View fulltext
View fulltext
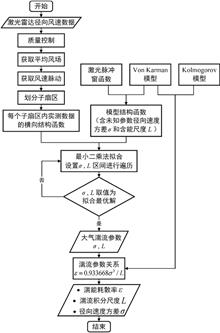
Atmospheric turbulence is widespread in the atmosphere, in which the slant turbulence has a significant impact on aerospace and military activities. On the one hand, the high spatial and temporal resolution wind field data obtaine
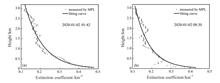
In order to enrich the measurment methods of aerosol optical depth of the whole atmosphere layer, a detection method integrating micro-pulse lidar and surface visibility data is proposed. In the method, the aerosol vertical extinc
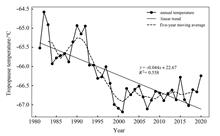
Based on NCEP/NCAR monthly reanalysis data from 1981 to 2020, the temporal and spatial variation characteristics, as well as the seasonal variations, of tropopause temperature over China in recent 40 years were studied. Linear reg
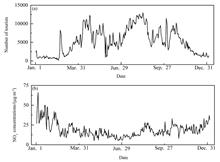
To quantitatively study the impact of short-duration high-strength human tourism activities on urban air quality, a novel model (EEMD-DCCA) integrating ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) and detrended cross-correlation a
To explore the characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 in Chengdu, China, and their relationship with meteorological factors, monthly average concentrations of PM2.5 and PM10 in Chengdu from 2015 to 2018 were collected, and their relati
The aerosol optical depth (AOD) product of Himawari-8 satellite can be used to estimate PM2.5 concentration near the earth surface with wide spatial coverage and high temporal resolution. Based on the three-dimensional variational
According to the problems that the change of temperature can affect the observation results of sun photometer and the temperature correction coefficient is inconvenient to obtain, a temperature control system of automatic sun phot
An organic matter detection system based on hydrogen flame ionization detection method is designed. The working principle of the system is introduced firstly, and then the structural design of the system is optimized based on the