View fulltext
View fulltext
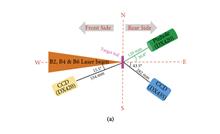
The laboratory generation and diagnosis of uniform near-critical-density (NCD) plasmas play critical roles in various studies and applications, such as fusion science, high energy density physics, astrophysics as well as relativistic electron beam generation. Here we successfully generated the quasistatic NCD plasma sample by heating a low-density tri-cellulose acetate (TCA) foam with the high-power-laser-driven hohlraum radiation. The temperature of the hohlraum is determined to be 20 eV by analyzing the spectra obtained with the transmission grating spectrometer. The single-order diffraction grating was employed to eliminate the high-order disturbance. The temperature of the heated foam is determined to be T = 16.8 ± 1.1 eV by analyzing the high-resolution spectra obtained with a flat-field grating spectrometer. The electron density of the heated foam is about Ne=4.0±0.3×1020cm-3 under the reasonable assumption of constant mass density.
We have employed the VULCAN laser facility to generate a laser plasma X-ray source for use in photoionization experiments. A nanosecond laser pulse with an intensity of order 1015 Wcm-2 was used to irradiate thin Ag or Sn foil targets coated onto a parylene substrate, and the L-shell emission in the 3.3–4.4 keV range was recorded for both the laser-irradiated and nonirradiated sides. Both the experimental and simulation results show higher laser to X-ray conversion yields for Ag compared with Sn, with our simulations indicating yields approximately a factor of two higher than those found in the experiments. Although detailed angular data were not available experimentally, the simulations indicate that the emission is quite isotropic on the laser-irradiated side but shows close to a cosine variation on the nonirradiated side of the target as seen experimentally in the previous work.
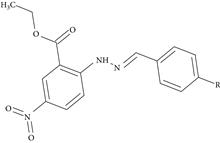
The third-order nonlinear optical properties of three hydrazone derivatives, namely, ethyl 2-((2E)-2-(4-(dimethylamino)benzylidene]hydrazinyl)-5-nitrobenzoate, ethyl 2-((2E)-2-(4-chlorobenzylidene)hydrazino)-5-nitrobenzoate, and methyl 5-nitro-2-((2E)-2-(4-nitrobenzylidene)hydrazino)benzoate were investigated by the single beam Z-scan technique with nanosecond laser pulses at 532 nm. The compounds were doped into PMMA (poly (methyl methacrylate)), and their third-order nonlinearity was studied with a prospective of reaching a compromise between processability and high nonlinear optical behavior. The optical limiting study of the samples was carried out at 532 nm. The measured values of the third-order nonlinear susceptibility, χ(3), and the nonlinear refractive index, n2, are of the order of 10-13 esu and 10-11 esu, respectively. The nonlinear absorption in materials was attributed to reverse saturable absorption. The results are quite promising for possible applications in photonic devices.
We investigate the production of intense ү-rays following the interaction of ultraintense laser pulse with a hybrid combination of under-dense plasma associated with a thin foil of fully ionized Al or Cu or Au at the rear side. Relativistic electrons are accelerated following the interaction of high intensity laser pulses with an under-dense plasma. These electrons are then stopped by the thin foils attached to the rear side of the under-dense plasma. This results in the production of intense-ray bursts. So, the enhancement of photon generation is due to the under-dense plasma electrons interacting with different over-dense plasma. Using open-source PIC code EPOCH, we study the effect of different electron densities in the under-plasma on photon emission. Photon emission enhancement is observed by increasing the target Z in the hybrid structure. Hybrid structure can enhance photon emission; it can increase the photon energy and yield and improve photon beam divergence. Simulations were also performed to find the optimal under-dense plasma density for ү-ray production.
We present a novel method that we call FAINE, fast artificial intelligence neutron detection system. FAINE automatically classifies tracks of fast neutrons on CR-39 detectors using a deep learning model. This method was demonstrated using a LANDAUER Neutrak® fast neutron dosimetry system, which is installed in the External Dosimetry Laboratory (EDL) at Soreq Nuclear Research Center (SNRC). In modern fast neutron dosimetry systems, after the preliminary stages of etching and imaging of the CR-39 detectors, the third stage uses various types of computer vision systems combined with a manual revision to count the CR-39 tracks and then convert them to a dose in mSv units. Our method enhances these modern systems by introducing an innovative algorithm, which uses deep learning to classify all CR-39 tracks as either real neutron tracks or any other sign such as dirt, scratches, or even cleaning remainders. This new algorithm makes the third stage of manual CR-39 tracks revision superfluous and provides a completely repeatable and accurate way of measuring either neutrons flux or dose. The experimental results show a total accuracy rate of 96.7% for the true positive tracks and true negative tracks detected by our new algorithm against the current method, which uses computer vision followed by manual revision. This algorithm is now in the process of calibration for both alpha-particles detection and fast neutron spectrometry classification and is expected to be very useful in analyzing results of proton-boron11 fusion experiments. Being fully automatic, the new algorithm will enhance the quality assurance and effectiveness of external dosimetry, will lower the uncertainty for the reported dose measurements, and might also enable lowering the system’s detection threshold.
Multi-GeV proton radiography is an important tool for diagnosing density distribution of thick objects. The magnetic lens system called Zumbro lens is widely employed because it compensates for the image distortion induced by small angle multiple Coulomb scattering (MCS) that occurs when the charged protons passing through the object. However, radiography is still suffering from chromatic aberration induced blurring, if the momentum of transmitted proton is different from the reference value of Zumbro lens. In this paper, two methods are employed to reduce chromatic aberration. The first is based on magnetic lens optimization. In addition, a new lens system is first proposed locating the downstream of Zumbro. It is named “auxiliary” lens, which can correct the chromatic aberration for certain protons with momentum far away from the reference of Zumbro lens. Monte Carlo simulation shows that this proposed lens can decrease chromatic aberration and improve the radiography image evidently.
In two-dimensional (2D) electron systems, the viscous flow is dominant when electron-electron collisions occur more frequently than the impurity or phonon scattering. In this work, a quantum hydrodynamic model, considering viscosity, is proposed to investigate the interaction of a charged particle moving above the two-dimensional viscous electron gas. The stopping power, perturbed electron gas density, and the spatial distribution of the velocity vector field have been theoretically analyzed and numerically calculated. The calculation results show that viscosity affects the spatial distribution and amplitude of the velocity field. The stopping power, which is an essential quantity for describing the interactions of ions with the 2D electron gas, is calculated, indicating that the incident particle will suffer less energy loss due to the weakening of the dynamic electron polarization and induced electric field in 2D electron gas with the viscosity. The values of the stopping power may be more accurate after considering the effect of viscosity. Our results may open up new possibilities to control the interaction of ions with 2D electron gas in the surface of metal or semiconductor heterostructure by variation of the viscosity.
The energy balance of the p-11B fusion scenario with compensation of the transfer of kinetic energy of protons and alpha particles to the gas medium by the electric field is considered. It is shown that such scenario cannot provide the use of p-11B fusion reaction for power production due to the very low ratio of the energy release of the fusion reaction to the energy necessary for compensation. The upper boundary of this ratio is about 2×10-3.