The quantum precision measurement system based on atomic ensembles possesses high accuracy and stability, making it one of the directions for the development of advanced measurement systems in the future. Among them, electric field measurements based on Rydberg atoms exhibit characteristics such as high sensitivity, ultra-wideband capability, and excellent electrical isolation, and have gained widespread attention in recent years. However, current research on electric field quantum precision measurement based on Rydberg atoms is mainly focused on the microwave frequency range, with limited studies on low-frequency electric field measurements below GHz. Given the significant scientific and practical value of high-sensitivity detection in DC-MHz frequency range electric fields in many areas such as geophysical exploration, biosensing, defense communication, and space exploration, this article reviews the recent progress in novel antenna research in the DC-MHz frequency range, summarizes the development trends of atomic antenna technology in recent years, outlines the principles of low-frequency electric field measurement based on Rydberg atoms, and discusses the potential improvement strategies for key performance indicators such as sensitivity and instantaneous bandwidth of atomic antennas, as well as their potential applications in the field of low-frequency detection in the future.
A light and compact imaging spectrometer (LCIS) optical system suitable for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) is designed in this work. The operating wavelength of the optical system covers400?1000 nm, with an F number of 3.3, a field of view of 11o, and a spectral resolution better than 3 nm. The optical system is simulated and optimized using Zemax software. The optimization results show that the maximum root mean square (RMS) radius of the dot plot for this system is 4.221 μm, which is less than half of the size of a single pixel, the maximum values of smile and keystone are 1.30 μm and 1.16 μm respectively, accounting for 8.69% and 7.73% of a single pixel size, and the modulation transfer function (MTF) value at 33 lp/mm is better than 0.7. All evaluation results show that the optical system has good imaging quality. In addition, the optical system has a volume of 190 mm × 160 mm × 90 mm, indicating that the system not only has high spectral resolution and good imaging quality, but also has the advantages of small size and compact structure. This research provides core technical support for the development of light and compact imaging spectrometer, and also lays a foundation for in-orbit radiometric calibration of remote sensors based on UAV borne imaging spectrometer.
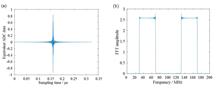
The time-frequency transmission technology based on two optical combs has been able to achieve stable time-frequency transmission in experiment. However, the linear optical sampling algorithm will suffer from Doppler effect when there is relative motion on both sides of the two optical combs. In order to accurately calculate the time delay and frequency shift of the interference signal caused by Doppler effect, a joint estimation algorithm of time difference and frequency offset based on wide-band cross ambiguity function is studied.Several groups of interference signal are simulated under specific parameters when the optical comb delay is 38.78 fs and the relative speed is between 0 and 1800 m/s. In this speed interval, the delay error is 0 and the speed error is less than 0.3 m/s. Compared with the narrow-band cross ambiguity function, the proposed algorithm has better performance of time and frequency scale estimation at high speed.
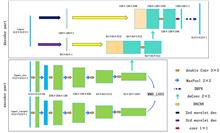
Due to the lack of high-quality paired datasets, the application and development of deep learning in neutron computed tomography (CT) reconstruction are severely hindered. Although the imaging principles of neutron CT and photon CT are both based on the Radon transform, the imaging characteristics of the two processes during particle transport are different, so the network trained for photon CT cannot be directly used to solve the reconstruction problem of neutron CT. Therefore, in this work, an unsupervised domain adaptive network is proposed that can solve the probability distribution difference problem in the migration process from photon tomography to neutron tomography.In the proposed method, the maximum mean difference is introduced to reduce the distribution difference between photon and neutron tomography image features, and furthermore, wavelet transform and convolution neural network are combined to enhance the effective features of reconstruction. The comparison experiments with other algorithms show that the proposed method can reconstruct high-quality neutron tomography images from low-flux neutron tomography results, effectively alleviating the degradation of low-flux neutron tomography.
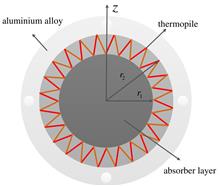
In order to achieve remote measurement of laser power and ensure the security of data transmission, a data acquisition and transmission module for non-networked wireless laser power meter is designed. The module consists of three parts: STM32 data acquisition module, wireless RS485 transparent transmission module and Qt host computer software. The STM32 data acquisition module converts the voltage analog signal collected by the detector into a digital signal. The wireless RS485 transparent transmission module is responsible for the data communication between the STM32 data acquisition module and the PC. The Qt host computer program processes the received data and displays the real-time laser power curve. The test results show that at a transmission distance of 1 km, the module successfully collected a complete laser power curve, with a data transmission error rate of 0. This module realizes long-distance and high-speed power data acquisition and transmission functions, and lays a foundation for the later development of wireless laser power meters.
An integrated optical system for cold 85Rb atom interferometer is designed and implemented in this work. The system includes five fiber-connected modules, and the size of the entire optical system is only 400 mm × 483 mm × 133 mm. This integrated and modular optical system is beneficial for further engineering and miniaturization of atomic interferometers. An active temperature control method is adopted to improve the stability of the optical system, and the long-term stability of laser intensity reaches 4.3 × 10-3@5000 s. This optical system has been successfully applied to an atom interferometer, and the interference fringes with a free evolution time of 71 ms and a contrast of 20% are obtained. The phase uncertainty of a single fringe is 22 mrad, and the corresponding gravitational measurement uncertainty is 26 μGal. The design and implementation of this optical system lays the foundation for the miniaturization and practical application of atom interferometers.
The effective suppression of laser noise is the basis of precision measurement research, and especially, it is required for modern quantum information science to reach shot noise limit in light field. A noise suppression system combining photoelectric negative feedback and mode cleaner is studied in this work. Based on the sideband model and Langevin equation, the noise spectrum of the output light field of the noise suppression system is analyzed, and the effects of the transmittance, feedback gain of the photoelectric negative feedback loop and the cavity linewidth of the optical mode cleaner on the noise suppression level are discussed. The results show that the system can not only effectively suppress the intensity noise at high frequency to reach the limit of shot noise, but also reduce the intensity noise at specific frequencies. In addition, the introduction of bandpass filter can further extend the level and bandwidth of noise suppression. The results provide direct reference and necessary basis for experimental research.
As a kind of supervised learning algorithm, ridge regression algorithm has a wide range of applications. A quantum ridge regression algorithm is proposed by combining quantum singular value estimation with classical ridge regression algorithm. In the proposed algorithm, the parallel property of quantum computation is utilized to solve the fitting parameters of ridge regression and obtain the predicted values. Complexity analysis shows that the proposed algorithm effectively solves the problem of matrix expansion or matrix operation when the data matrix is non-Hermitian matrix, and has exponential acceleration in running time compared with the classical algorithms. In addition, the quantum circuit diagram of the proposed algorithm is also provided and the key steps of the algorithm are simulated. The simulation results confirm its effectiveness and feasibility.
Improving the luminescence collection intensity of diamond NV color center is the key to realize single photon source. A tapered diamond-like carbon (DLC) gradient antireflection film is introduced into a diamond nanocolumn color center single photon source, aiming to improve the luminescence collection intensity of NV color center from the aspects of spontaneous radiation rate and photon collection efficiency of color center. The finite difference time-domain (FDTD) method is used to simulate the composite structure optically, the effects of DLC film with different structural parameters on the photon collection intensity, emission efficiency and spontaneous radiation rate of NV color center of diamond nanopillar are investigated, and the structural parameters at the maximum collection intensity are obtained through optimization. The simulation results show that the introduction of DLC film can make the NV color centers in diamond nanopillars achieve a higher photon emission efficiency (≥1%), change the internal electric field distribution of the nanopillar, increasing the spontaneous radiation rate of color center by 16.8%, and finally increase the total photon collection intensity by 15.5%.
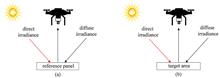
A dual-field-of-view oceanic lidar system was designed and developed to meet the actual demand of on line monitoring of seawater surface parameters such as chlorophyll-a and suspended matter concentrations. Firstly, the measurement experiment of chlorophyll-a concentration was carried out in the laboratory using an experimental tank. It was shown that the correlation coefficient between the results measured by the developed system and those of chlorophyll fluorimeter/nephelometer was 0.94, and the chlorophyll-a concentrations measured under different laser excitation energies were also consistent with those of chlorophyll fluorometer/nephelometer. Meanwhile, the calibration experiments were also carried out on the concentration of suspended matter with different particle sizes, and the corresponding correlation coefficient between the results measured by the developed system and those of the chlorophyll fluorometer/nephelometer was better than 0.91. Then, by using the developed oceanic lidar, the concentration of chlorophyll-a and suspended matter in the seawater surface off the coast of Qingdao were measured on-site, and the correlation coefficients between the results of the lidar system and of the chlorophyll fluorometer/nephelometer were 0.74 and 0.86, respectively, preliminarily verifying the feasibility of applying the self-developed oceanic lidar for detecting the concentration of chlorophyll-a and suspended matter in seawater surface.
A nanosecond pulse laser was used to scan and etch single crystal silicon in room temperature and atmospheric pressure environment in this work, and various black silicon samples with different structure were prepared by changing the scanning mode and scanning line spacing. Then the effects of scanning mode, scanning interval and high temperature oxygen blowing annealing time on the photoluminescence (PL) properties of black silicon were studied, as well as the effect of different microstructure of silicon surface on light absorption rate. The morphology, light absorption and PL characteristics of the prepared black silicon samples were detected and characterized using transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, optical microscopy, Raman and fluorescence spectroscopy, absorption spectroscopy, etc., and black silicon structure samples with an absorption rate higher than 90% were obtained. It is found that the PL spectrum of black silicon samples prepared by linear scanning is mainly distributed in the red band, while the PL spectrum of black silicon samples prepared by orthogonal scanning has a stable emission peak near 900 nm. In addition, the eletron localized luminescence near 630 nm was observed on the black silicon sample, and its luminescence mechanism was explained by establishing a corresponding physical model.
A photonic crystal fiber (PCF) with octagonal microstructure is designed in this paper, and the characteristics of the fundamental mode of the fiber, such as dispersion, nonlinear coefficient and confinement lose, are studied based on the finite element method. The results show that, by properly adjusting the structural parameters of the fiber, there is a zero dispersion point at a wavelength of1.55 μm, and at this wavelength, it has highly nonlinear coefficient of 94.97 W-1?km-1 and low confinement lose of 3.065 × 10-6 dB/km. This design provides theoretical guidance for obtaining zero dispersion, highly nonlinearity and low confinement lose at a wavelength of 1.55 μm, and has potential applications in dispersion control, nonlinear optics, and other fields.
BaGa4Se7 (BGSe) is currently attracting considerable attention as a new type of infrared nonlinear crystal. We explored the synthesis of BGSe polycrystalline raw materials using both the two-temperature zone method and the high-pressure-assisted method, and designed a rapid purification method with a large temperature gradient to purify the synthesized polycrystalline material firstly. And then, the phase composition and impurity concentration of BGSe polycrystals before and after purification were characterized using powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The X-ray diffraction spectra are consistent with theoretical simulation results, showing no impurity peaks. ICP-MS test results also show a significant reduction in the content of metal impurities such as Fe, Al, and O impurity in the ingot after purification. The research can provide a raw material basis for the growth of high-quality single crystal.