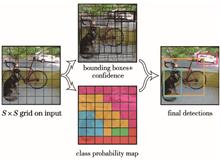
The traditional YOLOv3 model uses ImageNet and COCO datasets for training, in which the scene target characteristics are significantly different from those in test datasets, and leads to low detection accuracy of complex scene targets in high-resolution remote-sensing images. This paper optimizes the training process of the traditional YOLOv3 network using the idea of transfer learning. During the training of the YOLOv3 network, the model is pre-trained by generating an augmented dataset similar to the target domain. The training-optimized method improves the accuracy of the object boundary of target prediction. Also, the parameters of the pre-training model are fine-tuned using a training dataset from the target domain, thus, completing the whole training process of the network. The experiment on the detection of three types of object, including aircraft, playground, overpass, was carried out based on a subset of RSOD & DIOR dataset for remote sensing image object detection. The results show that the proposed YOLOv3 model effectively improves the detection accuracy of the three types of targets in complex urban scenes. The mean average precision of object detection using our model improved by 2% or more, compared with the traditional YOLOv3 model.
Aiming at the problem of large-capacity information embedded in information hiding technology reducing the concealment and robustness, an adaptive image block hiding technology based on optical spatial-frequency domain transform was proposed. The gray-level correlation analysis and echo state network were used to form the adaptive embedding mechanism. When the embedding capacity reached the saturation threshold, the embedding position was automatically adjusted using the mechanism based on the gray-level correlation order to avoid excessive deterioration in robustness. Based on this, the two-dimensional discrete cosine transform was used to hide images in the spatial-frequency domain and combined with the human eye’s characteristic of insensitivity to the optical high-frequency area to realize information hiding in the transform domain, thereby ensuring that the concealment was not affected. Simulation and comparative experiments prove that the visual perspective is unaffected after large-capacity information is embedded in the carrier image. After introducing Gaussian and salt and pepper noise interference and rotating and zooming geometric attacks, results show that the information carrier is insensitive to noise interference and geometric attacks, indicating the technology ensures large-capacity embedding while considering concealment and robustness.
The formation of carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) fatigue damage is complicated, and fatigue damage continues to expand over time and as the load increases. Focusing on the problems associated with existing probability-based diagnostic imaging methods, i.e., high misjudgment rate of damage location, low damage imaging clarity, and poor visualization effect, this paper proposes a CFRP fatigue damage-probability diagnostic imaging method based on a time-of-flight (ToF) damage factor. The method uses a new damage factor to improve existing probability-based diagnostic imaging methods, and studies the fatigue damage of CFRP plates under different fatigue loading cycles. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared with existing methods, the damage location error of the method is reduced by at least 49.85%, which provides a new method for the accurate quantitative analysis of CFRP fatigue damage.
In order to solve the problems of measurement difficulty and precision in manual assembly mode of large-size gear structure with coaxial internal meshing, a visual measurement method for gear profile structure assembly is proposed. In this method, a monocular vision measurement system is constructed, and its spatial pose is calculated by using its image features to realize high-precision measurement. First, based on the minimum kernel value similarity area algorithm of adaptive kernel and adaptive threshold, the tooth tip angle points are extracted, and Canny algorithm improved by OSTU is used to detect discrete arcs of auxiliary circle. Then, combined with the idea of random sampling consensus, the ellipse fitting algorithm based on geometric distance and Levenberg-Marquardt optimization is used to obtain the ellipse parameters, and the measurement model of gear profile structure and the principle of pose calculation are given. Finally, the experiment is verified, and the experimental results show that the measurement accuracy of this method can reach 0.050 mm, which meets the requirements of high-precision measurement of gear structure assembly.
To solve the problem of high missed rate and slow detection rate in the current multitarget tracking process, a multitarget tracking algorithm with an improved YOLOv3 network structure is proposed. First, the K-means++ algorithm is utilized to cluster the target boundaries in the dataset. The priori parameters of the network are optimized using the clustering results. Then, the deep separable convolution module is employed instead of standard convolution in the Darknet-53 feature extraction layer, thereby reducing the number of parameters. In addition, the key channel information of the feature map is highlighted by applying the SENet module in the YOLO prediction layer. Finally, the improved YOLOv3 algorithm is used to implement the detection of a target in the classic tracking-by-detection framework. Meanwhile, the Deep-SORT algorithm is adopted in the tracking part. Experimental results show that the proposed multitarget tracking algorithm can effectively reduce the missed detection rate and take into account the detection accuracy and real-time performance, simultaneously.
In recent years, deep learning has made a great achievement in image super-resolution reconstruction. Due to the complex ocean environment, the traditional image super-resolution algorithm has some problems, such as the difficulty in adjusting parameters. In addition, the single frame image super-resolution algorithm has an ill conditioned recovery and the generated pixels are uncertain. In this paper, a super-resolution reconstruction algorithm of multi-frame images is proposed for the study of sea surface image reconstruction. The convolution neural network in deep learning is used to learn the mapping relationship between multi-frame low-resolution images and high-resolution images, so as to realize super-resolution reconstruction. At the same time, because the ocean monitoring imaging system needs more high-frequency information to identify the target and lock contour, the residual network framework is proposed to improve the quality of network reconstruction images, recover more high-frequency information and enrich the image details. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has a better image reconstruction ability and better subjective and objective evaluation results compared with other methods.
This study proposes an underwater image enhancement algorithm based on the pyramid attention mechanism and generative adversarial network (GAN) to improve the enhancement effect of underwater images. It uses the generative adversarial network as the basic architecture, and the generative network adopts the encoding and decoding structures and introduces the feature pyramid attention module. The combination of multi-scale pyramid features and attention mechanism can capture richer advanced features to improve model performance, and the structure of the discriminant network is similar to the Markov discriminator. In addition, a multi-loss function including global similarity, content perception, and color perception is constructed to keep the structure, content,and color of the enhanced image consistent with those of the reference image. The experimental results show that the sharpness, color correction,and contrast of underwater images enhanced by the proposed algorithm are improved. The average values of the structural similarity, underwater image quality measurement, and information entropy are 0.7418, 2.9457, and 4.6925, respectively. For subjective perception and objective evaluation indicators, the experimental results of the proposed algorithm are better than that of the comparison algorithm.
In the optical lens defect detection, in order to improve the accuracy and speed of the optical lens image threshold segmentation, a new particle swarm optimization (PSO)+Otsu threshold segmentation algorithm is proposed. The algorithm improves the PSO weight factor update strategy, increases the time when the weight factor is at a larger value at the beginning of the iteration, enhances the global search ability, calculates the optimal position of the particle, and assigns the optimal position to the Otsu algorithm. Finally realize the threshold segmentation of the optical lens image. The improved weight factor update strategy can overcome the shortcomings of the typical linearly decreasing weight factor update strategy that the global search ability at the initial stage of the iteration is insufficient, which leads to the local extreme value in the later stage. Experimental results show that this algorithm improves the speed of threshold segmentation while improving the accuracy of image threshold segmentation.
This paper proposes an image semantic segmentation method based on an improved DeepLabv3+ network to address the DeepLab network’s inability to fully utilize multiscale feature information while ignoring the problem of high-resolution shallow features and the loss of important pixel information due to excessive direct upsampling multiples. First, the multiscale feature information generated by the network is fully utilized and the feature pyramid network is used to effectively fuse high-resolution shallow features. Then, layer-by-layer upsampling is used to improve the image’s pixel information continuity. Finally, in the atrous spatial pyramid pooling module, the standard convolution is replaced with depthwise separable convolution, enhancing the network model’s training efficiency. The experimental results on the semantic segmentation standard data set PASCAL VOC2012 verification set show that, the mean intersection over union of the method can reach 79.97%. It can predict more refined semantic segmentation results compared with the DeepLab network.
Factors such as illumination or imaging conditions can cause a nonlinear grayscale difference between images, resulting in poor matching of images. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a new image registration algorithm based on the stacked autoencoder (SAE) network and local binary pattern with a circular and linear neighborhood (CL-LBP). First, the CL-LBP feature descriptor is extracted and matched by combining the improved local texture operator with the regional feature. Then, the supervised learning classification method is used to eliminate mismatches. Finally, the constructed matching representation is trained using the SAE network and the depth features of the matching representation are extracted and connected to a logistic classification layer to classify the matching pairs. The experimental results show that the algorithm has good matching accuracy in matching the nonlinear grayscale difference images. Moreover, it has a good matching effect in the actual sea ice images.
An improved YOLOv3 algorithm that detects target vehicles is proposed to address the problems of low detection accuracy of small targets and poor robustness of systems in target vehicle detection. First, the proposed algorithm introduces the dilated convolution into the downsampling layer of the YOLOv3 algorithm, improving the resolution of the feature maps and detection effect of small targets. Second, to address the problem of small target recognition in vehicle images, the proposed algorithm increases the three detection scales of YOLOv3 to four in addition to connecting and fusing the information with different scales, and the improved feature pyramid structure further improves small target detection. Finally, using Complete IoU (CIoU) as the loss function makes the target frame regression more stable, and there is no divergence in training. The KITTI dataset test results show that the improved YOLOv3 algorithm can achieve high detection accuracy. The proposed algorithm improves the average detection accuracy by 4.6%, and the detection rate is approximately 44.1 frame/s. On the premise of improving the accuracy, the proposed algorithm maintains a high detection rate.
The description of a target’s appearance greatly influences the performance of a correlation filter tracker. It is difficult to obtain an accurate description of target’s appearance using a single feature. Therefore, the target appearance description based on multiple features can improve the tracking performance in complex scenes. For robust object tracking in complex scenes, we propose an object tracking algorithm based on multiple features with adaptive fusion and context-aware. First, we introduced a context-aware framework and extracted single-layer convolution features from four context image patches around the target to establish the background information. As a single feature may not accurately describe the target appearance, two correlation filters were used for feature extraction. The first filter extracted three-layer convolution features as deep features through a convolutional neural network, and the second filter extracted information from the directional gradient histogram and color histogram to obtain shallow features. Then, the deep and shallow features were adaptively fused. Finally, the average peak-to-correlation energy was used to evaluate the confidence of the response and we decided whether to update the model. The proposed algorithm was evaluated on the OTB-2013 benchmark, and the results show that it achieves excellent performance regarding accuracy and success rate and shows superior tracking performance compared with other state-of-the-art tracking algorithms.
With the construction of urban smart parking lots and the popularization of automatic toll collection systems at high-speed intersections, license plate recognition technology based on deep learning has been widely used. In order to solve a large number of blurred license plate character recognition in reality, a character free segmentation license plate character recognition algorithm based on improved CRNN+CTC(Recurrent Neural Network/Convolutional Neural Network+Connectionist Temporal Classification) is proposed. Firstly, the standard CNN in CRNN is changed into a micro-modified model of deeply separable convolutional network. Bi-directional long-term and short-term memory network is adopted in RNN, and CTC loss is introduced to train it. Secondly, in order to avoid the overfitting phenomenon in the training process, L2 regular term is added into the loss function and the training dataset is added. Finally, a batch normalization algorithm is introduced to accelerate the learning speed in the training process. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is applied to three experimental test sets. Experimental results show that compared with other methods based on complex environment, the proposed algorithm improves the average license plate recognition accuracy, recognition accuracy and speed on the three experimental test sets, and the robustness and generalization ability of the network are also stronger.
In view of the weak resolution ability of traditional spectral matching operators in the phenomenon of “foreign objects in the same spectrum”, a spectral matching operator based on position vector measurement (PVS) is proposed, and a method of improving target recognition by fusion of matching operators is proposed. PVS operator is an extension of the absorption depth in the spectral absorption feature. The operator first uses the position vector to amplify the spectral curve, and then uses the method of voting statistics to divide the ground features. The experimental results show that when the detection probability is 70%, the false alarm rate of PVS operator is reduced by 1.73 percentage points and 4.77 percentage points on average in the two datasets. At the same time, in the case of the detection probability of 75.43%, the false alarm rate of the fused PVS operator can be reduced by 2.35 percentage points and 8.26 percentage points on average on the two datasets, respectively.
A novel variational blind restoration approach based on the sparse prior of red channel is proposed according to the complete underwater optical image formation model. In order to simultaneously tackle the problems such as haze, low contrast, color distortion, and blur caused by the scattering and absorption of water and suspended particles in underwater scene, multiple regular terms with different purposes are merged into the proposed variational model. First, a guided image is produced for color rendering depending on the direct component and backscattering component of underwater optical imaging model. Subsequently, the data fidelity term is designed based on the forward scattering component. Additional, L0 norm form is introduced as the deblurring regular term on the basis of the sparse prior of red channel. Moreover, to accelerate the computational efficiency, an alternating direction multiplier method is employed to solve the proposed model. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method not only can remove haze, enhance contrast, and recovery color, but also has a good performance on deblurring and improving visibility.
Owing to the infrared diffraction limit, the resolution of infrared remote sensing images is generally low, which makes precise detection and recognition of infrared targets difficult. To address this problem, an infrared target super-resolution detection algorithm based on deep learning is proposed. The algorithm comprises two main parts. The first part implements Wide Activation for Efficient and accurate image super-resolution(WDSR) to reconstruct infrared remote sensing images, and uses infrared images processed by the downsampling method of the sensor as the training set. The second part involves target detection based on Faster region-based convolutional neural network (Faster RCNN). A multiscale feature transfer network structure is proposed. The low-level features are input to region proposal network (RPN), which reduces the simplification rate of weak and small target pixels. In addition, a nonmaximum suppression method is used to reduce the suppression of dense target detection frames. Compared with Faster RCNN using the same training set, the proposed algorithm increased target detection accuracy, the overall recall rate, and the recall rate of small targets by 5.33%, 12.22%, and 13.25%, respectively.
An improved three-dimensional Douglas-Peucker (3RDP) algorithm is proposed to optimize the normal estimation method and solve the problem of incomplete and inaccurate point cloud contours extracted when using an angle threshold to assess the point cloud contour through the normal estimation algorithm. First, the traditional normal estimation method is used to obtain candidate points of the boundary feature under a low threshold. And, the 3RDP algorithm is introduced to thin the candidate points. Then a method of using principal component analysis to select the base surface of the point set and finding the origin and end point in the main direction is proposed, and the point set is sorted by the minimum distance selection method. Finally, according to the distance from the point to the base surface, it is judged whether the point belongs to the point on the contour line, and the internal points are removed at the same time to extract the contour feature of the target. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively eliminate the candidate points that do not belong to the contour line in the normal estimation method. Compared with the traditional normal estimation algorithm, the extracted object contour line is more complete and accurate.
To address problems associated with capturing underwater images, i.e., blur details and color distortion caused by the absorption and scattering of light, an underwater image enhancement algorithm based on multiscale generative adversarial network is proposed. This algorithm uses an adversarial network as the basic framework, combining residual connections and dense connections to strengthen the propagation of underwater image features. First, the visual information in different spaces of a degraded image is extracted through two parallel branches, and a dense residual block is added to each branch to learn deeper features. Then, the features extracted from the two branches are fused and the detailed information of the image is restored through a reconstruction module. Finally, multiple loss functions are constructed and the adversarial network is repeatedly trained to obtain enhanced underwater images. The experimental results demonstrate that an underwater image enhanced using the algorithm has brighter colors and better dehazing effect. Compared with the original image, the average quality of the underwater color image is increased by 0.1887; compared with the underwater residual network algorithm, the number of matching points of the speeded up robust features is increased by 17.
Weber local descriptor (WLD) is an effective image feature descriptor. However, the differential excitation and gradient orientation, which are two components of WLD, can not accurately describe the difference of local image blocks and the orientation of palm lines, so the performance of palmprint recognition based on WLD features is not high. In order to improve palmprint recognition performance, multi-scale Gabor orientation Weber local descriptors are proposed in view of the rich line features of palmprint images. First, multi-scale Gabor filter is used to filter the palmprint image to generate multi-scale energy maps and orientation maps. Then, the differential excitation is calculated based on energy maps. Finally, the histogram features are constructed based on multi-scale differential excitation maps and orientation maps, and the feature vectors from different scales are then concatenated to produce the final feature set of a palmprint image. The experiments on PolyU, PolyU Multi-spectral and CASIA palmprint databases show that the proposed method can achieve higher identification rate and lower equal error rate compared with some existing palmprint recognition methods.
To address the problems associated with the large amounts of data and high redundancy of three-dimensional point cloud related to complex object surfaces obtained by a laser line structured light scanner, a point cloud simplification algorithm based on self-adaptive neighborhood and local contribution value is proposed. First, according to the local geometric characteristics of the point cloud, the best neighborhood range is selected. Then, the best neighborhood, internal shape feature algorithm, and local surface patch algorithm are combined to calculate the local contribution values of all point cloud data and the feature points of the point cloud are extracted. Finally, K-means clustering algorithm is used for classification and the point cloud is simplified based on the classification results and the contribution values. The experimental results show that for complex surface test objects, the proposed algorithm can adjust the simplification of characteristic and noncharacteristic areas while ensuring the simplification rate as well as the overall integrity and detailed feature information of the point cloud. Consequently, the simplification result has higher accuracy and fits the original appearance of the object more closely.
Aiming at the problem that traffic signs only occupy a very small area in the image and are difficult to accurately identify, an anchorless frame traffic sign recognition algorithm based on the attention model is proposed. The densely connected network DenseNet-121 is used as the backbone network and features are extracted. In order to solve the problem of low accuracy of small traffic signs, an attention model is added to the backbone network to make adaptive adjustments to the space and channel of the feature map. The recognition performance of small traffic signs can be improved by strengthening or suppressing the weight of elements in the feature map. In order to reduce the semantic gap between the encoding path and the decoding path, the residual network connection method is introduced and a semantic connection path is proposed. In order to solve the problem of the imbalance of positive and negative samples in the anchor frame, the detection method without anchor frame can locate the center point of the traffic sign to regression the position and size information of the boundary box. The proposed algorithm is verified on the TT100K dataset, and the experimental results prove the superiority of the proposed algorithm.
The traditional dehazing algorithm using a dark channel is insufficient for studying the sky area and its restoration effect is accompanied by color distortion and halo. To solve this problem, we propose a dehazing algorithm combining sky region segmentation and weighted fusion. First, the cloud map is divided into sky and nonsky regions by setting mode constraint threshold from the brightness of the sky region. Second, the fusion dark channel is constructed by combining dark channels with different filter sizes. Then, the weighted technique is used to obtain a more reliable atmospheric light value based on the sky region segmentation. Finally, a transition region is set to combine the transmittance of the sky and nonsky regions. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm dehazes the fog map in the sky region, improves the color distortion of the sky region, and restrains the halo effect of the edge region.
The recognition of biometrics is an attractive research field in computer science and technology. As a soft biometric, the iris has the advantages of uniqueness, stability and anti-counterfeiting. Recognizing the gender of a person from the iris image is used in identity verification and security. Monitoring and other fields have broad application prospects. Aiming at the shortcomings of traditional machine learning and shallow neural networks in gender classification of iris image and the advantages of convolutional neural networks in image feature extraction, a residual network (ResNet)-based gender classification of iris image model is proposed, which uses ResNet combined with transfer learning is used for pre-training on ImageNet image dataset. The model is used to train an end-to-end iris image gender classifier on the dataset, the accuracy rate reaches 94.6%. Comparing the trained model with other related models on the same dataset, the results show that the test accuracy and recognition efficiency of this model are better than other models.
Considering the high computational complexity and low detection speed of the common object detection algorithms on an embedded platform, this study proposes a lightweight object detection network (BENet) suitable for embedded platforms. First, the proposed network added a channel feature interweaving module to the MobileNetv2 lightweight network to design the backbone network, which effectively enhanced the feature expression of the lightweight backbone network. Second, an adaptive multiscale weighted feature fusion module was proposed to learn the correlation between the features with various scales by assigning weights to the features with different scales. Finally, we attempted to introduce a spatial pyramid pooling structure to obtain the context information of different receptive fields. The experimental results on the VOC dataset show that the proposed BENet maintains high object detection accuracy and speed while has lower computational complexity and smaller parameters. Additionally, it is more suitable for embedded platforms.
In order to solve the problem of dehazing a single image, a new end-to-end network is proposed, which uses an improved multi-scale feature loop to generate a confrontation network. Unlike previous models, the proposed network does not rely on traditional atmospheric scattering models, and does not need to correspond to matching images during the training process, which greatly simplifies the training process. Next, a new type of multi-scale generator is designed, which uses a dual-channel fusion feature pyramid structure to extract the features in the image to the greatest extent, and introduces multiple global and local discriminators to improve network performance and image quality. Experimental results show that the proposed model can achieve good results on different datasets.
This study proposes a multiobjective optimization scheme for synthetic aperture imaging array based on the simulated annealing algorithm (SAA). The spectrum optimization objective of the aperture array is designed in multiple directions based on characteristics of the modulation transfer function (MTF) of synthetic aperture imaging. The degraded Golay6 structure is used as the initial array to perform simulation calculations. The results show that SAA can effectively improve the stability of the MTF in the medium frequency range and considerably increase the actual cut-off frequency of the imaging array. When filling factor F=11.5%, compared with Golay6 aperture array, the average correction factor of the optimized aperture array reaches 8.61% when the annealing attenuation parameter α=0.97.
The initial value of the digital image correlation method has a great influence on the calculation efficiency and solution accuracy of the algorithm. For this reason, an algorithm using dense feature matching to obtain the initial value is proposed. The AKZAE operator is used to detect the feature points, the Daisy descriptor is used to describe the feature points, and then the grid motion statistics (GMS) algorithm is used to filter the feature points to obtain the initial value, and finally the initial value into the reverse combined Gaussian in the Newton (IC-GN) method is substituted, the sub-pixel displacement is solved iteratively. Compared with SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) and SURF (Speeded-Up Robust Features) algorithms, the AKAZE operator improves the accuracy of positioning and has higher computational efficiency. It is a feature point detection algorithm that takes into account both speed and stability. The Daisy descriptor is an efficient dense feature extraction descriptor, which can achieve denser feature extraction compared to other descriptors.
Railway rail fastener system is prone to defects such as fastener missing, elastic strip fracture, elastic strip skew, and bolt loosening or over tightening. The traditional detection method based on two-dimensional intensity images can identify the first three diseases, but it is difficult to detect the bolt looseness or over tightening defect. In order to solve this problem, a detection method of fastener bolt fastening state based on line structured light is proposed. The 3D point cloud data of track structure are obtained by 3D camera. The rail area and fastener area are segmented by building a height integral function and prior knowledge, and the height difference between the bolt to be measured and the non-wear area outside the rail head is calculated. Based on this, a method to determine the threshold of bolt fastening state based on online updating threshold library is proposed. The height difference is compared with the threshold database to realize the detection of bolt fastening state. The experimental results show that the detection rate of fastener looseness or over tightening is more than 80% under the condition of detection speed of 20 km·h -1. This method makes up for the shortcomings of the traditional fastener detection methods and realizes the automatic detection of fastener fastening state.
This paper proposes a vision-language navigation algorithm based on cosine similarity using the Regretful model to solve the problems of low navigation accuracy and weak generalization ability in vision-language navigation tasks. By increasing the cosine similarity loss function to guide neural network learning and predict navigation direction, the difference in intraclass features in feature space is reduced. The distribution range of interclass features increases, and the navigation accuracy of the model without search strategy improves. Simultaneously, a feature-smoothing method of panoramic view is proposed to enhance data and improve the generalization performance of the model. Experimental results show that the algorithm improves the navigation accuracy and other model indicators on the R2R(Room-to-room) dataset. Additionally, its effect is better than that of the Regretful model, confirming the superiority and robustness of the proposed method.
To solve the problem of noisy samples easily interfering with the online updating tracking method and resulting in a drift phenomenon, a method suitable for long-term tracking is proposed, and the proposed method is combined with a multi-task learning training mode and a loss detection step is added into the tracking process. The proposed method constantly collects the appearance of the target during tracking to construct a dynamic sample set, which detects the loss of target according to sample similarity to reduce the tracker’s learning of noisy samples; further, the dynamic threshold is used to adapt to different targets. To make the tracker build a complete model of the target appearance, short- and long-term memory subtasks are jointly trained. During redetection, after the target is lost, regions are proposed based on regional outline features and scale information about the target to improve the quality of target redetection. The proposed method is evaluated on the object tracking datasets OTB-2015 and VOT-2016, and the tracker has an accuracy of 90.8% and a success rate of 68.1%. Experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively track a target in complex scenes, such as occlusion.
This study proposes a visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm based on dynamic target identification to address the problem of low positioning accuracy of conventional visual SLAM algorithm in dynamic scenes. First, the input image frame is preprocessed in front of the visual SLAM system, and the potential dynamic area of the image is deleted by the target detection network you look only once, v3 (YOLO, v3). Furthermore, the input image optimizes the homography matrix using reprojection error to obtain the motion compensation frame and four-frame difference image. Then, the four-frame difference image is filtered, binarized, and morphologically processed. Finally, combined with YOLO v3 network to optimize the dynamic target detection results, reduce noise generated by strong parallax and image blur. The feature points of the static area are used for visual SLAM tracking, mapping, and loop detection. The experimental results regarding common TUM data sets indicate that the algorithm can effectively improve the accuracy of visual SLAM in a dynamic environment.
Traditional sparse representation algorithms attempt to build a robust appearance model to track targets according to the linear combination of sparse dictionaries. However, such algorithms ignore the hierarchical structure features of the tracking object; thus, handling complex tracking scenery is difficult. In this paper, an innovative convolution-based sparse tracking algorithm (CSTA) is proposed to address this limitation. Local image patches extracted within the object region serve as local descriptors. According to the sparse representation theory, a group of sparse image blocks is selected as the fixed convolution kernel, and the results obtained by convoluting the convolution kernel with the input image demonstrate that the hierarchical structure of tracking objects has been preserved. In addition, a selective online updating mechanism is presented to avoid the drift problem caused by erroneous model updating. Quantitative and qualitative analyses are conducted, and the proposed CSTA and advanced sparse representation algorithms are compared using open datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed CSTA outperforms state-of-the-art sparse tracking algorithms in terms of accuracy and robustness.
To resolve the problems of the difficulties in detecting the salient object area under poor lighting conditions in an RGB image and the salient object boundary because of the infrared thermal radiation in a thermal infrared (T) image, a salient detection algorithm based on the complementary fusion of RGB and T image information is proposed. First, image-lighting conditions are established based on the IHS color space to determine the lighting conditions of RGB and T images. An RGB-T image adaptive lighting fusion algorithm is proposed to guide the fusion of RGB-T images according to the lighting conditions of the images, generating a multilevel RGB-T lighting fusion image to improve the ability of salient object area detection. Second, the Gaussian filters with different convolution kernels and standard deviations are used to extract the high-frequency information of the objects’ edges in the RGB and T images, generating different levels of RGB and T high-frequency detailed images. The deep learning network based on encoder-decoder is used to fuse RGB and T high-frequency detail images to generate RGB-T detail fusion images with different levels, which improves the boundary detection ability of salient objects. Finally, a multilevel fusion of RGB-T lighting fusion image and RGB-T detail fusion image is performed according to the image-lighting information, and the algorithm based on learning is used for salient object detection. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm improves the detection accuracy of the salient area and boundary detections. The proposed algorithm is competitive compared with EGNet, PoolNet, CPDNet, DMRA, and A2dele, which are excellent salient object detection algorithms in Fmax value, Fave value, and average absolute error.
In order to enable the quayside crane surface corrosion detection task to be deployed to embedded devices and mobile devices to obtain faster inference speed, an improved lightweight object detection network MobileNetV2SSDLiteV1/V2 is proposed without sacrificing accuracy. The improved network uses feature maps of 5 convolutional layers as the detector input, and uses 3×3 depthwise convolution to predict classification and location scores. In order to reduce the number of parameters of the backbone network, the original 17 inverted linear bottleneck block structure is designed into 14, and the image with a resolution of 256 pixel × 256 pixel is used as the network input to change the coefficients of the original default box. The number of is reduced by 82.51%, and then all convolutions are normalized and the network is trained from scratch. The above improvements can make the network parameters become 0.96×10 6, which is reduced to 1/4 of the original. The number of floating-point operations of the network is 0.12×10 9, which is 81.25% less than the original, the mAP value is as high as 77.40%, and the inference speed reaches 45 frame/s.
Search and recognition of targets by using unmanned aerial vehicle depend on the speed and accuracy of target detection algorithms. Aiming at the complex network structure of classic target detection algorithms, high computer performance requirements and slow target detection speed, a real-time detection method based on an improved lightweight detection model (Tiny YOLO-V3) is proposed. First, a new network structure is proposed as the backbone network, compressing the maximum number of channels to 128, further reducing the time complexity and space complexity of the model. Secondly, the single detection head combined with context information is used to enhance the detection ability of targets of different sizes, and the detection speed can be improved while the detection accuracy is maintained. Finally, the remote sensing dataset of Wuhan University is used to carry out the experiment. The experimental results show that the improved model has a significant increase in detection speed, while the accuracy has increased by 0.22.
Aiming at the influence of stray light, noise, baseline drift and other factors in the spectral signal of complex samples on the quantitative analysis results, this paper proposes a pretreatment and combined method based on near-infrared spectroscopy. First, no pretreatment and single pretreatment on 2 selected datasets is performed. Then, 9 pretreatment methods are divided into four categories according to their effects, including scale scaling, baseline correction, scattering correction and smoothing. Finally, the optimal pretreatment method of each type of pretreatment method is selected for combined research, and the optimal pretreatment method is selected according to the root mean square error cross-validation after modeling. Experimental results show that the use of appropriate pretreatment combination methods for different data sets can improve the modeling effect, while the difference between the information and complexity of different data sets will lead to different optimal pretreatment methods, and the optimal pretreatment method is related to the predicted components and the original spectra. Therefore, the best pretreatment effect can be obtained by classifying and combining the pretreatment methods according to their effects.
Aiming at the problems of current retinal image segmentation methods, such as blurring of fine vessels pixels and loss of details at the edge of thicker retinal vessels, we designed a two-stage segmentation method based on the combination of improved U-Net and Mini-U-Net network in this paper. Firstly, we added a small-size Mini-U-Net to the full-size U-Net network to perform secondary training on the blurred vessel pixels in the retinal image to improve the segmentation effect of blurred blood vessel pixels; secondly, the original convolutional layer in the encoding and decoding processes of the two networks is changed to a residual convolution module to preserve the original feature information more completely; finally, an attention mechanism is introduced at the jump connection of the two networks to improve fine vessels segmentation precision. The precision ratio of this method on the DRIVE and STARE public fundus image datasets were 0.8331 and 0.8563, the recall rates were 0.8396 and 0.8639, the F1-Score were 0.8351 and 0.8609, and the accuracy rate were 0.9698 and 0.9787, respectively. The total segmentation results of the proposed method are better than those of other methods.
In the complex and rapidly changing environment of a battlefield, information is lost by factors such as interference of the enemy and limited sensor performance. To ensure that an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) can make threat assessments when sufficient information is lacking, this paper proposes a new Bayesian network (BN) learning method with a small dataset. For structure learning and parameter learning with a small dataset, the scoring function is constrained by the constraint matrix obtained by the Bootstrap method. The learning algorithm is proposed based on a BN structure learning with a small dataset and an interval a priori-constrained BN parameter learning algorithm. Simulation results demonstrated the higher accuracy and availability of the proposed method than traditional methods for UAV threat assessment on a small dataset.
To realize accurate identification of individual cows in a complex farm environment, the SSD (single shot multibox detector) algorithm was improved to solve the problem of poor detection effect for overlapping objects. First, different feature maps were fused to ensure that different feature maps complemented each other and improved the detection effect of overlapping objects. Then, Conv4_3 was removed from the network. The number of candidate frames in other feature maps increased, ensuring the real-time performance of the algorithm and also improving the detection accuracy. Finally, the transfer learning method was used to improve the average accuracy of the algorithm. The experimental results show that compared with the traditional SSD algorithm, the average accuracy (AP) of the improved SSD algorithm is improved by 4.32% in real-time detection, and the AP of the improved SSD algorithm is increased by 3.85% after migration.
This paper proposes a method based on ground-based laser three-dimensional (3D) scanning and drone tilt photography to obtain the route point cloud and the true 3D situation around the route, addressing the difficulty of quickly and comprehensively obtaining the spatial relationship of the route and accurately and quantitatively determining the problem. For automatically and swiftly evaluating the spatial state of the route in the simulation environment, the point cloud matched by the enhanced Bursa algorithm and geographical coordinates of the 3D scenario are fused and transferred into the geographic information system platform. The experimental results suggested that laser 3D scanning and tilt photography can complement one other in data collection when using the created data fusion registration technique as an example. The accuracy of the enhanced Bursa algorithm may be raised by 10%--50% compared to the original Bursa algorithm, and the registration and fusion accuracy of the point cloud and 3D situation is better than ±2 cm. After fusion, the 3D effect is lifelike, spatial information is complete, and human-computer interaction is strong, which can quickly complete the fine measurement of the route.
In this study, a set of tunable hyperspectral lidar system with 91 channels, spectral resolution of 5 nm, wavelength range of 650--1100 nm, and high biological safety is built, and the detection experiments of forest tree samples such as Ailanthus altissima, Pinus yunnanensis, and Koelreuteria paniculata are completed. The target echo intensity is detected through experiments, and the target spectral reflectance is obtained. Finally, the support vector machine classifier is used to classify and identify different types of healthy and diseased samples. The classification accuracy of Ailanthus altissima samples can reach 96.98%. The classification accuracy of Pinus yunnanensis samples can reach 91.21%, and the classification accuracy of Koelreuteria paniculata samples can reach 66.21%. The experimental results have research significance and reference value, and provide a new development direction for forestry pest monitoring.
The explosive development of deep learning technology has led another wave of machine learning in recent years. Deep neural network, with the ability to recognize and extract abstract features, fit nonlinear relationships, against interference factors and generalization, is widely used in autopilot, target recognition, machine translation, speech recognition and other fields. The convolutional neural networks (CNN) are popular in optical information processing. In this paper, we introduce the basic concepts and structural components of CNN in detail, and review the applications in digital holography, fringe patterns analysis, phase unwrapping, ghost imaging, Fourier ptychographic microscopy, super-resolution microscopy, scattering medium imaging, optical tomography imaging, etc. We summarize the typical applications and existing shortages of CNN in optical information processing, and finally prospect the future development of convolutional neural networks.
The development of precision manufacturing has put forward a higher requirement for the 3D topographical measurement of complex microstructures. It is a little difficult for the existing non-contract measurement method to measure a slope surface with a big gradient although it has a high vertical solution. In recent years, the focus variation measurement method based on ultrashort depth-of-field imaging performs well in the measurement of tilted surface and can be used to truly realize the 3D surface measurement of a microscopic complex structure. Firstly, the principle of microscopic 3D measurement based on focus variation is summarized. Then, the latest theoretical and technological research progress on this method is addressed. Finally, the challenge and future development trend of microscopic 3D measurement based on focus variation are discussed and prospected.
As an important three-dimensional (3D) data type, point cloud has been widely used in many applications with the development of 3D acquisition technology. Owing to its high efficiency in processing large-scale data sets and the autonomy of extracting features, deep learning has become the leading method for investigating the latest studies in a point cloud classification. This paper introduces the current research status of the point cloud classification methods. Furthermore, some main and latest methods of point cloud classification based on deep learning are analyzed and classified according to the data processing method. Additionally, this paper summarizes the key ideas, advantages, and disadvantages of each type of method and discusses the realization process of some representative and innovative algorithms in detail. Finally, the challenges and future research directions of the point cloud classification are outlined.
Factors such as low spatial resolution and material heterogeneity result in the issue of mixed pixels in images, which makes pixel-level data processing and applications unable to meet the practical requirements. Spectral unmixing extracts information of endmembers and abundances at the sub-pixel level and offers technical support for fine quantitative analysis of data in real applications. This paper introduces research advances of spectral unmixing theories, methods, and applications in recent years. Technical research results include linear and nonlinear mixture models, and methods under the principle frameworks of geometry, regularized optimization, and statistical machine learning. Moreover, improvements provided by spectral unmixing for other techniques such as classification, and theoretical and practical values of spectral unmixing in handling problems from remote sensing to indoor applications such as medical science are analyzed. Finally, drawbacks in spectral unmixing technical and application researches and the necessity of their synergistic development are summarized.
Lung cancer is the malignant tumor with the highest mortality rate in the world. Its early diagnosis can remarkably improve the survival rate of lung cancer patients. Deep learning can extract the hidden layer features of medical images and can complete the classification and segmentation of medical images. The application of deep learning methods for the early diagnosis of lung nodules has become a key point of research. This article introduces several databases commonly used in the field of lung nodule diagnosis and combines the relevant literature recently published at home and abroad to classify the latest research progress and summarize and analyze the application of deep learning frameworks for lung nodule image segmentation and classification. The basic ideas of various algorithms, network architecture forms, representative improvement schemes, and a summary of advantages and disadvantages are presented. Finally, some problems encountered while using deep learning for the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules, conclusions, and the development prospects are discussed. This study is expected to provide a reference for future research applications and accelerate the maturity of research and clinical applications in the concerned field.
The brain-computer interface (BCI) technology enables direct interaction between the human brain and computers or other external devices by analyzing and decoding neural activity. It can be used as a means of information exchange or the restoration of motor functions and has been applied in communications, intelligent robot control, biomedicine, and neurorehabilitation, etc. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), an optical imaging technique that can be used to detect changes in hemoglobin concentration within the cerebral cortex, has been employed recently in the development of noninvasive BCI. The development history, composition principles, key technologies, future development trends, limitations, and problems of fNIRS-BCI are reviewed systematically and in detail. Particularly, the feature-classification algorithm was analyzed comprehensively, and the result was compared with statistical data from its predecessors to summarize several valuable conclusions and opinions. This review is designed to provide a comprehensive and specific understanding of fNIRS-BCI and references and guidance.
Minute amounts of noncotton fiber impurities that mix with cotton fiber during cotton picking, drying, transportation, and processing are known as cotton foreign fibers. Foreign fibers reduce the cotton grade and affect the quality of cotton processing, causing problems such as stains and uneven dyeing of textile fabrics, leading to quality decline of the final product. Therefore, detecting foreign fiber in cotton is essential. In this paper, we analyze the harm due to foreign fiber in cotton and problems associated with its detection and summarize the foreign fiber-related detection equipment. Simultaneously, a summary of the recent studies and progress in foreign fiber-detection technologies and methods with regard to image segmentation, feature selection, and image classification, and prospects for future research directions is discussed in this paper.
Aiming at the problem that the existing wine detection technology cannot quickly and efficiently identify the quality of wine, this paper proposes a method to capture the spectral information of wine samples by laser-induced fluorescence technology, which is based on the clustering algorithm without label build and complex tuning. Four wine samples from three brands and two vintages were selected. After being mixed with water at 1∶10, under the premise of the same alcohol content, 100 spectral informations were collected for each wine sample. We used K-means, self-organizing competition network and self-organizing feature mapping neural network (SO-FMNN) to identify wine samples. The experimental results show that the three clustering algorithms have superior performances in spectral information analysis, and the recognition accuracy rate can reach more than 99%. The classification accuracy rate of SO-FMNN is even 100%, the average time is 5.875 s, and it has high robustness and generalization ability. It is verified that the clustering algorithm for wine quality detection is feasible.
Coffee is one of the top three beverages in the world, and it is crucial to strictly control the quality of coffee. Using three different varieties of coffee beans as the object, the terahertz time-domain spectroscopy combined with chemometrics is used herein to identify three different coffee beans quickly. Various pretreatment methods are used to reduce the experimental errors, and principal component analysis is used to reduce the dimensions of the spectral matrix. The dichotomous model based on partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) is established, and another model based on a support vector machine (SVM), a back propagation neural network, and a random forest multiclassification discriminant is then established. The PLS-DA dichotomous model exhibits the ideal qualitative discrimination effect whose accuracy is 98%. Among various classification models, the SVM model based on baseline correction is the most effective model, with the total accuracy reaching 98%. This study shows that it is feasible to use terahertz spectroscopy to quickly identify coffee bean varieties and a better support vector machine model is established based on baseline correction, which provides an empirical reference for the qualitative detection of other agricultural products using the terahertz time-domain spectroscopy.
Some enhanced common gemstones via filling and coating treatments in the market were selected for the regular gemological test and infrared spectral investigation. The research discloses that the enhanced gemstone cannot be distinguished using the regular gemological features, but it can be accurately and quickly identified using the infrared spectral features. The test results show that the absorption bands ranging from 2800 cm -1 to 3200 cm -1 observed using a transmission method can be used to identify whether the gems have been treated with organic material filling. The absorption bands around 2850, 2928, and 2966 cm -1 can be seen in oil-soaked and wax-soaked gemstones, and the characteristic identification bands around 3035, 3056, and 3095 cm -1 can be found in colloid-filled gemstones. Further, a stronger spectrum indicates a higher degree of filling. The spectral bands around 2235 cm -1 and 2609 cm -1 are the identification characteristics of gems filled with lead glass. The organic-material-coated gemstones can be directly identified using an infrared reflection method.
In forensic scientific evidence identification, the classification and recognition of disposable masks is critical. Therefore, in this study, a classification and recognition method for disposable masks is proposed using Raman spectroscopy and machine learning. First, the Raman spectra of 37 types of disposable masks are gathered from different cities and manufacturers. Then, the data are processed using Savitzky Golay smoothing and normalization algorithms, and the mask categories are classified using principal component analysis method and the Raman spectrum characteristic peak comparison method. Finally, a disposable mask classification and recognition model is constructed based on support vector machine (SVM), Bayes discriminant analysis, and back propagation (BP) neural network algorithm. The experimental results show that the accuracy rates of the training and tests set of the SVM model are 93.3% and 100.0%, respectively, whereas the those of the training and test sets of the Bayesian discriminant analysis model are both 100.0%. Furthermore, the accuracy rates of the training set, validation set, and test set of the BP neural network model are 93.9%, 60.0%, and 60.0%, respectively. Therefore, as the best model for mask classification and recognition, the Bayes discriminant analysis model provides a certain reference for forensic science and technology.
The prediction of available nitrogen content has attracted significant attention in soil nutrient diagnosis. The available nitrogen spectrum detection model prediction accuracy can be effectively improved using feature selection and regression prediction algorithms. This study selects 188 yellow-red loam samples in southern Anhui as objects, uses seven preprocessing methods to correct the spectral data. It combines the moving window method and five intelligent optimization algorithms for feature selection. Then, it establishes 36 regression calibration models for analysis and comparison based on different ensemble boosting (Boosting) algorithms. The experimental results show that 202 spectral features selected using the feature optimization algorithm based on particle swarm optimization (PSO) are concentrated in the range of 600--1000 nm. The Adaptive Boosting (AdaBoost) model developed using these features has the best performance, with the prediction accuracy of soil available nitrogen of 0.944. This study improves the prediction accuracy of soil available nitrogen and discusses the optimization algorithm of characteristic interval, which has a certain theoretical value.
An elevator wire rope is a key component for carrying the weight of carriages. To address the problem that wire rope defects cannot be detected online, a method to identify broken wires using hyperspectral image processing is proposed. First, the spectral band image with the greatest difference between the sample and background was selected. Then, Otsu adaptive threshold segmentation combined with the Hough transform was used. The number of pixels in the diameter of the wire rope in the image was used to determine whether the extent of breakage meets the scrapping requirement. The mean square error, peak signal-to-noise ratio, and structural similarity values experimentally obtained using this method were 650.9, 19.9957, and 0.9404, respectively. Results indicate that combining Otsu threshold segmentation and the Hough transform to process images of elevator wire ropes is effective, providing a new method for the rapid detection of wire rope defects.