In view of the high complexity and low detection accuracy of the existing visibility detection methods, a road visibility detection method based on monitoring images is proposed in this work. First, the transmittance of dark and bright primary colors is obtained by using the prior theory of dark and bright primary colors; then, the atmospheric light value and atmospheric transmittance are optimized by using adaptive defogging weight and adaptive filtering window, and the transmittance of the front and rear ends of the lane line is one-to-one corresponding to that of the optimized transmittance of dark and bright primary colors; finally, the atmospheric extinction coefficient and visibility are calculated by combining the distance between the front and rear ends of the lane line. Experimental results show that the method can achieve high precision detection within 100--600 m, and the relative error is less than 10%. Compared with other methods, the method has faster detection efficiency, higher accuracy and easier implementation.
Protection and restoration of cultural relics are applicable to various disciplines such as archaeology, physics, chemistry, and biology. Conservators have always been interested in exploring a nondestructive test. Among these in situ analysis, terahertz technology has widely applied to various areas as an emerging subject in the past 20 years, including security check, drug quality supervision, semiconductors and so on. Recently, the application of terahertz imaging in the field of cultural security has become a popular topic. In this paper, a lacquer box is investigated through terahertz time-of-flight imaging. Experimental results demonstrate that the lacquer box has a bilayer structure. The completed wood material is considered to be the carcass, the surface of which is painted with different decorative patterns. In addition, terahertz time-of-flight imaging can be used to detect damage inside the carcass, i.e., the wood structure in the painted box.
Due to the coherence of the distributed holographic aperture imaging system and the sidelobe effect of the amplitude spread function (ASF), it is very difficult to analyze the imaging resolution. The Rayleigh criterion between the two-point resolution model is extended to the multi-point resolution model, and the resolution performance of the observation point and its nearest neighbor is judged according to the superposition curve of the multi-point ASF under different phase distributions. The genetic algorithm is used to take the valley-to-peak ratio between the observation point and its nearest neighbor as the objective function, and the maximum valley-to-peak ratio at a certain angular spacing is obtained by optimizing the phase distribution between multiple points. When the maximum valley-to-peak ratio is not greater than 0.81, the energy of the observation point and its nearest neighbor can be distinguished. The critical angular spacing with a valley to peak ratio of no more than 0.81 is obtained for any phase distribution, which can be regarded as the angular resolution of the system. Simulation and experimental results show that this method can more accurately analyze the system resolution and equivalent aperture.
In order to improve the problems of low contrast, lack of detailed information, and poor fusion effect of the fusion image, a new algorithm for infrared and low light image fusion, that is, a fusion algorithm based on Cauchy fuzzy function under Tetrolet transform, is proposed. First, the source image is decomposed into two sets of high-frequency and low-frequency coefficients by Tetrolet transform; then, a regional energy-Cauchy fuzzy function rule is proposed for the low-frequency coefficients and the regional Laplacian energy sum is used for high-frequency coefficients; finally, the inverse Tetrolet transform is used to transform the new high-frequency and low frequency coefficients into the final fusion results. Experimental results show that the proposed method has certain advantages in improving the contrast of fused images and preserving image details.
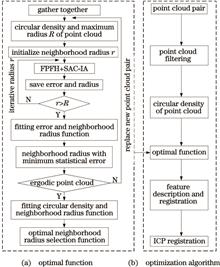
A preset fixed value is adopted as the neighborhood radius based on the features of a three-dimensional (3D) point cloud fast point feature histogram (FPFH), resulting in some problems such as arbitrariness, incompleteness, and inefficiency in feature description. Thus, the entire process of point cloud registration becomes less automated and requires more time. To solve these problems, an algorithm is proposed in this study to automatically select the radius of the FPFH neighborhood in 3D point cloud registration. First, the circumferential density of a multipair point cloud was calculated and the maximum circumference radius was retained. Second, the number of iterations was established and the single neighborhood radius was automatically divided according to the number of iterations and the maximum circumference radius of each pair of point cloud. The features of FPFH were extracted based on the divided neighborhood radius and used for registration in the sampling consistency initial registration algorithm. Finally, the circumferential density of the multipair point cloud and the corresponding optimal neighborhood radius were estimated. Further, the mapping function was obtained using the polynomial fitting method; thus, the FPFH feature extraction optimization algorithm was developed. Results show that the proposed algorithm can automatically adapt to the optimal neighborhood radius according to the circumferential density of the point cloud, effectively reduce the incompleteness and redundancy associated with point cloud description, and improve the speed and accuracy of point cloud registration while improving the degree of automation associated with point cloud registration.
Considering the problems of moving multi-target in video images, fuzzy edge features, and difficult target tracking, a kernel correlation filtering tracking algorithm based on edge features of multi-target video images is proposed in this paper. First, the time of 3 frame images of the target motion trajectory in video images is set as the linear segment. Then, the linear judgment method is used to capture the target. In addition, the dynamic edge evolution technology is used to accurately extract the edge features of the captured target; combined with the gradient angle histogram and color information of video images, the gradient angle-chroma saturation histogram color features are obtained, and the feature weight of the tracking target is obtained. Finally, the kernel correlation filtering tracking algorithm is used to realize the multi-target tracking of video images through cyclic shift, cyclic matrix, and ridge regression model-learning classifier. The experiment results show that the multi-target tracking success rate of the algorithm is above 99%, and the number of images that can be tracked per second is above 65 frames in the complex environment, such as size change, color change, and occlusion, which has superior tracking performance.
In view of the large amount of calculation of Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm and the serious noise in the statistical results, an X-ray image reconstruction method based on a hierarchical model and low-rank approximation is proposed. First, a total variation (TV) regular term is introduced to construct the objective function, and hyperparameters are defined based on Jeffreys prior to establish a hierarchical Bayesian model. Then, the variable split method is used to obtain the conditional probability density distribution of each variable in the split form. Finally, according to the low-rank nature of the forward model, the objective distribution function of the low-rank approximation is calculated, so as to obtain the closed solution of the parameters to be sought. The results show that the proposed method can effectively solve the large amount of calculation in the Bayesian inverse problem. Compared with the existing reconstruction methods based on uncertainty quantification, the proposed method can effectively suppress the image noise while retaining the edge details of the image better.
Current methods of expression recognition based on deep learning exhibit problems such as a large number of parameters and poor real-time performance. To resolve these problems, this paper proposes a facial expression recognition method by merging the multilayer features of a lightweight convolutional network. First, the improved inverted residual network was considered as the basic unit for building the lightweight convolutional network model. Then, the shallow features associated with the convolutional network subjected to the methods of pooling, 1×1 convolution, and global average pooling were merged with the deep features of the network for expression recognition tasks. The proposed method was verified by employing RAF-DB and AffectNet, which are commonly used expression datasets. Results indicate that the facial expression recognition accuracies of the proposed method when considering the RAF-DB and AffectNet datasets are 85.49% and 57.70%, respectively. Furthermore, the number of model parameters is only 0.2 × 10 6.
In order to improve the accuracy of the intrusion detection system, a back propagation neural network model based on the crow search algorithm (CSA-BP) is proposed. BP neural network is an important method to solve nonlinear problems, but its predictive ability is easily affected by the initial parameters. To solve this problem, the relative percentage error is used as the objective function of the model, and the optimal weight and threshold are found through the strong global search ability of the crow search algorithm. Then, the CSA-BP model is validated with five standard datasets. Finally, the CSA-BP algorithm is used in the intrusion detection system. The results show that the proposed algorithm makes the intrusion detection system more accurate, reaching 96.6%, and speeds up the convergence.
The convolutional neural network is used to identify eight diseases of rice leaf, including dry tip nematode, bacterial leaf blight, bacterial stripe disease and so on, to realize the automatic recognition of multiple rice diseases by computer vision. After the disease images were expanded through random rotation, random change of brightness and contrast, and so on, 80% of the images were randomly divided into training samples and 20% were divided into test data. The training samples were directly input into the AlexNet and LeNet5 networks for training, and the AlexNet and LeNet_models were obtained. FCM_model and BN_model are obtained using two methods of image recognition on AlexNet network: fuzzy C-means clustering image processing and batch normalization layer after activation function of each layer. From the identification results of the four models and the analysis of model performance evaluation indexes, it can be seen that the BN_model has the best recognition effect. The BN_model has a final recognition rate of 99.11%, which is increased by percentage points of 0.23, 0.59,4.43 than AlexNet_model, FCM_model, and LeNet_model, respectively. The model has strong recognition and generalization ability, which provides reference for the research of rice diseases based on convolutional neural network.
The amount of point cloud data is very large, so it is an important research content to reduce the point cloud data reasonably. Aiming at the problems of missing details and containing holes in traditional point cloud reduction algorithm, this paper proposes an adaptive point cloud reduction algorithm based on multi parameter k-means clustering. In this method, k-neighborhood of point cloud is created based on KD tree, curvature and normal features of point cloud data are calculated by surface fitting, and point cloud features and boundaries are detected and preserved by multi parameter mixed feature extraction method; initial cluster center is determined by KD tree index, k-means clustering is conducted, and clustering results are refined according to maximum curvature deviation. This algorithm, curvature sampling method, uniform grid method and random reduction method are applied to different types of point cloud models for experiments. The results show that the proposed algorithm has the lower standard deviation than the latter three methods in complex model, and can retain the detailed feature information of point cloud. In addition, the reduction effect and model integrity of the proposed algorithm are better than those of uniform grid method and curvature sampling method.
Video tracking technology based on shoe patterns is commonly used by public security organizations in criminal investigations and is crucial in actual public security combat. However, this technology relies heavily on manual screening with a heavy workload and low efficiency, and it is prone to missed inspections. In view of this, an automatic shoe detection algorithm based on Single Shot MultiBox Detector (SSD) model is proposed herein to achieve automatic detection and positioning of pedestrian shoes. First, the structure of the SSD model and the parameters of the prior frame are designed to meet the practical application of shoe detection. Then, the method for adjusting network parameters is used to improve the detection performance and stability of the network and the network model and method suitable for shoe detection are improved. Thus, an accurate and efficient single-category shoe detection network is obtained. Finally, performance evaluation in the shoe sample database constructed by the research group in the early stage is conducted. Experimental results show that the average accuracy of the proposed algorithm is 0.891.
Aiming at the problem of how to accurately detect the focusing region and how to overcome the registration error and noise sensitivity in the process of multi-focus image fusion, a multi-focus image fusion algorithm based on filter operator and double-scale decomposition is proposed. First, the algorithm performs Gaussian-Laplace filtering on the source image, and performs difference operation between the filtered image and the source image to separate out the high frequency information of the multi-source focused image. Then, an initial decision graph with complementary edge information is generated after decomposing the multi-source image edge and local high frequency information by the structure-based double scale focus measurement method. Finally, the initial decision graph is refined step by step based on the consistency test method to generate the fused decision graph, and the fused image is obtained according to the per-pixel weighted average rule. The experimental results show that, compared with other focusing strategies, this focusing region detection method has higher robustness and better recognition ability for different noises, and the processing time is less than 0.5 s.
Aiming at the limitations of dark channel and linear transformation algorithm, an iterative optimization dehazing algorithm based on improved linear transformation is proposed in this work. First, starting from the minimum color component, the adaptive linear transformation model of the atmospheric dissipation function and the minimum color component is established to obtain the initial estimation of the medium transmission rate. Then, the medium transmission rate of the bright region in the fog image is adaptively modified. Second, the high-order filter composed of Kirsch and Laplacian operators is used for iterative processing to obtain the optimal medium transmission rate. Finally, the optimized medium transmission rate and the atmospheric light value obtained by quadtree sub block search method are substituted into the atmospheric scattering model to obtain the restored image. Experimental results show that the algorithm can restore the clear and natural image, and has good dehazing effect on a single image.
Aiming at the problem of small target (pixel ratio less than 0.02) detection that the target features are easily lost and the resolution is low, a detection method based on improved YOLOv3 (You only look once) convolutional neural network is proposed in this paper. First, the small targets in the data set are copied and transformed to enhance the network''s attention to the small targets during the training process. Second, for the scale fusion of shallow visual information and deep semantic information, a cross-scale detection layer network structure is proposed, which improves the network''s adaptability to small targets. Finally, for the detection effect of high-resolution images, a residual block transfer structure combining depth and breadth is proposed, which enriches the receptive field of deep feature maps. Experimental results show that compared with the YOLOv3 network, the precision rate of the network detection of small targets with the improved cross-scale prediction layer increased by 1.9 percentage points, and the recall rate increased by 5.9 percentage points. The precision rate of the network detection of small targets with the optimized receptive fields increased 31.6 percentage points, the recall rate increased by 46.4 percentage points.
In order to solve the shortcomings of poor recovery effect and timeliness of current rain removal algorithms, this paper proposes a fast video rain removal algorithm that combines temporal gradient and horizontal direction gradients. First, the rain image is divided into a background layer and a rain race layer, and the model function is constructed by using the time direction gradient of background layer, the horizontal direction gradient of rain trace layer, and the corresponding pre-trained Gaussian mixture model of each layer as priori conditions; second, the semi quadratic splitting method is used to transform the non-convex function to obtain the objective function for minimization; finally, fast total variation method is used to optimize the model function to obtain the optimal solution of the model function. Experimental results show that, compared with other algorithms, the algorithm has better rain removal recovery effect, good timeliness and faster speed, and the average peak signal-to-noise ratio is improved by more than 1 dB.
Various types of noises are unavoidable during the three-dimensional reconstruction of a point cloud. In the existing methods, noise points are usually removed by analyzing and calculating the geometric relation of the point cloud in a three-dimensional space; this involves complicated and time-consuming calculations. This paper proposes a point cloud filtering algorithm based on image processing. First, the point cloud was preprocessed and mapped onto the image. Second, the noise area was removed from the image and restored to a three-dimensional point cloud by applying image processing. Thus, the point cloud without noise was obtained. This paper analyzes the implementation of the proposed algorithm in detail and verifies the effectiveness and real-time performance of the proposed algorithm based on experimental results.
Most existing deep clustering methods are employed to minimize the reconstruction loss. However, the identification ability of potential representation is not necessarily related to the reconstruction loss. Moreover, these deep clustering methods focus only on extracting useful features from the sample itself and seldom consider the structure information behind the sample. To resolve these problems, a new structured deep discriminant embedded coding network clustering (SDDECC) algorithm is proposed for unsupervised image clustering. First, the maximum mutual information and minimum prior distribution constraints are embedded in a multilayer convolutional autoencoder network. Then, the feature representation learned by the deep discriminant error correction network (DDECN) module is integrated into a graph convolutional neural network (GCN) module by the transfer operator. Finally, Kullback-Leibler (K-L) divergence is used in combination with the potential feature distribution generated by the dual network structure and is trained end-to-end to guide the clustering learning. The experimental results show that SDDECC algorithm can effectively extract more discriminative deep features than those obtained using traditional methods. Moreover, because the attribute information of the sample itself and the structural information between the samples are integrated in the GCN, the model shows good clustering.
As one of the most important optical solar telescopes for studying solar physics, the new vacuum solar telescope (NVST) suffers from various noise interferences in the process of collecting image data, which affects the study of observation data. Some methods based on standard supervised deep learning have achieved remarkable results in the field of image denoising. However, this type of method becomes inapplicable to the field of astronomical images where clean data is difficult to obtain. To solve this problem, this paper applies the image denoising method based on self-supervised deep learning to NVST image denoising. In order to quantitatively evaluate the performance of the network model, first, add simulation noise to the reconstructed data; second, the noisy data is estimated through the noise level estimation network to estimate the noise level; then, self-supervised convolution blind spot network is used to learn image features, and the image is restored by Bayesian inference; finally, the experimental results are quantitatively analyzed through the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity evaluation indicators, correlation analysis, and power spectrum analysis. Experimental results show that, whether for simulated noise data or actual observation data, compared with other image denoising methods in the experiment, the proposed method can effectively reduce the interference of noise on NVST images and improve the image PSNR. At the same time, it also provides solutions for other engineering fields where clean image data is difficult to obtain.
In view of the fact that traditional neural networks cannot effectively classify Chinese food with high similarity, a Chinese food recognition model of RNA-TL (ResNet with attention and triplet loss) based on an improved residual network is proposed. The algorithm first fuses the multi-scale features to extract the semantic information of deep-level images, and then adds an attention mechanism layer to give more attention to the important parts of the images. Finally, the similarity among classes is calculated by using triplet-loss, whose result is input into support vector machine (SVM) for classification. The experimental results indicate that the proposed RNA-TL model possesses more superior performances in recognition accuracy on the public dataset of Chinese food and the dataset collected by our project team, compared with the other mainstream algorithm models.
To deal with the problem that the camera tracking module of traditional visual simultaneous localization and mapping (vSLAM) can''t make pose estimation accurately, a semantic-based visual odometry is proposed. First, while using pyramid Lucas-Kanade optical flow to track and match the inter-frame feature points, the frame is pixel-wisely segmented. Then, the semantic information and geometric features are combined closely to accurately remove the outliers in the frame, thus the pose estimation and mapping can rely only on the trusted static feature points in the frame. Finally, a multi-scale random sample consensus (RANSAC) scheme is proposed. The matching points are sampled step by step, and different scale threshold are used for each step, which can reduce the detection time and improve the robustness of outliers simultaneously. Experimental results on the TUM data set show that, compared with ORB-SLAM2, the absolute trajectory error and relative pose error of the proposed system are improved by more than 90% in the high dynamic sequence. And the proposed scheme reduced the detection time by 30%-40% while the robustness of pose estimation is improved when compared with similar DS-SLAM.
During underwater detection operations, the water body is disturbed by the external environment, which changes the underwater refractive index, enhances the scattering effect of the water body on light, and causes the underwater optical target to be blurred and the image quality is reduced. In view of this, the ghost imaging method is used to overcome underwater disturbances, and the second-order coherence of the reference light field and the measurement light field are used to measure separately. At a certain moment, the light field distribution of the reference beam on the collection plane and the measurement beam on the collection plane. According to the total light intensity, the ghost image is reconstructed. During the experiment, ultrasonic waves are used to disturb the water body, the imaging results of ghost imaging methods and classic imaging methods are compared, and the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the two imaging results are compared to study the anti-disturbance ability of the ghost imaging system under water. The experimental results show that the image quality of ghost imaging method is higher than that of classic imaging method in the environment of underwater disturbance.
In order to overcome the problems of poor robustness and low registration accuracy of the iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm, this paper proposes an improved ICP point cloud registration algorithm based on fast point feature histograms (FPFHs). Firstly, the point cloud feature is extracted based on the improved internal shape descriptor and the change of the normal vector angle. Secondly, an exponential function is used to improve Euclidean distance, which is used as the weight coefficient of the FPFH algorithm for describing the feature points, therefore ensuring that the initial alignment estimation obtains more accurate positions of point clouds. Then the double constraint and unit quaternion algorithm are used to complete the initial registration. Finally, in order to reduce the iteration time and reduce the influence of bad correspondence in the registration, the bidirectional k-d tree is constructed for the ICP algorithm, and the ratio of the Euclidean distance of a point pair to the maximum Euclidean distance is used to calculate the weight of each point pair, which is used as a weight coefficient of the ICP iteration error function. Experimental results show that the registration accuracy of the proposed algorithm is 2--6 orders of magnitude higher than that of the ICP algorithm, and the proposed method has stronger robustness.
This paper proposes a visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) loop closure detection algorithm based on an improved line band descriptor (LBD) and data-dependent measures with point and line features to improve the accuracy and recall rate associated with visual SLAM loop detection. First, each band descriptor was subjected to an internal comparison operation for solving the problem of low matching accuracy that can be attributed to the existing binary conversion operation of LBD, wherein only the sizes of the individual band descriptors were compared and their internal attributes were ignored. Then, we used a method based on data-dependent to estimate the image similarity considering the influence of the visual word frequency distribution information on similarity. Finally, the results obtained via verification using public data sets show that the proposed algorithm can achieve a high recall rate with 100% accuracy.
To address the problem of low detection accuracy and poor robustness of the traditional helmet wearing recognition algorithm, we propose a deep learning-based helmet wearing detection method. The method is based on the YOLOv3 detection algorithm, and its network structure and loss function are improved. Firstly, the poor detection of small targets by the original YOLOv3 algorithm is compensated by adding feature maps. Then, on the basis of adding feature maps, the K-means clustering algorithm is used to cluster the collected helmet datasets and select the appropriate a priori anchor frames. Finally, GIoU Loss is adopted as the boundary frame loss, and Focal Loss is added to the loss function to reduce the errors due to positive and negative sample imbalance. Experimental results show that, compared with the YOLOv3 detection algorithm, the improved algorithm improves the average accuracy by 3.47% and the accuracy of helmet identification by 4.23%, which is advanced and effective in helmet identification.
A real-time target tracking algorithm based on improved SiamFC (a fully convolutional Siamese network) is proposed herein to improve the target tracking speed and the network discrimination ability of traditional SiamFC. First, after the first conventional convolution layer, a depth-wise separable convolution is set to improve the tracking speed by reducing the amount of parameter calculation. Second, the third convolution layer is set as a mixed depth-wise convolution (MixConv) to improve the recognition ability of the network. We extracted features from the convolution kernel of different sizes and concatenated them in the channel to achieve a multifeature fusion and extract more robust features. Finally, the preprocessed ILSVRC2015 data set was used to train the network using the random gradient descent method, and the performance of the algorithm was tested on the OTB2015, VOT2016, and ILSVRC2015 data sets. Experimental results show that compared with the SiamFC algorithm, our algorithm shows a certain improvement in the tracking success rate, tracking accuracy, and tracking speed, and can meet real-time tracking requirements.
The crack-detection method based on deep learning relies heavily on a large amount of pixel-level annotation information. Thus, a crack-detection method based on semi-supervized learning is proposed. The proposed method introduces multiscale modules into the network model of crack-detection. It uses only a small part of pixel-level annotation data for fully-supervized training. For the unlabeled data, the fusion of multiple saliency area detection methods to generate pseudolabels can reduce pixel-level reliance on the labeled information. The improved network is experimentally verified on the crack dataset. It is compared with the commonly used semantic segmentation network and weakly supervized experimental benchmarks from the perspective of subjective evaluation, accuracy, recall rate, and F1-score. The experimental results show that the improved network can effectively enhance crack recognition accuracy. The proposed semi-supervized training method can achieve recognition accuracy and recall rate equivalent to the fully-supervized method when only 6.25% pixel-level label information is required.
Driving distance detection is one of the key technologies of the car''s active safety driving assistance system. This paper proposes a method of real-time monocular depth estimation, to improve the accuracy and real-time performance of the distance detection during the vehicle driving process. First, the distortion model is constructed, and the camera calibration algorithm is used to calibrate the monocular camera. Then, the license plate is used as the target location benchmark of the front vehicle, and the license plate information of the front vehicle is extracted quickly by using the license plate filtering algorithm of color and contour. Finally, based on directional gradient histogram feature and support vector machine, the license plate is located accurately. Experimental results show that, compared with other methods, the perspective N-point depth estimation model fused with known license plates has high accuracy and good real-time performance. This method has a recognition rate of 99.326% for the location of the license plate of the front vehicle, and the detection error of the driving distance is less than 10%, and the time required to process an image is about 170 ms, which meets the application requirements for the detection of the distance between vehicles during the vehicle driving process.
To balance the vision imperceptibility and robustness of a watermark and address copyright protection and content authentication issues in digital multimedia products, this study proposes a robust watermarking algorithm that is based on structured forests edge and the scale invariant feature transform (SIFT). First, a color image is converted from an RGB space to a Lab space, and the 1024 stable SIFT points are extracted based on an L component as the embedding position of watermark. Second, the image edge is extracted using a trained random decision forest model as the watermark image that is decomposed by the discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to obtain a low-frequency sub-band that is divided into nonoverlapping blocks. The maximum values of the blocks are obtained and encrypted using the Arnold transform. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm exhibits better imperceptibility and robustness to resist various attacks, such as cropping, speckle noise, and motion blur, in comparison with other related algorithms. Furthermore, it effectively protects the original edge features of an image.
For the problem of larger location error in distance vector-hop (DV-Hop) localization algorithm, an improved DV-Hop ranging-based dynamic parameters differential evolution localization (IDV-Hop-DPDE) algorithm is proposed in this paper. IDV-Hop-DPDEL uses multi-communication radius to broadcast the positions of anchor nodes. Based on near-degree of the nodes, the ranging between unknown nodes and anchor nodes is modified. Finally, to improve searching efficiency and obtain the most optimal position, the scaling factor and the crossover probability of the traditional differential evolution algorithm are dynamically changed. To verify the effectiveness of the algorithm, the localization parameters in the simulation remains unchanged, while the three parameters vary within a certain range, i.e., the total number of nodes in the network, the proportion of the anchor nodes, and the communication radius. The simulation results show that the localization error of the IDV-Hop-DPDEL algorithm was reduced by 51.56%, compared to the DV-Hop algorithm. And the proposed algorithm has better performance than the other two classical improved DV-Hop algorithms.
In order to improve the safety factor of scientific expedition personnel when detecting unknown environment, realize non-contact measurement, and to solve the problem that two-dimensional planar imaging cannot obtain the distance information and size information of the object, a set of three-dimensional scanning imaging system based on single-point pulsed laser rangefinder is designed and realized. First, variance filtering and Gaussian fitting are used to improve the accuracy of single-point laser ranging. Second, after correcting the angle deviation of the pan-tilt, the point cloud data on the surface of the object can be obtained through the rotation of the pan-tilt. Finally, density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) algorithm is used to filter the acquired point cloud noise to obtain a three-dimensional point cloud image with clear outline, clear angle, and accurate distance. Indoor imaging experiments on ordinary paper boxes show that the system distance measurement error, object area size measurement error, and angle fitting error are all within 5%; and outdoor imaging experiments on large buildings within 200 m show that the system can effectively detect unknown environments and perceive obstacles.
Aiming at the problem of reduced alignment accuracy caused by sloshing interference and constant error of inertial devices during the in-motion alignment process of a vehicle-mounted strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS), an anti-interference moving alignment method for the vehicle-mounted laser SINS based on rotation modulation is proposed.Aiming at the sloshing interference during the alignment process, the attitude real-time update method based on the inertial system is used to track attitude changes so as to overcome the interference of angular sloshing, and the integral for the force equation is conducted to reduce the line vibration interference. At the same time, the attitude at the starting time is obtained by combining the optimal estimation of the attitude. In the process of updating the direction cosine matrix, the equivalent rotation vector algorithm of "monad sample+previous cycle" is adopted to reduce the influence of the non-exchangeable error on the accuracy of attitude calculation. Then, the single-axis continuous rotation modulation method is used to realize the self-compensation of the constant error of the inertial devices. Simulation results show that the autonomous initial alignment method can overcome interference during the alignment process, eliminate the influence of the constant error of the inertial devices, and improve the alignment accuracy.
An oblique incident longitudinal wave probe is used to form creeping waves on the inner wall of the tube to achieve the purpose of detecting defects on the inner wall of the thick-walled tube. First, the finite element method is used to simulate the creeping wave formation process on the inner wall of the obliquely incident longitudinal wave. Then, the laser ultrasonic visualization technology is used to observe the creeping wave formation process on the inner wall to verify the results of the finite element simulation. Finally, the developed ultrasonic flaw detector is connected the creeping wave probe obtains the reflected signal of the creeping wave on the artificial defect on the inner wall. The experimental results show that the ultrasonic longitudinal wave undergoes modal conversion on the inner wall of the tube to form a creeping wave. The creeping wave energy is related to the incident angle of the longitudinal wave, The distance between the probe and the defect affects the amplitude and time of the defect reflection signal. Longitudinal waves are only partially converted into creeping waves on the inner wall and there are other modes of ultrasound. The trial-produced creeping wave probe can effectively detect the inner wall defects of thick-walled pipes and provide an effective non-destructive testing method to ensure the safe operation of thick-walled pipes.
To overcome the problems of accuracy degradation and divergence of the iterative extended Kalman filter (IEKF) when applying target tracking to model mismatches and noise time-variations, an adaptive IEKF algorithm based on multiple fading factors is proposed. First, a limited memory innovation covariance estimator based on the normal distribution is used to calculate the estimated value of innovation covariance and the multiple fading factors are distributed to each filtering channel according to the estimated covariance. Then, the filtering anomaly according to the χ 2 test principle is determined and the fading factors are introduced only when the system is abnormal. Finally, the radial distance and azimuth between the target and the observing station are used to determine the adaptive control of the IEKF iteration number. The simulation results show that compared with the traditional IEKF, when the system model is mismatched, the mean estimation error of position, velocity, and acceleration of the proposed algorithm is reduced by 86.97%, 33.18%, and 15.56%, respectively. When the process noise is time-varying, it is reduced by 60.35%, 18.42%, and 6.02%, respectively. When the measurement noise is time-varying, it is reduced by 50.60%, 18.78%, and 5.41%, respectively. Therefore, the proposed algorithm effectively improves filtering accuracy and robustness.
Due to the absorption of water body and strong scattering of suspended particles, there is a serious “curtain effect” in underwater optical imaging, which causes the details of the target in the scene to be submerged in the background scattered light, and the image contrast is greatly reduced. Due to the uniqueness and difference of target information and background information, the underwater polarization imaging technology developed from the polarization characteristics of light field can effectively suppress the scattering light of underwater background. The polarization differences between the target information light and the background scattered light are used to separate them effectively and realize the clear imaging. At present, underwater polarization imaging technology is developing rapidly, which has been widely used in many fields and new research results. This paper systematically introduces the basic principle, implementation algorithm, and imaging effect of underwater polarization imaging technology, and analyzes and prospects the future development of underwater polarization imaging technology according to the advantages and disadvantages of existing technologies.
The positioning accuracy of star points is essential in astronomical navigation, which affects the accuracy of astronomical navigation. The traditional method for improving the resolution of a star map based on linear interpolation directly uses the linear relationship to calculate the gray value of insertion, however it ignores the own change characteristics of original functions. In view of the imaging characteristics of star points, a method of star location is proposed based on improved linear interpolation. First, we establish the imaging model of star points, deduce the one-dimensional model, and obtain the concave convex boundary point by calculating the second-order derivative. Then we give the method for calculating the weighting factor of improved linear interpolation, and finally the location of star points is realized. The simulation results show that, compared with the traditional method, the proposed method has an average deviation error reduced by 15.4%, and it can effectively extract the center of star points.
The basis of various laser-biological tissue interaction studies such as photothermal, actinic, and photomechanical effect studies is the accurate description of the light distribution in biological tissues under laser irradiation, and the effective methods to accurately describe the light distribution are various mathematical models and simulation methods. Therefore, the paper systematically summarizes the main theories, research models, and quantitative analysis methods that describe the light distribution in the biotissue at home and abroad. At the same time, the horizontal comparison and analysis of the application scope, advantages, and limitations of each method model is carried out. We longitudinally review the theoretical basis of most simulations and experiments, and focus on summarizing the latest theoretical breakthroughs and solutions of practical problems proposed by domestic and foreign scholars, so as to facilitate readers to track the frontier quickly and comprehensively. Finally, we point out some deficiencies in the current research in this field and make a certain prospect for the future development direction.
The detection of video abnormal behavior is paramount to ensure public safety. In this paper, the abnormal behavior detection algorithm based on deep learning is classified and summarized. First, the overall process of abnormal behavior detection is presented. Then, based on the neural network training method, the development and application of deep learning in the field of abnormal behavior detection are discussed from three aspects: supervised learning, weakly supervised learning, and unsupervised learning, and the advantages and disadvantages of different training methods are analyzed. Finally, commonly used datasets and performance evaluation criteria are presented, the performance of the different algorithms is analyzed, and future directions are discussed.
The traditional microscope usually needs to change the magnification of the system by changing the magnification of objective lens, which is same as that of the eyepiece, and the magnification is not continuous. Applying the continuous zoom optical system design to the microscopic imaging system can realize the continuous change of imaging magnification. Continuous zoom optical systems and their zoom principles are summarized in this review. Various types of continuous zoom microscopes are discussed. The future development of continuous zoom microscopes are also discussed and prospected.
Bloodstain is a biological examination material with high occurrence rate in the scene of violent cases. Inspection and identification work can provide a lot of information for the rapid detection of these cases. Hyperspectral imaging technology can be used for nondestructive and rapid imaging of bloodstains in crime scenes. Compared with the chemical reagent method and traditional spectral analysis method for bloodstain detection, the characteristic of image-spectrum merging is a significant advantage of hyperspectral imaging technology. Based on the brief analysis of the characteristics of hyperspectral imaging, data expression, and data processing methods, this paper introduces the applications of hyperspectral imaging technology in the fields such as national defense, ecology, and food. This paper focuses on the application status of hyperspectral imaging technology as a technical means of bloodstain detection in potential bloodstain appearance, bloodstain component analysis, bloodstain classification and identification, and bloodstain age prediction. The paper summarizes the challenges encountered in the application process and the later key research directions and development prospects.
The inversion of the geometric parameters of the ellipsoidal particle group through the extinction coefficient is an important problem in the field of particle measurement. The traditional inversion technology based on evolutionary algorithm requires multiple numerical integration to solve the extinction coefficient, which is low in efficiency. To solve this problem, an acceleration method based on machine learning is proposed in this work. First, the particle size and shape are expressed parametrically; second, the training and testing datasets of ellipsoidal particle extinction coefficient are established based on the anomalous diffraction approximation theory; finally, the mapping between particle parameters and extinction coefficient is realized by using multilayer perceptron artificial neural network, and the effects of the number of neurons, wavelength, particle group distribution model and other factors on the prediction accuracy and efficiency are studied. Experimental results show that when the number of hidden layer neurons is 20, the average prediction error is less than 0.05%, and the single machine prediction time is about 0.6 μs. The technology provides an efficient and accurate extinction coefficient calculation tool. With further employment of evolutionary algorithms, it is expected to realize the real-time inversion of spherical and ellipsoidal particle size and shape parameters.
The inspection and analysis of heavy mineral oil plays an important role in dealing with traffic-accident cases. In order to obtain accurate classifications of heavy mineral oils, we collected infrared and Raman spectral data for 120 samples of five kinds of heavy mineral oils, including gasoline engine oil, diesel engine oil, grease, gear oil, and hydraulic oil. We established a classification and discrimination model for heavy mineral oil by using a support vector machine (SVM) combined with a spectral-fusion method. The results showed the accuracy of modeling classification using single-spectrum data to be rather low. When we modeled and analyzed the data obtained from primary spectral fusion, the classification and recognition rates for the five heavy mineral oils were slightly better, with an accuracy up to 75%. However, modeling that used data from intermediate spectral fusion combined with principal component analysis achieved complete differentiation among the five heavy mineral oils, with feature extraction from the 26-dimensional matrix being the best, with an accuracy up to 100%. In summary, spectral-fusion data combined with SVM modeling analysis can achieve complete separation among heavy mineral oils. The method improves the efficiency of inspection and identification, which fulfills the goal of rapid and accurate inspection for frontline law-enforcement personnel. It also provides theoretical support and a reference method for relevant cases.
Subjective color analysis is affected by factors such as lighting sources and observers. To avoid this subjectivity, the pigments of ancient murals are identified using visible spectroscopy, and the characteristics and historical evolution of the ancient murals'' color are then analyzed objectively using the chromatic theory. We built a nondestructive acquisition system and used it to capture the visible spectra of the typical Mogao Grottoes murals painted in different dynasties. Many typical pigment samples were prepared by simulating the ancient process. The visible spectra and particle sizes were measured to construct a standard reference database from the obtained results. After analyzing the relationships among the visible spectra, material composition, particle size, and color attributes, a pigment identification method was proposed to identify the pigment used on the murals. The color attributes and historical evolution of the Mogao Grottoes murals were analyzed by comparing the identified pigments with those in the reference database.
Cigarette ash is one of the important material evidences in forensic science research. In this work, using the chemometric method, the energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF) was used to inspect 42 cigarette ash samples, and the rapid non-destructive detection of cigarette ash was realized. First, after standardizing the XRF data in the early stage, the value of K was determined by the sum of square errors within the group. At the same time, K-means clustering method was used to perform preliminary clustering of the samples and explain the information of the samples and chemical components reflected by the clustering results. Then, the clustering results were verified by principal component analysis and single factor analysis of variance. Finally, the discriminant function model was established by using discriminant analysis. A classification model based on K-means clustering method was established. The results show that the K-means clustering using sum of square errors within groups is accurate and reliable. The clustering results are also well verified in principal component analysis. Different categories are well differentiated. Each element in single factor analysis of variance has good significance. Discriminant analysis shows that the accuracy of the classification model reaches 100%. This classification model is simple, fast, accurate, and reliable, which provides a reference for the public security grassroots to handle cases.
Computer color matching has gradually become the mainstream color matching method to ensure the consistency of packaging and printing products in the color reproduction process. The basic spectrum database is the basic condition of computer color matching, and its establishment method is too complicated, which affects the promotion and application of computer color matching technology. According to Kubelka-Munk theoretical analysis, the spline mass concentration (concentration for short), ink concentration gradient, and the number of ink gradients have a great influence on the color matching results in the process of establishing the basic spectrum database. In order to optimize the basic spectral database and obtain more accurate color matching results, based on the single factor experiment method, orthogonal experiment method, and related evaluation methods, an optimal combination of concentration gradient, gradient number, and concentration range of spline ink in the process of color matching database building is proposed. In the experiment,we use the established database to match Pantone colors, calculate the color difference, and analyze the results based on the concentration range. Experimental results show that the optimized spectrum color matching database greatly reduces the workload of database construction. At the same time, the accuracy of the target color matching results obtained by calculation is high, which meets the production requirements, indicating that the method can effectively select the best parameter combination.
The meridional lobster-eye lens has a better focusing ability than the square-channel lobster-eye lens. In order to study the influence of the characteristics of the reflective surface of the meridional lobster-eye lens on the X-ray focusing imaging characteristics, one ray tracing algorithm for the meridional lobster-eye lens is established based on the principle of prism expansion. In addition, the effects of coating material, coating thickness and surface roughness on the focusing characteristics of X-rays with different energies are analyzed based on the Fresnel reflection principle. The research results show that the X-ray focusing ability of the meridional lobster-eye lens is mainly determined by the transfer efficiency of the reflective surface, and the transfer efficiency is determined by the chosen coating thickness and coating roughness and simultaneously modulated by the channel-cone apex angle. The X-ray energy determines the effective object aperture angle of the meridional lobster eye lens, and the matching of the lens field of view with the effective object aperture angle also influences its focusing ability and focal spot distribution.