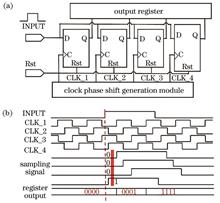
Multi-beam single-photon radar has important applications in fields such as earth surveying and long-range imaging, and multi-channel timing measurement technology significantly determines the performance of the entire system. Therefore, we propose a parallel measurement method of multi-channel time-to-digital conversion based on clock phase shifting method. Through a single Xilinx Artix-7 series field-programmable gate array chip, the method can realize the simultaneous timing measurement of 100 channels single-photon signal. The timing resolution of 1.0 ns, the measurement accuracy is 360 ps, and the range of 65 μs. Based on the device, the multi-channel single-photon echo signal measurement are remarked on the advantages as high stability, low power consumption, high speed, and compact structure, which meets the timing requirements of the multi-beam single-photon radar.
To address the problem of a single deep-learning model being unable to reconstruct the wavefront of digital holograms with multiple scales, an improved network structure based on the U-Net model is proposed to simulate the digital holographic imaging process and generate holographic images with different scales as data sets. Digital holograms with different scales are used in different parts of the training network, and a depth learning model is obtained, which can reconstruct the wavefront information of digital holograms with three different scales. The experimental results show that the proposed network structure can reconstruct digital holograms with various scales and obtain accurate wavefront information of digital holograms. The research content solves the problem of using a single deep-learning model to deal with digital holograms with varying scales.
Light field cameras simultaneously capture light intensity and direction information of a scene from a single shot which has potentially very broad applications in the reconstruction of three-dimensional scenes and their focus from previously captured images. However, compared with ordinary cameras, the images captured by light field cameras are not sufficiently sharp, i.e., the spatial resolution of the image is low. In this study, we propose a super-resolution reconstruction algorithm of light field images based on sparse representation. The algorithm used the redundant information from multiview light field images of a scene to reconstruct a high-resolution image. First, the middle image of the multiview light field images was selected as the low-resolution image to be reconstructed. The images from the other views and their down-sampled versions were used as samples for training, wherein the sparse K-singular value decomposition (SVD) method was used to obtain a pair of dictionaries for both high- and low-resolution representations. Finally, an improved Gaussian Laplace method was used to extract features of the low-resolution light field image in the image reconstruction process. Experimental results show that the improved method is capable of recovering more image detail and greatly reduces the time required for dictionary training.
Considering the uneven brightness of the cell images collected by the phase contrast microscope and the low contrast between the cells and background, a fast cell image segmentation method based on dual-Gaussian filtering is proposed according to the characteristics of the sharp changes in the gray level of the cell area and the slow gray changes in the background area. The proposed method constructs a dual-Gaussian filter from the perspective of frequency domain to filter low-frequency information while retaining high-frequency information, which is beneficial to enhance the difference between cells and background and reduce the interference of uneven brightness factors. The cells are segmented using an adaptive threshold, and the morphological closing operation is used to improve their shape. The area constraint is used to remove the influence of impurities on the accuracy of segmentation to a certain extent. The proposed method was tested on a C2C12 dataset, and the accuracy, recall, and F values are 0.9770, 0.9457, and 0.9609, respectively, which were better than the comparison algorithms. The results show that the proposed method has good accuracy and robustness and can achieve fast and accurate cell image segmentation.
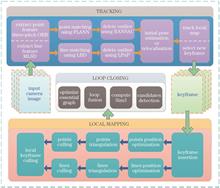
At present, the real-time localization technology in simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm has become stable, and the research field turns to the semi-dense SLAM based on point-line feature. Aiming at this research direction, a SLAM algorithm based on point-line feature is proposed. First, an oriented fast and rotated brief (ORB) algorithm based on three patches and local gray difference is used in the visual front end to extract and match feature points. Meanwhile, multiscale line segmentation detector (MLSD) algorithm is used to extract and match line segment features, so that the system adds constraint conditions of line features on the basis of point feature geometric transformation to calculate pose transformation. Then the position and orientation are optimized using point and line constraints through the local bundle adjustment (BA) method. Finally, loop closure detection is performed for repositioning. The proposed algorithm is tested on Euroc dataset and compared with similar algorithms. The experimental results show that the map is relatively dense, with clear outline and high accuracy. At the same time, the root mean square error (RMSE) in V1-02-mdeium, V2-02-mdeium, MH-02-easy, MH-03-medium, MH-04-difficult datasets is 0.045, 0.0561, 0.0539, 0.0491, 0.0623 respectively, which is relatively the lowest. The results show that the proposed algorithm has relatively good mapping effect and high accuracy among similar algorithms.
In order to realize multi face image tracking across camera regions,a cross camera tracking network based on double three branch twin network (DTN) is proposed. The specific method is to apply Chinese Whisper(CW) face clustering algorithm to cluster the face images of the same pedestrian, and determine the captured target face through intelligent monitoring according to the results of face clustering. By improving the network structure and training function of FaceNet, pedestrian face tracking is realized accurately. After training DTN on LFW data set, the face recognition rate can be improved to 99.51% through margin sample mining loss (MSML) and focus loss difficult sample balance training. Experimental results show that by comparing the similarity of face features in the same video surveillance field, the proposed network can track pedestrian face targets through this area; through the real-time transmission of face features between cameras, cross camera face tracking is realized.
Based on the YOLOv4 target detection method, in this study, we proposed an intelligent insulator burst fault recognition model. Considering images of normal and burst insulators in a power supply bureau within one year as samples, the proposed model was trained to obtain its weight. The proposed model was further used to identify insulators and their bursting faults. Experimental results showed that the proposed model had an average precision of insulator positioning of 92.6%, an average precision of insulator burst fault location of 91.78%, and the model's resolution was 46 frame/s. Compared with Faster R-CNN and SSD models, the constructed insulator burst fault identification model can accurately and quickly identify insulators and their burst faults.
System parameters and shooting conditions influence digital cameras and other image acquisition equipments. With a real background, a partial color and distortion phenomenon results in a large error in automatic color matching. In this study, we made 98 green swatches. The chromaticity value of swatch acquired using digital camera imaging equipment was considered an independent variable, whereas the true color chromaticity value obtained from the test spectrum was considered a dependent variable. Then, a coefficient matrix equation was constructed and solved. The resulting coefficient matrix was used for background color correction. The results show the image color information obtained by digital equipment after the application of the correction coefficient matrix. In addition, the average color difference with real background color is less than 3, which meets the requirements of camouflage performance and lay the foundation for the high fusion camouflage background color reproduction technology.
In the case of detecting motion object in the first frame by visual background extractor (ViBe) algorithm, motion objects frequently stay in the initial position for a long time, leading to a false foreground and lowering the detection accuracy. In this study, we focus on solving the problems. The initial background model is established by selecting pixels with similar color and spatial position as the sample set. Furthermore, the weight of color and spatial position in the similarity function is determined by the entropy approach. In addition, the adaptive threshold is determined by the iterative approach in classification to enhance the segmentation accuracy under various conditions. Finally, the updated probability of the background model is determined using a binary exponential distribution model with the result of the frame difference approaches. The experimental results show that the algorithm can guarantee the accuracy of the results in the presence of noise, illumination, and dynamic background. Compared with ViBe algorithm, the algorithm's precision in this study is increased by 21.56%, which effectively eliminates the effect of ghosting.
Aiming at the problem of complex noise and fringe artifacts in current low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) reconstructed images, a LDCT denoising method based on dual attention mechanism and compound loss is proposed. This method obtains global feature information by introducing spatial attention mechanism and channel attention mechanism, and recalibrates the feature weights, so that important structural details can be retained, thereby improving the denoising performance of the network; at the same time, the perceptual loss measurement function is added to preserve the texture information sensitive to human eyes. Experimental results show that, in terms of visual effects, the proposed algorithm not only removes noise and artifacts in LDCT images, but also retains more texture features and structural details; objective indicators such as peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) are are higher than that of other comparison methods.
To address the poor performance of most defogging algorithms on images with large areas of sky, an improved dark channel apriori defogging method is proposed. First, segment the sky area according to the image gradient information, and based on the sky area segmentation, combine the high brightness and smoothness of the atmospheric light reference pixels to set the discriminant formula and reasonably estimate atmospheric light values. Second, a piecewise linear function is used to dynamically modify the adjustable parameters in response to the value of the dark channel to solve the local shadow caused by excessive defogging. Then, the transmittance estimated by the bright channel model and improved dark channel a priori model are fused and guided filtering is used for edge optimization. Finally, the defogging image is obtained by combining brightness compensation and contrast stretching using the atmospheric scattering model. The experimental results show that the improved method effectively reduces image distortion, improves image contrast and details, and has advantages in preserving the visual authenticity of the sky area.
Aiming at the problem that it is difficult to accurately segment the chest lung field affected by the lung shoulder area, thoracic diaphragm angle and ribs, we propose a lung field segmentation algorithm based on improved U-Net. First, the inception module is used to replace the convolutional layer in the U-Net coding block, which can increase the network width while capturing more image features. Then, the residual network is introduced in the coding block and the decoding block to increase the depth of the network and ensure the stability of the network. Skip connections are used between encoding and decoding to enhance the transfer and utilization of features, and to solve the problem of the loss of chest and lung field features due to continuous downsampling in the encoding part. Finally, the channel and spatial attention mechanism are combined in the encoding and decoding parts to analyze the image. Features are re-calibrated to effectively improve the segmentation accuracy of the algorithm. The experimental results show that compared with other segmentation algorithms, the segmentation performance of this algorithm is better. The accuracy, recall rate, specificity, and average intersection ratio on the public Montgomery County data set are 98.90%, 97.81%, 99.28%, and 97.17%, respectively.
Aiming at the problems that the data set used by the existing recognition algorithms is too simple, the recognition accuracy of dangerous goods in security inspection images in real scenes is low, and it is easy to lead to false detection and missed detection, we propose a class-balanced hierarchical refinement algorithm based on penetration hypothesis, which combines multi-layer channel attention mechanism and space attention mechanism. First, based on the hierarchical modeling of security image, channel attention mechanism is added to the feature map to give different weight to different channel features. Then, spatial attention mechanism is added to give different weight to the unique color features of security image in space. Finally, the residual network is used to add double attention mechanism to different layers of security image for ablation experiment. The experimental results show that after adding double attention mechanism to the fixed two layers at the same time, the network can significantly improve the identification accuracy of dangerous goods in security inspection, and verify the effectiveness and robustness of the multi-layer attention mechanism algorithm.
To solve the problems of low detection accuracy and slow detection speed of small targets in the task of detecting the brightness of the runway edge lights in the airport, a method for detecting the brightness of the runway edge lights based on improved RetinaNet is proposed in this paper. Based on the RetinaNet, the inverted residual structure and depth separable convolution are introduced to improve the feature extraction ability and detection speed of the network. The K-means clustering algorithm is used to optimize the size of the anchor box of the target sample to improve the detection accuracy of the network. The experimental results show that compared with the original method, the performance of the method is significantly improved, with the average detection accuracy of 97.2% and detection speed of 25.9 frame/s.
In order to solve the problem that the traditional variational level set segmentation algorithm is poor in segmenting uneven gray images and sensitive to the initial contours, we propose an adaptive active contour model based on local and global information coupling. By adjusting the proportion of local region fitting energy and global region fitting energy by weight function, a weight function which is adaptively updated with the evolution of the contour is given. Experiments results in synthetic images, real images and natural images show that the algorithm is robust to noise and insensitive to the initial position of the contours.
Aiming at the problems of hyperspectral image with high dimension, a few training samples, over fitting and too many training parameters, we propose an modified dense connection network (DenseNet) combined with spatial spectrum attention mechanism network (MDSSAN). First, the hyperspectral images are analyzed by principal component analysis, and the spatial neighborhoods of the central pixels are input into the modified network model. Then, three-dimensional DenseNet is improved, and the three-dimensional convolution block in the model is decomposed into the sampling convolution of the spatial dimension and the spectral dimension. Finally, the spatial attention mechanism is introduced in the spatial dimension, and the channel attention mechanism is introduced in the spectral dimension to reduce the training parameters of the model and extract more discriminative space-spectrum joint features. Experimental results show that the overall classification accuracy of the MDSSAN model on the Indian Pines, Pavia University, and KSC data sets are 99.43%, 99.74%, and 98.98%, respectively. Compared with other comparison models, the model has faster convergence speed and better classification performance.
When the eye tracker is collecting infrared eye movement data, due to the rapid movement of the subject’s eyeballs or the inability to keep relatively still with the instrument, some of the collected eye area images are defocused and blurred. This paper proposes a semantic segmentation optimization system, which is called super real-time semantic segmentation network (S-RITnet). First, a pixel-level annotation data set with a 4∶1∶1 ratio of images in the training set, validation set, and test set is created. Then, the enhance super-resolution generative adversarial network and contrast-limited adaptive histogram enhancement algorithm are used to repair the blurred eye area data set image. Finally, based on real-time semantic segmentation net and the autonomous data set (including the repair data set), perform network training to realize the semantic segmentation of the eye area image and evaluate the obtained segmentation module. The experimental results show that the optimization scheme can effectively optimize the quality of eye area images. Compared with the low-quality eye images training module, the mean intersection over union and F1-score evaluation of S-RITnet increased by 0.0247 and 0.024 respectively.
Satellite image translation is one of the important application scenarios of generative adversarial networks. The existing satellite image translation has the problems of low generation quality, weak generalization ability, and high computational cost. Based on the cycle generative adversarial network, a lightweight attention residual module is designed to improve the image translation quality and reduce the parameter computation of the model. At the same time, the least squares loss is introduced to improve the stability of the training process. The experimental results show that the proposed method has good translation quality in satellite image translation tasks while maintaining high training stability and low model computation.
The classification of biological and abiotic targets in the air is an important part of bird strike control in the airport. Target classification based on trajectory information has the advantages of easy access to trajectory information and high degree of discrimination of some features, but improper feature selection will result in large classification errors of close-range trajectory samples. Aiming at this problem, an aerial target classification algorithm based on double-layer feature selection is proposed. First, fully feature extraction is performed on the three-dimensional trajectory data of dynamic targets to expand the range of feature selection. Second, the feature subset is selected through the designed two-layer feature selection algorithm, which reduces the computational complexity of the algorithm and improves the classification precision. Finally, online sequential extreme learning machine (OSELM) is used to realize the real-time classification of aerial biological and abiotic targets. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm takes into account the accuracy and speed of classification, the classification accuracy reaches 99.7%, and the average classification time is only 1.26 ms, which meets the needs of real-time monitoring and early warning. The proposed algorithm provides a potential solution for real-time classification of air targets under airport conditions.
Aiming at the problem of environmental illumination in face recognition and age estimation system, a face recognition and age estimation method based on multi-task convolutional neural network under varying illumination is proposed. The recognition rate of face images and the accuracy of age estimation under varying illumination are improved by the proposed method. Retinex image enhancement algorithm in YCbCr color space is used to improve the accuracy of face recognition and age estimation, and the face recognition and age estimation experiments under 10 kinds of dimming level for three kinds of distance are carried out. Experimental results show that compared with the original images, the recognition rates of the face images obtained by the improved method are improved, and the average absolute errors of age estimation are decreased. When the dimming level is 40%, and the distance is 1, 2, and 3 m, the face recognition rates are increased by 3 percentage points, 19 percentage points, and 25 percentage points, and the average absolute error of age estimation is decreased by 1.20, 2.99 and 2.00. At the same time, it is found that the effect of face recognition and age estimation is better when the gray mean value of face image without image enhancement algorithm is more than 50.18. When it is lower than the value, it is necessary to add the image enhancement algorithm to improve the accuracy of face recognition and age estimation. After adding the image enhancement algorithm, when the gray mean value of the face image is more than 56.61, the effect of face recognition and age estimation is better, and the visual effect and image quality are better.
The particle size of ore is an important reference to judge the crushing effect of crusher, and image segmentation is the key step of ore particle size detection. To solve the problems of image segmentation inaccuracies caused by complex shape, adhesion and stacking of broken ore, and serious image noise, a broken ore image segmentation method based on improved HED (Holistically-Nested Edge Detection) network model is proposed. First, the bilateral filtering pre-processing operation is carried out on the collected ore image to reduce the influence of noise on segmentation. Second, the residual deformable convolution block is used to replace the ordinary convolution block to enhance the feature extraction ability of the model for ores of different sizes and shapes, and the void convolution is used to replace the original pooling layer to expand the receptive field and retain the global information of ores. Finally, the HED network framework with a bottom-short connection structure is used for feature extraction of ore, and the extracted features are combined with low-level detail information to reduce the problem of undersegmentation of cohesive and stacked ore particles.
Aiming at the problems of halo artifact, dark distortion and detail loss in traditional dark channel prior defogging algorithms, a defogging algorithm based on image features and wavelet transform is proposed. First, The gray-level co-occurrence matrix method is introduced to obtain the complexity of image texture features as a constraint condition,and the problem of false texture and blocking effect in dark channel images is solved by use of dynamic sliding window; second, combined with the image brightness information, K-Means clustering algorithm is used to calibrate the bright and dark areas to optimize the atmospheric light value and transmittance map; finally, aiming at the problems of darkening and loss of detail features in the restored image of atmospheric scattering model, the image enhancement technology based on wavelet transform is used to improve the image contrast. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can recover the scence and detail features well, and performs well in peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index (SSIM), and mean absolute error (MAE).
Aiming at the disadvantage that the existing detection algorithms are difficult to resist combined attacks, a copy-move forgery recognition algorithm based on mixed features is proposed. Different from the traditional algorithm using fixed threshold, the proposed algorithm uses the similar sub-block extraction method without threshold to select the sub-block with high correlation. At the same time, in order to obtain more local information, an adaptive sub-block synthesis scheme is proposed to avoid sub-block aliasing. In addition, aiming at the problem that scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) features cannot distinguish natural similar regions from tampered regions, the proposed algorithm combines the advantages of moment features to extract the progressive hybrid features of synthetic sub-blocks, so as to reduce the false alarm rate of the algorithm. The experimental results show that the true positive rate (TPR) and F1 of the proposed algorithm are 97.2% and 92.9% on MICC-F2000 data set and 98.2% and 95.1% on MICC-F220 data set, respectively, indicating that the proposed algorithm has good detection ability.
In the light field computational imaging, scene depth reconstruction is transformed into a problem of disparity reconstruction. Efficient disparity reconstruction based on monomer light field data is realized by introducing YCbCr color space light field data. Region matching in Y channel can avoid the redundant calculation of RGB three-channel matching, and improve the matching efficiency. Monomer edge occlusion and internal disparity consistency constraint can be realized by Cb, Cr channel monomer to solve the problem of mismatching between occlusion region and smooth region. Cb, Cr chromaticity information provides effective clustering information for monomer. The accurate segmentation of monomer is realized by combining the region growth and dichotomy. At the edge of the monomer, the matching window shape and the visible viewpoint are selected according to the edge of the monomer to avoid the appearance of the edge occlusion mismatching. In the monomer, the disparity map is optimized based on disparity consistency prior. Experimental results of simulated data and real data show that the proposed method can achieve accurate reconstruction in texture, occlusion, and smooth regions, and has strong robustness for disparity reconstruction in occlusion regions.
In this paper, a model that regards lens with aberration as a combination of ideal thin lens and prisms array is proposed, which is dedicated to verify that the transmissive phase measuring deflectometry is feasible to measure the wavefront aberration of the lens. The simulation results of ZEMAX and Matlab verify that the wavefront aberration of lens obtained in raytracing and in reverse raytracing are approximately equal. Based on this conclusion, an experimental setup is built and the wavefront aberration of a single lens with an aperture of 75 mm is measured. The experimental results show that the method only needs a CCD camera and a LCD display to complete the measurement, which has the feature of simple equipment and easy operation without complicated calibration, providing a method for online measurement of wavefront aberration of the lens.
Aiming at the adverse effect of high reflection and high curvature of metal sphere on surface micro-defect detection, a detection method based on spatial omni-directional light source and image fusion is proposed. The image information is obtained by scanning the spherical surface through different illumination schemes provided by the spatial omni-directional light source system. Image fusion is used to accumulate the difference between micro defects and background in the effective detection area, enlarge the difference between micro defects and background, and improve the ability of micro defect detection. The experimental results show that the detection device based on the proposed method can detect the micro defects at different positions on the surface of bearing steel ball with a diameter of 20 mm and a precision of G16 significantly, and solves the problem of blind area caused by high reflection of metal sphere, and has good detection ability for various micro defects on the surface of bearing steel ball.
Artificial neural networks are widely used in different types of laser technologies. However, traditional accelerators based on the pipeline deployment architecture cannot manage various back propagation (BP) neural networks needed for different laser calculation tasks, such as the extraction of laser welding parameters and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis. Based on the Xilinx PYNQ-Z2 development platform, a configurable accelerator architecture-based BP neural network for laser welding technologies is designed and implemented herein. By introducing the configurable accelerator architecture and the interconnection of multiplexing operation units, the hardware circuit can be fitted to various BP network structures and the accelerator shows flexible configurability. Furthermore, the data reading method based on a multilevel cache structure is adopted, which addresses the bottleneck of reading speed. Experimental results show that the proposed accelerator can efficiently accelerate the BP neural network with various types of neurons. Compared with the embedded processor platform, the typical network operation performance of the proposed accelerator improves by 10.5 times on average and the large network operation performance with more than 100 neurons improves by 56.4 times on average. The proposed accelerator is superior to the general accelerator, which is realized on the same development platform.
Aiming at the problem of poor global applicability of the object image mapping model in the direct calibration method of structured light measurement system, this paper proposes a subarea calibration method based on the distortion model. First, the projection matrix of camera linear imaging is estimated by using Zhang Zhengyou's plane calibration rule. Then, the matrix as the initial value is taken to solve the camera distortion parameters by ordinary least square. Finally, the image subarea is divided according to the distribution law of distortion shift vector for calibration. The experimental results in the same scene show that compared with the global direct calibration method, the calibration accuracies of the method in X direction and Y direction are increased by 37.40% and 56.20%, respectively, and it has wide applicability in the field of structural light measurement.
Age change is one of the main reasons that affect the performance of face recognition. In order to solve the problem of low face recognition rate caused by the change of age, a cross-age face recognition model (CA-CNN) based on deep learning is proposed for cross-age face recognition. First, the overall face features are extracted from the face image by the convolutional neural network; then, an efficient convolutional attention module is proposed to obtain age features from overall face features, and combined with multi-layer perceptrons and multi-task supervised learning, the overall face features are non-linearly decomposed into age features and identity features; finally, for better distinguish between identity features and age features, an approved batch kernel canonical correlation analysis module is put forward to analyze the correlation between the decomposed identity features and age features. After the training of adversarial learning, the correlation is minimized and cross-age face recognition is realized. The proposed model achieves the recognition accuracy up to 99.03% of rank-1 on the MORPH Album 2 dataset, and the face verification of equal error rate of 9.8% on the CALFM dataset, which indicates the effectiveness of the proposed model.
In the augmented reality field, it is a challenge to achieve the illumination consistency of virtual objects. To address the low shadow detection efficiency problem when virtual objects are endowed with shadow, a method based on the shadow area is proposed to construct a shadow volume to achieve the illumination consistency of virtual objects. The proposed method first performs superpixel merging based on the color distance similarity according to adjacent superpixel centers. Superpixel collection is obtained using an improved simple linear iterative clustering (Ⅰ-SLIC) algorithm on the images. The number of superpixel collections and the subsequent processing complexity are reduced accordingly. Then, a Gaussian mixture background model is employed to detect the shadow of the segmented image, and the shadow body is constructed using the shadow region and illumination parameters. Finally, the registration of the virtual object is completed according to the transformation matrix combined with the shadow volume for rendering. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method realizes the shadow rendering of virtual objects and greatly improves the realism of augmented reality applications. Compared with existing methods, the proposed method demonstrates an obvious advantage in terms of time efficiency.
Lidar and camera fusion system can perceive the geometric size and color information of the environment, which has been widely used in many fields. In order to accurately fuse the two kinds of information, we propose a calibration method of external parameters of lidar and camera based on natural feature points. First, on the basis of lidar self correction, the gray image is generated by central projection of the point cloud using the intensity information of lidar data. Then, the scale-invariant feature transformation algorithm is used to extract and match the feature points of the gray image generated by projection and the camera image. Finally, the calibration mathematical model is established based on the information obtained from the feature points with the same name, and the data are optimized to calibrate the external parameters of the three-dimensional lidar system and camera system. The experimental results show that the re projection error from the point cloud to the image pixels calculated by this method is 2.3 pixel, which verifies the effectiveness and accuracy of the pose calibration method.
It has become an important technique and tactics for the public security organs to infer the type of shoes worn by the perpetrators according to the shoe prints left at the scene, and then search the suspected type of shoes in the surrounding surveillance video. This technique is completely dependent on manual screening, which is greatly affected by subjective factors and easily leads to problems such as missed detection. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a shoe type recognition algorithm based on attention mechanism. First, close to the actual combat of public security criminal investigation, a multi background monitoring shoe data set with sample size of 300 is established. Then, an attention mechanism model is proposed to enhance the ability of the residual network (ResNet50) to extract important features of shoes. Finally, the effects of selecting the output of different feature layers as shoe features and different convolution feature aggregation methods on the recognition accuracy are compared. In order to enhance the generalization ability of the model, label smoothing is added to the loss function. The experimental results on the multi background data set show that the Rank-1 and mean average precision of the algorithm are 74.32% and 56.97%, respectively.
Image target search is a key technology in the fields of intelligent security and regional surveillance. In recent years, with the explosive growth of video data, how to quickly search for objects of interest in massive amounts of video data has become a key issue to be solved in the current intelligent video processing field. A fast and intelligent search method based on the hierarchical cascade of bottom-level features and deep learning features is proposed. First, the intelligent target detection technology is used to intelligently detect the types of targets of interest in the video data. Second, for a large number of target detection results, a gating mechanism based on the bottom-level feature correlation measurement is designed to achieve the screening of target frames. Finally, high-dimensional deep learning features are used to complete the accurate recognition of the target. The experimental results show that the proposed method has a mean average precision (mAP) of 88.5% on the Market1501 dataset. At the same time, the calculation amount of the network reasoning process is reduced by 81.75% compared with YOLO and re-identification network direct cascade target search method, which significantly improves the target search speed.
In multi-target tracking, the interaction between targets, partial occlusion or complete occlusion can cause degradation of tracking accuracy or loss of targets. To address these problems, a multi-target tracking algorithm that combines optical flow and Markov random field (MRF) is proposed. First, the target optical flow is extracted by using the optical flow field of the first frame image to obtain the velocity information of the target; then, the target motion characteristics are fused with the established MRF model and constrained to optimize; finally, in the proposed model, the optimal state distribution of the target is obtained by the kernel correlation filter algorithm to achieve the tracking of multiple targets. The experimental results show that, compared with similar advanced algorithms, the proposed algorithm can continue to accurately track targets after multi-target interaction, reduce the false alarm rate when targets are obscured by each other, and has superior accuracy.
Aiming at the problems of slow convergence, long alignment time, and matching error due to low overlap rate in the traditional iterative nearest point (ICP) point cloud alignment algorithms, an improved ICP alignment algorithm based on chunked feature point extraction as the core and chunked alignment point cloud overlap rate as the constraint is proposed. First, the average distance density of the point cloud is calculated, the point cloud is chunked within the set number threshold, and the scale invariant feature transform (SIFT) feature points are extracted in parallel from the chunked point cloud, and the fast point feature histogram (FPFH) is used for feature description; then, the sampling consistency initial alignment (SAC-IA) algorithm is used to realize the matching of the point cloud, and the overlapping region of the point cloud is extracted based on the 50% inter block matching rate; finally, the initial attitude is calculated based on the matched feature points, and the overlapping part is used to achieve accurate alignment of the two point clouds. The experimental results show that the point cloud with low overlap rate after segmentation and overlapping region extraction can greatly shorten the running time and improve the registration accuracy.
Aiming at the problems such as the low algorithm robustness and easily blurred fingerprint of channel state information (CSI) in indoor localization, a location algorithm based on locally linear embedding (LLE) and gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT) is proposed. In the offline stage, first, the preprocessed amplitude and phase are regarded as joint CSI fingerprints, and then the individual subcarriers of the joint fingerprint are weighted using the elastic network (EN) algorithm before dimensionality reduction by LLE, which not only ensures the authenticity of CSI fingerprint after dimensionality reduction, but also enhances its unique characteristics. Finally, GBDT algorithm based on fruit fly optimization algorithm (FOA) is used to train the reduced dimension data to improve the reliability and stability of CSI fingerprint, and the fingerprint database is established. In the online stage, the LLE+GBDT algorithm is adopted to find the fingerprint information of the test point, so that actual physical locations can be predicted by matching with the fingerprint library. The indoor localization experiments results show that the proposed algorithm has higher localization accuracy and robustness compared with the comparison algorithm, and has certain application value.
Speckle noise will inevitably exist in medical ultrasound images. Therefore, this study proposes a medical ultrasound image noise reduction model based on the dual attention mechanism to effectively remove noise in the medical ultrasound images. First, due to the limited number of medical ultrasound images, we rotated and zoomed 400 images in Berkeley dataset to receive 23700 images. Then, we added speckle noises using the speckle noise model to simulate the ultrasonic images. Second, during the construction process of the noise reduction model, aiming at some disadvantages of traditional convolutional neural networks in the feature extraction, we introduced position attention mechanism, channel attention mechanism, and full convolutional network to improve the existing model and build a better ultrasonic image noise reduction model. Finally, we introduced a batch normalization operation to prevent the gradient from disappearing during the model training process. The experimental results show that the noise suppression effects of 11 simulated ultrasound images and 2 real ultrasound images (the physical body membrane and liver ultrasonic images) are better than other models in terms of visual observation effect and objective evaluation index. Therefore, the proposed model is an effective noise suppression model for medical ultrasound images. It can effectively reduce speckle noise and retain the image details.
A set of high resolution microscopic imaging system based on long-distance microscopic objective lens is designed and processed to meet the needs of high resolution imaging of ultracold atoms. The simulation results show that the numerical aperture of the designed high resolution microscopic imaging optical system is 0.55 near 671 nm wavelength, the working distance is up to 14 mm, and the optical transfer function (MTF) curve approaches the theoretical diffraction limit in the field of view of 200 μm×200 μm. The experimental results of the actual point source diffraction show that the resolution of the microscopic imaging objective lens system is better than 1 μm when the pinhole with a diameter of (300±50) nm is used as the point light source, and the aberration introduced by the vacuum window with a thickness of 3.35 mm can be corrected and the resolution of the ultracold quantum gas imaging system can be improved. By precisely controlling the lens spacing in the tube, the high-resolution microscopic imaging system can be applied to other commonly used ultracold atoms, such as Na, K, and Rb, and provide a more intuitive and convenient imaging detection tool for ultracold quantum gas experiments.
The radar cross section(RCS) of reed and zizania in the frequency range of 2?17 GHz were measured in the anechoic chamber of the microwave characteristic measurement and simulation imaging platform. The scattering and polarization characteristics of reed and zizania under continuous frequency were analyzed, and the optimal mode of measuring reed and zizania was discussed. The results showed that all polarization RCS values of reed and zizania were the largest in Ku band, followed by X-band and C-band, and the RCS in copolarization is much larger than the RCS in the cross polarization especially in low frequency when the incident angle is 35°. The RCS difference between HH and VV polarization of reed in high frequency while zizania in total frequency is obviously when the incidence angle is 55°. Through the comparative analysis of the RCS characteristics of reed and zizania, we found that reed and zizania can be basically distinguished by VV polarization and VH polarization at 7.8?17 GHz when the incident angle is 25°. And they also can be easily identified through HH polarization and VV polarization at 7?17 GHz when the incident angle is 55°. This study enriches the scattering spectral library of wetland features, and has an important significance for the follow-up monitoring of reed and zizania.
The non-line-of-sight error in the terminal can lower the accuracy of the trilateral positioning algorithm. To address this issue, an adaptive trilateral positioning algorithm is used. By introducing the mean difference as the standard of base station selection, the algorithm selects the three base stations with the smallest mean distance difference and improves the reliability of the base station to label distance information. In the three-sided positioning algorithm, the Euclidean distance is used to decide the position relationship between the two circles, and the radius of the circle with a high error possibility is corrected by combining the distance information. Then, the circle's radius is iteratively updated. The distance between the intersection points of two circles is set to 10 cm as the iteration threshold, and the center of the circumscribed circle at the intersection point of three circles is used as the label's position. Simulation experiments are used to validate the algorithm's effectiveness after adding Gaussian noise to approximate the non-line-of-sight error. Under 10% Gaussian noise, the tag positioning error is 10.5 cm. Finally, an actual passenger positioning system experiment is constructed to verify that the tag positioning accuracy of the proposed algorithm is less than 10 cm, and position error of the proposed algorithm is 13% lower than that of the weighted centroid method in X, Y, and Z directions.
The flame image at the tail section of the sintering machine can reflect the state of the sintering endpoint directly and effectively. It is feasible and practical in engineering to utilize the effective information in the flame image to classify the state of the sintering endpoint. Therefore, this paper proposes a classification algorithm based on K-means with the image color features to classify the sintering states of the flame at the tail section of the sintering machine. First, 90 flame images were preprocessed. The section images with 320 m2 that were collected by the sintering machine were cut uniformly in the red fire area according to the resolution of 3024×1700 pixels. Then, the core areas were extracted and sintered. The K-mean segmentation of the clipped image and the comparison of the segmentation images with K values of 2, 3, and 4 show that the segmentation results when K=3 can be used to segment the red fire area of the flame more accurately. Second, the color features of the red fire area are further extracted to obtain the final red fire target area segmentation image, since there are still other nonred fire areas in the segmented image. Finally, the geometric features of the extracted target image were taken as the dataset, and a fuzzy C-means (FCM) algorithm was used to classify the sintering end state. The classification effect of the proposed flame image classification method improves more than that of the traditional FCM algorithm.
Ground hourly, daily, and CALIOP data from nine meteorological stations in the Yuncheng area of Shanxi Province from January 1, 2017 to December 31, 2019 were used to analyze the vertical aerosol distribution characteristics on haze and clear days. The results showed that aerosols were mainly concentrated in the atmosphere layer of 0-2 km on haze days, especially the layer of approximately 0.517 km, and the maximum aerosol extinction coefficient was 0.61 km-1. Within 0-1 km, on haze days, the maximum extinction coefficient was approximately three times greater than that on clear days. There was a significant difference in the vertical distributions of aerosols during the day and night. When the aerosol extinction coefficient was the same, the aerosol height was higher during the day than that at night. When haze events happened, volume depolarization ratios of aerosols concentrated in 0-0.2. On clear days, the frequency of near-surface volume depolarization ratios ranged from 0 to 0.2, which was lower than that on haze days, and the number of small-particle aerosols was greater than that of large-particle aerosols.
In order to solve the problem that the deep learning model PointNet only uses independent point convolution for feature extraction, which leads to the lack of local information, a fusion graph convolution deep learning model based on spatial domain features and spectral domain features is proposed in this paper. In this model, the graph structure is constructed by spatial and spectral methods to extract different neighborhood features, the deep abstract features are obtained by fusing neighborhood features and independent point features, the spatial pyramid pooling method is used to deepen the fine-grained description in the pooling layer. Experimental results on airborne LiDAR scanning point clouds and multispectral aerial images provided by the International Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Association show that compared with other comparison methods, the classification effect of the method is better, the classification accuracy is 84.3%, and urban scenes can be realized effective classification of point cloud data.
Aiming at the problem of poor performance of the scale-invariant feature transform algorithm when registering optical and synthetic aperture radar images, this paper proposes an improved optical and SAR scale-invariant feature transform based on registration algorithm for optical and SAR images. First, the nonlinear diffusion filter is used to create the nonlinear diffusion scale space of optical and SAR images, and the multiscale Sobel operator and the ratio of exponentially weighted averages operator are used to compute the consistent gradient information of optical and SAR images, respectively. Then, the image block strategy is adopted, the scale space is divided into blocks after skipping the first layer of the scale space, and Harris feature points are extracted based on consistent gradient information to obtain stable and uniform point features. To overcome the nonlinear radiation difference between the images, the gradient location and orientation histogram descriptor template are used to build the descriptor. Finally, for feature matching, the Euclidean distance is used and the fast sample consensus algorithm is used to eliminate mismatches. The experimental results show that compared with the scale-invariant feature transformation algorithm combining position, scale, and direction and the OS-SIFT algorithms, the algorithm's matching rate is considerably improved, and the root mean square error is relatively low.
Space positioning of mobile robot is an important link to realize unmanned driving, but using a single sensor only for localization would produce positioning error and the error keeps accumulating. In order to improve the spatial positioning accuracy of mobile robot, a spatial positioning method integrating three kinds of sensors is proposed, which uses LiDAR, inertial measurement unit (IMU) and photoelectric encoder. First, the extended Kalman filter algorithm is used to fuse the photoelectric odometer information based on distance flow algorithm, IMU yaw data information and wheel odometer information with dual photoelectric encoders; second, the differential improvement of the extended Kalman filter is used to eliminate the oscillation caused by the existence of two absolute attitude information in the fusion process; finally, the positioning accuracy after optimization is verified by experiments on a self-built driverless wheelchair mobile platform. The results of repeated experiments show that compared with the track obtained by encoder odometer, the track optimized by multi-sensor fusion significantly reduces the maximum value of positioning deviation and the mean value of absolute error, and the more complex the environment is, the better the optimization effect is, which shows that the proposed method can effectively improve the spatial positioning accuracy of driverless wheelchair.
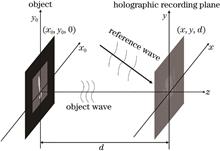
Ghost imaging and single-pixel imaging originate from different physical concepts. They have been closely integrated and developed together due to many similarities they share in the system schemes and image reconstruction algorithms. As typical computational imaging technologies, these two imaging schemes have received extensive attention in the fields of optics, imaging, and information acquisition. Different from traditional area array imaging, ghost imaging and single-pixel imaging obtain images by using the reconstruction algorithms, which is one important feature of computational imaging. In this paper, the history of ghost imaging and single-pixel imaging is briefly reviewed with a focus on typical image reconstruction algorithms. The principles of ghost imaging and single-pixel imaging using light field second-order correlation, sampling theory, compressed sensing, and machine learning are explained. Their application potential and prospects are discussed.
Synthetic holographic stereogram technology is a research hotspot in the field of three-dimensional display, which is widely used in military, economics, and other industries. Based on the development of synthetic holographic stereogram technology at home and abroad, we summarizes the basic writing methods, image quality improvement methods, and performance improvement methods. We introduce the development process and research status of basic writing methods, summarize their implementation methods, and evaluate the comprehensive performance of several main methods at this stage. Focusing on the imaging quality and comprehensive performance of synthetic holographic stereogram technology, we summarize the recent progress in improving synthetic holographic stereogram technology. Finally, the conclusion and prospect are given.
Ultrasonic imaging detection (UID) technology has the advantages of intuitive test results, and is one of the main development directions in the field of nondestructive testing in the future. Compared to traditional ultrasonic testing methods, laser ultrasonic detection has gained popularity due to its non-contact characteristics. The time reversal imaging method has a potential application in locating and detecting targets in inhomogeneous media due to its ability of acoustic beam self-focusing in time and space domains. This study primarily reviews the time reversal method and other conventional ultrasonic imaging methods. The results of different imaging algorithms used in the data post-processing are compared and analyzed. Moreover, the professional simulation softwares available for use in the ultrasonic imaging field are briefly summarized. Starting from laser ultrasound and compared to conventional ultrasound, the general situation of the modern ultrasonic testing technology and the advanced industrial ultrasonic imaging testing instruments and equipment at home and abroad are discussed. Further, the future imaging testing technology is briefly analyzed.
The wavefront modulation system, which swiftly and flexibly performed the wavefront measuring and shaping in a coherent time, is vital in biomedical and optical communications. This high-speed wavefront modulation system, in particular, sets the basis for the effective application of coherent beams in the rapidly-changing scattering media, and digital micromirror devices combined with computed holography are an efficient method for the implementation of this technology. In this study, first, the importance, research advancement, and the application of high-speed wavefront modulation at coherent optical areas were introduced; thereafter, various binary computed holographic methods used in the current wavefront modulation technique were reviewed. The principles and the features of the holographic methods were specifically discussed, existing challenges in the holographic algorithm were summarized, and the trend of the binary computed holography was forecasted.
Recently, with the developments of deep learning technology, deep neural networks have been widely applied in the field of medical image segmentation. Due to its good segmentation performance, U-Net has gradually become a research focus in the field of image segmentation. First, the improved works of U-Net are summarized from two perspectives: structural and non-structural improvements. Then, four medical images of retinal vessels, pulmonary nodules, liver and liver tumors, and brain tumors are used as examples to demonstrate the characteristics and segmentation difficulties of various images and to summarize the application of U-Net and its improved networks in relevant images. Finally, the problems encountered in the improvement of U-Net are discussed, and future developments are forecasted.
Aiming at the problem that stray light interferes with imaging in the process of space-based optical observation, a simulation algorithm of space-based optical observation images affected by stray light is proposed. First, by analyzing the imaging principle of the space-based optical observation image, the simulation process of the space-based optical observation image is designed and the calculation method corresponding to each process is provided. Next, the principle of ground-air-light interference imaging is examined, a mathematical model of ground-air-light imaging simulation is established, and the microelement method is used to realize ground-air-light imaging simulation. Finally, the principle of moonlight interference imaging is described, the mathematical model of moonlight imaging simulation is established, and the moonlight imaging simulation is realized using the extended intercept method. The results obtained from the simulation show that the image fidelity is high when the proposed algorithm is used to simulate the image, and the imaging simulation of stray light is more realistically realized. The accuracy and rationality of the proposed algorithm are demonstrated through relevant documents.
Rapid and nondestructive analysis of sedative drugs plays an important role in forensic science. To demonstrate the potential of classifying benzodiazepine sedative drugs, we examined 81 samples from eight types of benzodiazepine sedatives. Spectral data of each sample were analyzed by attenuated total reflection-surface enhanced infrared spectroscopy (ATR-SEIRAS). Fisher discriminant analysis (FDA) and multilayer perceptron neural network (MLPNN) models were constructed based on the original spectral dataset, first derivative spectral dataset, and spectral fusion dataset. The results showed that there were some differences in the physical and chemical details of different samples. ATR-SEIRAS spectra could reflect these differences, which laid a foundation for the effective classification of different benzodiazepine sedatives. The classification accuracy of the FDA model based on the spectral fusion dataset was the highest (100%), and the classification accuracy of the first derivative spectral dataset and original spectral dataset was 96.3% and 92.6%, respectively. Based on the above datasets, the classification accuracy of the MLPNN model was 97.5%, 96.3%, and 88.9%, respectively. Overall, the results demonstrate that ATR-SEIRAS combined with FDA and MLPNN classifiers can achieve rapid and nondestructive classification of eight types of benzodiazepine sedatives.
In view of the loss of agricultural production caused by bird pecking in recent years, a target detection algorithm based on YOLOv3 bird detection was proposed to optimize the switching strategy of traditional bird repellent machine by identifying birds accurately in real time. This method improves the feature fusion in YOLOv3 network, and brings SE module embedded in the Darknet53 network of the trunk network, focusing on the importance of different channel characteristics. Using adaptive spatial feature fusion (ASFF) enhanced network feature pyramid network (FPN) feature fusion to enhance the detection capability of all scales. The loss function of CIOU boundary box regression is used to take into account the overlap or even inclusion of the prediction-box and the target-box, so that the target-box regression becomes more accurate and stable. The improved YOLOv3 model was used on the self-made bird data set. The average precision (AP) reached 96.65%, and the detection time of single image was only 0.058 s, which increased by the 2.54 percentage point compared with the original YOLOv3 model under the condition of little change in detection speed. The improved method can achieve good real-time performance and better detection accuracy, and provide a basis for optimizing the switching strategy of bird repellent for farmland bird prevention and control.