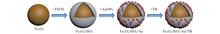
In order to detect terbutaline (TB) quickly and sensitively, a nuclear-satellite nanostructured Fe3O4/SiO2/Au-MNPs magnetic substrate was prepared for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) detection. The linear relationship between the concentration of terbutaline and the intensity of the Raman spectrum was investigated by magnetic separation andpH adjustment of the system and a calibration curve was drawn. The experimental results showed that the detection limit of TB using the core-satellite magnetic SERS substrate was 3.77 × 10-10 mol/L. The detection had a linear relationship with the concentration range from 5×10-5 mol/L to 5×10-9 mol/L. The linear correlation coefficient R2 obtained by least square fitting was 0.996. The preparation method of the composite material was simple and easy, which provided inspiration for the synthesis of other nanocomposite materials.
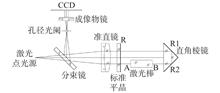
Due to the special shape characteristic of a laser rod, the traditional double-pass test method, which has high sensitivity, tends to have obvious diffraction effect and edge black ring caused by multiple imaging. The result leads to the reduction of the effective measurement area, which has a negative impact particularly on the measurement of small aperture optical components. To avoid these problems, the wavefront aberration of laser rod is measured by the single-pass method. The right-angle prism is used as the reflection part to ensure the test light passes through the laser rod only once, so that the number of equivalent circular holes and the imaging times can be reduced. We use the expanded multi-hole model to discuss the diffraction effect and analyze the cause of edge overlap from the perspective of imaging to derive the advantages of the single-pass method. In addition, considering the matching of the reference light and the test light, it is necessary to rotate the right-angle prism by at least 5.40° to improve the contrast of the interferogram. Finally, the measurement result of the laser rod wavefront was as follows: the peak-valley value is 0.068λ and the root mean square is 0.012λ.
Thermostat, as the automatic temperature control device of the cooling system of the engine, has an important effect on the engine. In order to solve the problems in traditional mechanical thermostat performance detection, such as data deficiency, low measuring accuracy, high security risk, and inconvenience to operate. We find a non-contact way to get the real time lift of the thermostat based on laser ranging technology, and get the synchronous temperature by the temperature sensor. In this way, we can obtain the complete data of the thermostat. This method is an accurate, safe, convenient, and non-contact way, temperature measurement accuracy is 0.1 °C, and lift measurement accuracy is 1 mm. We setup a thermostat detection system and verify it by experiments with the Jiefang J6 thermostat. The result shows this system can detect the performance of thermostat accurately and efficiently, such as temperature stability, performance consistency, and fault diagnosis criterion. It is applicable to ordinary engine maintenance as well as educational practices.
In order to solve the problem of difficulty in preparation of gallium selenide (GaSe) crystals and poor chemical properties, the traditional chemical vapor deposition (CVD) preparation method for GaSe crystal is improved, and the moving heating source method for preparing GaSe crystal is adopted. A movable device for preparing GaSe crystals is built, driven by a single-chip microcomputer. The parameters such as heating temperature and moving position of the high-temperature furnace for preparing crystals are precisely controlled, and the characterization of the prepared GaSe crystal is carried out by optical microscopy (OM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). According to this research, the monolayer smooth-faced large two-dimensional GaSe crystal is obtained by moving the heating source method. Due to the automatic precision movement of the electromechanical equipment, the high-quality large-scale production of monolayer two-dimensional GaSe crystals is realized, which is conducive to the wide application of GaSe crystals in optoelectronics and nanoelectronics.
A series of molecular dynamics (MD) simulation are performed to study the surface deformation behavior of silicon substrate scratched by an atomic force microscopy (AFM) probe. A modified MD model is established, a quantitative index is proposed to describe the pile distribution, and the structure recognition algorithm is used to reveal the generation process of non-crystal layer. On these bases, the effects of scratching velocity, tip radius and probe wedge angle on the scratching process are investigated. Results show that (1) The scratching velocity has little effect on the groove surface. The piles on substrate surface are the least when the scratching velocity is less than 0. 3 nm/ps or greater than or equal to 1.5 nm/ps. (2) The probe wears and tears when the tip radius is less than or equal to 1 nm. The probe deforms elastically when the tip radius is greater than or equal to 1.5 nm. The tip radius should be 2-3.5 nm for the best scratching results. (3) The large wedge angle helps to reduce the piles distributed on the substrate surface.
Based on the theory of near-field scanning detection, a scattering terahertz scanning near-field optical microscopy (THz s-SNOM) system is designed and built. The system achieves nanoscale spatial resolution, breaking the diffraction limit. Using a frequency multiplier module with an operating frequency of 0.1-0.3 THz as the emission source, the THz beam is focused onto the tip of an atomic force microscope (AFM) probe. The tip of the needle acts as a nano-light source, interacting with the sample. After the evanescent waves are converted into radiation waves, they are collected by the parabolic mirrors and imaged point by point in the far field. The topography image of the sample surface and the near-field amplitude map without background can be obtained simultaneously. The resolution of the system depends on the tip radius of the AFM probe, which is independent on the wavelength of the beam used. The near-field image obtained by scanning different samples shows that the resolution is less than 60 nm and spatial resolution achieves λ/26 000.
The impedance characteristics of the fiber-optic gyroscope (FOG) source die are non-linear. In order to ensure the stability of the optical wavelength and output optical power, it is necessary to control the die injection current to be constant. In this paper, after analyzing the super luminescent diode (SLD) light source die, the corresponding constant current driving circuit is designed by using LM324 as the core device, and an experimental test is conducted. The experimental results show that the constant current driving circuit can meet the performance requirements of medium and low precision, low power FOG with the change of the constant environmental temperature. The average output voltage at normal temperature is 100.242 mA, and the relative difference is 0.013 7%.
Aiming at the measurement of the moving velocity of two-phase flow particles, a dual-path laser velocimetry experimental system was designed based on the principle of cross correlation, and an optical cross correlation velocimetry experiment was carried out by using a known rotating linear velocity device driven by a variable frequency motor. By measuring the intensity signal of the dual-path lasers around the rotating wire, rotation line velocity of wire at the measured point was calculated by the cross correlation analysis of the two intensity signals of the dual-path lasers. Compared with the calculated line velocities of wire at the measured point by using the rotate speed of motor, the relative deviations were less than 6%, verifying the accuracy of optical mutual light velocimetry.
Aiming at the detection of water pollution, an online real-time detection system of water turbidity based on STM32 is designed. Based on the transmission method in ISO7027—1984, the system determines the turbidity of water samples by measuring the attenuation of the transmitted light intensity by striking a beam of light into a water sample with a certain thickness. The experimental results show that the average relative error between the actual measured value and turbidity standard liquid value is less than 4%. It is feasible to realize the real-time monitoring of water turbidity. The designed system has the advantages of low cost, small volume, convenient carrying, and simple detection mode, and can be used for water quality monitoring in daily life.
Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) can obtain the far-infrared spectrum of the material and identify the unknown samples according to its fingerprint characteristic spectrum. In this experiment, FTIR was used to test the absorption spectra of five standard drugs, such as cocaine, ketamine hydrochloride, cannabinol, heroin and morphine, in the far-infrared band (30-350 cm-1) under vacuum conditions, and some absorption peaks were described and analyzed. The results show that the five standard drugs have obvious characteristic absorption peaks in the far infrared band. This study provides a data basis for the establishment of far infrared spectrum database for drug identification.
In order to realize the clinical detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in vivo, real time and earlier, a normal liver cell line L02, a low-metastatic-potential hepatocellular carcinoma cell line MHCC97-L and a high-metastatic-potential hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HCCLM3 were measured, respectively, based on the established fiber confocal back scattering micro-spectrometer (FCBS). The principal component analysis (PCA) and the support vector machine (SVM) algorithm were used to classify the acquired spectrums, respectively. The PCA was used to study the spectrum in wavelength range of 500-900 nm. The first two of the principal components have taken 95.4% of the whole information; therefore, the three kinds of cell distribution were distinguished obviously on the scores diagram of principal component. 69 object data were chosen randomly to train the SVM classification model. 50 sets of these data were used as training sets and 19 sets were used as testing sets. The classification accuracy of the model has reached 94.7%. These results have indicated that the back-scattering micro-spectra of cells measured by fiber confocal back scattering micro-spectrometer (FCBS) combined PCA or SVM could classify liver cancer cells with different metastatic potential automatically. This will provide the necessary testing tools for the research of hepatocellular carcinoma cell in vivo and real time.
To compare the imaging effects between compressed sensing ghost imaging (CGI) and pseudo-reverse ghost imaging (PGI) and explore the effect of morphological weight adaptive on correlated imaging to remove noise. Different images were selected, and simulation experiments were carried out by MATLAB software. The target images were sampled with 64, 256, 512, 1 024, 2 048, and 3 000 rate respectively. The images were reconstructed by correlation imaging, compressed sensing ghost imaging and pseudo-reverse ghost imaging. The two methods to reconstruct the image effect, and then using the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and correlation coefficient (CC) as the quantitative indicators, the compressed sensing ghost imaging and pseudo-reverse ghost imaging were used under different usage times. A comparative analysis was conducted. At the same time, in the experiment, morphological weighted adaption was used to remove noise from compressed sensing ghost imaging. pseudo-inverse ghost imaging is better than compressed sensing ghost imaging in the case of low-order sampling. Under high sampling rate, the imaging effect based on compressed sensing ghost imaging is better, but in the actual reconstruction, compressed sensing ghost imaging still has noise, and the morphological weight adaptation can effectively remove the noise in the ghost imaging experiment.
High-throughput colony sorter is an important equipment for bacteria screening in the biopharmaceutical industry. It uses colony image for intelligent identification and selection, but at present, the equipment only recognizes two-dimensional location information. In order to solve the problem of three-dimensional colony information extraction, this paper proposes a monocular image colony depth extraction algorithm based on transfer learning. The algorithm is based on residual network, combined with multi-scale network structure to extract features, and adopts unsupervised transfer learning training mode, so that the network can estimate the colony depth information. The experimental results show that the average relative error of the algorithm is 0.171, the root mean square error is 6.198, and the log root mean square error is 0.256. The accuracy of the results under the threshold value of 1.25 is increased to 76.4%. The algorithm can obtain the depth information and surface characteristics of the colony at the same time, which provides a referencefor further improving the screening accuracy and effectively selecting the colony.
Due to the influence of expressions, illuminations, gestures, etc., large errors often occur when positioning key points of a face. In order to accurately locate the key points of the face, a detection algorithm for key points on a face based on attention mechanism is proposed. Firstly, the deformable part model(DPM) algorithm is used to detect the face region in the picture, and then the focal point of the face is located in the region using ResNet and SeNet. The experimental results show that the algorithm achieves good accuracy on the face dataset, and prove the effectiveness of the algorithm.
With the development of sensor technology, information acquisition and processing technology, internet technology, portable, intelligent, networked, precise and modular monitoring equipment have gradually become the development trend of physiological parameters. By investigating the research results and market trends in the field of physiological parameter monitoring in recent years, this paper summarizes the research status of physiological parameter monitoring technology and monitoring equipment, analyses the problems and challenges it faces, points out its future development trend, and puts forward the prospect of future work. The purpose is to provide references for the study of physiological parameters monitoring and to pave the way for the further development of this field.