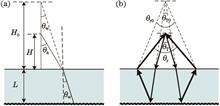
Water depths are the basic data for surveying and mapping seabed topography, which is of great significance for marine scientific research. A diffractive optical system has the advantages of small size and light weight, and a conformal design can reduce the impact of the load on the aerodynamic performance of an aircraft, which is conducive to the formation of a large optical aperture. This paper introduces the system scheme and parameters of airborne bathymetry lidar based on a large-aperture receiving conformal diffractive optical system. The narrow bandwidth characteristic of the diffractive optical system is used to suppress the received background light noise. To realize both direct and coherent detection methods, the seawater depth detection of airborne lidar is analyzed based on the minimum detectable signal-to-noise ratio. The results demonstrate that when the receiving aperture is 0.6 m, the instantaneous receiving field of view is 50 mrad, the average transmitting power is 50 W, the detection depth of the system in the direct detection mode during the day is 69 m, and the detection depth in the coherent detection mode is 86 m.
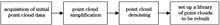
Existing traditional three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction methods focus on preserving surface details of 3D objects; however, they cannot realize rapid reconstruction of 3D objects but can only reflect the category, shape, and other typical features of 3D objects. To tackle this problem, a rapid batch method for 3D object reconstruction is proposed. First, point clouds are simplified before they are denoised; an enhanced k-neighbor denoising algorithm with double-threshold constraints is proposed. The denoising performance of this algorithm is compared with that of two traditional denoising methods. Second, the categories of 3D point clouds are obtained using the dynamic graph convolutional neural network(DGCNN). Finally, after matching each category with the categories in a pre-built 3D model library, corresponding 3D models are called sequentially to achieve the batch rapid 3D reconstruction. If there is no corresponding category in the pre-built 3D model library, the 3D point clouds of the corresponding category can be acquired and added to the DGCNN for training and evaluating. The 3D reconstruction result of each category is added to the pre-built 3D model library to increase the number of categories in the library. The effectiveness of our proposed method is verified using the incremental ModelNet40 model. The experimental result shows that the 3D reconstruction method incurs the cost of 11.98 s for 120 point clouds of 100000 points, 29.06 s for 120 point clouds of 700000 points, and 109.98 s for 120 point clouds of 1200000 points, which is approximately 10 times faster than that of the traditional method considered in this study. Overall, this method can significantly improve the efficiency of 3D reconstruction for point clouds with both large order of magnitude and a large number, as well as realize real-time batch rapid 3D reconstruction of point clouds.
Chip on carrier (COC) is an important component of transmitter optical subassembly and is widely used in the field of optical communication. With the progress of chip manufacturing process, COC is developing towards miniaturization and high density, and the types of defects become more complex and diverse. Optical inspection technology based on traditional image processing methods can no longer meet the requirements of COC multi-category defect detection. In this paper, YOLOV3 is introduced into the detection of typical defects of COC, such as collapse, positioning column damage, and waveguide stain. Aiming at the problem that the waveguide stain defect target is small and the scale changes greatly among different types of defects, the original YOLOV3 feature extraction network is improved, and the 4 detection scales are designed taking into account the multi-scale characteristics of the target, and the multi-scale detection is improved by enhancing feature fusion. The K-means method is used to perform cluster analysis on the data set, and select the optimized initial prior frame. Experimental results show that the accuracy of YOLOV3-COC, a COC defect detection method based on improved YOLOV3, is 97.4% for the detection of 3 types of defects: COC chipping, broken positioning pillars, and waveguide stain.
When the image histogram is a single peak, the traditional Otsu method can easily obtain wrong results in detecting defect in the electrowetting display. In some improved methods, the segmentation results are unstable when the defect color depth is different, and the contrast between the background and defect is low. In this study, an improved maximum between-class variance method is proposed to solve these problems. To improve the difference between the peak and non-peak ranges of the histogram and to better extract the peak information, the proposed method adds a weight value that decreases with an increase in the cumulant of gray histogram gradient before the target variance. It ensures that the threshold obtained by the method is always on the left side of the single peak for a single peak. Experimental results showed that the average misclassification error of the proposed method in multiple application scenarios is reduced by 0.4781 compared with the traditional Otsu method. Besides, the average defect segmentation rate of the proposed method is increased by 0.6795. The method can successfully segment electrowetting display defect and various types of defect. The segmentation effect is better when the contrast between the defect and background is low.
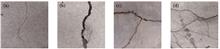
Aiming at the problem that traditional bridge crack detection algorithms have poor antinoise ability and difficulty processing crack images with complex backgrounds, and the conventional deep learning image segmentation algorithm has low spatial accuracy, a bridge crack detection method based on multi-resolution and high spatial accuracy is proposed. First, the unmanned aerial vehicle is used to collect bridge images. The bridge crack dataset is obtained through image enhancement processing. Then, the parallel connection is used to connect multi-resolution subnets and repeated multi-scale fusions, so that the detection model maintains high-resolution representations throughout the process, while performing repeated multiscale fusion using low-resolution representations of the same depth and similar level. This is to improve the high-resolution representation so that high-resolution representation also exhibits strong high-level semantic features. Finally, the proposed algorithm is trained and verified on the dataset. The results show that all the segmentation indexes of the proposed algorithm are significantly improved, the accuracy of crack detection is as high as 93.8%, and the average interaction ratio reaches 85.48%.
To solve the problem of the extensive feature-matching time of the grid motion statistics (GMS) algorithm when the image is rotated, an improved fast GMS image matching algorithm is proposed herein. First, a fast feature point extraction and description algorithm is used to violently match the image to obtain the initial matching point pair. The feature matching pair with a higher matching quality is selected according to the Hamming distance. Second, the approximate rotation angle of the two images is obtained by calculating the difference between the main directions of the matching and the feature points. The best form of the motion core is directly determined according to the rotation angle. Finally, the GMS algorithm is used to distinguish between correct and wrong matching points according to the motion core, avoiding the loop calculation of the matching results of different forms of motion cores and reducing the running time of the algorithm. The experimental results show that the number of correct matching points of the improved algorithm is at least 28% higher than that of the traditional feature point matching algorithm, and the matching speed can be at least 36% higher than that of the GMS algorithm.
Aiming at the problem that melanoma and non-melanoma have high visual similarity, diverse colors, blurred edges, and foreign body occlusion, which leads to poor segmentation of skin lesions, this study proposes a U-shaped structure-based context encoding and decoding network. This study uses an efficient dual-channel attention mechanism and Atrous spatial pyramid pooling modules to capture more semantic and spatial information to improve the accuracy of skin lesion segmentation. Training and testing were performed on the ISIC 2017 Dermatoscopy Image Dataset. The experimental results show that the similarity coefficient (Dice_Coefficient) of the segmentation results of the proposed algorithm is as high as 88.74%, which is 3.15 percentage points higher than the existing mainstream semantic segmentation network model DeepLab V3 Plus and is 9.93 percentage points higher than the classic U-Net network in the medical field. It has a fast running speed and good stability, and can effectively segment melanoma. The segmented image has continuous edges and clear outlines. It has good effects on quantitative analysis and recognition.
Aiming at the problems of casual writing of the offline handwritten text, difficulty in character segmentation, and the dependence of recognition accuracy on a dictionary, an offline handwritten text recognition algorithm based on connectionist temporal classification (CTC)-attention is proposed. The convolutional neural network and bidirectional long short-term memory are used to encode the image features. Multitask learning framework based on CTC and Attention-based models is used to decode feature sequences. In the training process, the CTC model and the attention mechanism model are used to train at the same time, which effectively solves the problem of ignoring the overall information when CTC predicts local information, and the problem of unconstrained decoding of the attention mechanism.Experiments on IAM dataset, i.e., the classical handwritten English word dataset, showed that the character accuracy rate of the proposed method is 93.4%, and the word accuracy rate is 81.8%, proving the proposed method’s feasibility.
Aiming at the problems of artifact existing in activated sludge phase contrast microscopic images and low segmentation accuracy of existing image segmentation methods for filamentous bacteria, a segmentation model of an activated sludge microscopic image based on the U-Net network, residual network, channel attention mechanism, and atrous spatial pyramid module is proposed. The ResNet network based on channel attention mechanism is used as an encoder. Channel attention mechanism explicitly establishes the dependence among feature channels, and analyzes the feature extraction ability of the residual network reinforcement model. At the end of the encoder, the atrous spatial pyramid pooling is added, which can obtain the multi-scale information of filaments and flocs without increasing the parameters. In order to enhance the ability of network reconstruction, the feature information is supplemented by using jump connection in the decoder. Experimental results show that the proposed model has better segmentation performance and effect than U-Net and DeepLabV3+.
In image segmentation, many fuzzy C-means algorithms considering neighborhood information can effectively reduce noise interference, but these algorithms need additional parameters, and the large cluster difference between nondestructive test images easily causes segmentation failures. To solve this problem, this paper presents a fuzzy C-means algorithm insensitive to cluster difference based on image patchs. First, the image patch is used to replace the pixel to enter the clustering process. The weight of the pixel in the image patch is adaptively determined by the spatial distance and gray scale of the pixels. Second, based on the concept of information quantity, the expression of cluster information quantity is given and introduced into the objective function to improve the sensitivity of common fuzzy C-means algorithms to the cluster difference. Third, the new expressions of membership degree and cluster center are obtained based on the new objective function, and the algorithm flow is given. Finally, the proposed algorithm is tested by the non-destructive test images with large cluster difference. The results show that the proposed algorithm has high segmentation accuracy and better visual effects.
Aiming to solve the problem of low accuracy and poor stability of random sample consensus (RANSAC) algorithm in feature point matching, an image registration algorithm based on smoothness constraint and cluster analysis is proposed in this paper. First, the scale information and spatial angle order of neighborhood matching feature points are used to construct a smoothness constraint, and the initial matching points are divided into a sampling set with a high inlier rate and a verification set with a high inlier number. Then, the solution is solved by repeated sampling and model testing. Next, the inlier set is temporarily determined, and cluster analysis is performed on it. Further, the optimal inlier set is selected according to the distribution quality of the cluster center in the image overlapping area. Finally, the optimal inlier set is used to solve the model parameters to achieve image robust registration. The simulation results show that compared with the RANSAC algorithm, the registration accuracy of the algorithm improved by 26.83%, and the error standard deviation is reduced from 0.68 to 0.19.
In this study, a manifold regular correlation filter tracking algorithm based on dual-core model context is proposed to balance the tracking speed and accuracy of the algorithm. The main module combines the context-related framework and the relevant filtering algorithm is responsible for the main tracking task, which can compensate for the background information filtered using the cosine window in the relevant filter-learning model. The manifold regular processing of context-related samples can achieve the purpose of penalizing context-related framework and optimizing the main module model. The auxiliary module combines kernel correlation filtering algorithms and convolution features. When the tracking target is occluded, deformed or exceeds the line of sight, the auxiliary module is activated when the tracking confidence is lower than the empirical threshold to prevent the drifting of main module model. The main module has fast-tracking speed and low accuracy, whereas the auxiliary module has slow tracking speed and high accuracy. These modules can complement each other in terms of speed and accuracy. The test results on the OTB2015 and VOT2016 data sets show that the algorithm has better accuracy and robustness than other correlation filtering algorithms.
The accuracy of image detection and classification will be reduced by image nonlinear distortion, hence distortion correction is an important preprocessing step in image processing. This paper proposes a non-metric distortion correction method based on adaptive corner detection to better solve the image distortion problem. First, the distorted checkerboard image is used as the research object, and the sub-pixel corner coordinates obtained by adaptive corner detection are used as input information. The distortion loss function is established based on the invariance of straight-line projection and the weight coefficient based on the radius of curvature is set to adjust the distortion of each curve. Then, the nonlinear optimization method is used to calibrate the distortion coefficient and the distortion center to realize the distortion correction. Two sets of experiments are designed: standard image simulation experiment and real image experiment. At the noise level σ=1 in standard image simulation experiment, the relative error of distortion parameter k1 is 0.733%, and the relative error of the distortion coefficient is 4.933%, which is close to the true value. In the real image experiment, the average straightness of the method in this paper is only 0.5152 pixel, which shows that the correction accuracy is high, and the average operation time is about 8.4 s, which shows that the correction efficiency is better. Experimental results show that the method is feasible, accurate and efficient.
To prevent numerous hyperparameters and to overcome poor generalization ability and imbalance between positive and negative samples in anchor-based multiclass object detection algorithms, an object detection algorithm based on an improved anchor-free method is proposed herein. To address the difficulty faced by traditional algorithms in obtaining robust feature representations in multiclass object detection tasks, a self-calibration dual-attention module based on contextual combination is first constructed herein. It obtains the multireceptive field information through a mixed dilated convolution group. Then, a low-dimensional spatial embedding method is self-calibrated to obtain the contextual spatial information. Finally, the spatial information and channel information are combined to enhance the feature representation ability of the proposed algorithm. To prevent the usual introduction of background noise owing to large changes of object scale and irregular appearance in multiclass object detection tasks, the improved deformable convolution is used to adaptively sample the target position. Experimental results obtained using the large multiclass object detection data set MSCOCO show that the proposed algorithm can effectively improve the detection accuracy of multiclass object and outperforms the existing detection algorithms.
In object detection algorithms based on convolutional neural networks, high-resolution features from lower levels contain more detailed information, which can help the abstract features complete the accurate positioning task; deep-level features contain abstract semantic information, which is more suitable for target existence prediction task. When the most existing anchor-free detection method directly predicts all tasks on the same feature map, it does not match the above features and prediction tasks, which limits the detection accuracy. To this end, the MFT detector, a real-time object detection algorithm, is proposed to match multi-scale features and prediction tasks of targets. MFT detector is based on CenterNet detector, which can match shallow detail features with accurate positioning task, and match multi-scale, multi receptive field abstract features with target existence prediction task. Experimental results show that the proposed MFT detector alleviates the mismatch between features and prediction tasks, and significantly improves the detection precision while maintaining a high speed of 94.5 frame/s, which meets the requirement of a real-time vision system.
To improve the encoding capacity and decoding accuracy of encoded marker points in close-range photogrammetry, a method of cooperative encoding and positioning corresponding circular markers comprising positioning crosses, initial numbers, and encoded characters is proposed. Gaussian filtering is used to smoothly preprocess the collected images to eliminate noise. The adaptive local threshold method is employed to segment the target to obtain the character area and cross mark area. TensorFlow-MLP (Multilayer Perceptron) neural network is trained using the character sample library to classify and recognize characters. Finally, the cross mark area is filled and repaired. Sub-pixel positioning is achieved through the gray square weighted centroid method. This type of cooperative coding sign is uniquely identifiable in practical applications with high positioning accuracy and accurate and efficient decoding.
Compared with convolutional neural networks, graph convolution network is more suitable for processing irregular point cloud data. However, it has the problem that the number of network layers is limited and the fixed and standardized aggregation method affects the result of point cloud semantic segmentation. To solve these problems, a depth graph attention convolutional network for point cloud semantic segmentation is proposed herein. The network uses residual connections to deepen the number of layers of the graph convolutional network, which can effectively solve the problems of gradient disappearance and network degradation caused by the network being too deep. The attention mechanism is used to make the network selectively focus on the most relevant neighborhood points, and it assigns different attention weights to it. Simultaneously, the graph is reconstructed after each layer of graph convolution to better characterize the graph structure. Experimental results show that the average intersection ratio of the network on Stanford large-scale three-dimensional indoor spatial dataset reaches 64.5%.
Dual-frequency fringe projection method is a common phase unwrapping algorithm. Due to the influence of factors such as random noise and camera defocusing, the fringe order calculation results of the dual-frequency phase unwrapping algorithm often have errors, leading to phase errors. In order to solve this problem, this paper proposes a phase unwrapping correction algorithm to correct the high-frequency fringe orders. First, the entire fringe region is divided into two masks according to the value range of high-frequency truncated phase. Then, the connected components of these two masks are marked, respectively. In addition, the fringe orders that appear most frequently in each marked region are counted, whose values are assigned to all pixels in the current marked region. Finally, the absolute phase is obtained by unwrapping the corrected fringe orders. The simulation and actual experimental results show that the proposed method can be used to effectively eliminate the phase unwrapping errors in the dual-frequency fringe projection method.
Aiming at the problem of poor tracking effect of correlation filters in dealing with in-plane rotation and scale changes, this paper proposed a scale adaptive correlation filter target tracking algorithm with rotation characteristics based on ECO_HC (efficient convolution operators handcraft). Firstly, we train a scale and rotation filter, and then use the phase correlation algorithm to obtain the scale factor and rotation angle. Secondly, we adopt a dynamic adaptive update strategy for rotation and scale updating. Finally, in the position model update stage, we fuse the background information of front frames to enhance the stability of the template. Experimental data shows that our method is not only robust against in-plane rotation and scale changes, but also can meet real-time requirements.
In order to solve the problem that there are many and irregular bone fragments in the focal area of the distal radius fracture, which causes the doctor’s missed diagnosis and high rate of misdiagnosis, this paper uses the clinical cases of distal radius fracture collected by the research group to propose a supervised automatic distal radius fracture deep learning model. The experiment also introduces the concept of migration learning, which improves the training efficiency of the diagnostic model. Finally, the experiment uses a cross-validation method to evaluate the model. The results show that the classification results of the proposed diagnostic model are better than traditional machine learning and classic deep learning classification models. The classification accuracy rate reaches 84.2%, which is 4% higher than the classic deep learning model. The network structure is simple, the calculation speed is fast, with certain robustness and strong generalization ability.
In the process of image style transfer, the main target of the stylized image is blurred due to the blurring of the foreground and background boundaries in image reconstruction. Image style transfer algorithm with clear target edges is proposed. The deep matting neural network used to extract outline of the content image is merged with the style transfer network to form a transparent mask to constrain the style transfer process, highlighting the outline of the main target of the stylized image. By replacing the max-pooling layer in the transfer network, more image background information is retained, and the overall structure of the stylized image is refined. The network model parameters are reduced by replacing the larger convolution kernel in the transfer network, and the calculation process of style transfer is simplified. Then, the normalization of the conventional-convolutional layer realizes parameter sharing between similar style transfers, improving the speed of style transfer. The VGG-19 neural network as a feature extractor extracts feature maps from the input content and style images, constrains the transformation from the input image to the output image in local affine of color space, and merges the target mask on the RGB channel of the input image so that the main goal of stylized images is to achieve texture synthesis in mask constraints. Experimental results show that compared with the traditional method, this method has obvious boundaries in the foreground and background of the stylized image, and the content structure is preserved well.
The safety monitoring of insulators on transmission lines is particularly important because these insulators are exposed to strong electric fields and harsh environments. To quickly and accurately identify insulators in aerial images, an insulator detection algorithm based on Gaussian YOLOv3 (you only look once) is proposed in this work. First, in order to output the prediction box, the output of the network is increased and the loss function of the network is improved. Then, the mean and variance of the corresponding prediction box coordinate are output by combining the strategy of Gaussian distribution. Finally, the overfitting problem of small data sets is resolved via multi-stage transfer learning. Experimental results show that the algorithm can accurately determine the location of an object. Detection accuracy levels of 93.8% and 94.5%, which are better than the Faster regional convolutional neural network and YOLOv3 algorithm under the same conditions, are realized for insulators in the test set and insulator defects, respectively. The detection accuracy is important for power transmission. Moreover, the intelligent detection of line insulators yields a certain reference value.
In the research on facial expression recognition of deep learning models, a lightweight facial expression recognition method based on convolutional attention is proposed in this paper to solve the problems of large dataset demand and high hardware configuration requirements. First, the model parameters are decomposed and convolved for dimensionality reduction. Then, the convolutional attention mechanism module is embedded in the model to improve its feature extraction ability. For the problem of category imbalance in a dataset, the model is optimized using a cost-sensitive loss function. Finally, the model is pretrained on a face recognition dataset before performing a facial expression recognition task to improve the model’s ability of extracting facial features. Experiment results show that the method effectively reduced the model complexity while maintaining a high level of detection effect along with having strong practicability.
Aiming at mitigating the problems of low contrast, blurred details, and color distortion in underwater images, an underwater image enhancement method based on preprocessed image penalty and generative adversarial network (GAN) is proposed in this paper. First, an improved red channel histogram stretching algorithm is used to preprocess the input underwater image to improve the image contrast and avoid over enhancement of local blocks after traditional histogram stretching. Then, GAN with preprocessed image penalty is designed to realize underwater image enhancement. Moreover, multiscale convolution is used for the first two layers of the generator coding-decoding structure to enhance the detailed information learning ability of the network. Finally, a multiloss function is established in which the preprocessed image is used as a false truth value to impose loss penalty on GAN to improve generalization performance of the network. Experimental results show that compared with traditional image enhancement methods and deep learning-based image enhancement methods, the method performs better in terms of color deviation, contrast, and detailed information of underwater images, and has better robustness.
Aiming at the under-qualitative problem in solving the inverse problem of electrical capacitance tomography, a sparse regularization algorithm that approximates the L0 norm is introduced to obtain the sparse solution vector. An iterable sensitivity gradient optimization method of the sensitive field is proposed to address the imaging quality problem caused by the uneven sensitivity distribution of the sensitive field. This method uses the finite elements of the sensitive field as the core to divide the sensitive field into several regions and the data of sensitivity in the region around the core finite element is extracted for mean filtering. And the filtered data is returned to the core finite elements and used as the parameters in the next filtering area. Cyclic filtering can gradually reduce the sensitivity gradient between the center area and edge area of the sensitive field. The sensitivity gradient optimization method is combined with the approximate L0 algorithm to verify the feasibility of the proposed algorithm. The results show that compared with the traditional Landweber algorithm, the proposed algorithm reduces the relative error of a reconstructed image to 0.24 and the correlation coefficient to 0.91. The actual static experiment also proves the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
To solve the problem of the lack of effective evaluation of environmental pre-judgment by the intelligent inspection robot of the substation, the meter reading in the fog environment is considered the research object, and a support vector regression (SVR)-based meter reading environmental pre-judgment model is proposed. The proposed model uses discrete cosine transform (DCT) frequency domain and spatial structure features based on the local binary pattern rotation invariant operator to reflect the fog density. Besides, it uses the statistical features of the depth image to reflect the distance and SVR to train and fit all image features. Thus, the influence of fog density and distance on the meter reading is comprehensively considered, and the discrimination accuracy is improved. The proposed algorithm is tested on the collected image database and compared with the existing algorithms. The experimental results show that the addition of the depth map feature significantly improves the performance of each algorithm compared with the absence of the depth map feature. It effectively shows the influence of the screen ratio on the meter reading. Compared with other related algorithms, the performance of the proposed algorithm is optimal. The proposed algorithm can effectively solve the problem of environmental pre-judgment.
Aiming at addressing the problems of dimensionality disasters and feature redundancy in Gabor wavelet extraction, a face feature extraction method based on wavelet transform and multifeature fusion coding is proposed. The proposed method uses a 2D-Gabor wavelet to extract normalized input image feature information to obtain Gabor features at different scales and directions. For each feature image, a multifeature fusion coding model based on the Gabor wavelet is used to extract the image L-F (Local Gradient Coding-Fusion) features. Finally, a histogram is used to count the image features to select the appropriate number of blocks, and the information entropy is used to multiply all sub-block images by their respective weighting coefficients to obtain the final face features, and use training samples for the Euclidean distance to set the confidence interval and identify it. The experimental results show that the proposed method has better performance than other feature extraction methods and can demonstrate good robustness under the influence of different poses and complex illuminations.
Hyperspectral images are nonlinear and have a strong inter-spectral correlation. It is easy to lose some information when using a linear method to transform the dimension of hyperspectral data. In this paper, the kernel function is introduced into the minimum noise fraction (MNF), and the kernel minimum noise fraction (KMNF) is proposed. The data is mapped to the high-dimensional feature space through nonlinear mapping, and the minimum noise separation components are extracted in the high-dimensional space. The hyperspectral images have a strong inter-spectral correlation and a spatial neighborhood correlation, and the weights of the two wavebands and the spatial neighborhood are used for multiple linear regression processing to accurately estimate the noise of hyperspectral data. The constrained energy minimization (CEM) method and the matched filter (MF) method are the more classical methods in hyperspectral target detection. The KMNF is applied to two classical target detection methods, and the airfield data from AVIRIS data are used to carry out the hyperspectral target detection experiments.The results show that KMNF can well highlight targets and improve the detection effect and accuracy of hyperspectral targets.
Based on the analysis of the single shot multibox detector (SSD) target detection algorithm, we propose a deep multi-scale feature fusion target detection (DMSFFD) algorithm based on deep learning. The SSD feature layer and its adjacent layer are first fused and the 3 pixel×3 pixel convolution layer is added into the feature map after fusion to reduce the aliasing effect of upsample. Then the deeper feature fusion is conducted and the upsample operation is performed respectively for three small convolution layers. Subsequently the concate operation is performed for four feature layers to generate feature maps with richer semantic information, and thus the multi-scale small target detection is realized. In order to save computing resources and improve the real-time performance of the algorithm, VGG16 is selected as the basic network here. Although the fused algorithm is more complex than SSD, its real-time performance is basically guaranteed. Moreover, the DMSFFD algorithm can successfully detect the small targets missed by most SSD networks, and its detection accuracy is also greatly improved compared with that of SSD.
The image semantic description model usually adopts the encoder-decoder method to realize the image semantic description. The model has problems such as insufficient utilization of image features and insufficient location information extraction of image objects. In response to this problem, an image semantic description algorithm is proposed that integrates the attention mechanism in the encoder part, and the attention weight of different image features is allocated through the context information of the decoder, thereby improving the expressive ability of image semantic description. And verified on the Flickr30k and MSCOCO data sets, the model improves the BLEU-4 evaluation index by 1.9% and 0.8%, respectively. The experiment proves the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
For incomplete scanning data, the traditional algorithm cannot guarantee that the medical computed tomography (CT) reconstruction image meets diagnostic requirements. According to the compressed sensing theory, the medical CT image with sparse representation can be reconstructed from the incomplete scanning data, providing reliable information for diagnosis. From the perspective of reconstruction, this paper proposes an image reconstruction algorithm based on total variation and convolutional sparse coding in gradient domain. Gradient domain convolutional sparse coding is to apply gradient constraint to feature images, and gradient regularization constraint is used to suppress outliers, which solves the problems of structure loss and new artifacts caused by the inaccurate filter. The proposed algorithm directly processes the whole image to obtain the correlation of local neighborhoods, and uses the global correlation of gradient images to generate better edge and clear gradient image features, which can effectively capture the local features of the image. In addition, by introducing total variation as the regularization term, the micro structures and details of the image can be further restored and the noise can be effectively suppressed. Qualitative and quantitative experimental results show that, compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm retains more details and has higher reconstruction quality, which verifies the effectiveness of the method.
Wavefront detection is the main technical means of enhancing telescope alignment. Due to the limited internal space for the large aperture optical system, we propose a computer-aided alignment method based on eigenmode coefficients to solve misalignments in telescopes. Compared with the traditional sensitivity matrix method, in the proposed method, the amount of calculation is small, the detector does not need to be partitioned, and the structure of the wavefront reconstruction matrix is simplified. We analyze the relationship between the eigenmode coefficient and the misalignment of the secondary mirror, and establish a sensitivity matrix model between the two. The alignment of the 1-m aperture on-axis three-mirror telescope was simulated. In the misalignment range of decenter ±0.3 mm and the tilt ±0.2° for the secondary mirror, an aberration correction was achieved in two-step iteration, and the root-mean-square of the central field wavefront aberration was less than λ/14, which has a good practical value for the alignment of large aperture optical systems in the future.
Aiming at the technical difficulties of the visual online inspection of large workpieces, an image mosaic method based on binocular vision feature point matching is proposed. Feature points are detected and matched based on an improved scale-invariant feature transform algorithm. A random sampling consensus algorithm is used to estimate the parameters of the transformation model to eliminate mismatched points, and a weighted smooth fusion method is used to fuse the spliced traces to complete the image splicing and fusion. The flexible visual detection system platform is built and the detection experiment of the workpiece feature area is carried out. The experimental datas are compared with the actual value of the workpiece feature area to verify the correctness and effectiveness of the mosaic method. Experimental results show that the proposed method meets the requirements of fast image stitching using a binocular-vision system in actual industrial production.
Three-dimensional (3D) artificial compound eyes (ACEs) are helpful for wide field-of-view imaging and sensing system applications. However, existing batch preparation methods are technically challenging. A bio-inspired, simple, and high-efficiency batch preparation method is proposed, which involves bonding a sticky microlens array (MLA) polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) film to an elastic PDMS hemisphere under pressure, followed by abrupt pressure removal. Characterizations from a scanning electron microscope and laser scanning confocal microscope show that 3D ACEs prepared using the proposed method have high numbers of uniformly distributed ommatidia with a high-quality finish. Furthermore, optical imaging investigations demonstrate that the proposed preparation method can achieve clear, distortion-free imaging with a wide field-of-view (up to 140.2°).
The dual-frequency fringe projection is an important method for three-dimensional (3D) shape measurement. In the actual measurement process, how to balance the speed and accuracy has a remarkable impact on practical applications. This paper introduces a hybrid dual frequency algorithm, which needs to project four fringe images, including three high frequency fringe images and one low frequency fringe image. First, the background intensity and truncation phase of high frequency fringes are calculated based on three-step phase shift. Second, the background intensity is subtracted from the low-frequency fringes, and the low-frequency truncated phase is extracted by Hilbert transform. The low frequency truncation phase is unwrapped by the geometric constraint method, and the low frequency truncated phase is used to unwrap the high-frequency truncated phase. In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, simulation and experimental studies are carried out respectively. Experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively restore the three-dimensional shape of the measured object.
Police laser blinding devices are primarily used in the field of security. A human target will lose vision temporarily when exposed to the green laser emitted by the device because the human eye is sensitive to the 532-nm green laser. The laser light must cover the target human body as much as possible to improve utilization of the laser. This subject obtains video from the camera and detects pedestrian targets through a video processing system based on digital signal processing (DSP) using the Gentle Adaboost algorithm. The detection results include the size and location of the pedestrian targets. According to the size of the pedestrian, a single chip microcomputer control circuit controls the laser lens to focus on pedestrian targets automatically to accommodate pedestrian targets.
To detect the abnormal quality of smooth surfaces under standardized quality control, a single-pixel detection theory about the abnormal reflectivity of a flat surface is proposed. The proposed method uses a single-pixel detector and only needs to project a single frame of structured light (illumination design). First, the radiation flux distribution of a single-pixel detection about the abnormal reflectivity of a flat surface is derived. It is shown that under uniform illumination conditions, the spatial distribution of the radiation flux to the detector is nonuniform. Thus, a special illumination design can achieve the uniform radiation flux distribution and convert the abnormal reflectivity distribution of a flat surface into the cumulative reflectivity anomaly (or total radiation flux anomaly). In the experiment, the corresponding detection device is designed. The radiation flux distribution on the flat surface to the detector under uniform illumination and the illumination design for achieving uniform radiation flux distribution are numerically calculated. They are consistent with the actual results. Under the illumination condition of uniform radiation flux distribution, the total radiation flux of seven types of qualified ceramic tiles and the abnormal total radiation flux caused by two kinds of surface defect—cracks and scratches were investigated. The results showed that the two surface defects lead to significant changes in the total radiation flux. The effectiveness of the theory and feasibility of the technology are preliminarily verified.
The digital image correlation (DIC) method is a non-contact, full-field deformation measurement method. The three-dimensional DIC breaks through the requirement that the surface of the test piece is planar in the two-dimensional DIC system, and obtains the three-dimensional surface displacement field data of the test piece through a stereo or multi-view camera system. First, a local subset is used to fit the least square plane, and the discrete points on the three-dimensional spatial curved surface are projected into the two-dimensional plane. Then, the Savitzky-Golay filter is used to solve the local strain tensor. Finally, the characterization of the strain field of a free-form test piece is realized, especially the errors of the small-plane projection method are investigated. The results show that the calculation error of the strain field caused by the projection process is much smaller than the transmission of the systematic error component contained in the displacement field data. When the strain subset size M=5, the strain field error is about 30 με. When M=10, the strain field error is about 10 με.
Buildings are extremely important artificial feature objects. Extracting buildings can provide technical support for urban planning, population estimation, and landscape analysis. Object-oriented classification is an effective method for extracting ground objects and has been widely used in the extraction of building information. The object-oriented morphological building index method has good practicability, but the effect of extracting sparse buildings still needs to be improved. To solve this problem, the median absolute deviation is applied to the object-oriented building extraction, and the two situations of dense and sparse buildings are analyzed. Precision, recall, and F1 score are used to evaluate the extraction results. Experimental results show that the object-oriented median absolute deviation method extracts sparse buildings significantly better than the object-oriented classification and object-oriented morphological building index methods.
Based on the three-dimensional (3D) measurement technology of grating fringe projection, phase principal values are extracted using the phase shift method. The accuracy of the phase principal value expansion is the key factor in determining the accuracy of the entire 3D measurement system. Temporal phase unwrapping algorithms can realize the phase unwrapping of isolated and discontinuous objects; however, owing to the influence of sensors and environmental noise, the phase unwrapping result has large errors. To select a good antinoise algorithm, herein, several temporal phase unwrapping algorithms were compared using simulations and experiments. Results show that the multi-frequency (hierarchical) phase unwrapping and negative exponential fitting methods exhibit good antinoise performance and high phase resolution accuracy. Alternatively, the multi-wavelength (heterodyne) method and multi-wavelength (heterodyne) method based on the fringe location exhibit a poor antinoise performance and large phase errors. The findings of this study can provide guidance to researchers in selecting phase decomposition algorithms, and they have important application values.
To address the problems associated with online detection, low recognition efficiency, and strong subjectivity of the flotation dosing state, this paper proposes a flotation dosing state recognition method based on multiscale convolutional neural network (CNN) features and ranks automatic encoder kernel extreme learning machine (RAE-KELM). First, the flotation foam image is subjected to non-subsampled Shearlet multiscale decomposition, and the CNN is used to extract the depth features of each scale image and perform multiscale feature fusion. Then, the RAE-KELM is constructed, and an improved bacterial foraging algorithm based on quantum computing is used to optimize the RAE-KELM parameters. Finally, the optimal RAE-KELM model is obtained through self-built dataset training to realize the adaptive recognition of the flotation dosing state. The experimental results demonstrate that the recognition accuracy of the method can reach 98.88%. Additionally, the method reduces manual interventions, which can improve production efficiency.
In order to improve the real-time performance of the traditional stereo matching algorithm based on census transform, which has low matching accuracy in weak texture regions and is easy to be affected by noise points, a novel stereo matching algorithm based on Census transform and adaptive window is proposed. In the cost calculation stage, the window size is adaptively matched according to the strength of the regional texture, three kinds of state information are used for Census transformation to calculate the initial cost, which improves the matching accuracy of single pixel and reduces the consumption time. Then, in the cost aggregation stage, a low time complexity guided filter is used to solve the problem of low accuracy caused by low cost discrimination of single pixel matching. Finally, the left-right consistency detection principle is used to reduce the outliers, and the final disparity map is obtained. The proposed algorithm is tested using Middlebury platform standard images. The experimental results show that the average error matching rate of the proposed algorithm is 5.51%, and the matching accuracy is improved to some extent. The average time-consuming is shortened by 36.60% compared with the traditional Census algorithm, and the real-time performance of the algorithm is improved.
Aiming at solving the problems that the existing stereo matching algorithms have, a low matching rate in noise intrusion and low disparity accuracy in discontinuous disparity and weak texture regions, a stereo matching algorithm based on fusion cost of Census transformation and mutual information (MI) and the segment optimization is proposed in this study. The proposed algorithm mainly involves two steps: initial disparity map acquisition and disparity map optimization. In the first step, the initial matching cost is formed by the fusion of MI and Census, and then, the cost is aggregated by improved guided filtering to obtain the optimal matching cost; the winner-take-all(WTA) strategy is used to obtain the initial disparity map. In the second step, the reference image is divided into superpixels, and a disparity plane is fitted to each superpixel; next, the average disparity of the superpixels is estimated using the Markov random field (MRF). Then, the average disparity is used to process the occlusion area in the adjacent system and optimize the disparity accuracy. Finally, the final disparity map is obtained by median filtering. The experimental results show that the average mismatch rate of the disparity maps of the 15 sets of Middlebury test datasets obtained using the proposed algorithm in a nonocclusion area is only 7.60%, running time of each stage is short, and average processing time for each pair of images is 6.8 s. Overall, the proposed algorithm runs efficiently.
The composite C-beam will undergo springback deformation after forming. The calculation and analysis of the deformation amount using the scanned data are prone to mismatches, which make it impossible to accurately describe and evaluate the actual deformation amount. In view of this, a C-beam point cloud registration and deformation detection method based on the constant characteristics of the web area and the symmetry plane is proposed. According to the deformation characteristics of the C-beam, the springback deformation is quantitatively described, and the calculation method of the deformation amount is given. Principal component analysis and iterative nearest point algorithm are used to extract the symmetry plane of the C-beam to obtain the symmetry degree of the C-beam. Combined with the point cloud constraints of the web area with small deformation, the measurement data is registered with the model data, and the global deformation distribution of the C-beam is obtained. The simulation point cloud of C-beam with springback deformation is constructed, and the deformation amount is calculated by the proposed algorithm. The results show that the proposed algorithm can realize the calculation of the deformation amount, the relative error of the maximum springback deformation is 0.0461%, and the deformation amount is consistent with the simulated set value, and the detection of the C-beam deformation amount is realized.
In visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), the loop closure detection module is used to eliminate pose drift and obtain globally consistent trajectory and map. Aiming to solve the problems of low efficiency and accuracy in traditional SLAM loop closure detection methods, an SLAM loop closure detection method based on the Harris hawks optimization (HHO) algorithm is proposed in this article. First, the features from accelerated segment test (FAST) algorithm is modified to extract image features and generate robust descriptors of image features. Then, the problem of solving the maximum similarity between the current and historical frame images in loop closure detection is transformed into a maximum optimization problem. Finally, the HHO algorithm for solving the loop closure detection problem is obtained by designing individual coding mode and fitness function. The experimental results show that the proposed SLAM loop closure detection method based on HHO algorithm has higher efficiency and accuracy compared with the loop closure detection methods based on bag of word and particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm.
The position-pose relation between cameras is the main factor that affects the accuracy of an image-based ballastless track subgrade monitoring system. Each camera in the monitoring station must face the corresponding monitoring target surface, so there is often no public field of view between the cameras. According to the equivalence between the hand-eye calibration problem in robot vision and the calibration of position-pose relation between cameras, a position-pose calibration method based on feature points is proposed. Four feature points with square distribution are set on the monitoring target surface. A set of cameras is moved twice in small step and takes the pictures of the target surface in three different positions. The P4P (perspective-four-point) algorithm is used to solve the position-pose relation between the camera and the target, and then obtains the movement trajectory of the camera. The matrix rearrangement method is used to obtain the pose conversion matrix between the cameras, and the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm is used for nonlinear optimization. Simulation results indicate that the angle error is less than 0.03° and the translation error is less than 0.3 cm when the noise variance is less than 1 pixel. The effectiveness and practicability of the method in this paper are verified by simulation, and the method in this paper can meet the needs of the settlement measurement of the ballastless track subgrade.
Point cloud classification and segmentation are key steps in understanding three-dimensional (3D) scenes. Aiming at the problem that sparse point cloud input and occlusion cannot effectively identify point clouds, an improved classification and segmentation network linked-dynamic graph convolutional neural network (DGCNN) is proposed. First, the deep-level point cloud features were extracted by increasing the number of EdgeConv convolutional layers based on DGCNN. Next, the transformation networks of DGCNN were removed to simplify the network structure. Finally, the idea of introducing a deep residual network was used to link the output features of different network layers to form point cloud features, making the network training more stable. The proposed network was compared with other point cloud networks on ModelNet40 and ShapeNet Parts datasets. The experimental results show that the network has higher accuracy of point cloud classification and segmentation than other methods under the sparse point cloud input and occlusion. Besides, it has stronger robustness.
Atherosclerosis is closely related to various cardiovascular diseases, directly leading to arterial wall hardening, thereby producing a series of vascular physiological function abnormalities and inducing various cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, the detection of atherosclerosis is crucial in cardiovascular medicine. In order to verify the photoacoustic platform’s ability to detect atherosclerosis in living tissues and explore the application prospects of photoacoustic spectrum analysis in peripheral blood vessel detection, we carried out simulation and in vivo animal experiments. The K-wave simulation verified the theoretical feasibility of photoacoustic spectrum analysis. A photoacoustic detection system was developed, and an atherosclerosis mouse model fed with a high-fat diet was established for collecting the corresponding signal data and performing analysis. The spectral data of the photoacoustic signal of atherosclerosis model mice and normal mice are significantly separated after variance analysis, and the spectrum analysis results of the experimental data are in good agreement with the K-wave theoretical analysis results. Experimental results show that photoacoustic spectrum analysis shows potential for detecting arteriolosclerosis in vivo. This analysis is expected to be an effective method for detecting arteriolosclerosis.
The railway system is one of the major means of transport in the transportation system, and the hidden danger to railway safety is mainly from the intrusion obstacles on the railway, such as dangerous rocks, animals, and pedestrians, and thus the technology for real-time detection of small obstacles is essential. In this paper, the 16-ray 3D lidar is used to collect data and realize point cloud imaging. The background point cloud and the point cloud collected in real time are first spatially voxelized based on the octree method, and then difference operations are performed on them. In addition, the statistical filtering and radius filtering are used to denoise the point cloud. Finally, the real-time detection of small target obstacles is realized. The research results provide some references for the data collection of a 16-ray 3D lidar scanning system.
Multispectral LiDAR can directly and effectively obtain point clouds containing spectral information, and it has become a new trend of LiDAR imaging technology. The point clouds obtained by this new multispectral LiDAR have more spectral and color information, which puts forward higher requirements on the data quality of point clouds; therefore, point cloud denoising becomes the key to improve the data quality. The traditional monochromatic point cloud denoising algorithm mainly uses spatial information to remove noise, but it is not suitable for multispectral LiDAR point clouds. In this paper, a multispectral LiDAR point cloud denoising algorithm based on color clustering is proposed. First, the point clouds containing color information are inverted according to the spectral information obtained by the multispectral LiDAR. Then, the point clouds are clustered by color difference. After the clustering, the density of noise points in each cluster is lower than that of the real point. Finally, the noise is identified and removed in each cluster. The results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively remove the noise from the multispectral LiDAR point cloud with a ground object identification accuracy of above 95%.
Super-resolution microscopy invented at the beginning of the 21 st century has rapidly become a indispensable method in life science research owing to their nanoscale spatial resolution, low damage of sample preparation, and so on. Among a variety of super-resolution imaging techniques, single-molecule localization super-resolution microscopy (SMLM) with straightforward principle and outstanding spatial resolution gains more and more attention from researchers, thereby continuously making significant progress on the techniques and applications. Firstly, this paper reviewed the principle of SMLM and discussed some technical problems including the optical path building, the image reconstruction, and the drift correction. Two types of representative SMLMs were indroduced and discussed. Then, diversified multi-color SMLMs were introduced and their advantages and disadvantages were analyzed. The improvement of imaging parameters including the lateral/axial spatial resolution, imaging field, and imaging depth of SMLM was subsequently discussed. The research progress of correlated imaging of the SMLM combined with deep learning and SMLM combined with the electron microscope was further introduced. Moreover, the extraction and analysis methods of SMLM data were discussed. Finally, some important applications of SMLM in cell biology were listed and the development prospects of SMLM were discussed. We hope the present review could be a useful reference for the SMLM users and provides novel insights for them, thus promoting the in-depth applications of SMLM in life science research.
Image semantic segmentation is an important research field of computer vision and also one of the key technologies for scene understanding. In the field of unmanned driving, high-quality semantic segmentation of road scenes provides a guarantee for the safe driving of autonomous vehicles. First, this paper starts with the definition of semantic segmentation of road scenes and discusses the current challenges in this field. Second, this paper divides the semantic segmentation technology into a traditional segmentation technology, a traditional segmentation technology combined with deep learning and a segmentation technology based on deep learning, focuses on the semantic segmentation technology based on deep learning, and elaborates it according to three different network training methods of strong supervision, weak supervision and unsupervison. Then, the datasets and performance evaluation indicators related to the semantic segmentation of road scenes are summarized and compared, and the segmentation results using the common image semantic segmentation methods are analyzed. Finally, the challenges faced by the road scene semantic segmentation technologies and the future development direction are prospected.
In this study, a rapid nondestructive testing model for the textural quality of freshwater fish using near-infrared spectroscopy is developed to study the relationship between storage periods and the textural quality of freshwater fish. Spectral data for the Parabramis pekinensis fish samples were collected using the Antaris Ⅱ Fourier transform near-infrared spectrometer, and the hardness, springiness, and chewiness values of the samples were measured using the TMS PRO type structure instrument. The S-G smoothing method was used to pretreat the raw spectra, and competitive adaptive reweighting sampling, stable competitive adaptive reweighted sampling, and successive projections algorithms were integrated to extract the characteristic wavelength for the first time. Based on the above three textural indexes,the least partial square regression (PLSR) model was established. Based on the primary characteristic wavelengths extraction, the SPA algorithm was used to extract the secondary characteristic wavelengths. Then, the optimal model of hardness, springiness and chewiness of freshwater fish was established according to the extracted secondary characteristic wavelengths. The correlation coefficients Rc and Rp of the correction and prediction sets are 0.968, 0.947, and 0.927, and 0.964, 0.939, and 0.926, respectively. The root mean square error of the correction and prediction sets are 0.753, 0.827, and 0.986, and 0.846, 0.897, and 0.964, respectively. The results show that this method is suitable for rapid and nondestructive testing of the textural quality of freshwater fish in storage and has high accuracy.
The spectral characteristics of jades from Burma, Russia, and Guatemala are compared and analyzed. Based on the infrared spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy combined with the principal component analysis (PCA) and the back propagation (BP) neural network, the model is built for discriminating jade origins, whose discrimination effect is tested. The results show that the infrared absorption spectra of jades from different origins are basically similar, but there exists certain difference in their Raman spectra. In addition, Jades from Burma, Guatemala, and Russia all possess the characteristic Raman spectra. Based on the PCA-BP neural network discrimination model of infrared spectra, the discrimination accuracies of training samples and test samples are 94.2% and 91.6%, respectively. In contrast, based on the PCA-BP neural network discrimination model of Raman spectra, the discrimination accuracies are 93.48% and 100.0%, respectively. It can be seen that the PCA-BP neural network discrimination models based on infrared spectra and Raman spectra both have high accuracy in identifying jade origins, indicating they have certain practicability and feasibility for rapid identification of jade origins.
This paper proposes a complementary tracking algorithm with high-confidence updating strategy to address target tracking problems in complex scenes such as target occlusion, deformation, rotation, illumination changes, and background interference. The algorithm is based on the core-related filter-tracking algorithm and the statistical color feature-tracking algorithm. First, the Laplacian of Gaussian operator and local binary mode are used to enhance the edge information and texture features of the target. Then, the tunable Gaussian window function and scale estimation model based on the key points optimization algorithm are introduced. Finally, the response peak value and a high-confidence updating strategy are designed for the merged rate of the tracking frame to adaptively updating the template. Experimental results show that the precision and success rate of the algorithm on the OTB2013 data set are 88.3% and 72.4%, respectively.
Spectral estimation has received extensive research in the field of spectral imaging. A spectral estimation method based on adaptive weighted linear regression is proposed. First, a global training model is developed based on pseudo-inverse algorithm, homogeneous polynomial expansion of digital response, and Tikhonov regularization constraint. Second, based on the influence of global training sample on the accuracy of spectral estimation, the adaptive weighted training model is developed to further improve the spectral estimation accuracy by introducing the Gaussian weighted method. The sensitivity functions of 28 digital cameras is used to build a simulation imaging system, the Munsell Matte color sample and the X-rite ColorChecker SG color chart are used as experimental samples, and the metrics of spectral root-mean-square error and color difference are used to evaluate the spectral estimation accuracy. The results show that for the global training model, the new method can achieve almost the same accuracy as the existing methods, and can overcome the exposure sensitivity problems of the existing methods. The new method achieves better results than the existing methods in both spectral accuracy and colorimetric accuracy under the adaptive weighted training model.