOK, BPSK, DPSK, QPSK, and DQPSK. We also process and develop multimodulation format compatible transmission hardware and conduct experimental tests on the performance data of the system. The simulation results show that the five formats can be compatible with the same IQ modulator. The Q value decreases as the modulation level increases. In contrast, the EVM value increases as the modulation level increases. The experimental results show that this hardware system can support more than five compatible formats; high-speed communication sensitivity is high, and the sensitivity is close to -39.8 dBm (40 Gbit/s@10-7). The rate at each format is adjustable in three levels (2.5, 5, and 10 GBaud), and the communication bit rate can reach 40 Gbit/s.
ConclusionsThe simulation and experimental results show that the fiber laser at both ends of the fixed way has a greater influence on the natural frequency of the fiber laser. The metal diaphragm hard fixed way of practical constraints can be considered in the middle state of the clamped and simply supported beam model boundaries, which is closer to the simply supported condition. At low frequencies below 1 kHz, the bending vibration response of the fiber laser is highly related to the first-order natural frequency. In a certain range, the first-order natural frequency of bending vibration of fiber laser increases as prestress increases, which also increases the resonant peak frequency of hydrophone acoustic response. Moreover, hydrophone acoustic response changes dramatically near the resonant peak. Subsequently, the constraint boundary of the fiber beam model can be reset for different design structures. Combined with finite element simulation and experiment, the influence of different fixing modes and packaging structures on the bending vibration of the fiber laser can be further studied.In the beam model, the variation of the natural frequency of the fiber laser with prestress is consistent with the actual situation. However, the numerical solution of the natural frequency of the fiber beam model is larger than the actual situation under simply and fixed supported boundaries. This is because the small axial displacement is usually ignored in the transverse vibration analysis of the actual beam model. However, the natural frequency of the fiber laser is inevitably affected by the Poisson effect; it decreases the natural frequency. Additionally, the optical fiber beam model of simply and fixed supported on both ends of the constraint conditions and actual packaging are slightly different. Furthermore, packaging materials and the installation of combined components affect the vibration characteristics of fiber lasers. Considering the concrete structure finite element model, the corresponding natural frequency and vibration fluid column experiments have a good match. Therefore, the theoretical model can be refined according to the fixed mode and structure of the fiber laser, combined with the characteristics of the fiber laser to obtain a corresponding numerical solution, which is consistent with the actual solution.
ConclusionsIn summary, a pulsed ultra-violet laser at 289.9 nm with good beam-quality has been investigated. And based on the nonlinear conversion of type-I phase-matched LBO and BBO crystals for extra-cavity SHG and FHG, a 289.9 nm UV laser is achieved. The average output power is 108 mW with a repetition rate of 10 kHz and a pulse duration of 8.0 ns at a total pump power of 20 W.
ConclusionsAn optical structure with a single fiber dual-wavelength output and self-inspection function is designed using spatial combining, wavelength beaming, and beam shaping techniques. We obtain a 976 nm ignition laser with an output power greater than 10 W and a 1310 nm detection laser with an output power greater than 1 mW. The structure can simultaneously realize the power and optical path self-inspection of 976 nm ignition and 1310 nm detection laser. The divergence angle and beam size of the laser are effectively reduced using a self-focusing lens. This can improve laser power density and solve the randomness problem of the PD detector. It is crucial to realize the quantitative detection of optical detection system feedback and improve the effectiveness of the optical path continuity testing.
ConclusionsIn ladder type EIT, decreasing probe optical power and increasing coupling beam power can minimize the population of the middle state in vapor cell. This is essential for the lifetime of coherent state between Rydberg atom and ground state. Due to the broadening of the atomic spectral by increasing probe power, we set the probe power below the saturated intensity. In comparison, the EIT peak increases as the coupling laser power increases; however, the spectrum linewidth is only broadened slightly. For a high electric-field strength, we should increase the coupling laser power to distinguish AT splitting peaks. We have developed strong engineering applicability and high stability Rydberg atomic excitation light system based on CEDL. The laser linewidth is about tens of kHz, with a flexible wavelength tuning, providing fast and slow feedback channels for locking center frequency. The 1018 nm CEDL is the ideal seed laser for YDFA. Based on the fiber-coupled single-pass crystal frequency doubling, the power of the single-frequency narrow line width of 509 nm laser is about 470 mW. Meanwhile, its power and the linewidth parameter can meet the Cs atomic Rydberg atom EIT spectrum applications. The preparation and optimization of EIT signal measurement is the next step in building a reliable microwave field strength measurement system based on the above laser system.
ConclusionsIn view of the influence of cloud environment on the ranging accuracy of pulsed laser short-range detection system, the characteristics of laser cloud interference echo signal are analysed. A variable step-size filtering algorithm with step-size memory effect is proposed based on the principle of LMS adaptive filtering to characterise laser cloud echo interference signals. To verify the anti-jamming performance of the proposed filtering method, we analyse three factors of random jamming, pulse width, peak intensity, and echo time interval. A comparative experiment of pulsed laser cloud environment interference filtering is conducted. The results show that the proposed adaptive filtering algorithm can effectively target random parameter cloud interference signals and improve the working stability of pulsed laser short-range detection systems in a cloud environment.
ConclusionsThis paper proposes a laser far-field focal spot measurement method based on multistep phase retrieval. The effectiveness of the method is verified through theoretical simulation and experiments. The theoretical simulation results show that the near-field complex amplitude and far-field focal spot of lasers are effectively retrieved. Additionally, the PIB curves of the theoretical and retrieved focal spots are coincident. Moreover, the experimental results show that the profile of the retrieved phase is consistent with that of the theoretical phase loaded using SLM. Therefore, the retrieved and theoretical focal spots have the same distribution of the main lobe. However, there is a small difference in the side lobes because the optical components introduce small aberrations, and the surfaces of these optical components will interfere with each other. The side lobe information of focal spots using the long-focal-length lens imaging method is lost because of the limited dynamic response range in CCD. Therefore, the proposed method has higher precision of laser far-field focal spot than the traditional long-focal-length lens imaging method. The results show that the proposed method can provide a technical means for the high-precision measurement of laser far-field focal spots.
ConclusionsIn this paper, we propose a laser far-field dynamic indication accuracy measurement method without reference distance using dual-perspective correction. First, we simplify the image registration process of the dual-imaging system and improve the image registration accuracy of the dual-camera imaging system for the registration standard deviation of 0.08 pixel. The actual registration standard deviation for a corresponding imaging distance at 1 km is 0.94 mm. Furthermore, we calibrate the dynamic measurement accuracy of the measurement system using a cooperative self-test lamp on the target plate by dual-perspective correction theoretical model without reference distance. The average measurement error of the measurement system is 2.45 mm with a dynamic measurement standard deviation of 9.90 mm. Finally, we perform practical dynamic indication accuracy tests of laser irradiation systems, to further verify the effectiveness of the proposed measurement method.
ConclusionsAiming at the problem of deviation in measurement results caused by background interference when using CMOS sensor static light scattering method to measure particle size, this paper proposes a background interference elimination method based on the baseline method, and uses 120 μm and 9.86 μm national standard samples for the experimental analysis. The experimental results show that the baseline method can effectively reduce the deviation in measurement results caused by background interference, which provides a technical reference for the use of CMOS sensor to carry out an accurate particle size measurement of suspended particles in water body by static light scattering.
ConclusionsIn this study, we investigate the key factors affecting the half-wave voltage of an electro-optic slitter. Results show that an effective method for reducing the voltage is applying the crystal with large effective electro-optic coefficient and designing the transverse/longitudinal ratio of the crystal. Thus, a low half-wave voltage LN electro-optic slitter is designed and fabricated. Furthermore, the electro-optic effect is maximized using 90° x-cut crystals with radiation propagating along the x-axis and the control voltage applied along the z-axis. Also, compensation of natural birefringence is achieved using two LN crystals whose z-axes are rotated relative to one another by 90°. The optical quality of the z-faces of the LN crystal is good. The half-wave voltage is measured at ~900 V under DC high voltage, and the dynamic extinction ratio is 200∶1. Upon driving the electro-optic slitter using a pulsed high voltage of 800 V, 0.95 ns, and 1 Hz, we obtain a 1.46 ns, 1 Hz laser pulse output from a 1064 nm continuous wave laser. The output laser pulse waveform of the electro-optic slitter is related to the electrical pulse waveform of the driving power supply. For future work, we hope to obtain a laser pulse with a narrower pulse width by reducing the width of the electrical pulse.
ConclusionsIn this paper, we propose a new scheme front-end of the 2 μm OPCPA system. The visible and near-IR supercontinuum spectra are realized through dual laser filamentation processes based on different YAG crystals. The 2 μm laser seed pulse is produced by the DFG process between the two supercontinuum spectra’s difference and amplified by two optical parametric amplification stages. The amplified spectrum of seed laser ranges from 1830 to 2320 nm with a bandwidth of 243 nm. The amplified pulse laser has average power, single pulse energy, pulse duration, and pulse repetition rate of 167 mW, 16.7 μJ, 29 fs, and 10 kHz, respectively. The beam quality M2 factor is less than 1.3. It is expected that the pulse energy of 2 μm laser seed pulse can be further amplified to the mJ-level and peak power to GW-level for further driving the noble gas to generate water-window X-ray.
ConclusionsWe theoretically and experimentally demonstrate the generation of flat millimeter-wave noises by optically mixing multiple Gaussian wavelength-sliced ASE lights. The proof-of-principle experiment has shown the effectiveness of our proposed method with a satisfactory relative flatness as low as 0.46 [@(35±15)GHz]. Considering the non-dependency of fibers loss on frequency and the use of a photodetector with faster response such as uni-traveling-carrier photodiode (UTC-PD), the experimental implementation of our method in a higher frequency band can be expected. Our proposed method exhibits potential features for the noise parameter measurement of millimeter-wave devices.
ConclusionsIn this study, we proposed a scheme for generating high-frequency terahertz waves in MgO∶LiNbO3 slab waveguides using optimised cascaded difference frequency generation at polariton resonance. Unlike previous methods for generating high-frequency terahertz waves with difference frequency generation by two near-infrared lasers, we employ our proposed scheme to generate high-frequency terahertz waves by the simultaneous interaction of a series of cascaded optical waves. With hundreds of cascaded Stokes processes, where the phase mismatches are optimised by adjusting the dimensions of the slab waveguide, high-frequency terahertz waves are efficiently generated. Moreover, terahertz wave intensities are further enhanced with the gigantic nonlinear optical coefficients at polariton resonance of MgO∶LiNbO3 crystal and the reduced terahertz wave absorption coefficients by the slab waveguide. The energy conversion efficiency from pump wave to terahertz wave exceeds 40% using this method at room temperature. This study presents a novel scheme for generating high-power high-frequency terahertz waves, which can promote the applications of high-frequency terahertz waves.