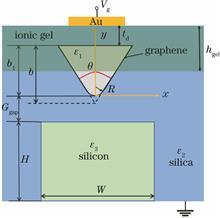
This paper proposes a plasmonic waveguide with a triangular-shaped graphene-coated nanowire integrated on the silicon substrate. The transmission properties of the fundamental graphene plasmon mode and their dependence on the geometric and physical parameters are fully investigated by the finite element method. The results show that the gap distance, vertex angle, corner radius, and chemical potential of graphene have significant influences on the modal transmission properties. By optimizing the design, the proposed structure can be used to achieve the deep-subwavelength modal field transmission with a propagation length of up to 10 μm and a normalized mode area of only about 10 -6. The proposed graphene plasmonic waveguide may offer a certain theoretical basis for the design of tunable nanophotonic devices.
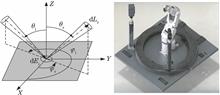
In this study, a sub-aperture scanning Fourier transform system is proposed for performing the fast measurement of the bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF). The sub-aperture scanning Fourier transform method that uses a single Fourier transform lens exhibits an expanded single-measurement field of view, a long working distance, and a low cost. Furthermore, the system is simple; thus, rapid and effective measurement of the BRDF can be realized over a large space frequency range. When compared with the angular subdivision spectroradiometer method, the proposed method exhibits higher sensitivity, accuracy, and detection speed. The scattered light field on the sample plane was evaluated through sub-aperture scanning, and numerical splicing was conducted in the Fourier space; the BRDF angle measurement range was expanded. Finally, the proposed method was verified based on the experimental data. The experimental results denote that the relative error between the proposed method and the angular subdivision spectroradiometer method is less than 1%. Further, the measurement time of the proposed method is 1/10 of that of the angular subdivision spectroradiometer method, and the system accuracy can become 0.005°. These results provide theoretical basis and technical support for the application of sub-aperture scanning Fourier transform systems in BRDF measurement.
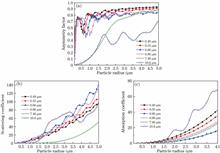
In this paper, the transmission characteristics of polarized light in Martian dust are investigated. First, the relationship among the particle scattering coefficient, absorption coefficient, asymmetry factor, and particle size of Martian dust is analyzed. Then, the multiple scattering of polarized light in the Martian atmosphere is simulated using polarized Monte Carlo method. The effects of wavelength, particle size distribution, wind speed, height, and particle number concentration on the transmission characteristics of polarized light are calculated and analyzed. The results show that the degree of depolarization of polarized light increases with the increasing transmission distance, and the greater the particle number concentration, the more severe the depolarization degree. When the wavelength is 0.55 m, the depolarization of the selected two groups of particle size distribution is serious for the small effective particle size, and the depolarization difference corresponding to the wind speeds of 15.3 m/s and 1.7 m/s is nearly two orders of magnitude. The polarization retention of 7.46 μm laser is the best in the six selected wavelengths, and the 0.66 μm laser has the highest transmittance in the Martian dust.