Associated radioactive mines are widely distributed in China, with many industries, complex processes and technologies, close relationship with the public, and great impact on the radiation environment. They are relatively weak links in nuclear and radiation safety supervision. In the process of implementing the upper level document, some specific problems have to be faced, such as the definition of associated radioactive ore, the scope of associated radioactive ore development and utilization, etc. In the field of radiation environment supervision, there are issues such as effluent and radiation environment monitoring specifications that need to be solved. In particular, the treatment and disposal of associated radioactive solid waste is the key problem that currently restricts the sustainable development of associated radioactive ore development and utilization. The second national census of pollution sources reported the cumulative storage of associated radioactive solid waste in the country, and the radiation environment supervision situation is grim. In the scope of associated radioactive mines and some problems encountered in the supervision of radiation environment, this study aims to formulate a reasonable and feasible supervision system for associated radioactive mines, standardize supervision and management activities, and ensure the safety of the radiation environment according to scientific management methods, combined with the practice of supervision of associated radioactive mines. Suggestions on the definition of the scope and development and utilization of associated radioactive mines and the management of the inventory are put forward for solving the radiation environment supervision system with consideration on the storage period of associated radioactive solid waste, the management of nearby centralized disposal and disposal facilities. As the radiation environmental supervision of associated radioactive mines is still a relatively weak area in nuclear and radiation safety supervision system in China, radiation environmental impact assessment and environmental radiation self-monitoring need to be strengthened.
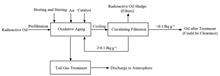
BackgroundRadioactive oil is one of the organic "difficult wastes" produced by the operation of nuclear power plants.PurposeThis study aims to develop a nuclide separation and treatment technology for radioactive waste oil and explore engineering application.MethodsFirst of all, a set of radioactive oil nuclide separation and purification treatment engineering equipments was developed and applied to obtain test samples collected from one NPP. Then a nuclide separation and purification process based on the oxidative aging method were developed. Finally, the high-purity germanium for nuclide γ spectrometer was employed to measure 58Co, 60Co, 54Mn, 110mAg, 137Cs, 134Cs, 124Sb, 125Sb, 59Fe, 95Zr, 95N, etc., γ nuclides, low background liquid scintillation counter was applied to the measurement of 3H and 14C, and high sensitive automatic liquid scintillation counter was used to measure 55Fe and 63Ni. Total α and total β were obtained by using low background α/β measuring instrument. [Results and Conclusions] The results show that the decontamination coefficient of the oxidative aging process reaches more than 2 orders of magnitude; the radioactive oil treated by the engineering device amounts to the clearance level, hence can be managed as ordinary hazardous waste. The additional dose that may be caused in the process of incineration (including transportation) for the treated radioactive oil is far below the dose limits, which meets the dosage guidelines for reuse, and is in line with waste minimization principles.
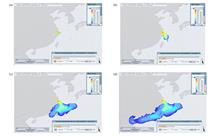
BackgroundIn the aspect of long-distance transport and deposition of airborne nuclear pollutants, Eulerian-Lagrangian method can combine the theoretical advantages of the Lagrange method and Euler method, but and there are few studies in China.PurposeThis study aims to verify the effectiveness of this method for long distance transport and deposition of airborne nuclear pollutants by simulating a nuclear leakage accident of one nuclear power plant in China.MethodsAssuming that a nuclear power plant in the eastern coastal area of China has a leakage similar to the Fukushima nuclear accident, the numerical simulation of the long-distance transport process of nuclear pollutants in the atmosphere was carried out by using the Euler-Lagrangian method of MATCH (Multi-scale Atmospheric Transport and Chemistry) module in JRODOS (Java Real-time On-line Decision Support) system. The results of surface deposition and the distribution of dose rate field were combined with the actual weather map to verify the trend.ResultsThe simulation and verification results show that the wet deposition plays an important role in the removal of nuclear pollutants, and the Eulerian-Lagrangian method can give the main characteristics of long-distance transport and deposition of nuclear pollutants in the atmosphere.ConclusionsThe simulation results are in good agreement with the actual weather trend, and this method can provide auxiliary reference for China's nuclear accident consequence assessment and emergency decision-making.
BackgroundThe current radiation dose calculation technology can only give 3D static dose results of upright human body, which cannot meet the needs of future accurate protection.PurposeThis study aims to achieve 4D dose calculation by establishing a complete method.MethodsFirstly, three algorithms, namely, the rotation matrix method, the volume graph Laplace operator method and the As-Rigid-As-Possible (ARAP) method, were employed to realize the deformation of mesh phantom. Then the phantom deformation guided by motion capture was investigated, and the tetrahedral cutting technology based on Delaunay algorithm was applied to the high speed Monte Carlo calculation. Finally, the 4D dose calculation application system was implemented and used for field test of nuclear power plant (NPP).ResultsThe comparison between the calculated and measured individual 4D dose values shows that the deviation of Hp(10) is less than 10%, and the deviations of Hp(3) and Hp(0.07) are less than 15% are verified.ConclusionsThe reliability and practicability of 4D radiation dose calculation of human body proposed in this study are verified by application results in specific radiation operation process in NPP, which is expected to achieve precise protection of personnel in the future scenarios such as NPP operation and maintenance, nuclear facility decommissioning and medical interventional treatment.
The associated radioactive waste residue has characteristics of long half-life of nuclides, wide range of radioactive levels, and so on. There are many industries involved in associated radioactive waste in China with wide sources, large types and quantities, hence restrict the healthy development of the industry. This study aims to propose effective safety disposal measures suitable for the complex physical and chemical properties of such waste residues, large differences in regional distribution and disposal status. Through comparison and analysis with hazardous waste, medium and low level radioactive waste, uranium mining and smelting waste, the technical support for the regulatory concept of associated radioactive waste residue was provided. The current disposal methods, design requirements, applicable scenarios, advantages-disadvantages and application examples of this kind of waste residue were systematically introduced, and the disposal strategies of associated radioactive waste residue were suggested. Meanwhile, a typical case of a regional disposal site project was taken as example, the characteristics of the project and waste residue were deeply analyzed, and the countermeasures were given to provide reference for relevant disposal work. Finally, based on above work, some suggestions are put forward to promote the final disposal of associated radioactive waste residue in China.
As a wide variety of radioactive materials with different characteristics and potential environmental risks existed, the domestic classification of radioactive items management was made, and The Classification and List of radioactive materials (Trial) was formulated. In order to optimize the classification of radioactive materials in China, the current situation of the classification of radioactive materials and classification basis at home and abroad were investigated. The main differences of classification basis were summarized and followed by analysis of problems existing in the classification of radioactive materials in China. New ideas and suggestions to solving the problems was put forward. First, the enumeration items such as radioactive sources and radioactive wastes in the classification of radioactive materials needs to be deleted. Second, the Classification and List is suggested to be revised by adopting the United Nation (UN) Number corresponding to different classifications of radioactive material which is unique and consistent with the international. Finally, a reference for the revision of The Regulations on the Safety Management of The Transportation of Radioactive Materials and The Classification and List of radioactive materials (Trial) is provided.
BackgroundIn the long-term uninterrupted work of the real-time on-line monitoring system of water radioactivity, the spectrum drift, line broadening and shift of peak position are caused by the temperature change of the detector and various electronic components and the aging of components, which leads to the difficulty of spectral line analysis and the error of analytical results.PurposeThis study aims to develop a calibration device for real-time on-line monitoring system of water radioactivity based on cerium bromide detector.MethodsThe device was designed to consists of 137Cs standard source (exemption source), lead block, lead chamber with calibration hole and linear motor. The optimum opening radius of the calibration hole and the optimum thickness of the lead block were obtained by Monte Carlo simulation. The standard 137Cs source was used as the standard reference peak, and the calibration of peak position and peak area, the peak position drift and peak area of 137Cs full-energy peak was analyzed by software with real-time gain calculation and parameters adjustment. Finally, the device was applied to the field application verification.Results & ConclusionsResults of Monte Carlo simulation indicate that the optimum radius of the calibration hole is 2.2 cm and the optimum thickness of the lead block is 5 cm. The verification results shows that the device can limit the change of peak position and peak area to ±1% and ±5%, respectively.
BackgroundWith the development of negative ion based neutral beam injection system (NNBI) for China fusion engineering test reactor (CFETR), the output power control system of its supporting the radio frequency (RF) power source is one of the key technologies to realize the improvement of its performance.PurposeThe study aims to design an improved output power control system of RF power source to solve the problems of output power stability and insufficient control accuracy in the use of existing RF power sources.MethodsThe software and hardware separation control structure designed by ARM+CPLD dual-core were employed to ensure the operation efficiency of the output power control algorithm of the RF power source and the communication stability of the peripheral equipment. Multi-stage progressive power control method and 12-bit digital signal were adopted to control the opening and closing of RF power amplifier, so as to realize high-precision control of output power. The capacitive voltage divider method and current transformer method were combined to accurately sample the actual output power of the RF power source for implementing high-stability control of output power with a closed-loop power control method. Meanwhile, the upper computer software design of man-machine interaction based on serial communication of self-defined protocol was adopted to complete the man-machine interaction function of output power control.ResultsThe control system has perfect human-computer interaction software function, and test results of the prototype RF power output power control system with simulation load show that the control accuracy of the output power is higher than 0.1% when the rated output power is 50 kW, and the stability fluctuation is less than 0.5%.ConclusionsThis scheme with impedance matching networks is expected to meet the performance requirements of CFETR NNBI RF power supply for output power control.
Background55Fe is a low-energy radionuclide that is difficult to measure and decays to a ground state of 55Mn through pure electron capture (EC), accompanied by the emission of Auger electrons and low-energy X-ray. As iron is the main component of nuclear reactor building materials, significant amounts of 55Fe have been produced in nuclear reactors and other neutron-producing nuclear facilities.PurposeThis study aims to develop an 55Fe nuclide standard through the absolute measurement of 55Fe activity and provides activity traceability services for 55Fe measuring instruments to ensure the accuracy and consistency of the measurement results of calibration instruments.MethodsThe liquid scintillation triple-to-double coincidence ratio (TDCR) method was applied to determining the activity of 55Fe. First, based on nuclear and atomic data of 55Fe, the electron deposition spectrum of 55Fe in a scintillator was calculated using a random atomic rearrangement model. Second, the counting efficiency of single-energy electron was computed based on the free parameter model. The total efficiency curve of 55Fe was then obtained by summing the efficiency of all deposited electrons. Finally, the experimental counting efficiency was derived by measuring the TDCR value and combining it with the total efficiency curve to realize an absolute measurement of 55Fe activity.ResultsThe experimental results show that correction factors for the asymmetric effect of photomultiplier tube (PMT) quantum efficiency obtained on test samples are between 1.001 and 1.005. The measured specific activity of 55Fe is 94.15 kBq?g-1 with a relative standard uncertainty of 0.45%. Experimental efficiency is better than 63% for double coincidence logic sum of liquid scintillation counter.ConclusionsThis study demonstrates that low relative standard uncertainty of 55Fe activity could be achieved using the liquid scintillation TDCR method with high detection efficiency, and more consistent measurement results can be obtained after applying the asymmetry correction of PMT quantum efficiency.
BackgroundSawtooth oscillations are macroscopic instabilities in plasma. To better control the sawtooth oscillation in an advanced experimental superconducting tokamak (EAST) device, it is necessary to develop sawtooth controlling methods that help improve the confined performance of plasma in the EAST device.PurposeThis study aims to analyze sawtooth behavior under the on-axis heating by ion cyclotron resonance frequency (ICRF) wave in the EAST device.MethodsFirst of all, the soft X-ray integrated signal intensity data was used to analyze the sawtooth period and amplitude. The radius of q=1 surface and the plasma pressure gradient at q=1 surface were calculated using a soft X-ray intensity profile. Then the neutron yield flux was obtained from the neutron yield flux diagnostic data. Finally, the equilibrium reconstruction results of the equilibrium fitting algorithm (EFIT) were combined with polarimeter-interferometer (POINT) diagnostic data to investigate the relationship between the variation of ICRF and plasma current density.ResultsExperimental results show that the sawtooth period is positively correlated with the ICRF power, and the variation in sawtooth period is roughly same as that in sawtooth amplitude and plasma pressure gradient at q=1 surface. The ICRF power needs to exceed 0.8 MW to change the radius of q=1 surface. The sawtooth period and q=1 surface with ICRF power change are more sensitive under solely ICRF heating than under ICRF+lower hybrid wave (LHW)+electron cyclotron resonance heating (ECRH).ConclusionsSawtooth behavior of EAST plasma is affected by the fast ions produced by ICRF and the radius change of q=1 surface.
BackgroundNuclear critical safety analysis is the key technology to ensure the safety of spent fuel reprocessing plant. However, the present critical safety analysis codes for solution system are either limited in the geometric scope of application, or have poor engineering practicability due to low computational efficiency.PurposeThis study aims to develop a method suitable for wide application range and high accuracy for nuclear critical safety analysis, so as to provide technical support for spent fuel reprocessing plant.MethodsAccording to the characteristics of spent fuel solution system, a set of methods, such as the zero-dimension cross-section calculation and whole system group condensation model, the three-dimensional space-time neutron dynamics model based on PCQS, and the R-Z two dimensional thermal and radiolysis gas simulation model, were combined to establish a paralleled 3D critical safety analysis code hydra-TD. In addition, some experiments of SILENE facility at France were modeled and calculated by using hydra-TD code to verify its effectiveness.ResultsThe verification results indicate that there are very small errors of key parameters such as the first fission power peak, multiplication time and total fission times.ConclusionThe code hydra-TD developed in this study can be applied to simulation of the multi-physics processes in the critical transients of the fuel solution, hence has the ability of critical safety analysis.
BackgroundCompared with conventional rod-type nuclear fuel, annular fuel has higher power density and better heat transfer efficiency, which can significantly improve the safety and economy of the reactor.PurposeThis study aims to investigate the effect of ring fuel element geometry on the thermal performance and to correct the initial parameters.MethodsThe initial parameters of the ring fuel element were set and the thermal conductivity calculation program of the ring fuel element was prepared. The effects of the ring fuel flow distribution ratio, inner and outer cladding thickness, inner and outer air gap thickness and core block thickness on the thermal performance of the ring fuel element were investigated by three evaluation criteria developed and geometric corrections are made.ResultsAppropriately increasing the flow distribution ratio, decreasing the inner casing thickness, increasing the outer casing thickness, decreasing the inner and outer air gap spacing and decreasing the core block thickness can improve the thermal performance of the components; setting the flow distribution ratio to 1, the inner casing thickness 0.06 cm is amended to 0.04 cm, the outer casing thickness 0.06 cm is amended to 0.07 cm, the inner and outer air gap spacing 0.035 cm. The thickness of core block is amended to 0.5 cm.ConclusionsThermal performance of annular fuel elements is significantly improved after appropriate geometry correction is made.
BackgroundAmong the mitigating strategies for severe accidents, the in-vessel retention (IVR) is one of the useful remission measurements. The key point to evaluating IVR is to analyze that the final steady-state thermal load of the melt does not exceed the critical heat flux (CHF), which occurs during boiling heat transfer on the outer wall of the lower head, and the remaining wall thickness of the lower head can carry the melt to prevent the structural failure.PurposeThis study aims to analyze heat transfer of the reactor pressure vessel (RPV) lower head under severe accidents by using ASTEC code.MethodsFirst of all, the composition and mass of the molten substance were assumed to be UO2, 92 353.29 kg; Fe, 43 000 kg; Zr, 23 133.9 kg; Zr oxidation, 41.8%, for a large advanced pressurized water reactor (LAPWR). With the heavy metal oxide layer and metal layer of stable molten pool in the lower RPV of this LAPWR, the average value of core decay power and the physical properties of molten materials in RPV were input as the condition boundaries for ASTEC, the middle break accident sequence was selected for the calculation of the thermal parameters of the coolant, the outer wall CHF and the final thickness of the lower head. Then, the CHAWLA-CHAN heat transfer relationship was used to calculate the heat transfer coefficient between the melt and the inner wall of the lower head. The key safety related issues such as the heat transfer parameters of the outer wall of the lower head, the heat transfer through the lower head, and the wall thickness of the lower head were analyzed. Finally, the IVR effectiveness was estimated by the thermal properties and the structure of the lower head.ResultsWhen the decay power is 21 MW and the core molten pool is divided into two layers, the average thickness of the oxide layer is 1.6 m, and the metal layer is 0.8 m. The results show that the heat exchange is more intense in the upper part of the lower head, and the maximum value of the heat flux occurs at the junction of the two melt layers, which the corresponding surface angle is 77.5°~80°. The inner wall of the lower head will be melted by the molten metal layer in the location of the minimum thickness of the lower head, and the final remaining thickness is less than 2.0 cm.
BackgroundWith advantages of low system pressure, stable operation and good economic performance, molten salt heat exchanger has recently been widely applied to the field of energy as concentrating solar power, nuclear power engineering, high temperature hydrogen production, and so on.PurposeThis study aims to analyze the thermal stress generated in the main components of the U-tube heat exchanger due to the high operating temperature of the molten salt and the large temperature difference between the hot and cold fluids.MethodsFluid-thermal-solid coupling method was adopted in this study. First of all, the main thermal performance parameters of the heat exchanger were obtained by using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) computation, and compared with experimental results to verify the accuracy of the CFD fluid simulation results. On this basis, the heat transfer process was analyzed in details for the molten salt tube-shell heat exchange under the operating condition, and the flow field and temperature field of the heat exchanger were obtained. Finally, the stress field generated by the coupling of flow field, pressure field and temperature field was calculated by Ansys workbench finite element software, and the stress distribution of the tube sheet connected with the heat exchange tube and shell was emphatically analyzed to find the maximum stress value of the tube sheet and the stress change rule of some paths.ResultsThe result shows that the CFD fluid simulation method is feasible with a maximum deviation of 3.07%. The larger stress is found at the connection area between the tube plate and the non-tube, which is located near the inner tube wall on the shell-side with about 2 mm away from the lower surface of tube plate.ConclusionsResults of this study provides important reference for the actual operation and structural deign of molten salt heat exchanger.