By selecting laser power, laser pulse frequency and scanning speed as optimization variables, we establish a multi-objective optimization model of laser closure process parameters in vitro skin tissue. Based on MATLAB software, we use second generation non-dominant sequencing genetic algorithm (NSGA-II) to find the Pareto optimal solution set, obtain the optimal process parameters, and then analyze the response sensitivity of optimization objectives to the variation of process parameters. Under the optimized process parameters, the tensile strength of the incision is tested and the microstructure is analyzed. The results show that the incision tensile strength has high sensitivity to the laser process parameters, and the laser power has significant effect on the incision tensile strength and the tissue peak temperature. The proposed optimized process can achieve the in vitro skin tissue closure in full-thickness. In the case of tissue peak temperature decreasing, the tensile strength of in vitro skin tissue incision is 5.6% higher than that of single-objective optimization.
Based on the principle of mode field matching, we analyze the influence of tilt aberration on coupling efficiency, and then the laser nutation tracking method is simulated and analyzed according to theoretical analysis. The simulation results are verified by experiments based on fast steering mirror and PIN (Positive-Intrinsic-Negative) photodiode. The results show that the nutation radius is inversely proportional to the convergence rate, and the steady-state oscillation amplitude increases with the increasing radius, while the convergence rate decreases with the increase of the number of sampling points. In addition, the proposed algorithm can significantly suppress the dynamic disturbance in a certain range.
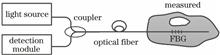
The obtainment method of fiber Bragg grating (FBG) reflection spectra is analyzed, and according to the characteristics of reflection spectra, a theoretical method is proposed for improving the optimization objective functions in the demodulation algorithm of FBG strain distributions using correlation coefficients. The performances of improved and traditional algorithms are compared by simulation combined with the differential evolution algorithm. The simulation results show that the traditional algorithm is only suitable for the situation where the true reflectivity of FBG is known, in contrast the improved algorithm can be applied to the situation where the true reflectivity of FBG is unknown. The proposed method can be used to improve the practicality of demodulation algorithms of FBG strain distribution.
Based on the principle of mode coupling, the calculated sidelobe height of output waveform of acousto-optic tunable filter (AOTF) is up to -9.5 dB. The experimental result is about -8 dB. The mechanism of sidelobe production is illustrated. A method is proposed to bend the spiral when we change the width of the three waveguides. The sidelobe can be reduced to -23 dB by this method.
A beacon image tracking algorithm during daytime is proposed. The camera view field noise reflected by sunlight and detector noise in the spatial and frequency domains are analyzed. Two frequency domain filters are used to detect candidate regions. The results show that the algorithm has high precision, high speed, and high reliability, and can be applied to the daytime satellite-to-ground beacon tracking.
The influence of phase-only encoding method on the generation of circular Airy beams is investigated and the commonly used coding method is discussed in detail, which is compared with the other introduced encoding method. The results show that both methods can be used to produce high quality circular Airy beams. The beam generated by the commonly used method has a good quality, little affected by beam parameters, and has a wide application. Although, the quality of the beam generated by the other method is relatively poor, which is also dependent on beam parameters, the diffraction efficiency is high, 2.4 times that by the original method, which indicating that there exist many advantages on the applications of laser processing, nonlinear excitation, and so on. The circular Airy beams are generated experimentally by both methods. The experimental results show that the quality of the beam generated by the commonly used method is affected seriously by the background noise due to its low diffraction efficiency, while the beam generated by the other coding method is well consistent with the theoretical result and its feasibility is experimentally confirmed.
The basic principle of one-step holographic stereogram printing method based on effective perspective images' segmentation and mosaicking (EPISM) is briefly introduced. The influence of EPISM method on the reconstructed quality change of different scene depths is analyzed. The causes of visual hopping in holographic stereogram based on EPISM are studied. The curvature distortion of holographic stereogram is also analyzed. The effect of curvature distortion on the reconstructed quality of holographic stereogram is verified. The reconstructed quality of the three dimensional scene with short depth is effectively improved when we reduce the size of holographic hogel.
A high precision and accuracy wavelength tunable system for a modulated grating Y-branch (MGY) tunable laser is built. The high-precision wavelength scanning and calibration are realized by coarse scanning and fine scanning. Based on this, the temperature drift characteristics of the output wavelength and the internal Fabry-Perot (F-P) etalon are tested. It is found that there exists a good linear relationship between the output wavelength of this MGY laser and temperature, whose slope is constant. The intercept varies linearly with temperature. A high precision and accuracy wavelength calibration method based on external gas absorption reference is researched and its experimental test is conducted. The research results show that within the temperature range of -25-+75 ℃ and the wavelength scanning range of 40 nm, the established system possesses a tuning curve linearity better than 0.9999, a tuning wavelength precision better than 0.18 pm, and an accuracy better than 0.12 pm.
A compact, closed-circle, high repetition frequency non-chain HF chemical laser is demonstrated based on the electric-discharge ignition mode via self-acting ultraviolet pre-ionization. A pair of asymmetric electrodes defines a 12 mm×17 mm×460 mm discharge volume. The circle gas flow is forced through this discharge volume to flush spent gas and replace it with fresh gas. The circulating gas flow in the vertical direction to the optical axis and the flow rate is 9 m/s. When the total gas pressure is 14 kPa, an average power of 50 W is realized with 100 Hz repetition rate in the gas mixture with mol-fractions of 92% SF6 and 8% C2H6.
The 976 nm laser diodes are utilized to provide the bi-directional pumping sources for the fiber amplifier based on 20/400 μm gain fiber. The transverse mode instability and the stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) effects are effectively suppressed under the operation of optimizing the coiling bending of gain fiber, pumping method, and pumping power distribution. A 3 kW level all-fiber amplifier with near-single-mode output is finally achieved. The optical-to-optical efficiency is around 73%, the SRS rejection ratio is 20 dB, and the beam quality factor is below 1.7. There are no mode instability characteristics detected in the time/frequency domain. A continuous 10 h test of this amplifier is carried out and the results show that the amplifier is stable, and is possible for its application in areas such as industrial processes.
A switchable multi-wavelength erbium-doped fiber laser is proposed. Based on the mode field mismatch principle, an in-fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) is fabricated by the non-core fiber combing with the polarization maintaining fiber. A stable and switchable multi-wavelength fiber laser can be realized by adjusting the curvature radius of MZI and controlling the polarization controller. The maximum wavelength spacing of the output multi-wavelength fiber laser is about 40.184 nm, and the side mode suppression ratio is larger than 50 dB. In the test of output fiber laser stability, the maximum wavelength variation of output wavelength is less than 0.06 nm in 1 h. The research results show that the proposed switchable multi-wavelength fiber laser has the advantages of a wide switchable wavelength range and a wide wavelength spacing range, a high SMSR, a stable output, and so on.
The plasma is produced during the monocrystalline silicon material is ablated by femtosecond laser, whose spot image can obtained by the collection of the radiation signals of plasma with CCD camera. Considering the characteristics that the contrast between the edge and background areas of plasma spot is not obvious and the signal to noise ratio is low, the spot image is enhanced and the brightness characteristics of this spot image are further analyzed. Firstly, the original spot images are filtered and then enhanced by the principal component analysis method. The obtained first principal component image is pseudo-color processed in order to analyze its energy distribution, and the core region of the spot is segmented according to its energy distribution information. Secondly, the centroid and long axis of the original image as well as the centroid, long and short axes of the core ablation zone are calculated, and the geometrical features of the image are analyzed. Based on these, the laser ablation direction is determined. Thirdly, the Niblack segmentation method is used to divide the gray image of the original image, and the luminance characteristics of the spot image are obtained based on the luminance information of the segmented binary image mask. Finally, the relationship of brightness characteristics of spot with laser ablation processing direction and laser power is analyzed. The correlation coefficient between brightness characteristics and processing direction is less than 0.09, and the correlation coefficient between brightness characteristics and laser power is more than 0.5. The results show that the luminance characteristics of spot image are not affected by the processing direction and the spot light intensity is stable, which can be used for the identification of laser ablation power.
On the basis of numerical simulation and experiments, the formation mechanism of solidification microstructures on the alumina ceramic surface by selective laser melting (SLM) is clarified. The research results show that as for the SLM of alumina ceramic, the forming condition of Bénard-Marangoni surface instability is satisfied. As laser energy decreases, the convection is close to its steady state. The preheating of substrate can change the Bénard-Marangoni convection state. Low laser power,fast scanning speed and low preheating temperature are all beneficial to the formation of a steady laminar flow on the liquid surface.
In order to improve the welding quality of 6061 aluminum alloy, we utilize the nanosecond pulse laser to pretreat 6061 aluminum alloy, and then observe its surface morphology with scanning electron microscope. The contents and distribution of oxygen at different laser parameters are studied by line analysis and surface analysis. In order to verify the laser cleaning effect, we carry out the welding experiments. The research results show that the optimal laser pretreatment parameters is cleaning the aluminum alloy surface 5 times with 15 W pulse laser power, which makes the mass fraction of oxygen is 3.23%, and oxygen is mainly distributed in the overlapping place of the spot. The weld is smooth and uniform,and without any obvious defects after pretreatment with laser optimum process parameters. The lower surface oxygen content, the higher weld quality. The small amount of oxygen distributed around the spot does not affect the welding quality.
Au films are deposited on fused silica substrates using the magnetron sputtering technique. The phase structure and surface morphology of the Au film after femtosecond pulse laser irradiation near laser induced damage threshold (LIDT) are investigated. The results show that the Au film prepared by magnetron sputtering is (111) oriented growth film. Laser irradiation energy near LIDT causes Au film to form large grains in the irradiated area and become polycrystalline structure from (111) single orientation. The increase of grain size leads to the increase of surface roughness. The experimental results provide a certain basis for exploring the damage process and later application of Au film under femtosecond laser.
Single crystal InxGa1-xAs film is grown on a GaAs (100) substrate through molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) growth technique, and the growth of InxGa1-xAs film is monitored in real time by a reflective high energy electron diffractometer (RHEED). The InxGa1-xAs film is characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), and the InxGa1-xAs exhibits a high-quality film with the In component (atomic fraction) of 0.51. The luminescence peak at room temperature is found to be around 1.55 μm by photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy, and the blue shift of the spectrum is observed due to the existence of compression strain in the InxGa1-xAs film. The Raman spectra show that the peak of the GaAs-like transverse (TO) optic phonon mode is obviously broadened, which proves that the strain exists in the ternary alloy InxGa1-xAs film.
Numerical models of a textured surface under hydrodynamic and mixed lubrication conditions are established , respectively, based on the Reynolds equation and the P-C (Patir and Cheng) model. The models are solved via Matlab programming using the finite difference method combined with numerical iteration. The pressure distribution in the calculation domain and the theoretical friction coefficient of the textured surface are obtained, which are used as the criteria for judging the tribological properties of the textured surface. To explore the coating design parameters for improved wear resistance, an elliptical texture with different arrays and a circular texture with different coverage ratios are processed using a femtosecond laser on the surface of a zirconia-reinforced hydroxyapatite bioceramic coating. The friction and wear tests are conducted on a reciprocating test platform. The wear depth of the coating is characterized by a three-dimensional profiler, and the proposed numerical models are verified.
A hardware-in-the-loop simulation platform for high-precision position measurement system based on two-dimensional grating is designed. The reasons for the error of the measurement model in the programming process are analyzed, and the simulation platform is used to test the accuracy and operation time of the measurement model. The results show that the accuracy of the measurement model is better than 0.79 nm when the calculated frequency is 20 kHz, and the error caused by simulation platform is 8.84×10-7 nm. The simulation platform can effectively detect the errors generated by the measurement model based on the two-dimensional grating in the process of program realization, and test the operation time of the model.
A three-dimensional reconstruction method based on micro-electro mechnical system structure light is proposed. This method uses micro-electro mechnical system structure light to acquire image data, and object 3D reconstruction according to the multi frequency heterodyne method. The acquired three-dimensional data are matched and located with the reference model by point pair feature matching. The three-dimensional coordinates and normal information of arbitrarily placed objects in the robot coordinate system are obtained. The experimental results show that the method based on micro-electro mechnical system structure light achieves the reconstruction accuracy of about 0.1 mm and the processing time is about 0.4 s, which can meet the requirement of positioning and grasping of most industrial robot bin-picking.
A method of point cloud splicing is proposed based on the iGPS (indoor Global Positioning System) world coordinate system. A point cloud splicing mathematical model is established and the coordinate transformation relationship in this splicing model is solved. Based on the standard ball measurement experiment, the point cloud splicing based on the robot base coordinate system and that based on the iGPS coordinate system are realized, respectively. The research results show that the point cloud splicing method based on the iGPS world coordinate system is not affected by the positioning accuracy of robots, and moreover the splicing precision is high.
A three-dimensional shape measurement method for large-area and high-reflection objects is proposed. Based on the theory of two-color reflection model, the diffuse reflection components of the fringe image collected by the camera are extracted. The reflection component of the image is separated by the improved reflection component separation algorithm. And the improved seed search algorithm is used to repair the image hollow caused by the reflection component separation. The three-step phase shift and quality guide algorithm are used to obtain the continuous phase. And the height information of the object is obtained by the phase height mapping relationship calibrated by the system.. The experimental results show that the measured error of this method is about 0.23 mm, which can eliminate 93%-97% of the number of high-light pixels, effectively overcomes the reflected light interference, and has good robustness for large-area reflected light.
Aiming at the requirements of three-dimensional shape measurement of profiled surfaces with the deep hole feature, a method based on CAD (Computer Aided Design) digital model extraction information for self-adaptability measurement and a trajectory planning measurement method based on normal precision control are proposed. The simulation analysis of the displacement-time, speed-time and acceleration-time curves of a robot verifies the smoothness of the trajectory curve obtained by the high-order polynomial interpolation method. The positional deviation and angular deviation of TCP (Tool Centror Point) in the process of shape measurement are verified by the shape measurement experiment based on the normal precision control. The position deviation is within 0.092 mm and the angular deviation is within 0.19°, which proves the feasibility of the proposed method.
A spectral purity measuring system based on long path absorption cell is built to measure the spectral purity of 1572 nm laser. The error calculation formula of this system is deduced and the factors influencing the measurement accuracy is theoretically analyzed. The results show that the accurately measured spectral purity range is 90%-99.999%. Based on this system, the spectral purity of a self-developed 1572 nm injection-seeded optical parameter oscillator is measured to be (99.996±0.0005)%, which fulfills the industrial application requirements.
Particle image velocimetry (PIV) technique is used to measure the flow field in the gain zone of a closed loop pulsed XeF(C-A) blue-green excimer laser. The flow velocity characteristics of the steady flow field in the center of the flow field, near the laser window and between the two parts in the discharge zone are studied. The flow field states in different time during the process of the discharge are analyzed. Furthermore, the relationships between the recovery time after discharge and the fan rotation frequency or the discharge voltage are discussed. The results show that there exit vortexes with slow flow velocity near the laser window. While in the center of the gain zone, the field is even with fast flow velocity. And in the moment after discharge, the flow field stagnation phenomenon with extremely slow velocity occurs.
In order to realize high-precision and low-cost detection of wavefront power spectral density (PSD) of large aperture optical elements, a detection method combining the interference and splicing techniques is proposed. The method for calculting the wavefront PSD is deduced, and the subaperture stitching method is proposed based on the correlation match algorithm. Then the error sources in the stitching interferometry are analyzed. The simulation by the stitching method is performed and the results show that the relative deviations of the wavefront distortion peak-valley value (dpv) and the root mean square value (PRMS) of the PSD during the stitching detection are 1.2% and 0.1%, respectively. Five experiments with 620 mm×450 mm aperture elements are accomplished and the corresponding stitching results are compared with the direct test results of the full aperture elements. The distributions are consistent with each other. The deviation of dpv is 0.012 λ(λ=632.8 nm) and that of PRMS is 0.03 nm, which indicating the proposed mehtod is stable and reliable for the stiching test of wavefront PSD of large aperture optical elements。
Based on the laser ultrasonic method, the transmitted ultrasonic signals are monitored in real-time when the crack is irradiated with a heating laser and naturally cooled. Under the irradiation of different power heating laser, three typical processes of the crack wall asperities are obtained when the crack is closed by the irradiation of heating laser, and the causes of these different processes are analyzed and discussed. The results show that the change of crack under heating laser irradiation and natural cooling condition is related to the initial morphology characteristics of the crack when it is not heated.
Based on the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) effect caused by a modified Otto structure of cylindrical lens, a method for measuring the thickness of metallic thin films is proposed. For this proposed method, the background intensity can be fitted only with the single SPR absorption image obtained under the p-polarized light incidence, no need using the s-polarized light. Hence, the normalized reflectivity curve in the vertical direction is obtained. The reflectivity curve is fitted by establishing a model of the optical thin film and the thickness parameters of the metallic thin film are derived. In the experiment, a sample of Au film with a thickness in the nanometer range is measured. The measurement results show that the difference between the measured average thickness of Au film and the result obtained by commercial spectroscopic ellipsometer is only 0.1 nm, which verifies the effectiveness of this method.
A metal-dielectric-metal (MDM) waveguide-coupled square cavity structure with bimetallic baffle is proposed based on the transmission characteristics of surface plasmon polaritons in sub-wavelength structure. The Fano resonance is an asymmetric spectral line formed by the destructive interference between the wide continuous state generated by the Fabry-Perot (F-P) resonator and the narrow discrete state interference generated by the square cavity. Based on the coupled mode theory, the generation mechanism of the Fano resonance of the structure is qualitatively analyzed. The structure is simulated by finite element method , and the influence of structural parameters on the refractive index sensing characteristics is qualitatively analyzed. The results show that the refractive index sensitivity of the proposed structure reaches 1080 nm/RIU and the figure of merit reaches 7.35×105 after optimizing the parameters.
The SiO2 microsphere cavity and the TiO2-SiO2 hybrid microsphere cavity with diameters of 206 μm are prepared with the electrode spark discharge method and the sol-gel method. The Q values of two microsphere cavities at 1550 nm are 2.15×107 and 1.36×106, respectively. The broadband resonant transmission spectra show that compared with those in the same size of SiO2 microsphere cavity,the absorption depth ratios of the resonant peaks of the high-order whispering gallery modes in the hybrid microsphere cavity increase obviously, indicating that the high-order modes are effectively excited. Moreover, the average red shift of the resonant wavelengths is 0.706 nm and the corresponding free spectral range is reduced by 0.020 nm, indicating that the resonant characteristics of the SiO2 microsphere cavity can be effectively tailored by the TiO2 film. The average red shift of resonant wavelength and the average reduction of free spectral range of the microsphere cavity with a diameter of 134 μm are 1.012 nm and 0.022 nm, respectively, indicating that small size microsphere cavities have strong resonance-tailoring capability.
A scheme for realizing high-order nonlinear diffraction harmonics in a nonlinear photonic crystal is described. Based on the multiple conical fourth-order harmonics observed, the feasibility of realizing the fifth-order and sixth-order harmonics via nonlinear diffraction is theoretically analyzed. The simultaneous generation of red, green, and blue conical harmonics is observed under only one input laser beam, which is beneficial to the realization of three primary colors, continuous harmonics and even ring white light sources. The blue conical output harmonics may be attributed to the cascaded nonlinear diffraction process of fifth-order harmonic involving the reciprocal vectors. Under the same fundamental wavelength, the conical angle of the fifth-order nonlinear cerenkov harmonic is always larger than those of the other lower-order harmonics. Moreover, there always exists a minimum conical angle for the fifth-order nonlinear cerenkov harmonics under different input wavelengths. When the input fundamental wavelength is 3319.5 nm, the generation process for the fifth-order harmonic e light is corresponding to nonlinear Bragg diffraction, which is helpful for the effective generation of a sixth-order nonlinear diffraction harmonic.
The Monte Carlo simulation method based on phase function fitting with random sampling is used to simulate the polarization characteristics of polarized light after multiple scattering by ellipsoidal particles, and its correctness is also verified by experiments. The ellipsoidal yeast particles with a long and short axis ratio of 1.5 are taken as study target, and the polarization transmission characteristics of laser are studied when propagating in soot. The polarization changes of 532 nm laser with 0° linear polarization, 45° linear polarization and left circular polarization are investigated during the ellipsoidal particle diffusion process. The results show that the higher the ellipsoidal particle concentration is, the greater the randomness of the polarization degree change is. Moreover, the polarization-maintaining property of a circularly polarized light is better than that of a linearly polarized light. At the same concentration, the effects of linearly polarized light with different polarization angles on polarization state are not much different.
Based on stimulated Raman scattering (SRS), we study a method for obtaining multispectral laser. The frequency doubled Nd∶YAG laser at 532 nm is used as the pumping light, and the high pressure CO2 is used as Raman active medium, and ten different Stokes lasers between 390 nm and 755 nm are generated simultaneously. By optimizing CO2 pressure, the maximum photon conversion efficiencies for first-order Stokes (S1, 574 nm), second-order Stokes (S2, 624 nm) and third-order Stokes (S3, 683 nm) reach 36.6%, 19.6% and 11.2%, respectively.
An external cavity is built with a plane grating to narrow the linewidth of the diode bar laser, and the pumped laser with center wavelength of 766.5 nm and linewidth of 0.12 nm is obtained. After the beam shaping, the laser is focused on a potassium vapor cell center, which is 8 mm long and is filled with 600 Torr (1 Torr=133.322 Pa) helium as buffer gas. Keeping the potassium vapor cell's temperature at 190 ℃, we obtain output power of 138 mW with 769.9 nm center wavelength of potassium laser.
Aiming at the problem that the traditional feature representation ability is weak, we propose a polarization synthetic aperture radar image semantic segmentation method based on the multi-layer deep feature fusion. The pre-trained VGG-Net-16 model is used to extract multi-layer image features with strong representation ability, and then deep features of each layer are used to train the corresponding conditional random field model. The output results of multiple conditional random field models are finally merged to realize the final semantic segmentation of the images. The results show that compared with the methods based on classical features, the proposed method achieves the highest overall accuracy, indicating that the fusion features used by the proposed method have stronger representation ability than traditional features.
A novel photonic crystal fiber (PCF) structure is designed. A sensor based on the newly designed PCF and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is proposed, which is applied to temperature and magnetic field detection. The theoretical model is analyzed by the full-vector finite element method. The results demonstrate that the temperature sensitivity is -493.6 pm/℃ with temperature from 20 ℃ to 50 ℃, and the magnetic field sensitivity is 82.69 pm/Oe with magnetic field from 20 Oe to 300 Oe.
A laser detection platform with an open single path and short optical distance is constructed, and a Levenberg-Marquardt (L-M) algorithm based on linetype is proposed. The method uses second order derivative of Gaussian linetype and Lorenz linetype as the fitting function of L-M algorithm. The samples with oxygen volume fraction of 0%-21% are corrected. The results show that the correlation coefficients of oxygen content and peak is the highest in L-M algorithm correction based on Lorentz linetype (0.9995). The sample with oxygen volume fraction of 1% is measured several times on the basis of Lorentz linetype. Compared with the measured results before and after the correction, the predicted maximum deviations of oxygen volume fraction are 0.38% and 0.22%, respectively, and the root mean square errors of prediction are 0.25% and 0.16%, respectively.
A nanosecond laser is used to excite the aluminum foil to generate plasma. The aluminum foil is heated and the influences of sample temperature on the intensity and the signal-to-noise ratio of laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy are investigated. The diameter of ablation crater is measured, and the relaionship between the crater diameter and the sample temperature is observed. The research results show that the increase in sample temperature leads to the increase in the spectral intensity and the signal-to-noise ratio of two spectral lines of aluminum, the crater diameter also increases with the increase of sample temperature. It is validated that increasing the sample temperature can improve the sensitivity of the laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy.
Taking anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) with different pore diameters as research object,we study the effects of pore size of AAO on the morphological evolution and temperature of laser-induced plasma based on high-speed photography and atomic emission spectroscopy. The light reflectance of samples is tested and simulated by absorption spectroscopy and finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method.The results show that within a certain pore range, as the AAO pore size decreases, plasma duration becomes long, the spectral line intensity becomes large, and the plasma electron temperature becomes high. The plasma parameters of AAO are larger than those of polished aluminum sheet, in which electron temperature of plasma of AAO is 2000-3500 K higher than that of polished aluminum sheet. Within a certain pore range, the smaller the AAO pore, the higher absorption coefficient of light in the sample, which explains the reason of AAO plasma enhancement.
A concise scheme of laser frequency stabilization method is presented, multi-laser frequency are stabilized to wavemeter directly by this method. In order to check the laser frequency stabilization results, we measure the laser frequency by a femtosecond optical comb referenced to a hydrogen clock when the frequency is locked. The results show that the frequency jitter of 548 nm fiber laser frequency which locked to wavemeter is smaller than 1 MHz, and the Allan deviation at 20 s reaches 5×10-11. The frequency stability of tunable diode lasers with wavelength of 397 nm and 866 nm are evaluated with frequency jitter of ±5 MHz and long-term drift rate of smaller than 2 MHz/h.
GaAs nanowires are treated with Ar plasma, and the effects of the bias power of plasma on the photoluminescence properties of the GaAs nanowires are studied by the photoluminescence test. The source and mechanism of each photoluminescence peak in photoluminescence spectra are studied at different temperatures and different excitation powers. The experimental results show that the free exciton emission of GaAs gradually disappears and the bound exciton emission decreases first and then increases with the increase of the power. When the power increases to 200 W, the donor-acceptor pair (DAP) emission appears. Comparing the photoluminescence spectra of different samples at 283 K, we obtain the structural changes of GaAs nanowires during plasma treatment. When the processing power is low, the Ar plasma eliminates the surface state and introduces a vacancy defect in GaAs; when the processing power is high, the crystal structure of GaAs is destroyed, and the DAP emission appears.