View fulltext
View fulltext
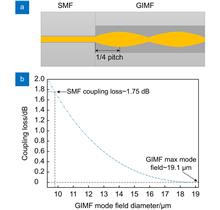
This paper presents a low-loss fusion splice method between the nested hollow-core anti-resonant fiber (HC-ARF) and single-mode fiber (SMF) by introducing a graded-index multi-mode fiber (GIMF) as a transition fiber. The mode field matching between the nested HC-ARF and the SMF is achieved by using the GIMF as the mode field adapting fiber and expanding the mode field in the SMF by using its self-imaging effect. The effects of discharge time and discharge power on fusion splice loss during fusion splicing are explored in the experiments. Based on an optimized fusion splicing scheme, the integrity of the microstructure of the nested HC-ARF fusion splicing end face is effectively protected, and the average fusion splicing loss is as low as 0.60 dB. The experimental results provide a reference to improve the compatibility of the nested hollow-core anti-resonant fibers with the existing fiber system.
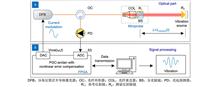
A fiber microprobe vibration measurement system based on internal modulation has been developed. A sinusoidal phase modulated laser source is generated by modulating the current of the distributed feedback laser (DFB) with a sinusoidal signal. After passing through a fiber circulator and a fiber microprobe, the output laser beam is used to measure the displacement of a vibration source. The returned laser beam interferes with the reference laser reflected by the fiber microprobe to generate a phase generated carrier (PGC) interference signal. A real-time PGC signal processing algorithm is designed through a programmable logic gate array (FPGA) digital computing platform. A five-parameter ellipse fitting method is unitized to extract the error items introduced by additional intensity modulation and other factors and compensate for the phase nonlinear error. The fast Fourier transform (FFT) algorithm is unitized to analyze the vibration displacement. Theoretical analysis was conducted and a vibration measurement system was built. A series of experiments were conducted, including PGC signal demodulation, displacement measurement, and vibration measurement. The experimental results show that the vibration frequency range of the system covers 1142 Hz. In the 10 μm step displacement experiment, the average deviation measured is 0.173 μm. The resolution of vibration measurement is 1.221 Hz, and the harmonic distortion is less than 1.36%. The measurement system is expected to be applied in the field of precise vibration measurement.
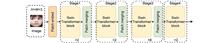
A lightweight Swin Transformer and multi-scale feature fusion (EMA) module combination is proposed for face expression recognition, which addresses the problems of the Swin Transformer model, such as excessive parameter quantity, poor real-time performance, and limited ability to capture the complex and small expression change features present in the expressions. The method first uses the proposed SPST module to replace the Swin Transformer block module in the fourth stage of the original Swin Transformer model to reduce the number of parameters of the model and realize the lightweight model. Then, the multi-scale feature fusion (EMA) module is embedded after the second stage of the lightweight model, which effectively improves the model's ability to capture the details of facial expressions through multi-scale feature extraction and cross-space information aggregation, thus improving the accuracy and robustness of facial expression recognition. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves 97.56%, 86.46%, 87.29%, and 70.11% recognition accuracy on four public datasets, namely, JAFFE, FERPLUS, RAF-DB, and FANE, respectively. Compared with the original Swin Transformer model, the number of parameters of the improved model is decreased by 15.8% and the FPS is improved by 9.6%, which significantly enhances the real-time performance of the model while keeping the number of parameters of the model low.
Aiming at the issues of discontinuous road edge segmentation, low accuracy in segmenting small-scale roads, and misclassification of target roads in high-resolution remote sensing imagery, this paper proposes a road extraction method that integrates ResNeSt and multi-scale feature fusion for road extraction from remote sensing imagery. Referencing the ResNeSt network module, a U-shaped network encoder is constructed to enable the initial encoder to extract information more entirely and ensure more continuous segmentation of target edges. Firstly, Triplet Attention is introduced into the encoder to suppress useless feature information. Secondly, convolutional blocks replace max pooling operations, increasing feature dimensionality and network depth while reducing the loss of road information. Finally, a multi-scale feature fusion (MSFF) module is utilized at the bridge connection between the encoder and decoder networks to capture long-range dependencies between regions and improve road segmentation performance. The experiments were conducted on the Massachusetts Roads dataset and the DeepGlobe dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method achieved Intersection over Union scores of 65.39% and 65.45%, respectively, on these datasets, representing improvements of 1.42% and 1.74% compared to the original MINet model. These findings indicate that the ResT-UNet network effectively enhances the extraction accuracy of road features in remote sensing imagery, providing a novel approach for interpreting semantic information in remote sensing images.
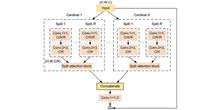
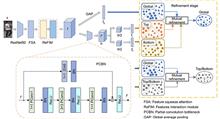
To address issues of insufficient receptive fields and weak connections between global and local features in unsupervised domain adaptive person re-identification, a multi-scale feature interaction method was proposed. Firstly, the feature squeeze attention mechanism compressed image features, which were then fed into the network to enhance rich local information representation. Secondly, the residual feature interaction module encoded global information into the features by interaction, while increasing the model's receptive field and enhancing its ability to extract pedestrian features. Finally, a bottleneck module based on partial convolution conducted convolution operations on the part of the input channels, reducing redundant computations and improving spatial feature extraction efficiency. Experimental results on three adaptation datasets demonstrate that the method mAP reached 82.9%, 68.7%, and 26.6%, the Rank-1 reached 93.7%, 82.7%, and 54.7%, the Rank-5 reached 97.4%, 89.9%, and 67.5%, by comparison with baseline, respectively, demonstrating that the proposed method allows for better pedestrian features representation and improved recognition accuracy.
A dynamic SAR image target detection algorithm integrating space-frequency domains is proposed to address challenges such as significant feature differences in SAR image samples, imbalanced target scales, and high speckle noise in the background, which result in low detection accuracy and slow inference speed. First, a dual-stream perception strategy constructs spatial-frequency perception units, leveraging dynamic receptive fields and fractional-order Gabor transforms to enhance the model’s ability to capture spatial diversity and frequency scattering features. This way improves the retention of global contextual information, accelerates inference, reduces the similarity of feature mapping patterns, and mitigates background noise interference, effectively reducing missed and false detections. Second, a re-parameterization-based adaptive feature fusion module is designed to optimize interactions across multi-scale features, enriching feature diversity, alleviating mapping discrepancies and information loss caused by feature sampling, and enhancing the salience of small target and key frequency information during fusion, thereby improving detection precision. Finally, the DY~~IoU dynamic regression loss function is introduced, utilizing adaptive scale penalty factors and a dynamic non-monotonic attention mechanism to address anchor box expansion and positional deviation, further enhancing the localization and detection capabilities for multi-scale targets. This way also accelerates model convergence and reduces computational overhead. Experiments conducted on the public datasets SAR-Acraft-1.0 and HRSID demonstrate that the proposed method achieves mAP@0.5 values of 95.9% and 98.8%, respectively, representing 5.2% and 1.2% improvements over baseline models and outperforming other comparison algorithms. These results indicate that the proposed algorithm improves detection accuracy and exhibits strong robustness and generalization capabilities.
To address the low efficiency in metal surface defect detection, and the problems related to numerous model parameters and low precision, a lightweight detection method based on an improved YOLOv8n was proposed. The partially inverted bottleneck cross-stage partial fusion (PIC2f) module was introduced, replacing the bottleneck module with a partial IRMB bottleneck (PIBN) module. This combination of partial convolution and inverted residual blocks reduced the algorithm’s parameters and enhanced the model’s feature extraction ability. The attention-based intra-scale feature interaction (AIFI) module was applied, integrating location embedding and multi-head attention to improve the model’s small-target detection performance. Lastly, the average pooling down sampling (ADown) module replaced traditional convolution as the feature reduction module, reducing parameters and computational complexity while maintaining detection accuracy. The experimental results show that, compared to YOLOv8n, the PIC2f-YOLO method improves mAP50 by 2.7% on the NEU-DET steel defect dataset and reduces parameters by 0.403 M. Generalization experiments on aluminum sheet surface industrial defects, PASCAL VOC2012 and surface defects of strip alloy functional material datasets also confirm the method’s effectiveness.
Due to the low high air pressure during the flight, if a fire occurs in the cargo hold of the aircraft, the smoke particles are suspended in mid-air. The traditional smoke detector is difficult to detect, and there is also a high false alarm rate and difficult visualization in other environments, an image-based fire detector was designed, and the improved YOLOv5s algorithm was used to realize the pyrotechnic target detection. First, the backbone network is replaced with a lightweight GhostNet backbone network to facilitate hardware deployment. A collaborative attention module is embedded in the connection between the backbone and the converged network to strengthen the extraction of effective features. Then, according to the development and change characteristics of fire targets, the C3 structure in the feature fusion network was improved, the VoV-GSCSP module was built, and the Slim-ASFF module was embedded between the fusion network and the detection head, so as to jointly strengthen the feature fusion of different scales and realize the further lightweight of the overall network. Finally, the regression loss is replaced by focal EIOU, which solves the problem of penalty term failure and improves the prediction ability of positive samples. The image-based aviation fire detector takes the domestic AI chip RK3588 as the core, connects to the CMOS image sensor for data collection, and realizes information interaction with the airborne display system through the network. The test results show that the equipment can be arranged at the top four corners of the cargo compartment of the simulated aircraft, which can realize the flame alarm within 10 seconds and the smoke alarm within 20 seconds, which provides a feasible solution for ensuring the safety of the aircraft.
This paper proposes a smartphone image quality assessment method that combines the Swin-AK Transformer based on alterable kernel convolution and manual features based on dual attention cross-fusion. Firstly, manual features that affected image quality were extracted. These features could capture subtle visual changes in images. Secondly, the Swin-AK Transformer was presented and it could improve the extraction and processing of local information. In addition, a dual attention cross-fusion module was designed, integrating spatial attention and channel attention mechanisms to fuse manual features with deep features. Experimental results show that the Pearson correlation coefficients on the SPAQ and LIVE-C datasets reached 0.932 and 0.885, respectively, while the Spearman rank-order correlation coefficients reached 0.929 and 0.858, respectively. These results demonstrate that the proposed method in this paper can effectively predict the quality of smartphone images.