RFeO3 with orthogonal perovskite structure is a class of transparent ferromagnetic materials in the near-infrared wave band, and research on the ultrafast spin reorientation transition of RFeO3 and its coherence control has become a hot topic in related fields in recent years. As the excitation energy of the basic properties of materials such as magnon and electron spin resonance is within the terahertz energy range, a series of breakthroughs have been made in the terahertz ultrafast optical regulation of RFeO3 crystals due to the rapid development of THz technology in recent years, which is of great significance to the basic research of magnetism. Combined with the author's research work in recent years, the progress of terahertz optical regulation of RFeO3 crystals at home and abroad has been reviewed in this paper and the future ultrafast photomagnetic research of RFeO3 crystals are also prospected.
Terahertz metamaterial absorber has the advantages of strong absorption, thin thickness and light weight, and has been widely used in stealth materials, frequency selective surfaces, terahertz imaging, communication sensing, and so on. However, as for the traditional terahertz metamaterial absorbers based on metal-patch, once they are processed, their absorption performance will be unchangeable. To solve this problem, researchers have designed tunable terahertz absorbers by adding active metamaterials. Combined with the research status of tunable terahertz metamaterial absorbers at home and abroad, this paper classifies and expounds several typical of tunable terahertz metamaterial absorbers, focusing on the research work of single-band, multi-band, broadband, and switchable dual-function terahertz metamaterial absorbers, and finally analyzes their future development trends.
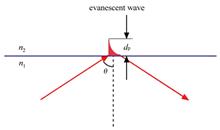
THz-attenuated total reflection (THz-ATR) spectral detection technology for water-containing samples has the advantages of no labeling, no ionization and high detection sensitivity. It has great application potential in the qualitative and quantitative detection of disease markers, so it is of great practical significance for the early diagnosis and staged diagnosis and treatment of major diseases. On the basis of a brief introduction to the basic principles of THz-ATR technology for the detection of aqueous samples, the application of THz-ATR spectroscopy detection technology with different radiation sources in biomedical detection is analyzed and compared in detail. Finally, the research status and future development trend of THz-ATR spectral detection technology are briefly summarized.
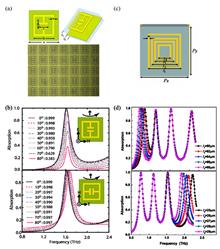
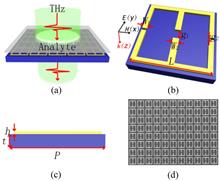
A terahertz toroidal dipole metamaterial sensor based on mirror symmetric square ring structure with double split is designed and fabricated, and a transmission resonant valley with a Q value of 16.8 at 1.436 THz can be provided by the sensor. The surface current analysis of the structure at resonant frequency shows that the device can rapidly strengthen the toroidal dipole while suppressing the electric dipole and magnetic dipole. As a toroidal dipole metamaterial biosensor, the device has a sensitivity of up to 348.8 GHz /RIU when the analyte thickness is saturated, and can sensitively detect the small changes of the surface dielectric environment. The experimental results have demonstrated the perfect resolutions for discrimination between standard edible oil and gutter oil, indicating its great application prospects in food safety monitoring.
The molecular vibration and rotation energy levels of explosives have unique fingerprint characteristics in the terahertz spectrum, and terahertz wave has strong permeability and low energy to non-polar substances and dielectric materials. Therefore, the use of terahertz spectrum can realize the non-destructive detection of dangerous goods in hidden environment. However, the standard library of terahertz absorption spectroscopy of materials is not perfect presently, the parameters of terahertz spectrometers on the market are different, and the detection standards are not uniform, resulting in the unreliable identification methods solely relying on absorption peaks. To address the problems, an identification technical route that no longer depends on the absorption peaks is proposed. In the method, firstly, terahertz absorption spectrum of substances with different frequency resolutions and different obstacle hidden conditions are extracted, the continuous wavelet transform of Marr is used to get a wavelet frequency domain scale map with unique characteristics, and then a data set is established. Secondly, combined with the transfer learning method, the transfer learning of Xception network is used to train and identify the data set. Experimental results show that this method is very effective in identifying explosive dangerous goods with different obstacle hidden conditions, and the recognition rates can reach 94%. It is indicated that the recognition accuracy of the proposed method can not be affected by system factors such as frequency resolution, which provides a new technical approach for non-destructive identification of dangerous goods hidden by obstacles such as package.
α-lactose hydrate is an important hydrate, and the effect of its bound water on the structure of lactose molecule has been one of the hot topics in the related fields. By setting the temperature step, the terahertz kinetics of α-lactose monohydrate at low temperatures was investigated using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy technique, and the temperature dependence of the two characteristic absorption peaks of α-lactose monohydrate at 1.2 THz and 1.3 THz was found. In order to further investigate the generation mechanism of the three absorption peaks of α-lactose monohydrate, the vibrational analysis of the absorption peaks was carried out based on density functional theory for single-molecule and unit cell theory calculations, respectively. The results show that the absorption peaks of α-lactose hydrate originate from intermolecular interactions between water molecules and lactose molecules and the vibrations of lactose molecular skeleton, and it is also shown that unit cell calculations are more accurate in predicting the vibrational modes than single-molecule calculations.
The quality and safety of wheat is an important part of food safety. The traditional identification and detection method of moldy wheat seed requires complex processing steps, which is time-consuming and has poor feature extraction capability, and is prone to the loss of effective image information, resulting in poor wheat moldy seed identification detection. To solve the above problems, a terahertz spectral image recognition method for moldy wheat based on denoising convolutional neural network-broad learning system (D-BLS) is proposed in this paper. The method improves the traditional broad learning system (BLS) algorithm and constructs a D-BLS moldy wheat classification and recognition model by introducing a denoising convolutional neural network (DnCNN) denoising network to enhance image quality and improve the recognition accuracy of moldy wheat terahertz spectral images. The results show that D-BLS outperforms the traditional BLS algorithm in terms of recognition accuracy, with a recognition accuracy of 93.13%. Fruthermore, support vector machine (SVM), back propagation neural network (BPNN), convolutional neural network (CNN) are used for modeling to compare with D-BLS. The experimental results show that the classification accuracy of the D-BLS network is 13.83%, 7.79% and 3.96% higher than that of SVM, BPNN and CNN, respectively. Therefore, it is believed that the proposed D-BLS algorithm can provide a new effective method for early identification of wheat mold.
In order to meet the demand of highly integrated RF transceiver link in terahertz communication and imaging systems, a precise model of the device is established on the basis of the self-developed terahertz Schottky diode, and then a frequency doubling/mixing monolithic integrated chip based on diode is designed and fabricated, which solves the problems of difficult assembly and poor consistency of traditional diode, and improves the performance of the device. The 170 GHz, 340 GHz frequency multiplier and 340 GHz mixer modules are successfully developed, and then the integrated 340 GHz transmitting and receiving links are further developed. The integrated module of the transmitter realizes the output of 342 GHz with a power of 22 mW, and the integrated module of the receiving end realizes a frequency conversion loss of 10 dB up or down at 330-350 GHz single sideband. The development of the module lays the foundation for the future application of terahertz communication and imaging technology.
A quantitative analysis model for detecting Cr in soil with laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) was established by using correlation vector machine (RVM) combined with principal component analysis (PCA). Fourteen soil samples with different Cr concentrations were prepared, of which ten were selected as training samples for model construction, and the other four as test samples for model performance evaluation. The results show that the prediction accuracy of PCA-RVM model is significantly better than that of RVM model for the measurement of Cr content in soil. The root mean square error (RMSE) of the whole prediction is reduced from 8.00% of RVM model to 3.21% of PCA-RVM model, and the prediction accuracy is improved by 59.9%. Compared with RVM model, the relative standard deviation of repeated prediction results of PCA-RVM model for all four samples in the test sample set is significantly reduced and is less than 1.89%, indicating that the prediction results of PCA-RVM model have better stability.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) can rapidly and nondestructively measure the composition and content of organic matter. As an important organic chemical raw material, ethylene is widely used in the manufacturing of bulk chemicals such as plastics, alcohols and fibers. However, due to its volatility, ethylene is harmful to the environment and human body. To improve the accuracy of FTIR in the detection model of ethylene concentration, an improved IRIV-SA infrared spectral wavenumber optimization algorithm is proposed based on the advantages of iteratively retains informative variables method (IRIV) and simulated annealing algorithm(SA). On the basis of stable selection of a large number of spectral characteristic wavenumbers by IRIV algorithm, this method uses SA to further screen a small number of effective characteristic wavenumbers, so as to reduce the complexity of the model and improve the detection accuracy of organic matter spectrum. In the experiment, IRIV-SA is used to select the wavenumber of the concentration of ethylene infrared spectrum at first, and the number of characteristic wavenumbers obtained is reduced from 271 to 5, then the characteristic wavenumber is used for modeling. The results show that the correlation coefficient and root mean square error of validation set are 0.9989 and 0.3943, and the correlation coefficient and root mean square error of prediction set are 0.9978 and 0.6652, which indicates that the modeling accuracy of the proposed algorithm is significantly improved compared with that of the whole spectrum modeling. To further verify the effectiveness of the improved algorithm, IRIV, SA, CARS (competitive adaptive reweighted sampling algorithm), SPA (successive projections algorithm), IRIV-CARS and IRIV-SPA wavenumber selection models are established for comparative experiments on the same data set. The comparison results show that IRIV-SA algorithm is superior to the above six wavenumber selection methods, and is an effective feature wavenumber selection method.
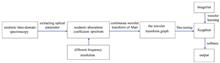
Using a homemade 776.9 nm semiconductor laser as seeder, a 2.3 W fundamental frequency output is obtained through amplification of a tapered amplifier (TA) and shaping. Then, a 388.4 nm continuous-wave laser is generated by the second harmonic generation (SHG) of a Class I phase matched lithium borate (LBO) crystal with an external bow-tie cavity. It is shown that the severely thermal effect of TA can change the waist position of the generated laser beam and limit the conversion efficiency of the second harmonic generator. Therefore, the thermal effect of TA is analyzed, and a laser beam shaping scheme consisted of cylindrical lens, prism pair and lens is proposed to compensate for the thermal effect. Furthermore, by optimizing the beam waist size and cavity parameters of the cavity, the conversion efficiency of the second harmonic is improved. Finally, the basic frequency input of 2.3 W can generate a ultraviolet laser output of 940 mW, with SHG efficiency of 41%.
Negative feedback avalanche photodiode (NFAD) is an InGaAs avalanche photon diode counting device with monolithic integrated negative feedback resistance. In single photon detector based on NFAD, a high-sensitivity refrigeration system is a necessary condition to ensure its normal operation. Therefore, a set of refrigeration system with high sensitivity has been designed by combing passive and active refrigeration in this paper. Through theoretical calculation, simulation and measurement, it is shown that the internal power consumption of the refrigeration system is reduced by 58.63%. Moreover, at room temperature of 25 oC and high temperature of 65 oC, the system can control the working temperature of negative feedback avalanche photodiode at (-20 ± 0.3) oC, indicating that the designed refrigeration system has the advantages of strong environmental adaptability, large refrigeration temperature difference and controllable refrigeration temperature.
Security analysis is an indispensable part of practical quantum key distribution (QKD) protocol, which can not only evaluate the eavesdropping ability of external attacks, but also provide a security bound for the key rate of system. Quantum channel attack is the main content of QKD security analysis, among which collective attack is considered to be one of the most powerful quantum channel attacks. In this paper, a generalized collective attack operation, composed of generalized bipartite coupling and the optimal positive operator-valued measurement (POVM) is constructed, and a theoretical study on the security analysis of E91-QKD against collective attack is carried out. The simulation results show that under collective attack, the mutual information between the eavesdropper and the communicator is less than that proposed by the entanglement purification protocol, and the key rate and bit error rate tolerance have been significantly improved. The security analysis developed in this work provides a theoretical method to increase the key rate for practical QKDs, which can be compatible with other experimental methods.
According to the requirement for the concentration gradient generator (CGG) in the chip laboratory, a method of moving focal plane front and back exposure to fabricate SU-8 photoresist microstructure is developed for fabricating CGG with vertical sidewalls. In the method, the thickness of SU-8 photoresist is divided into multiple layers according to the focal depth, and the focal plane moves one layer down with each exposure. When the number of exposed layers reaches half of the total layers, the sample is turned over, and the same exposure way is repeated. At last, the photochemical reaction channel inside SU-8 is formed, and SU-8 is fully exposed. Finally, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) CGG is fabricated using the SU-8 microstructure. The results show that the sidewall of the SU-8 microstructure is vertical, without "T" shaped structure, and the channel height of the SU-8 microstructure is 49.4 μm. The sidewall of PDMS CGG is also vertical with the channel depth of 49.3 μm, fully meeting the vertical requirements of CGG sidewalls.