View fulltext
View fulltext
NiCo2O4 nanomaterials exhibit great potential in the fields of energy storage and conversion especially in supercapacitors for their unique physicochemical properties. Given the important impact of morphology of nano material on its performance, this review focuses on preparation methods and application of NiCo2O4 nanostructure with various morphologies including nanoneedle, nanowire, nanotube, nanosheet, sphere, nanoflower, coral-like structure and three-dimensional hybrid structure. Furthermore, the influence of morphology and particle size of NiCo2O4 on its properties is also introduced. Finally, the future research direction of NiCo2O4 nanomaterials in the fields of energy storage and conversion is prospected.
Traditional NiCo2S4 vulcanization process requires high-temperature and high energy supply, and has disadvantage of low conductivity. In this study, an environmental friendly vulanization method was utilized to prepare unique NiCo2S4@ACF core-shell heterstructure materials with activated carbon fiber (ACF) as skeleton at room temperature. NiCo2S4@ACF composite electrode material owns layered structures, which can effectively expand contact area with electrolyte, improve electron transmission path, and better create electrochemical performance. Specific capacitance of NiCo2S4@ACF composite electrode materials reached 1541.6 F/g (678 μF/cm2) at the current density of 1 A/g. In addition, the asymmetric supercapacitors (ASC) device fabricated with NiCo2S4@ACF as positive electrode and ACF as negative electrode exhibited energy density as high as 49.38 Wh/kg at the power density of 800 W/kg, and preeminent cycle stability up to 90.28% after 2000 cycles. All these data demonstrated that NiCo2S4@ACF is a promising potential application in the field of high-performance supercapacitors in the future.
Ag2Se quantum dots (QDs) was synthesized by co-deposition method which was further applied as co-sensitizer in solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). The effects of different sensitization methods of Ag2Se QDs (TiO2/N719/QDs, TiO2/QDs/N719) and sensitization time (0-5 h) on the performance of QDs/dye co-sensitized solar cells were studied. Structure and optical properties of Ag2Se QDs were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis). Furthermore, the transmission of charge carriers of solar cell devices was characterized by photo-modulated photocurrent/voltage spectrum (IMPS/VS) and electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS). It was found that the device with TiO2/QDs/N719 showed higher incident photon-to-current efficiency (IPCE) and photoelectric efficiency than those of TiO2/N719/QDs, which was due to the fact that TiO2/QDs/N719 photoanode adsorbed more QDs and dyes. With the extension of Ag2Se QDs sensitization time, the photovoltaic properties of DSSCs firstly ascended and then descended, achieving the highest photoelectric conversion efficiency 3.97%. The incorporation of Ag2Se QDs could effectively promote the electron transport and inhibit the electron-hole recombination, which benefited from a blocking layer that QDs served in device. As sensitization time prolonged over 2 h, the photovoltaic performances of device deteriorated, which was attributed to the augmented trap sites in Ag2Se QDs layer.
Polyaniline-carbon pillared graphene composites (PGR) were successfully prepared by vacuum extraction induced self-assembly and pyrolysis method. Effects of the mass ratio of aniline monomer (AN) and graphene oxide (GO) on structure and electrochemical properties of PGR were investigated by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and electrochemical characterization. Results showed that the polyaniline-carbon pillars uniformly distributed between the graphene (GR) layers to form a three-dimensional conductive network with expanded interlayer space and nitrogen doping, which effectively improved the structural stability and electrochemical performance of GR. The as-prepared PGR with the mass ratio of AN and GO at 1 : 1 exhibits a high reversible capacity of 653 mAh/g at a current density of 100 mA/g and an excellent rate capability of 343 mAh/g at a current density of 1 A/g, all that is much higher than that of the GR electrode (101 mAh/g).
A novel rice-like copper oxide (CuO) was synthesized without using soft template and alkali by hydrothermal and in-situ decomposition methods. This rice-like CuO material was made into the chemically modified electrode (CME) with Nafion solution for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Structure and morphology of the prepared material and electrode were characterized by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. Electrochemical performances of the obtained electrodes were investigated by linear sweep voltammetry, cyclic voltammetry, amperometric response, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Results show that morphology of the obtained CuO particle is similar to rice grain. And its length and diameter are between 0.5-1.0 μm and 250-320 nm, respectively. The CME with 0.35 mg rice-like CuO (with 0.22 cm2 electrode surface area) has an obvious current response for glucose with the linear range from 0.0357 to 2.361 mmol/L, the linear equation Ipa(mA)= -0.00187+0.05239 c(mmol/L) (R2=0.998), the detection limit 0.0647 μmol/L, and the sensitivity 950.36 μA·L/(mmol·cm2). Therefore, the prepared CuO CME shows a promise selectivity and reliability for detecting glucose.
Antireflective (AR) coatings, which can suppress the undesired interfacial Fresnel reflections, are widely used in optical devices and energy-related instruments. Conventional single-layer quarter-wave AR coatings, which only work at a single wavelength, have been seriously limited in some practical applications because of this inherent property. In this work, broadband AR coatings were designed and prepared based on the concept of λ/4-λ/2 double-layer interference film by Sol-Gel dip-coating method. Substrates (K9 glasses) coated with the double-layer films attained consistent high transmittances at 500-700 nm with an average transmittance of 99.4%, and the average transmittance at visible region was 99.0%. The λ/4-λ/2 broadband antireflective coatings were achieved without low-refractive- index materials. So high-refractive-index TiO2 could be introduced into the double-layer films to endow the films with self-cleaning property. The double-layer films exhibited outstanding superhydrophilicity with water contact angle of 2.2° in 0.5 s, and the superhydrophilicity lasted for 20 d in the absence of UV illumination. The double-layer coatings also showed a good ability to decompose organic substances under UV irradiation. The broadband of AR coatings with photocatalysis and durable superhydrophilicity may be applied in the fields of opto- and microelectronics.
Visible-light-driven photocatalyst BiVO4 was synthesized via a facile microwave-hydrothermal method using BiVO3·5H2O and NH4VO3 as raw materials. Crystal structure of BiVO4 photocatalyst could be selectively controlled to be tetragonal or monoclinic by simply adjusting the pH of the precursor solution. The prepared samples were characterized by XRD, UV-Vis, Raman, and SEM. The mechanism of BiVO4 formation with different crystal structures was discussed. Meanwhile, the photocatalytic performances of the prepared sample were evaluated by degradation of methylene blue and photocalytic oxidation of NO gas in air under visible light irradiation. The results showed that BiVO4(z-t) microsphere was obtained when the precursor pH is 3-5, but when the pH is less than 2 or greater than 7, the as-prepared powders are BiVO4(s-m) with polyhedron morphology. This may be due to the change of pH that could form transformation of vanadate and bismuth ion in the precursor solution, and then affect the formation process of BiVO4, resuting in the change of crystal structure, morphology, crystal surface, and VO4 tetrahedron of BiVO4(s-m). The photocatalytic tests indicated that the activity of BiVO4(s-m) was much better than that of BiVO4(z-t). The BiVO4(s-m) sample prepared at pH 9 exhibits excellent visible-light photocatalytic activity, because of its higher crystalline, preferentially exposed facts (040), and higher degree distortion of VO43- tetrahedron.
Pt/hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites were successfully synthesized by the steam-assisted crystallization and subsequent wetness impregnation method. Structural features were characterized by XRD, N2 isotherm, SEM, and TEM. Its catalytic behaviors for o-xylene storage at room temperature, and catalytic combustion of stored o-xylene at elevated temperatures were evaluated. It was found that crystallinity of the product underwent a reducing tendency after introduction of mesostructure, but the mesoporosity and pore volume were remarkably increased. Compared with Pt/conventional ZSM-5 zeolite, the o-xylene adsorption capacity of Pt/hierarchical HZSM-5 was around 8 times as that of the counterpart without mesostructure. Moreover, the Pt dispersion was improved due to mesoporosity. The highly dispersed Pt nanoparticles were beneficial for catalytic combustion of o-xylene. Futhermore, Pt/hierarchical ZSM-5 showed the efficient bi-functional performance during adsorption/catalytic combustion cycling process for o-xylene. Carbon balance was kept for three cycles without secondary pollutants, showing higher adsorption capacity and better reusing stability.
Acid sites located inside the 8-ring side-pockets of mordenite are highly active for DME carbonylation. However, mordenite deactivates very fast during the reaction because of non-selective reactions happening inside the 12-ring main channels of zeolites. In the present study, HMOR was treated by acid leaching using acetic acid of different concentration, with the purpose to selectively remove framework Al which is located inside 12-ring channels. Physicochemical characteristics of the parent and acid-treated mordenites were studied by complementary methods including: XRD, 27Al-NMR, NH3-TPD, pyridine IR, and N2 adsorption-desorption. The results show that the acid treatment, if appropriately applied, increases both the Si/Al and micropore volume of the samples, without significantly changing the mesopore size distribution. Most of the framework Al species in the 12-membered ring channels of HMOR were removed, without impacting those located inside the 8-ring channels. The catalytic results show that the initial activity of catalyst decreased slightly from 45.6% to 43.8%. On the other hand, the activity stability improved substantially, with stabilization period prolonged obviously from 18 h to 50 h.
The varied-valence nanocatalyst MnOx was prepared using the oxidation-reduction method under ultrasonic. The optimal synthetic conditions of MnOx were explored by adjusting the ultrasonic time, concentration of reaction precursor, drying temperature, and pH of reaction solution. The results indicated that the optimal sample MnOx was synthesized under the condition of ultrasonic time of 20 min, 0.5 mol/L KMnO4, drying temperature of 80 ℃ and pH=7, which showed the super catalytic performance and the time of 100% NO removal rate was as high as 15 h at room temperature. The structure and morphology of the optimal catalyst MnOx were investigated by XRD, N2-adsorption-desorption analysis, SEM and TEM. Besides, XPS and FT-IR were also applied to explore the catalytic oxidation process of NO removal and the deactivation mechanism of the optimal sample MnOx. It is believed that the interpenetrating and hierarchal pore, the petaloid morphology and weak crystallization structure contribute to the gas adsorption and transmission. The presence of varied-valence Mn and oxygen vacancy can improve the adsorption and activation of NO and O2, thus, enhancing the NO catalytic removal on the optimal catalyst MnOx at room temperature.
Hierarchical semiconducting metal oxide is highly active due to its special stereostructure, which is potential adsorbent for dye contaminants. Precursors of MoO2 hollow spheres were successfully synthesized via a simple and one-step solvothermal method. And hierarchical α-MoO3 hollow microspheres were obtained after subsequent calcination at 400 ℃. Diameters of the α-MoO3 microspheres were about 600-800 nm which were assembled by nanorods with a width of 70 nm. The as-obtained α-MoO3 nanomaterials presented excellent adsorption performance for methylene blue (MB). MB removal percentage attained 73.40% in the first 5 min when the concentration of α-MoO3 absorbent was 0.5 g/L in MB solution at the concentration of 20 mg/L. The equilibrium was established after adsorption for 60 min, and the removal percentages stabilized in the range of 97.53%-99.65%. Their adsorption kinetics was well fitted to a pseudo-second-order model. The adsorption isotherm conformed to Langmuir isotherm model, and the maximum uptake capacity was 1543.2 mg/g. The α-MoO3 microspheres are cost-effective, fast and complete for MB removal owing to its hierarchical and hollow nanostructures, which also can be employed for adsorption of other organic dyes in waste water.
Calcium polyphosphate fibers (CPPF) were prepared by melt-drawing method. Effect of B2O3 with different mass fraction on degradation and mechanical properties of CPPF was studied. The obtained CPPF were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Results showed that tensile strength and modulus of CPPF were improved obviously with increase of mass fraction of B2O3. Moreover, the surface morphology of CPPF was influenced by the introducing of B2O3. In addition, the degradation ratio and cracks on the surface of CPPF decreased with increase of B2O3 content. Tensile strength and modulus of CPPF with B2O3 loading of 9% increased sharply by 146% and 153% compared to neat CPPF, respectively. After 16 d, the mass loss ratio of CPPF with B2O3 loading of 9% in the degradation process is reduced by 31% compared to the neat CPPF.
Silica-based ceramic core was produced by fused silica as matrix material, corundum powder as mineralizer, and Al powder as additive. Effects of aluminum powder contents on the ceramic core regarding shrinkage rate, physical performance, and microstructure were investigated. Results showed that through sintering process, aluminum powder was oxidized to alumina, accompanying with volume expansion and weight gain, which reduced sintering and casting shrinkages of silica-based ceramic core. There is no obvious inhibitory effect on devitrification by Al powder in the sintering process. Due to increased looseness of core skeleton structure in the casting process, the high temperature creep deformation increased. The sample with 1wt% Al showed good comprehensive properties, of which three-dimensional direction of sintering shrinkage rate were 0.01%, 0.03%, 0.03%, respectively, and porosity rate, deflection bending strength were 28.58%, 0.57 mm, 12.1 MPa, respectively. All these data demonstrated that the new core materials can meet the requirement of directional solidification and be expected to improve the dimensional accuracy of the hollow turbine blade.
Optical transition properties of trivalent rare earth ions in transparent luminescent materials can be investigated via Judd-Ofelt analysis. The traditional Judd-Ofelt analysis can not be applied to nontransparent powders since its absorption spectra are unable to be measured. Therefore, in this study, a procedure for calculating the Judd-Ofelt parameters was proposed by using defuse-reflection spectrum. Firstly, the defuse-reflection spectrum was transformed into relative absorption spectrum based on Kubelka-Munk function, and then the relative Judd- Ofelt parameters were confirmed from the relative absorption spectrum, at last the actual Judd-Ofelt parameters were obtained by using fluorescence decay data for calibrating the relative values. The method proposed for Judd-Ofelt parameters’ calculation was applied to Lu2O3:Er3+ phosphor prepared by solid-state reaction, and the method was confirmed. The obtained Judd-Ofelt parameters were examined by comparing the radiative transition rates of 4I13/2 derived from the absorption cross section with which obtained from usual route by using the Judd-Ofelt parameters. The present study demonstrated that the proposed Judd-Ofelt analysis route is reliable and practical.
Here we report a novel surface modified bamboo charcoal/TiO2 (SMBC/TiO2) nanocomposites with high adsorption and photocatalytic property. SMBC were prepared by a wet oxidization method of cheap natural bamboo charcoal (BC) with good absorbent and chemical stabilities. After modification, high density of carboxyl groups were generated on the surface of BC, thus SMBC particles can be easily dispersed in water and have stronger interactions with TiO2 nanoparticles, which ensure SMBC uniformly coated on TiO2. And SMBC/TiO2 nanocomposties have much higher specific surface area than BC/TiO2, which could offer higher adsorption capacity. The saturated adsorption capacity of SMBC/TiO2 is approximately 1.6 times, 12.1 times as great as BC/TiO2 and pure TiO2, respectively. The synergetic effect of adsorption and catalysis endow SMBC/TiO2 composites much higher photocatalytic activity than BC/TiO2 and pure TiO2 for MB degradation, and the rate constant for MB photocatalytic degradation of SMBC/TiO2 was almost 7 times and 6 times as large as BC/TiO2 and pure TiO2, respectively.
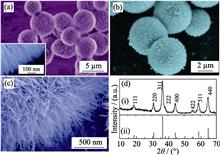
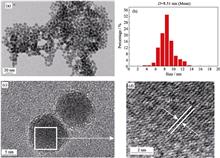
Sphere-like hierarchical Y zeolite was synthesized by a “steam-assisted conversion (SAC)” procedure. The as-synthesized samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), N2 adsorption-desorption, solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra, and Fourier transform infrared (IR) spectroscopy. Results observed by SEM displayed that the as-synthesized Y zeolite was sphere-like polycrystalline aggregates composed of primary crystals with size of about 50-300 nm. These results exhibited that some polycrystalline aggregates were hollow Y zeolite spheres. Combined with characterization results of FT-IR, 29Si NMR, SEM, and TEM, a mechanism illustrating formation of the hollow Y zeolite polycrystalline spheres was proposed.