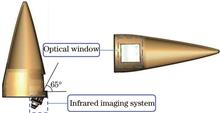
In the supersonic flight state of 3 Ma (1 Ma≈340.3 m/s), the temperature of the optical window heated by aerodynamics rises sharply, resulting in a large amount of infrared thermal radiation, which interferes with the imaging quality of the detector. In order to study the influence of aerodynamic thermal radiation on infrared imaging, this paper used ANSYS software to perform 3D modeling, finite element meshing and temperature field simulation on the seeker model; by using Planck's blackbody radiation formula and TracePro software, the irradiance generated by the target source and the optical window at different temperatures were calculated and simulated, and the signal-to-noise ratio model was established to analyze the influence of the temperature of the optical window and the relative distance of the target on the infrared imaging quality of the seeker. The results showed that the signal-to-noise ratio of the infrared imaging system decreased by 91.8%, 50.1%, and 20.7%, respectively after the seeker flew at an altitude of 2 km, 11 km, and 20 km for 10 seconds. The decrease of signal-to-noise ratio will seriously affect the imaging quality of the infrared system, and the cooling measures must be used to cool the optical window for reducing the interference. This paper will provide data reference for the design of the optical window of the seeker and the optical detection system, and will provide theoretical basis for the research on overcoming the interference of aerodynamic heat radiation.
Aiming at the problems of low recognition rate and hyper-parameter setting of deep learning model in electric load recognition, a non-intrusive electric load recognition model (PSO-CNN) combining particle swarm optimization algorithm (PSO) and convolutional neural network (CNN) was proposed. First, the pixelated image of VI trajectory of each appliance is used as the CNN input feature. Secondly, the influence of CNN hyper-parameter on model performance was analyzed, and PSO algorithm is used to find the optimal solution to improve model recognition effect. Finally, the PLAID and WHITED public datasets were used to compare and verify the PSO-CNN model. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracy and average F-measures of this model are better than other models. The model effectively reduces the confusion between devices and has good recognition and generalization ability.
In biological breeding and genomic research, the three-dimensional phenotypic structure information of plants is especially crucial. To extract the three-dimensional phenotypic information of plants efficiently, quickly, and nondestructively, taking corn as an example, a method for extracting the three-dimensional phenotypic structure information of maize seedling at leaf-scale from a three-dimensional point cloud produced from an image is proposed in this study. First, using a motion recovery structure algorithm, the image obtained from a mobile phone is rebuilt to produce a three-dimensional point cloud and then integrated with the ExGR index and conditional Euclidean clustering algorithm to automatically extract the corn seedlings from the surrounding environment. We employ the regional growth algorithm to segment the leaves. Finally, the three-dimensional phenotypic structure information of corn seedlings, including height, three-dimensional volume, leaf area, and leaf perimeter, are computed, and the dynamic changes of phenotypic information over time are examined. The findings demonstrate that the method in this study compares with the real value; the root mean square error (RMSE) of plant height, leaf area, and leaf circumference is 0.77 cm, 1.62 cm2, and 1.21 cm, respectively; the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) is 3.23%, 8.27%, and 4.75% respectively; and the determination coefficient R2 reaches above 0.98. The proposed method can efficiently and nondestructively extract the three-dimensional phenotypic structure information of corn seedlings and can be extended to the extraction of other columnar structure plant phenotypic information.
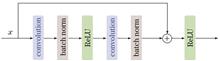
According to the issues of single-scale image feature extraction, small receptive field, and cannot highlighting salient features in existing deep learning based image fusion algorithms, this paper proposes a multi-scale dilated convolution network with attention mechanism for multi-focus image fusion. First, a multi-scale dilated convolution block (MDB) is proposed. The MDB with different dilation rates can provide different receptive fields, and consequently it can extract the multi-scale features. Moreover, the attention mechanism is introduced into the MDB, which can adaptively select the salient features and improve the performance further. The proposed fusion network consists of three parts, including feature extraction, feature fusion, and image reconstruction. Specifically, the feature extraction part is composed of several MDBs. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method is competitive to some existing deep learning based methods. Some ablation studies also verify that the MDB can enhance the ability of feature extraction and improve the image fusion quality.
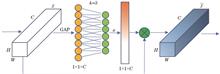
To explore the application potential of unmanned aerial Vehicle (UAV) remote sensing images for subtropical tree species recognition, the ECA-ResNet with residual module and effective channel attention is proposed to train and recognize single tree crown images. First, the single tree crown was extracted by single-tree segmentation algorithm. The single-tree crown image patch dataset of UAV visible image was constructed by means of clipping images with different window sizes, and they were divided into training data, validating data, and independent test dataset respectively. Second, with ResNet50 as a backbone network, by inserting effective channel attention into ResNet bottleneck and adjusting network structure, the ECA-ResNet was constructed. Then, the datasets were inputted into pretrained ECA-ResNet model for parameter training and validation iteratively, and independent test. After that, the optimum window size of single-tree crown image was determined. The results show that the ECA-ResNet gets a better recognition result for tree species in single-tree crown image patch dataset with window size of 64×64 pixel, the accuracy of training and validation of the proposed network reaches 98.98% and 96.60%, respectively. The recognition accuracy and Kappa coefficient of independent test reach 85.61% and 0.8140. The training, validation, and independent test accuracy of ECA-ResNet in this paper are 2.63 percentage points, 1.80 percentage points , and 5.31 percentage points higher than that of the ResNet50 respectively. It is proved that, convolutional neural network (CNN) can fully extract the spatial features of UAV visible images for tree species recognition, effective channel attention can effectively improve CNN' single tree species recognition capability.
The occurrence of apple leaf diseases has a significant impact on apple quality and yield. Disease monitoring is therefore an important measure to ensure the healthy development of the apple industry. Based on the ResNet structure, a lightweight disease recognition model based on multiscale feature fusion is proposed. First, the feature fusion mechanism is used to extract and fuse the high-dimensional and low-dimensional features of the network, strengthen the transmission of semantic information between convolution layers, and enhance the ability to distinguish subtle lesions. Next, multi-scale depth separable convolution is added to extract disease features of different scales by using multi-scale convolution kernel structure, which improves the richness of features and restricts the parameters of the model. Finally, a dataset containing five kinds of apple leaf diseases is used to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracy of the model is 98.05%, and that the number and calculation of the model network are only 4.02 MB and 0.92 GB, respectively. Compared with other models, it also has advantages, and can provide a new scheme for the accurate identification of diseases and pests in agricultural automation.
A multiscale fusion algorithm based on image enhancement and rolling guidance filtering is proposed to solve the problems of thermal target brightness loss and visible image detail information loss caused by infrared and visible image fusion. First, an adaptive image enhancement method is proposed to improve the overall brightness of the visible image and maintain the contrast of the details. Second, according to the different features, the source image is divided into three layers, and the luminance layer is obtained by using the significant extraction method based on guidance filtering. The favorable scale perception and edge preservation characteristics of rolling guidance filtering are used, and the basic layer and detail layer are obtained by combining Gaussian filtering. Finally, the fusion rule of large pixel value is used for the luminance layer, a least-squares optimization scheme is proposed for the basic layer, and the sum of the modified Laplace energy is used as a measure of sharpness for the detail layer. The experimental results show that, compared with other fusion methods, the proposed method has better performances in both subjective and objective evaluations.
Efficient registration of real-time image and standard image is one of the key steps to ensure the efficiency of cigarette package quality inspection. According to the structure and printing process of cigarette package, a single-angle region registration method is proposed. The method is divided into two steps: rough registration and accurate registration. Rough registration uses the boundary features of cigarette labels to adjust the posture and position of cigarette labels in the image, and removes redundant pixels in the image. The accurate registration uses the homography matrix between the real-time image and the standard image to complete the registration. The experimental results show that the single-angle region registration algorithm is superior than scale invariant feature transformation, ORB, and AKAZE algorithms in registration speed and effect, and can meet the real-time requirements of cigarette package quality detection.
To address the problems of underutilization of low-frequency information and easy mixing of high-frequency details with noise in the current infrared and visible image fusion methods, an infrared and visible image fusion method based on structure-texture (ST) decomposition and VGG deep network is proposed. First, the input image is decomposed into high-low frequency subbands using mean filtering, and ST is introduced to re-decompose the low-frequency subbands. The structure and texture are pre-fused by absolute maximum and neighborhood spatial frequency, respectively. Subsequently, the input image is input into the VGG network to get the multi-layer feature maping, and the Sigmiod function is used to realize the normalized prefusion of the high-frequency subband. Finally, the pre-fused high-frequency, low-frequency structure, and low-frequency texture are used for image fusion and reconstruction. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can fuse the deep detail features of images, retain texture details, and suppress noise effectively, and has significant advantages in noise assessment, structural similarity index measure, mean square error, peak signal to noise ratio, and other objective indexes.
A super-resolution computed tomography (CT) reconstruction method based on a residual attention aggregation dual regression network (RAADRNet) is proposed to improve the quality of CT image reconstruction. The multi-feature down-sampling extraction block (MFDEB) is used to complete multi-feature down-sampling extraction by employing average pooling, maximum pooling, and convolution operations, and channel learning attention (CLA) and spatial learning attention (SLA) are embedded after multi-feature fusion. Moreover, the shallow features of an image are extracted by combining the previous fusion features. CLA and SLA respectively introduce channel weight feature learning and activation function 1+tanh() to complete feature extraction. The residual attention aggregation block (RAAB) requires the use of the residual channel learning attention block (RCLAB) composed of a CLA-embedded residual network and the spatial feature fusion block (SFFB) composed of SLA for jointly extracting the deep features of the image. The primal network completes reconstruction after the feature fusion of shallow features and deep features amplified by sub-pixel convolution. The dual network further constrains the solution space of the reconstructed mapping function. Experiments show that the proposed algorithm improves the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity (SSIM) of the reconstructed image.
Underwater images often suffer from low contrast, color distortion, and poor visibility. To solve these problems, herein a novel underwater image restoration method based on scene depth estimation and background segmentation is proposed. First, the scene depth is estimated using multiple oblique gradient operators and attenuation difference among color channels. Then, according to the image gradient and color difference information, the degraded underwater image is divided into the foreground region and the background region. Accordingly, the background light (BL) is estimated in the background region and transmission maps are obtained using the estimated scene depth map. Subsequently, the scene radiance of the foreground region is recovered based on the underwater image formation model, and the background region is enhanced by performing histogram stretching in the HSV color space. Finally, the foreground and background are fused using a weight map of the transition region to obtain the final restoration result. Experimental results show that the proposed method can estimate the background light and transmittance with significantly greater accuracy, and achieves satisfactory contrast enhancement, color correction, and sharpness improvement. Compared with several classical methods, the proposed method affords 15% better performance on average in terms of the following four image quality evaluation metrics: UIQM, UCIQE, FDUM, and FADE.
Present image-defogging methods have a range of problems: insufficient numbers of real datasets, local contrast imbalance, and defogging image distortion. This paper proposes a novel defogging network model (Densely Resnet with SKattention-Dehaze Net, DRS-Dehaze Net) that mitigates defogging image distortion. First, the fogged image is transformed into a multi-angle feature input map by the preprocessing module. The feature information is then extracted and redistributed through a dense residual architecture with an attention mechanism. Finally, the features are fused to output a fog-free image. Experimental comparison results confirmed a better defogging effect of the proposed algorithm than that of other algorithms. Our model effectively improves the distortion in defogged images and enhances the image clarity to a certain extent.
Point cloud data has the characteristics of disorder and sparsity. The three-dimensional (3D) point cloud completion task of recovering the missing 3D geometric shapes through incomplete point cloud data is a challenging issue in 3D vision technology. The existing 3D point cloud completion network predicts the complete point cloud shape directly from a subset of the point cloud using the Encoder-Decoder model, which interferes with the original part of the point cloud, resulting in noise and geometric displacement loss. In this study, an end-to-end network model is proposed, which focuses on generating a smooth and uniformly distributed point cloud object. The proposed network model mainly consists of the following three parts: missing point cloud prediction, point cloud fusion, and point cloud smoothing. The first module mainly uses multiencoders to extract local information and global information from incomplete point cloud objects to predict the missing geometric parts. The second module merges point cloud objects by sampling algorithm. The third module is based on a Residual-Transformer (RT) to predict the displacement of the points, which can make the point distribution more uniform without destroying the spatial structure of the original input point cloud. On the benchmark dataset, Shapenet-Part, several experimental results indicate that the proposed network has achieved better quantitative results and visual effects in 3D shape completion.
For the characteristics of subtle differences between various subclasses and large differences between same subclasses in a fine-grained image, the existing neural network models have some challenges in processing, including insufficient feature extraction ability, redundant feature representation, and weak inductive bias ability; therefore, an enhanced Transformer image classification model is proposed in this study. First, an external attention is employed to replace the self-attention in the original Transformer model, and the model's feature extraction ability is enhanced by capturing the correlation between samples. Second, the feature selection module is introduced to filter differentiating features and eliminate redundant information to improve feature representation capability. Finally, the multivariate loss is added to improve the model's ability to induce bias, differentiate various subclasses, and fuse the same subclasses. The experimental findings demonstrate that the proposed method's classification accuracy on three fine-grained image datasets of CUB-200-2011, Stanford Dogs, and Stanford Cars reaches 89.8%, 90.2%, and 94.7%, respectively; it is better than that of numerous mainstream fine-grained image classification approaches.
During the acquisition and cross-media reproduction of videos, colors can be distorted because the color gamut of the camera is limited and may differ from the color gamut of the display device. Skin color is among the most sensitive colors to the human eye. Therefore, skin-color distortion can deteriorate viewers' video experience. Skin-color enhancement is a processing technology that adjusts a distorted skin color to improve the display quality. Particularly in video processing, the self-adaptability of a skin-color model must be improved while considering the real-time performance and computational load of the algorithms. For these purposes, the present paper proposes an adaptive skin-color enhancement method for real-time video processing. The update of the skin-color model is guided by shot boundaries, which can reduce the computational load of updating. Second, a dynamic skin-color model updated with the shot boundary is built for skin detection. Finally, the preferred skin-color model and skin-color enhancements for different races are achieved through subjective experiments. The proposed method achieved higher mean opinion scores than the existing methods in subjective evaluation experiments. In addition to achieving the targeted skin-color enhancement, the proposed method significantly reduced the computational load of model update.
To improve the encryption efficiency and security of images, this study proposes an optical double-image encryption method based on fingerprint keys. First, two grayscale images to be encrypted are modulated by two fingerprint-based random-phase masks, one placed at the input plane, the other at the Gyrator transform plane. The modulated results are then Gyrator transformed and combined into a complex-valued image. Subsequently, the encrypted image and two phase keys are obtained via phase-amplitude truncation on the complex-valued image. During the decryption process, the decryption key can be any of the following: the fingerprint, either phase key obtained by amplitude truncation, initial values and control parameters of the chaotic map, or parameters of the Gyrator transform. In the proposed encryption method, the secret key is associated with user identity, thereby enhancing system security. It also allows more convenient management of the secret keys because the phase-mask keys do not need to be transmitted over the network. Numerical simulations indicate the feasibility of the proposed encryption method and its high security and robustness against various attacks.
The point cloud data in the civil bridge construction scene includes a large number of vegetation, ground, and bridge construction point clouds. The extraction integrity of bridge buildings is still an issue for the existing filtering algorithms. This study proposes a bridge point cloud extraction algorithm based on combined filtering. First, the proposed algorithm applies the dispersion method to coarsely filter the vegetation by the feature of dispersion of vegetation point cloud distribution. Second, the radius filtering algorithm is improved to finely filter the residual vegetation point clouds based on the idea of radius filtering and making full use of color and elevation features. Finally, the ground point cloud is filtered using the normal filtering method. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm for extracting bridge point clouds has a 99.3% integrity rate and 0.73% error rate. When compared to existing filtering algorithms, the proposed algorithm extracts the bridge point cloud more completely and accurately.
Traditional imaging technology requires that there must be no obstacles between the detector and object. Single-pixel imaging technology does not have this requirement. Due to the various advantages of single-pixel imaging, such as easy construction of the physical system, low cost, and wide spectrum imaging, it has quickly gained significant attention and development in the imaging field. However, single-pixel imaging uses a single-point detector, which requires measurements equal to the pixel number of the target object to obtain a relatively perfect imaging quality. As a result, how to balance the imaging quality and the imaging speed has become not only a technical challenge but also a meaningful task. An adaptive sampling method based on Fourier transform single-pixel imaging is proposed to solve this problem. This method takes advantage of the characteristics of Fourier transform spectrum energy concentration to reasonably plan the sampling path in the frequency domain. Then it measures the spectral coefficient along the planned path, calculates the variance of the spectral coefficient of each sampling path, and performs curve fitting online. When the slope of the curve reaches a range small enough (or close to 0), it will automatically stop sampling and perform an inverse Fourier transform to realize image reconstruction. Thus, the proposed method greatly improves imaging efficiency.
In order to efficiently use infrared precipitation images to determine the precipitation intensity, a precipitation intensity recognition model with fused encoded and decoded features has been proposed. The coding and decoding convolution is introduced into the deep convolution neural network classification model, which can extract the deep-seated features of rain information while reducing the loss of local information. In the coding and decoding convolution module, multi-scale receptive field convolution is considered, and local features in different ranges are fused. At the same time, coding and decoding convolution feature maps of the same scale are fused during decoding, so as to improve feature utilization. Thus, a precipitation intensity recognition model integrating coding and decoding convolution features is constructed. The proposed model has the highest classification accuracy of 91.7% compared to state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, an ablation experiment demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed encoded and decoded model.
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a visualized method for detecting the structural health of carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs). An EIT image reconstruction algorithm based on L1/L2 sparse regularization is proposed for underdetermination and ill-condition in EIT image reconstruction. In this method, the objective functional of the L1/L2 regularization term is constructed, a regularization parameter is added to modify the solution vector during the solution process, and a constraint interval is added in the iterative process to make the solution vector closer to the actual distribution. The simulation and experimental results show that compared with the conjugate gradient (CGLS), Tikhonov, and L1 regularization algorithms, the damage location and size reconstructed using the L1/L2 regularization algorithm are closer to the actual damage model, the damage identification is higher, and the electrode artifact is significantly improved. The proposed algorithm is a new method for applying EIT to the damage detection of CFRP laminates.
The fringe projection three-dimensional measurement technology has been extensively investigated and used by numerous scholars owing to its high precision, high robustness, low cost, and other benefits. However, most traditional approaches require projecting numerous fringes to generate the object's three-dimensional shape. This study provides a fast fringe projection three-dimensional measurement approach, designing a symmetrical phase for phase unwrapping, which can efficiently decrease the number of projected fringes. In this approach, the projector is regarded as an inverse camera, the system is built as a stereo vision system, and a window matching approach is developed to improve the robustness of phase unwrapping using the epipolar limitation of stereo vision for the symmetrical phase information. Compared with the traditional frequency doubling approach and multi-frequency heterodyne approach, the number of fringes of the proposed approach can be reduced by 50% while assuring high accuracy and robustness.
Aiming at the problems of conventional detectors in detecting underwater objects, such as difficulty in feature extraction and missing detection of objects, an improved CenterNet underwater object detection method is proposed. First, a high resolution human posture estimation network HRNet is used to replace the Hourglass-104 backbone network in CenterNet model to reduce the amount of parameters and improve the speed of network reasoning; then, the bottleneck attention module is introduced to enhance the features in the spatial and channel dimensions, and improve the detection accuracy; finally, a feature fusion module is constructed to integrate the rich semantic information and spatial location information in the network, the fused features are processed by receptive field block to further improve the multi-scale object detection ability of the network. A comparison experiment is carried out on the URPU underwater object detection dataset. Compared with CenterNet network, the detection accuracy of the proposed algorithm can reach 77.4%, increased by 1.5 percentage points, the detection speed is 7 frame/s, increased by 35.6%, the amount of parameters is 30.4 MB, compressed by 84.1%. Compared with the mainstream object detection algorithm, this algorithm also has higher detection accuracy, which has higher advantages in underwater object detection.
To accurately identify microorganism species in the activated sludge of sewage treatment systems and modify the wastewater treatment process in real-time, using traditional machine learning methods is a challenge because of various complicated processes. In this study, a deep learning approach based on the integration of attention mechanism and transfer learning is proposed to accurately identify the species of microorganisms in sewage-activated sludge by overcoming the requirements of developing features manually, extracting features, designing classifiers, and other complicated processes. On the basis of transfer learning, the conventional VGG16 model is enhanced by including the attention module (SE-Net block) and modifying the output module, and the dataset is expanded using the data improvement approach. Experimental findings demonstrate that compared with the model before the enhancement, the enhanced model (T-SE-VGG16) can accurately recognize microorganisms in various types of sewage-activated sludge with a test accuracy of 98.21%, which enhances the recognition accuracy and reduces the training time. The model converges rapidly and has a strong generalization ability in terms of training time. Moreover, the T-SE-VGG16 model’s feasibility and reliability for the identification of microorganisms in sewage-activated sludge are verified.
The species diversity and community structure of planktonic algae are important appraisal indicators for evaluating aquatic ecological environment construction, and the recognition of phytoplankton by cell image is a crucial way to achieve the detection of phytoplankton. Compared with the conventional microscopic detection method, the target detection algorithms based on deep learning have been increasingly employed in planktonic algae detection because of their effective detection capability. Aiming at the low detection accuracy challenges of small shape, fuzzy boundary, and cohesive planktonic algae in the YOLOv3 target detection algorithm, spatial pyramid pooling (SPP) was employed to enhance the feature extraction method of the YOLOv3 target detection algorithm. Additionally, the generalized intersection over union (GIoU) boundary loss function was employed to replace the YOLOv3 target detection algorithm in this study. Finally the SPP-GIoU-YOLOv3 planktonic algae detection algorithm was constructed based on the YOLOv3 algorithm. The findings demonstrate that the mean average precision of the SPP-GIoU-YOLOv3 target detection algorithm for detecting planktonic algae is up to 95.21%, which is 4.24 percentage points higher than that of theYOLOv3 algorithm. These findings are important for developing accurate rapid detection methods and technologies of planktonic algae.
During semantic segmentation of images, a convolutional neural network easily misplaces the high-level features with low-level features after down-sampling and padding operations. To solve the mismatch problem between high- and low-level features and better aggregate the multiscale feature information, this paper proposes a semantic segmentation method with a multiscale feature alignment aggregation (MFAA) module. The MFAA module adopts a learnable interpolation strategy to learn pixel transform migration, thereby alleviating the feature-misalignment problem of feature aggregation at different scales. The module includes an attention mechanism that improves the decoder's ability to recover the important details. Using multiple MFAA modules, the semantic information of high-level features, and the spatial information of low-level features, this method aligns and aggregates the high- and low-level features to refine the semantic segmentation effect. The proposed network structure was validated on PASCAL VOC 2012. Using a ResNet-50 backbone network, the mean intersection-over-union reached 78.4% on the validation set. Experimentally, the proposed method achieved better evaluation indices than several mainstream segmentation methods and effectively improved the image segmentation effect.
Target detection is an important research direction in the field of computer vision. Although the single-shot detector (SSD) model achieves good results in terms of detection accuracy and speed, its use of shallow features with low semantic information for training small targets is prone to target misses and false detections. In this paper, an improved SSD target detection model based on a once bidirectional feature pyramid network (OBSSD) is proposed. First, a bidirectional feature fusion module is constructed based on the principle of hierarchical fusion to solve the problem of under-utilization of shallow features. Second, fusion weights are introduced to fuse features at different levels more effectively and mitigate the problem of low semantic information of shallow features. Finally, a detection unit based on the residual module is added before classification and regression prediction to address the problem of inaccurate target localization caused by the biased translational invariance of the classification network. The experimental results on the PASCAL VOC2007 test set show that the mean average precision (mAP) of the proposed model is 80.8%, which is 6.5 percentage points higher than that of the SSD model, and the detection speed meets the demand for real-time detection.
Diabetes would increase the risk of retinal vascular disease, and may further develop into diabetic retinopathy in severe cases. Among all pathological features of diabetic retinopathy, microaneurysms, bleeding, hard exudates, and soft exudates are usually typical. In recent years, with the development of deep learning, intelligent assisted diagnostic medicine has become a trend. The premise of intelligent aided diagnosis is that the corresponding lesion area can be extracted qualitatively and quantitatively. Therefore, a model of fundus lesion detection is proposed in this paper with cascade architecture parameter optimization, which effectively solves the multi-scale and small target problems of fundus lesions. The comprehensive test accuracy of detecting lesions on DDR dataset can reach 0.380, which is better in detection performance than the current mainstream detection network.
The automatic segmentation of glands and polyps is the foundation for the diagnosis of artificial intelligence-assisted colorectal adenocarcinoma. However, the size and shape of segmentation targets in medical images vary considerably, and the automatic segmentation approach based on a convolutional neural network has thus run into a hindrance. Therefore, a dual branch network (LG UNet) combining convolutional neural network and self attention is proposed to improve the accuracy of segmentation. First, the Local UNet branch was developed based on U-Net, and the convolutional neural network's benefits were employed to elucidate the segmentation target's local information. Subsequently, the segmentation details were optimized using the Transformer's learning ability of global dependencies in the Global Transformer branch. Finally, during the encoding process, feature maps of the Local and Global branches were merged by a cross-fusion module to complement their benefits. The two test subsets of Glas and findings of LG UNet were 93.62% and 88.44% for Test A and 88.17% and 80.49% for Test B, employing the Dice coefficient and intersection and union (IOU) coefficient as the primary examination indexes. Furthermore, the Dice and IOU coefficients in the polyp segmentation dataset Kvasir-SEG were 85.63% and 77.82%, respectively. The experimental findings demonstrate that LG UNet exhibits better performance efficiency in gland and polyp segmentation by combining the benefits of the Transformer and convolutional neural network.
A U-shaped colon polyp image segmentation network combined with HarDNet and reserve attention is proposed with the aim of solving the problems in the diversity of shape, size, color, and texture of colon polyps, the similarity between polyps and the background, and the low contrast of colonoscopy images, which affects the segmentation effect. The proposed model is based on the U-shaped encoder-decoder structure. First, the encoder uses HarDNet68 as backbone network to extract features for improving the reasoning speed and computational efficiency. Second, the decoder uses three reverse attention modules for fusing and refining the boundary features. Finally, multi-scale information fusion is realized between encoder and decoder through a receptive field module to provide more detailed edge information for the decoder. The iterative interaction mechanism between the encoder and decoder can effectively correct conflicting regions in the prediction results, improving the segmentation accuracy. The experimental results show that compared with existing methods, the proposed method improves segmentation accuracy and also has good real-time and generalization ability. The research results can provide a reliable basis for the early screening of colonic polyps.
To improve the accuracy of radiotherapy, it is necessary to monitor the displacement of the patient's focus area in real time during radiotherapy. Considering that the surface of the patient's body is blocked by the thermoplastic film used during radiotherapy, the material and shape of the marker were designed to minimize the impact of this thermoplastic film on the positioning accuracy of the marker. First, the markers covered by the thermoplastic film were segmented according to their color characteristics; thereafter, the convex hull algorithm was employed to calculate the outer contour of the markers. Next, the improved least squares ellipse fitting algorithm was adopted to fit the points on the outer contour of the markers and locate the markers. Lastly, based on the location of the markers, features were matched to the markers, and the patient's displacement value was thus calculated. Based on a simulation experiment platform and multiple experiments, this method for measuring patient displacement achieves an accuracy of 0.2 mm, with frame rates of up to 30 Hz. Thus, this approach can meet the requirements of real-time and accurate displacement monitoring in radiotherapy.
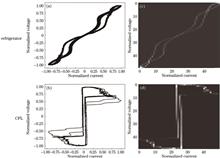
With the enhancement of the performance of image intensifiers in China, flicker noise becomes one of the obstacles to further enhance resolution. To examine and study the characteristics of scintillation noise, a scintillation noise testing system is developed by selecting the image intensifier with better performance and enhancing the production process. By operating the GSENSE400BSI low-illuminance CMOS image sensor, the image on the fluorescent screen of the image intensifier was collected, and the data were transmitted using a USB interface to the computer for image analysis. In the experiment, image intensifiers were evaluated, and the corresponding dispersion coefficient distribution of scintillation noise was generated. It is discovered that the noise is the most evident in the environment with 2.8×10-6 lx illumination, and the higher the signal-to-noise ratio, the lower the overall dispersion coefficient of the image intensifier. Through the connected domain detection algorithm, under the condition of a binarization threshold of 100, the average amount of highlight noise in 200 consecutive images of three types of image intensifiers is 5.18, 1.40, 0.86, and the repeatability is 1.26%, 3.23%, 2.66%, respectively. The discrete coefficient and the amount of highlight noise can be used as one of the indicators to evaluate the display quality of image intensifier.
Occlusion caused by gathering of marine creatures together is an important reason for false and missed detections. Therefore, this study proposes a marine creature detection method based on iterative fusion of sample-assisted network training. First, an improved deep hole residual structure is selected as the feature extraction network, which improves the feature extraction ability of the network. Second, because of the occlusion and dense characteristics of marine creature images, the loss function is improved to avoid false and missed detections. Finally, to solve the problems of target occlusion and data imbalance, a sample iterative fusion method is proposed to generate an extended training set of simulated images. This improves the effectiveness of network training and the ability to detect marine creatures with a small sample size. The experimental results show that the proposed method can achieve a detection accuracy of 91.36% on the URPC2018 dataset and 90.27% on the Taiwan fish dataset. The detection accuracy and speed of the proposed method are higher than those of existing target detection algorithms.
Object detection in remote sensing images is a challenging task in the field of computer vision. Existing remote sensing image detection methods ignore the speed with the aim of improving the accuracy; however, it is also essential to increase the detection speed in real-time detection scenes, such as in resource surveys and maritime rescue. This paper proposes a lightweight target detection network to realize a trade-off between detection accuracy and speed. The design replaces the original backbone network of YOLOv4 with the pruned MobileNetV2. In addition, the ordinary convolution calculation of the feature extraction method is replaced by deep separable convolution to considerably reduce the computational complexity of the model. Finally, the receptive field enhancement module and attention mechanism module are embedded to improve the detection accuracy of the model. The experimental results on the images in the dataset containing the remote sensing images show that the accuracy, as measured by the mean average precision, is 89.80%; further, the model detection speed is 33.4 frame/s. Compared with YOLOv4, the accuracy only decreases by 1.48 percentage points, but the detection speed increases by nearly 1.5 times. Compared with the YOLOv4-Tiny algorithm, the average accuracy is 9.05 percentage points higher. The proposed model successfully meets the trade-off requirements of speed and accuracy. The weight of the model is only 44 MB, which makes it easy to deploy and indicates that it meets the requirements of real-time detection scenarios.
Addressing the issues of point cloud simplification algorithms that rely on traditional parameters when extracting features, which is not comprehensive and easy to lose feature boundaries, this study provides a point cloud simplification approach using von Mises-Fisher (vMF) distribution to extract features. This method first uses a neighborhood center point to create a vector, divides the surface through the threshold of the relationship with the normal direction, reduces the impact of noise on the finer features. Then, the priority of surface points is extracted by using vMF distribution to realize global feature extraction. Finally, octree hierarchical simplification is operated based on features. Experiments described that the method in this study can successfully extract detailed features. Compared with methods based on curvature and Hausdorff distance, it has a better feature extraction effect. The simplification algorithms based on curvature, grid, and random, and the proposed method are used to analyze the reconstruction results, 3D bias, and quantitative analysis, results prove that the proposed simplification method is more effective. The proposed simplification method provides a fresh approach for point cloud feature extraction and simplification.
A multiscale object detection algorithm for satellite remote-sensing images is proposed to solve the problems of background confusion, low precision of small object detection, and high miss rate in multiscale object detection. The channel and spatial attention module is used in the backbone network, and the feature fusion network is redesigned to realize the multiple fusion of up-down-up sampling. The channel weight parameter is added to enable the network to pay more attention to critical channels, fully utilize different feature information levels, and enhance the detailed feature information. In a DIOR dataset, not only the detection effect of small objects but also the detection accuracy of objects in complex scenes is improved. Compared with that using YOLOv5m, the detection effect of some small or complex objects is improved significantly, the accuracy is improved by more than 4.5 percentage points, and the overall accuracy is improved by 3.1 percentage points.
To solve problems in the complex geometry scene, dense object distribution, and the large range of object size variations in high-resolution remote sensing object detection and to address the limitations of model resources in application scenarios, a lightweight remote sensing object detector based on YOLOX-Tiny is proposed. A multi-scale prediction method is used to enhance the detection capability of dense objects. Moreover, a coordinate attention module is introduced to improve the attention of important characteristics while suppressing background noise. The key prediction convolution layer is replaced by deformable convolution to strengthen the spatial modeling capability. Finally, the loss function is optimized to increase the localization accuracy of remote sensing objects. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is evaluated on the public remote sensing image target detection dataset DIOR. The experimental results show that compared with the benchmark algorithm (YOLOX-Tiny), the proposed algorithm improves the average precision (AP) and AP50 indexes by 4.1 percentage points and 4.42 percentage points respectively; on the premise of maintaining high accuracy, the number of detection frames per second (FPS) reaches 46, which can meet the needs of real-time detection and is superior to other advanced algorithms.
Feature extraction of the surface and form of stockpiled materials is performed for achieving the automation and intelligence of warehousing, and it provides the analysis basis for the automatic storage and acquisition control of the materials. First, the stockpiled material is scanned by using LiDAR to determine its morphology and coverage characteristics, a 3D point cloud is obtained, and a fusion algorithm is used to preprocess the material. Second, the supervoxel clustering of point clouds is performed based on the difference of the surface normal vector and spatial distance. Finally, the convex surface is extracted from the 3D point cloud surface after clustering by using the concave and convex judgment method to analyze the surface shape of the stockpiled material. The experimental results show that the method can precisely recognize the surface characteristics of the stockpiled material, and the recognition error is less than 3.11%. The proposed method can be directly applied to different stockpiled material scenarios without training.
Aiming at the challenges of difference between the research conclusion and actual situation resulting from inadequate selection of research scale and incomplete research dimension in the study of the urban thermal environment, an approach of quantitative analysis for the correlation between urban building spatial distribution pattern and urban thermal environment is suggested. First, from Landsat8 remote sensing images, the land surface temperature (LST) in the research area is extracted. Then, the quantitative expression system of urban building spatial distribution pattern in the research area is built. Next, correlation analysis (CA) and bivariate local spatial autocorrelation analysis (BLSAA) are employed to investigate the effect of urban building spatial distribution patterns on the thermal environment at 1- and 2-km scales. The investigation findings of the suggested approach to the thermal environment of the central urban area of Jinan demonstrate that one-, two-, and three-dimensional urban spatial structure indicators are sensitive to the change in research scale; one- and three-dimensional urban spatial structure indicators are extremely sensitive. The confidence of investigation findings on the 1-km scale is higher than that on the 2-km scale. The one-, two-, and three-dimensional urban spatial structure indicators' effect on the urban thermal environment is a primarily positive correlation, and the number of positive correlation indicators increases with the increase in dimension. The two- and three-dimensional urban spatial structure indicators have a greater correlation with the urban thermal environment compared with the one-dimensional urban spatial structure indicator.
With the increasing demand for intelligent construction in science and technology, semantic segmentation technology has attracted extensive attention from scholars in the field of graphics and images. This technology provides effective decision support for target tracking, visual control, and other technologies. However, the operation efficiency and segmentation accuracy of the three-dimensional (3D) point cloud semantic segmentation model are bottlenecks to its development. A semantic segmentation network model of the 3D point cloud, called point cloud+graph convolution network (PCGCN) is proposed. PCGCN uses the EdgeConv network to extract local features and ResNet to enhance the transmission of features, fuse the local features of different scales, and participate in semantic segmentation of the 3D point cloud. In the process of deep learning, PCGCN solves the problem of the lack of local features and improves the segmentation effect. Furthermore, in the point cloud deep learning network, the introduction of ResNet improves the accuracy of semantic segmentation. Experiments are carried out using ShapeNet and S3DIS datasets. The experimental results show that the PCGCN accuracies are 85.1% on the ShapeNet dataset and 81.3% on the S3DIS dataset.
To solve the problems of slow matching speed and large matching error in the precise alignment step of lidar target point cloud alignment technology, an iteration closest point (ICP) precision matching algorithm based on neighborhood curvature improvement is proposed. The registration provides a good initial position; the neighborhood curvature is introduced into the traditional ICP algorithm to achieve the fine registration. Perform registration and numerical analysis experiments on the Stanford Bunny and the scene point cloud. The experimental results demonstrate that the improved ICP algorithm based on the neighborhood curvature can efficiently perform the point cloud alignment, and compared with other algorithms, the alignment speed of the proposed algorithm is better than the alignment matching accuracy, which provides an efficient method to improve the 3D reconstruction and target recognition technology.
Remote sensing image segmentation algorithms are susceptible to interference from environmental factors, such as object occlusion and uneven illumination. Existing deep learning remote sensing image semantic segmentation methods usually adopt an end-to-end codec structure. However, they still suffer from inaccurate segmentation for the structure and contours of high similarity objects. Therefore, to improve the algorithm robustness and classification accuracy, a deep convolutional neural network remote sensing image semantic segmentation algorithm based on contour gradient learning is proposed. To improve the quality of the predicted feature maps, the adaptive attention-based multichannel multiscale feature fusion network (D-MMA Net) is proposed based on the SegNet model network. The D-MA block uses an attention-based adaptive multiscale module to adaptively extract different scale features according to the learned weights to obtain more effective high level semantic features. To further refine the extracted object boundaries, the contour extraction module, a learnable contour extraction module, is proposed based on the principle of the Sobel edge detection operator. Finally, the contour information is combined with multi-scale semantic features to enhance the robustness of the spatial resolution of the image. The experimental results show that the proposed method improves the segmentation accuracy and produces good segmentation results for irregular object boundaries.
For hyperspectral image classification tasks, a graph convolutional network can model the structural and similarity relationships between pixels or regions. To solve the problem of inaccurate construction of an adjacency matrix by calculating the node similarity using the original spectral features of pixels, a graph convolutional network based on spatial-spectral aggregation features (S2AF-GCN) is proposed for feature extraction and pixel-level classification. The S2AF-GCN considers the spatial position of the pixel as the center, aggregates other pixel features in the spatial neighborhood of the pixel, and uses the aggregated pixel features to dynamically update the weights of other pixels in the neighborhood. Through multiple aggregations, the pixel features in the region are smoothed, and the effective feature representation of the pixels is obtained. Next, the aggregated features are used to calculate the similarity and construct a more accurate adjacency matrix. Moreover, the aggregated features are simultaneously used to train the S2AF-GCN to obtain better classification results. The S2AF-GCN achieves overall classification accuracies of 85.51%, 96.95%, and 94.92% on three commonly used hyperspectral datasets, namely, Indian Pines, Pavia University, and Kennedy Space Center, respectively, using 1% labeled samples.
Vehicular light detection and ranging (LiDAR) has become a standard sensor in automotive by offering accurate geometric information of the surrounding region for intelligent driving vehicles. In order to overcome the limited performance of a single sensor for object detection, the geometric and spatial visibility features of LiDAR point clouds are fused with image semantic information in a network framework to achieve accurate three dimensional (3D) pedestrian detection. First, an effective 3D ray-casting algorithm is introduced to produce spatial visibility feature encodings. Second, the image semantic information is incorporated to improve point cloud features. Finally, the impact of added information and related hyperparameters on detection findings are quantitatively and qualitatively examined. Experimental findings demonstrate that compared with the single frame point cloud, the 3D pedestrian detection accuracy is enhanced by 32.63 percentage points after aggregating the last 10 frames of the point cloud in history. By further fusing image semantics and point cloud spatial visibility information, the proposed method's detection accuracy is enhanced by 2.42 percentage points compared with the benchmark approach, and exceeds some standard approaches. Our enhanced approach is more suitable for 3D pedestrian detection in a traffic environment.
Computational imaging compressively encodes high-dimensional scene data into low-dimensional measurements and recovers the high-dimensional scene information using computational reconstruction techniques. In the era of big data, the increasing demands for high spatiotemporal resolution have promoted the development of large-scale reconstruction algorithms with high accuracy, low complexity, and flexibility for various imaging systems. The existing large-scale computational reconstruction methods, including alternating projection, deep image prior, and plug-and-play optimization methods, have made great progresses over the past decades. Among the abovementioned methods, the alternating projection has been utilized in gigapixel quantitative phase imaging systems. Besides, the deep image prior and plug-and-play optimization techniques combine the advantages of conventional optimization and deep learning, which hold great potential for large-scale reconstruction. This work reviews the architectures and applications of these methods and prospects for the research trends, which can provide highlights for future works of large-scale computational imaging.
Image inpainting is a hot topic in the field of computer vision. It is a process that enables filling in damaged regions with alternative contents by estimating the relevant information either from surrounding areas or external data. With the advent of big data, image inpainting methods based on deep learning have attracted significant attention in image processing because of their excellent performance. This paper presents a brief review of existing image inpainting approaches and discusses the network structure and performance of each algorithm, along with a comparison of widely used datasets. In view of the existing challenges in this field, this paper proposes potential research directions and developmental trends in image inpainting.
Correlation imaging, also known as "ghost imaging", is a new imaging method. It calculates the coincidence between a detected light signal carrying the light intensity information of an object and the measurement matrix of the reference light path; the image information of the object is obtained by using the second-order intensity correlation characteristics between the two light paths. Different from traditional optical imaging, correlation imaging has the advantages of strong anti-noise ability and various imaging methods, which can reduce the influence of scattering medium on the disturbance and attenuation of optical signals. Since the first ghost imaging experiment in 1995, it has become one of the most popular research topics in classical and quantum physics. In this article, the history of ghost imaging development, its theoretical principle, and the latest research on ghost imaging applications are presented.
Raman spectrum can indicate the changes in the molecular structure of living tissues and be used for the detection of tongue squamous cell carcinoma tissues. While the existed technologies can only identify the characteristics of tongue squamous cell carcinoma tissue and establish whether the tissue is cancerous, they cannot locate crucial band sections of the Raman spectrum of tongue squamous cell carcinoma tissue. Therefore, based on a deep learning algorithm, this study aims to present a spectral region segmentation technique for identifying significant bands of Raman spectra of the tongue squamous cell carcinoma. First, the Raman spectrum data of 44 tumor tissues from 22 patients were obtained using fiber-optic Raman spectroscopy acquisition equipment. The data were preprocessed, annotated, and split into the training set and testing set. Next, a band region deep convolutional neural network model was created. This model is composed of three fundamental modules, namely, Raman spectral feature extraction network, crucial spectral band recommendation network, and critical spectral band regression network. Among these, the Raman spectral feature extraction network is used to extract the spectral characteristics of tongue squamous cell carcinoma tissues and crucial bands. The crucial spectral band recommendation network and the crucial spectral band regression network are used to segment the essential band regions of the tongue squamous cell carcinoma tissue spectrum. Experimental findings show that the average precision of the proposed method for significant bands in tongue squamous cell carcinoma tissue is 99% under the criterion of interest of union value of 0.7.
Multispectral reconstruction technology has widespread potential applications in biomedicine. Moreover, visual inspection is the typically used traditional method for skin and oral bacteria assessment. However, this method relies on naked-eye observations and is highly subjective. Even experienced clinicians face uncertainty while providing a definite diagnosis for the bacterial infection. This study proposes a fluorescence multispectral Wiener estimation-based reconstruction method to provide an objective and accurate bacterial evaluation. This method is based on a smartphone platform that is excited by a purple light source to capture spontaneous fluorescence images of skin and teeth. The Wiener estimation algorithm was used to reconstruct the acquired autofluorescence image into a multispectral data cube with 31 bands (400-700 nm). Furthermore, the spectral intensity of the porphyrin produced by the bacteria and the endogenous background tissue emission was extracted and compared. Based on the extracted autofluorescence spectra, a weighted subtraction method was utilized to obtain high-contrast and high-signal-to-noise identification of the bacteria on the skin surface. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method accurately reconstructs the multispectral fluorescence image and realizes the position of bacteria. After the weighted subtraction method was applied, the contrast increases by 12 to 46 times and the signal-to-noise ratio increases by 1.63 to 2 times.
Traditional virtual reality (VR) technology generates indoor three-dimensional (3D) map models using artificial modeling, which has the challenges of slow speed and deviation between the model and real object scale. Therefore, this study proposes a real environment 3D modeling system for mobile robots based on VR. First, the indoor high-precision dense 3D point cloud map can be rapidly obtained by using visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) technology. Second, the 3D point cloud can be reconstructed into the indoor 3D model through the surface reconstruction algorithm and imported into unity 3D. Next, the indoor 3D model is placed in the 3D virtual environment with the VR equipment's aid. Finally, the relocation of the mobile robot to the indoor environment is achieved by visual SLAM technology, and the pose of the robot in the model is mapped in real time to complete the interaction. Using visual SLAM technology to build the 3D map model is quick, solves the problem of scene scale deviation, and attains the reuse of map. Simultaneously, VR technology also allows operators to obtain a strong sense of immersion to better understand the working environment of the robot.
A new method of color image threshold involves dividing the color image threshold using the H component of the color image hue-saturation-intensity (HSI) model. Considering that the H component is a circular histogram, it is an effective method to break the circular histogram into a linear histogram and subsequently use the linear histogram threshold segmentation method to select the threshold. In information theory, the information energy is the dual of Shannon entropy, and this study first introduces the concept of cumulative distribution information energy of the linear probability distribution, which is used to determine the breakpoint of the circular histogram. Thereafter, it provides the information energy threshold method on the linear histogram, which is used to determine the threshold of the H-component circular histogram. Compared with the Shannon entropy threshold selection criterion based on logarithmic operation, the information energy threshold selection criterion based on square operation has the advantages of simple expression and fast calculation speed.
During the non-contact flaw detection of a rust-covered bronze mirror, X-ray imaging typically fails to reveal the extent of damage due to the thickness difference between the mirror edge and core. In this study, the X-ray signal from a bronze mirror was used as an input to construct a generative confrontation fusion network. An optimization strategy that enhances the bronze mirror X-ray information fusion was designed to address the reconstruction blur caused by the L2 loss and gradient operator, and the expression of multiscale feature details, such as textures and cracks. By utilizing the feature learning process of the L2,12 loss regularization generator, the smoothing of the data that was generated using the L2 loss was improved; moreover, the Laplacian Ltex pattern loss was defined to strengthen the effect of training network on the extraction of decorations and diseases. Furthermore, a multiscale feature fusion module was added to the training network to improve the quality of the generated information. Thus, considering the experimental comparison involving seven fusion methods, the cross entropy value of the proposed algorithm in two of the five groups is poor. However, the values are optimal in the control data, including entropy, average gradient, spatial frequency, joint entropy, and non-reference feature mutual information. This can effectively reveal the detection information of the bronze mirror during X-ray flaw detection.