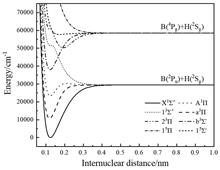
The potential energy curves of eight states (X1Σ+, a3Π, A1Π, 13Σ+, b3Σ-, 23Π, 15Σ- and 15Π) corresponding to the two lowest dissociation limits B(2Pu)+X(2Sg) and B(4Pg)+X(2Sg) of BX (X = H, D) molecules are calculated based on the correlation consistent basis sets aug-cc-pV6Z using the high-precision multi-reference configuration interaction (MRCI) method. The radial Schr?dinger equation is solved and the spectral constants of molecular Λ-S bound states are fitted using LEVEL8.0 program. Furthermore, the transition dipole moments, Franck-Condon factor and vibrational level radiation lifetimes of A1Π-X1Σ+ are calculated. Finally, according to the calculation results, the laser cooling scheme of the electronic transition system is developed, which lays a theoretical foundation for further study of BX (X = H, D) molecular spectral characteristics.
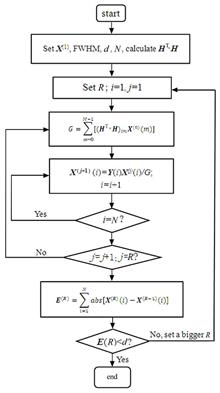
To effectively identify the overlapped peaks and diminish the interference of random noise in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), an automatic peak detection method using Gold deconvolution algorithm combined with smoothing is proposed. For the LIBS of standard samples NIST 1256b and NIST 1762, smoothing is performed first, followed by deconvolution using Gaussian system function, and finally, five-point method is used to detect the peak automatically from the deconvolution results. Thus, the effect of smoothing combined with system functions with different full width at half maximum (FWHM) on the ability to identify overlapped peaks and reduce the interference of random noise is studied experimentally. The results show that when the FWHM of 0.140 nm (slightly larger than that of weak peaks) is used, combined with smoothing, the resolution of Gold deconvolution algorithm to identify overlapped peaks can be up to 0.039 nm, and the wavelength, intensity of the peaks, as well as curve fitting, are well matched with NIST database. The preliminary results indicate that the automatic peak detection based on Gold deconvolution algorithm can be applied to LIBS data processing.
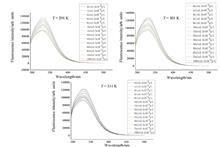
The effect of taurine on the microenvironment and conformation of human serum albumin (HSA) are studied using fluorescence spectroscopy and ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy. The results show that HSA can be quenched regularly by taurine through a static quenching mechanism at different temperatures, with quenching rate constants greater than 2.0×1010 L·M-1·s-1. The binding constant increases with the increase of temperature, and the number of binding sites also increases, approaching to 0.5. The thermodynamic parameters enthalpy change is less than 0, entropy change is greater that 0, and free energy change is less than 0, indicating that the binding process is spontaneous and the main force is electrostatic attraction. According to Forster's non-radiative energy transfer theory, the binding distance between taurine and HSA is estimated to be 2.645, indicating that there is non-radiative energy transfer. The results of this study indicate that taurine can affect the microenvironment of HSA and change the spatial conformation of HSA. This mechanism may be the essential source of taurine's ability to protect hepatocyte and improve the structure and function of portal vein.
To further improve the color image denoising algorithm in quantum image processing, a quantum color image filtering method based on quantum vector median calculation is proposed. The method uses quantum entanglement to bind neighbor pixels and central pixel to the same position to avoid quantum convolution, and introduces the complement code into the quantum circuit to simplify the quantum circuit for vector distance calculation. In addition, a quantum circuit of vector median extraction is designed by using one-time comparison and two-time exchange. Thereby, a complete quantum circuit of the vector median filtering is constructed. Relevant experimental indicators show that the proposed approach has the same noise suppression effect on color salt and pepper noise as the classical vector median filtering, but the time complexity is reduced from O22n of the classical vector median filtering algorithm to O (10n2+216q2) of the proposed algorithm.
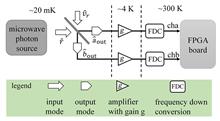
Detection and characterization of microwave photon sources is a key step in quantum information. For the optical photons, Hanbury Brown-Twiss interferometer can be used to measure the correlation of them. However, for microwave photons, as the signal-to-noise ratio of them is much lower than that of optical photons,multiple-calculation process is necessary for the elimination of noise influence. Here a new, fast and scalable measurement scheme is demonstrated to characterize a microwave photon source, in which real-time processing and full parallelism are realized by using field programmable gate array (FPGA). And the second-order correlation function of a coherent source with 3 MHz is investigated using the proposed scheme. The good agreement between the output of FPGA and that of the theoretical calculation indicates that, the scheme is promising for application in quantum information processing such as the characterization of microwave single-photon sources.
An all-solid-state laser with high environment adaptability and high repetition frequency is designed to meet the application requirements of laser source for vehicle-mounted lidar. In terms of design, ABCD transmission matrix theory is used to calculate and analyze the resonant cavity, thus realizing the best mode matching between the pumping light and the oscillating light in the laser medium. In the experiment, glue stability test and local temperature control test are carried out to improve the stability of the resonator. By measuring the power stability of the laser under different working conditions such as high temperature, low temperature and vibration, it is proved that the laser has high environmental adaptability. It is demonstrated that based on air-cooled heat dissipation, the laser can achieve stable operation of the whole machine in the temperature range from -10 oC to 55 oC and under the condition of road spectrum vibration. Under the pump power of 8.31 W and acousto-optic Q-switched mode, a 532 nm green light output with pulse width of 7 ns, repetition frequency of 4 kHz, average power of 0.95 W and single pulse energy of 0.24 mJ is obtained, meeting the application requirements of mobile lidar.
In high-speed machine device independent quantum key distribution (MDI-QKD) systems, high code rate is crucial to realize long-distance quantum communication. To achieve a higher code rate, each link of the system has more requirements on the light source. To meet the requirements, a pulse laser circuit for the high-speed MDI-QKD system is designed. According to the designed pulse laser circuit, by analog processing and driving the external or internal trigger signal, the pulse laser can be generated, and by using analog PID control and bidirectional TEC current control, the internel working temperature of the laser can be stabilized. The outgoing pulse laser can achieve an output with a repetition of up to 1.25 GHz, a full width at half maximum of 24.2 ps, an extinction ratio of 30 dB, a wavelength jitter of 0.95 pm and a wavelength tuning range of 2.014 nm, which is beneficial to the improvement of the code rate and meets the requirements of the high-speed MDI-QKD system.
Detector array target is a common device for measuring the distribution of laser spot, and the sampling panel of array target needs higher damage resistance under long-term high-power laser irradiation. In order to improve the damage resistance of the sampling panel, based on the finite element analysis software Ansys Workbench, from the perspective of thermal design, the research compares the temperature field and thermal stress of the protective sampling panels with different thicknesses, different heat pipe arrangements and different interface heat transfer coefficients under long-term high-power laser irradiation. The analysis results show that after adding a cross heat pipe arrangement, the withstand peak power density of the sampling panel with a thickness of 6 mm increases from 1470.9 W·cm-2 to 3632.1 W·cm-2when the laser irradiation lasts for 120 s. This simulation analysis provides effective theoretical and data support for the design of protective sampling panel for array target.
In order to meet the current demand for high-precision calibration of satellite-borne remote sensors, a high-altitude spectral radiance meter has been developed, which can be applied to the radiance method instead of the traditional site calibration method to improve calibration accuracy. The instrument has a spectral range from 400 nm to 2500 nm, and can be mounted on a high-altitude balloon platform to measure the reflected radiance to the ground directly at an altitude from 18 km to 35 km. The optical-mechanical system of the instrument is mainly composed of a front integrated lens barrel, a dispersion module and the optical-mechanical temperature control module. In order to verify the reliability of the high-altitude spectral radiance meter and the accuracy of the measured data, a comparison experiment between this instrument and the SVC spectrometer of Spectra Vista (USA), as well as a high-altitude flight experiment, was carried out in Dachaidan, Qinghai. The experimental results show that there is good consistency in the radiance measured by the two instruments, with a deviation of the two instruments generally within ±1% and a maximum deviation within ±3.5%. In the high-altitude flight experiment, the instrument can keep stable at an altitude of 25 km in the six-hour flighting, and the temperature of each module and detector remains at the setpoint. In the end, the result of high-altitude measurement radiance was obtained. The experimental result has verified the reliability of the entire instrument, indicating that the developed instrument can meet the high-precision calibration requirements of satellite remote sensors and is suitable for the high-altitude high-precision measurement.
Diamond has the advantages of high thermal conductivity, wide spectral transmission range, large Raman gain coefficient and large Raman frequency shift. Therefore, it has become an important Raman medium to expand the wavelength range and obtain new wavelengths with high power and high beam quality. Based on the first principle, the lattice parameters, band structure, density of states and phonon spectrum of diamond are calculated comprehensively in this work, and the structural characteristics, spectrum, band gap, and electron distribution characteristics of diamond are systematically analyzed. Furthermore, the electron motion state of diamond and the effects of the polarization direction of electric field on the band gap of diamond are analyzed. It is found that the crystal direction of diamond most easily affected by electric field is < 1 0 0 > and the best stability is < 1 1 1>. All intrinsic vibration modes and the corresponding frequencies are obtained, which shows that the Raman gain of diamond is the largest when the pump light is propagated along with the < 1 1 0 > and polarized along the < 1 1 1 >. The multiphonon absorption mechanism in the spectral region is also discussed. The work provides a theoretical basis for the improvement of Raman laser efficiency and wavelength expansion of diamond.
In order to deeply understand the wave particle duality of microscopic particles, explore the transitions between wave state and particle state, and prepare the coexistence states of multi-path wave state and particle state, a theoretical scheme to realize the continuous transition from wave- to particle-state in quantum walks by introducing quantum control is proposed. The variation of the position distribution and variance of quantum walks with auxiliary bit coefficients is calculated respectively. It is shown that quantum control can make the walker not only in the mixed state of wave and particle, but also in the coherent superposition state. The continuous morphing from wave state to particle state is displayed by the position variance in both the coherent way and the mixed way, and the difference between the mixed state control and the coherent state control is also demonstrated. Quantum walks provide a useful platform for in-depth study on the wave-particle duality of microscopic particles.
Based on a three-step photonic quantum walk scheme, a swapping protocol is proposed for the spatial state and polarization state of two remotely distributed photons, so that the high-quality spatially entangled state and the poor polarization-entangled state of two photons can be swapped, enabling the two remote photons to be in maximally polarization-entangled state. That is to say, the polarization entanglement of the remotely distributed photons can be enhanced with the help of the spatial entanglement of them. Since all the post-selected states are maximally entangled states, the swapping scheme is realized in a deterministic way. The scheme is not only applicable to Werner state but also to arbitrary unknown remote polarization-entangled state, so the scheme is universal in this sense. In addition, half-wave plates and beam displacers used in the scheme are ordinary optical elements, so the scheme is simple and feasible, providing an alternative scheme for manipulating remote polarization entanglement in quantum communication.
With the deeper research and application of quantum key distribution (QKD), the quality and generation rate of random numbers are facing greater challenges. In order to meet the use of random numbers in QKD system and in the scenarios with high requirements for key security, an experimental scheme for generating true random numbers based on vacuum fluctuations is presented. Compared with the 2 × 2 polarization beam splitter (BS) used in traditional solution, a single mode 1 × 2 BS is used in the proposed scheme to realize the transmission of optical path, which not noly saves device costs but also obtains a high random number generation rate. Under the action of 9.68 dBm light intensity, the signal-to-noise ratio of quantum noise to classical noise of 11.92 dB is obtained. The data collected through a 12 bits analog-to-digital converter is analyzed. The results show that both the classical noise and the vacuum shot noise are in accordance with Gaussian distribution, and the calculated minimum entropy is 9.92. The original data is subjected to Toeplitz post-processing, whose security can be proved according to information theory. Finally, the quantum random number generation with the rate of 7.6 Gbit /s is acheived, and it successfullly passes the NIST random number standard test, verifying the feasibility of the scheme.
A deterministic entanglement purification protocol (EPP) for polarization decohered Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger (GHZ) state is presented based on linear optical elements such as polarization beam splitter and half-wave plate. The proposed EPP makes use of spatial entanglement as an additional resource to purify polarization entanglement, and its essence is to transfer the bit-flip and phase-flip errors from polarization degree of freedom (DOF) to spatial one using the methods of linear optics and hyper-entanglement. The entanglement purification scheme can be implemented without knowing any parameters of the low-entanglement GHZ state to be purified, without converting phase flip errors to bit flips for purification, introducing the nonlinear effects. According to the proposed EPP, just in a purification step, both the bit-flip and phase-flip errors in the polarization mixed states can be deterministically corrected by using additional entanglement DOF in spatial mode, which greatly enhances the experimental feasibility of this scheme.
The limited connectivity between physical qubits is one of the most important constraints for noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) computing devices. Quantum circuit mapping makes all qubits in quantum circuits exchange mutually by inserting SWAP gates to satisfy the restricted connectivity constraints of physical devices. In a noisy computing environment, reducing the number of inserted SWAP gates is of great significance to improve the success rate of quantum computing. In order to minimize the number of SWAP gates, a heuristic quantum circuit mapping algorithm is proposed, and then based on the heuristic algorithm and the random search technology, a multi-iterative stochastic optimization model for quantum circuit mapping is proposed. The experimental results show that the method can greatly reduce the number of quantum gates inserted during the quantum circuit mapping process, and effectively reduce the dependence of the resulting physical circuit on the initial mapping.
Based on three-layer triangle network, the polygonal networks are established for mutually coupled semiconductor lasers. Firstly, the chaotic synchronization characteristics of the lasers in the three-layer triangle network are numerically analyzed and investigated. Then, the three-layer triangle network is extended to three-layer hexagonal network or even more complex polygonal network, and taking the first layer laser as the vertex laser for structural optimization, the proprieties of chaotic synchronization are studied between lasers in different layers for these complex structures. The results show that the lasers in three-layer triangle network, as well as in the three-layer hexagonal network or even more complex polygonal network formed by increasing side numbers of polygonal network, lasers except the apex can achieve chaotic synchronization in the same or different layers.
The buildup dynamics of conventional solitons with net anomalous dispersion and dissipative solitons with normal dispersion were studied using dispersive Fourier transform technique. In order to explore how these pulses evolve with the amplification power in the optical amplifier, experiment and simulation were carried out to investigate dynamic changes of the two kinds of solitons after amplification by amplifier. The results show that spectra of the two kinds of solitons undergo different oscillations during the establishment, the spectra of conventional solitons start from a modulated beat state with violent energy oscillation then transit to a stable state, while the spectra of dissipative solitons expand steadily from a disordered modulated state to a stable state. As the pump power of the amplifier increases, for conventional soliton, the center energy of spectrum will be transferred and the spectrum will be broadened, while the spectrum of dissipative soliton will exhibit a sharp peak at the edge with unchanged spectral width. These dynamic nonlinear phenomena in mode-locked fiber lasers and optical amplifiers have potential application value in ultrafast lasers and the corresponding amplification systems.
A metal-dielectric-metal (MDM) filter is designed which is composed of a slot cavity and two waveguides. The influence of main structure parameters on the transmission characteristics of the filter is analyzed in detail using the finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method. It is found that the lateral displacement Ld has a significant impact on transmission properties of the filter,which will lead to the appearance of new resonance peaks. In addition, it is shown that the increase of the cavity width Wc will not only make the number of transmission peaks increase, but also make the transmission peaks distribute more uniformly in the range from 600 nm to 1500 nm within limits. Through parameter optimization, a multi-channel filter distributed near the 550, 730, 920 and 1330 nm wavelength windows in optical communication systems is designed. The design has the advantages of narrow transmission peak, good quality factor, simple structure, easy integration and easy fabrication, which can be well used in wavelength-division multiplexing system and optical communication.