View fulltext
View fulltext
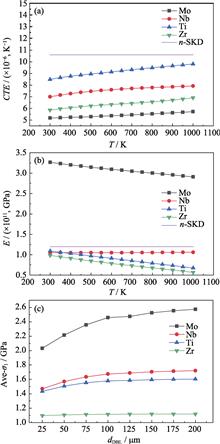
In thermoelectric (TE) devices, the interfacial reliability greatly influenced devices’ durability and power output. For skutterudites (SKD) devices, TE legs and electrodes are bonded together with diffusion barrier layer (DBL). At elevated temperatures, DBL react with SKD matrix or electrode to generate complex interfacial microstructures, which often accompanies evolutions of the thermal, electrical and mechanical properties at the interfaces. In this work, a finite element model containing the interfacial microstructure characteristics based on the experimental results was built to analyze the interfacial stress state in the skutterudite-based TE joints. A single-layer model was applied to screen out the most important parameters of the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and the modulus of DBL on the first principle stress. The multilayer model considering the interfacial microstructures evolution was built to quantitively simulate the stress state of the TE joints at different aging temperatures and time. The simulation results show that the reactive CoSb2 layer is the weakest layer in both SKD/Nb and SKD/Zr joints. And by prolonging the aging time, the thickness of the reaction layer continuously increased, leading to a significant raising of the interfacial stress. The tensile testing results of the SKD/Nb joints match the simulation results well, consolidating accuracy and feasibility of this multilayer model. This study provides an important guidance on the design of DBL to improve the TE joints’ mechanical reliability, and a common method to precisely simulate the stress condition in other coating systems.
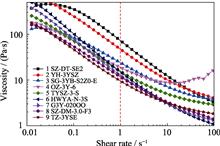
As for ceramic stereolithography technique, the preparation of suitable resin-based ceramic slurry is of primary importance. In this study, the effects of powder characteristics such as specific surface area, particle size and distribution, particle morphology on the rheological behavior of zirconia resin-based suspensions were investigated intensively. Results show that the specific surface area of the powder is the most important factor affecting slurry viscosity. Choosing low specific surface area and quasi-spherical shaped powder is more likely to obtain low viscosity slurries. In addition, the influence of solid loading on the flow behavior were also studied using Krieger-Dougherty model. Zirconia samples with the relative density of (97.83±0.33)% were obtained after sintering at 1550 ℃. No obvious abnormal grain growth in the microstructure of the sintered body is observed. Results indicate that after the optimization of the processing parameters with the help of rheology characterization, complex-shaped high-quality zirconia parts can be obtained using the stereolithography technique.
Rare-earth doped inorganic ferroelectrics are considered as novel photochromic materials, with potential applications for optical switch and information storage (K0.5Na0.5)1-xEuxNbO3 (KNN:xEu) ceramics were prepared by high temperature calcination, with precursor powder obtained by hydrothermal method. Strong red emission at 615 nm was observed which corresponds to the 5D0→ 7F2 transition of Eu 3+ under excitation of 465 nm. Under UV light irradiation for 3 min, the color of the ceramics turned from milky white to dark gray. The colored samples returned to the original color when heated at 200 ℃ for 10 min, showing strong photochromic behavior. Meanwhile, the luminescence intensity of Eu 3+ can be tuned without obvious degradation by alternating UV light and heat stimulus. Upon UV light irradiation, large luminescence modulation ratio (ΔRt) up to 83.9% was achieved for KNN:0.06Eu, indicating good luminescence switching behavior. A possible mechanism for non-radiative energy transfer from the luminescent center to the color center was proposed according to their luminescent behavior.
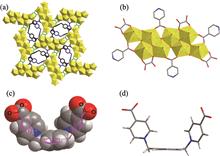
In this work, we report a novel octa-nuclear uranyl (U8) motif [(UO2)8O4(μ3-OH)2(μ2-OH)2] 4+ embedded in a uranyl-oxalate coordination polymer (compound 1) based on a U-shaped linker with extra-long xylylene chains for stabilizing the resulting high-nuclear motif through additional cross-linking connectivity. A comparison with dimeric and monomeric uranyl compounds obtained at different pH value from the same hydrothermal system reveals that, solution pH plays a vital role in formation of this octa-nuclear uranyl motif by promoting hydrolysis of uranyl source. Since high similarity of eight uranium centers in this nearly planar U8 motif here, overlapping and broadening of signals in fluorescence, infra-red (IR) and Raman spectra can be found.
Alum has an excellent safety record and is the only licensed inorganic adjuvant for human vaccines. However, the exploration of alum nanosheets as chemotherapy drug delivery system, especially the clarification about the relationship between structures and drug loading properties, is totally insufficient. Herein, aluminum hydroxides (AlOOH) nanosheets with tunable specific surface area and pore size were synthesized by adjusting the synthesis time in the presence of triblock copolymers. The obtained materials exhibited the highest surface area about 470 m 2/g. The structure-dependent chemotherapy drug loading capability for AlOOH nanosheets was observed: the higher specific surface area and pore size are, the higher amount of chemotherapy drug is loaded. AlOOH nanosheets loaded with doxorubicin showed a pH-dependent sustained release behavior with quick release in low pH about 5 and slow release in pH around 7.4. Doxorubicin-loaded AlOOH nanosheets exhibited much higher cancer cellular uptake efficiency than that in free form by flow cytometry. Moreover, doxorubicin-loaded AlOOH nanosheets with high specific surface area showed an increased cellular uptake efficiency and enhanced ratios of apoptosis and necrosis, compared with those showing low specific surface area. Therefore, AlOOH nanosheets are promising materials as chemotherapy drug delivery system.
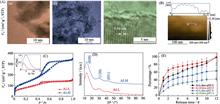
Titanium and its alloys have been wildly used as bone implants. However, it is still facing a severer issue: implant related infections due to the lack of antibacterial ability. Copper (Cu) has good antibacterial ability and can be used to improve the anti-infection capability of titanium. In this study, three kinds of Ti samples with different contents of Cu in the modified layer were prepared by plasma immersion ion implantation (PIII) technology, and their responses to bacteria and cells were explored in vitro. The results showed that the sample with low Cu content at the surface could promote the proliferation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (rBMSCs) and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) but not inhibit the proliferation of Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). As the implantation time extends, antibacterial ability of the samples with high Cu content at the surface was significantly enhanced, and no obvious cytotoxicity was observed. Therefore, it is possible to acquire a balance between antibacterial ability and biocompatibility of Ti by controlling the contents of Cu in the modified layer.
Aspirin/layered double hydroxides composite (A-LDHs) and aspirin/layered double hydroxide-nanosheets composite (A-LDHs-NS) were prepared by intercalation and exfoliation-recombination, respectively. Their morphology, drug loading property and drug loading mode of the composites were characterized by XRD, SEM, TG-DTG, and FT-IR. The releasing performances of aspirin from A-LDHs and A-LDHs-NS in the phosphate buffer solutions with different pH conditions were investigated. The results show that the typical lamellar structures are hold in as-prepared LDHs and LDHs-NS. The larger specific surface area (187 m 2·g -1) of LDHs-NS, the more aspirins are loaded on its surface, among which the max drug loading is 1.178 mmol·g -1. Its releasing process lasts for more than 1440 min, much longer than 20 min of the control materials, showing excellent sustained-releasing performance. This performance may because of the strong interaction between aspirin and LDHs-NS. Moreover, the sustained releasing performance is stronger at pH 7.4 than that at pH 4.8. All data from this study provides a reference for wider application of this kind of two-dimensional materials in biomedicine.
Titanate nanofibers were prepared on titanium mesh by alkali-heat treatment, and calcium phosphate coating was fabricated on the porous titanate nanofibers by electrochemical deposition technology. Then hBMP-2 was introduced into the coating by different methods to improve its osteointegration and bioactivity. Three kinds of composite coatings modified by hBMP-2 were prepared (TmhB, TmHedhB and TmHhBed). Surface morphology, chemical composition, phase composition and hBMP-2 amounts and hBMP-2 release performance of the composite coatings were characterized by SEM, ATR-FTIR, XRD, and hBMP-2 ELISA kit, respectively. Results showed that all of the coatings display porous fiber structure, calcium phosphate phase in TmHedhB and TmHhBed samples was hydroxyapatite (HA), and bead-like HA particles formed on the surface of titanate nanofibers. Protein adsorption experiments showed that introduction of bead-like HA phase increased the hBMP-2 adsorption on the composite coatings, and composite coatings prepared by electrochemical co-deposition technique further enhanced hBMP-2 adsorption up to 886 ng/mg, which were supported hBMP-2 sustained release within 6-48 h.
Zirconia is a kind of prospective hard tissue implant materials, which possesses superior mechanical properties and excellent biocompatibilities. To promote the stable osseointegration between Zirconia implants and tissue, zirconia-toughened trace Sr-, Si- and F- co-doped hydroxyapatite (ZrO2-DHA) was coated by plasma spraying on zirconia. The phase composition and structure of coatings were characterized, and the mechanical properties and in vitro biological properties were investigated. The results show that co-doping of trace Sr, Si and F enhances the biological properties of coatings on adhesion and differentiation of osteoblasts through the signal transduction pathway of osteogenic differentiation. All of ZrO2-DHA coatings promote the cell viability and gene expression in osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1. On the 7th day of cell culture, the relative expression levels of Alp and Col-I in the ZrO2-DHA coating containing 70% DHA (7DHA) were about 2.8 times and 2.3 times higher than those in the ZrO2 substrate group, respectively. Mechanical properties of ZrO2-DHA coatings are improved with the increment of zirconia ratio. Hardness of DHA coating and 7DHA coating are 250.8 and 313.8HV respectively and their bond strength are 25.1 and 31.8 MPa, respectively. 7DHA coatings with network structure possess both excellent mechanical and biological performance for the implant coating application.
To develop a new kind of non-viral inorganic gene vector, embedded dual-mesoporous silica spheres (EDMSNs) was modified with polyethyleneimine (PEI) or 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTMS). Then gene loading and transfection ability of the obtained EDMSNs-PEI and EDMSNs-NH2 was tested by choosing the pCMV-EGFP-N1 plasmids (pDNA) as a gene model. Particle morphologies, particle sizes, zeta potentials, and pore structure parameters of EDMSNs-NH2 and EDMSNs-PEI were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering and nitrogen adsorption-desorption. Both EDMSNs-NH2 and EDMSNs-PEI display obvious dual-mesoporous structure and well-defined spherical morphology. Average dynamic sizes of EDMSNs-NH2 and EDMSNs-PEI are 343.2 and 338.9 nm, while zeta potentials of EDMSNs-NH2 and EDMSNs-PEI are +18 and +43 mV, respectively. The results of gel electrophoresis, CCK-8 assay, and fluorescence microscope show that the pDNA loading amount of EDMSNs-PEI is 8%, much higher than that (1%) of EDMSNs-NH2. In addition, EDMSNs-PEI exhibits lower cytotoxicity than that of pure PEI polymers and lipofectamine2000. When the mass ratio of EDMSNs- PEI/pDNA is 33 : 1, the transfection rate of the 293T cells by EDMSNs-PEI/pDNA reaches a maximum at 72 h. In conclusion, EDMSNs-PEI, compared with EDMSNs-NH2, has a higher positive potential and pDNA loading capacity, which can be used as a promising non-viral inorganic gene vector for the treatment of diseases such as malignant glioma.
Chromium ion accumulation in environment is a health hazard to human being. A thiohydroxy-functionalized mesoporous material SBA-15-SH as adsorbent was prepared by the hydrothermal polycondensation method in this study. When 3-mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane was used as the silicon source, SBA-15 was successfully modified with the thiohydroxy group confirmed by FTIR. This designed mesoporous material was rod-like with regular and well-defined channel systems of 7 nm. The adsorption capacity of SBA-15-SH to Cr 6+ was affected by the adsorption temperature, Cr 6+ solution pH and its initial concentration together with the adsorbent dosage. The adsorption equilibrium was reached in 10 min which obeyed the Langmuir adsorption equation and the pseudo second-order kinetic mode. The maximum adsorption capacity of SBA-15-SH to Cr 6+ was 6.85 mg/g when the Cr 6+ solution pH and adsorption temperature was controlled at 4.0 and 25-45 ℃, respectively. This functionalized mesoporous material was successfully applied in spiked tap-water and industrial waste water, and the recovery rate can reach 95%-105%.
Being a typical Kondo topological insulator, samarium hexaboride (SmB6) attracts much interest in condensed physics and material sciences in recent years. In comparison with their bulk counterparts, SmB6 nanostructures have more abundant surface electron states due to larger specific surface area, which are believed as idea platforms for studying surface quantum properties and physic mechanism. Through chemical vapor deposition (CVD), SmB6 nanobelt and nanowire films were respectively prepared on Si substrate. Both SmB6 nanowires and nanobelts are proven as the cubic single crystals, and their growth directions are, along [100] and [110], respectively. Field emission (FE) results show that SmB6 nanobelts have a turn-on field of 3.24 V/μm and their maximum current density arrives at 466.16 μA/cm 2, which are better than SmB6 nanowires. Considering that SmB6 nanostructures have lower electron affinity, higher electron conductivity and more abundant surface states, they are regarded as excellent cold cathode nanomaterials if their FE performances can be further improved.
Yb:YAG transparent ceramics with high optical quality were fabricated by solid-state reaction and vacuum sintering method (1750 ℃×30 h) using high-purity Y2O3, α-Al2O3 and Yb2O3 powders as raw materials. The measured concentration of Yb 3+in 5.0at% Yb:YAG ceramics is 6.41×10 20 cm -3, and the cell density is 4.65 g/cm 3. The microstructures, spectral characteristics and laser performance parameters of Yb:YAG ceramics were studied in this work. FESEM results show that Yb:YAG ceramics have uniform and compact structure, clean and straight grain boundaries, and the average grain size is about (19±3) μm. The in-line transmittance of Yb:YAG ceramics with thickness of 4.0 mm reaches 82.5% at 400 nm and 85.2% at 1100 nm. The minimum pump saturation light intensity occurs at 940 nm, and the pump threshold power at 1030 nm is the lowest. The quality factor of 1030 nm laser pumped at 940 nm is 1.02×10 -22 cm·s. By calculating the gain cross section, it is indicated that Yb:YAG ceramics can be tuned broadband, and are ideal laser gain media.
Extrusion stress due to phase change of the NiS, internal stress due to CTE mismatch between the NiS and glass, and local concentrated stress around the NiS due to synergistic effects above were quantitatively calculated based on equal strength theory and the deformation coordination relation between NiS and glass in this work. The effects of NiS particle diameter, local strength of glass and ambient temperature on spontaneous breakage of tempered glass were analyzed. The critical diameter of NiS particles was determined as well. The results show that the fundamental reason for spontaneous breakage of tempered glass is the circumferential concentrated stress (tensile stress) near the NiS particle. There exists non-linear relations between circumferential stress and NiS particle diameter of which the circumferential stress decreases rapidly with the decrease of NiS particle diameter when it is less than 0.2 mm, but circumferential stress increases moderately when it is greater than 0.5 mm. The critical diameter of NiS particle which causes the spontaneous breakage of tempered glass decreases with the increase of surface stress in the tempered glass. It is difficult to induce spontaneous breakage of tempered glass when the diameter of NiS particle is less than 0.1 mm. The circumferential stress increases linearly with the increase of ambient temperature, and the stress increases slightly faster for the NiS with larger diameter.
A new inorganic/organic composite film PEDOT:Ce@TiO2 was prepared through drop casting-secondary polymerization method using the mixture solution of PEDOT oligomer and cerium-containing polyoxotitanate cage [Ti8O7(HOEt)(OEt)21Ce]. PEDOT:Ce@TiO2 exhibits a special nanostructure with gully-like rough surface, which shows strong hydrophobicity while good wettability to acetonitrile solution. PEDOT:Ce@TiO2 can be used as cathodically electrochromic film and supercapacitor electrode material. The mass specific capacitance of PEDOT:Ce@TiO2 is 71.2 F/g at a current density of 1 A/g, which is 1.7 times higher than that of the PEDOT film. An all-solid-state electrochromic supercapacitor prototype device was further assembled using PEDOT:Ce@TiO2. With charging completed the electrochromic area of this device shows dark green, and it turns bright yellow with discharging completed.
Bacterial cellulose (BC), an eco-friendly bio-product obtained from fermentation of various microorganism, consisting of the interconnected networks structure attracted widespread interest due to its unique physical properties, including the large specific surface area, remarkable mechanical strength, high water-holding ability, good chemical stability, and environmental benign material. These advantages enable BC to be applied to fabricate the highly versatile three-dimensional (3D) carbon nanomaterials, and tunable flexible scaffold to support other multifunctional materials. In this review, the production process of various carbon nanofibrous composites based on BC, such as carbon nanofiber (CNF), doped CNF, CNF/metal oxide and CNF/conducting polymer, is presented. Their emerging applications in supercapacitors are illustrated, in particularly, the design of hybrid bendable electrodes based on BC substrate for flexible supercapacitor is highlighted. The challenges and opportunities in this fascinating area of designing functional nanomaterials and flexible electrode from BC for various energy storage are addressed. Moreover, the perspectives are given for the future development, including several significant kinds of study for applications in the rechargeable battery.