View fulltext
View fulltext
Single molecules embedded in solid-state matrix have been actively investigated as model systems for fundamental molecular physics and as sources of single photons. In particular, single dibenzoterrylene molecules in crystalline anthracene matrix have been demonstrated as definite stable single-photon emitters with nonblinking emission and lifetime-limited linewidth at cryogenic temperatures. However, as a critical piece of information, their quantum efficiency has not been experimentally measured at the single-molecule level. Here, by monitoring the fluorescence lifetime change during the natural sublimation process of the anthracene matrix and its thickness, we experimentally probe the fluorescence quantum efficiency of single dibenzoterrylene molecules. Such a simple approach might be applicable to other solid-state single-molecule systems.
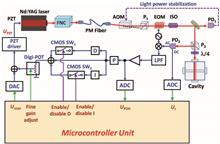
We report two ultra-stable laser systems automatically frequency-stabilized to two high-finesse optical cavities. By employing analog-digital hybrid proportional integral derivative (PID) controllers, we keep the merits of wide servo bandwidth and servo accuracy by using analog circuits for the PID controller, and, at the same time, we realize automatic laser frequency locking by introducing digital logic into the PID controller. The lasers can be automatically frequency-stabilized to their reference cavities, and it can be relocked in 0.3 s when interruption happens, i.e., blocking and unblocking the laser light. These automatic frequency-stabilized lasers are measured to have a frequency instability of 6×10-16 at 1 s averaging time and a most probable linewidth of 0.3 Hz. The laser systems were tested for continuous operation over 11 days. Such ultra-stable laser systems in long-term robust operation will be beneficial to the applications of optical atomic clocks and precision measurement based on frequency-stabilized lasers.
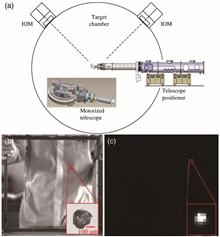
In-situ laser-induced surface damage inspection plays a key role in protecting the large aperture optics in an inertial confinement fusion (ICF) high-power laser facility. In order to improve the initial damage detection capabilities, an in-situ inspection method based on image super-resolution and adaptive segmentation method is presented. Through transfer learning and integration of various attention mechanisms, the super-resolution reconstruction of darkfield images with less texture information is effectively realized, and, on the basis of image super-resolution, an adaptive image segmentation method is designed, which effectively adapts to the damage detection problems under conditions of uneven illumination and weak signal. An online experiment was carried out by using edge illumination and the telescope optical imaging system, and the validity of the method was proved by the experimental results.
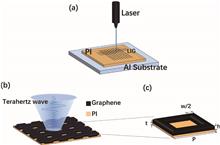
Terahertz (THz) absorbers for imaging, sensing, and detection are in high demand. However, such devices suffer from high manufacturing costs and limited absorption bandwidths. In this study, we presented a low-cost broadband tunable THz absorber based on one-step laser-induced graphene (LIG). The laser-machining-parameter-dependent morphology and performance of the absorbers were investigated. Coarse tuning of THz absorption was realized by changing the laser power, while it was fine-tuned by changing the scanning speed. The proposed structure can achieve over 90% absorption from 0.5 THz to 2 THz with optimized parameters. The LIG method can help in the development of various THz apparatuses.
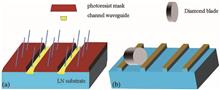
Lithium niobate (LiNbO3, LN) channel and ridge waveguides have been successfully fabricated by He ion implantation, which has energy of 500 keV and fluence of 1.5×1016 ions/cm2 and is combined with lithography and the precise diamond dicing technique. The refractive index profile of the annealed LN planar waveguide was reconstructed. The propagation loss of the channel waveguide with a width of 10 µm and that of the ridge waveguides with widths of 25 µm and 15 µm were investigated by the end-face coupling method. In our work, the factors that affect the waveguide properties of channel and ridge waveguides were revealed.
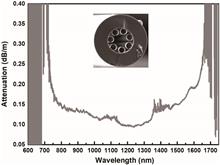
Continuous operation of fiber gas Raman lasing at the 1135 nm wavelength is experimentally demonstrated with an output power exceeding 26 W. Rotational stimulated Raman scattering (Rot-SRS) is generated in the hydrogen gas filled 50 m homemade anti-resonant hollow-core fiber (AR-HCF). A single-frequency fiber laser at the 1064 nm wavelength is used as the pump source, and a minimum threshold of 31.5 W is measured where the core diameter of AR-HCF reaches 37 µm. Up to 40.4% power conversion efficiency of forward Rot-SRS is achieved in the single-pass configuration, corresponding to a quantum efficiency of 43.1%. Over 1 W strong backward Rot-SRS is observed in the experiment, ultimately limiting the further increase of Rot-SRS generation in the forward direction.
An actively mode-locked fiber laser with controllable pulse repetition rate and tunable pulse duration is presented, in which an optical delay line (ODL) is used to adjust the cavity length precisely for regulating the repetition rate, and a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) is introduced for enabling the pulse duration control. Experimentally, continuous tuning of the repetition rate from 2 GHz to 6 GHz is realized, which is limited by the availability of an even higher repetition rate radio-frequency (RF) source. Specifically, when the repetition rate is fixed at 2.5 GHz, the pulse duration can be tuned from 4 ps to 30 ps, which is, to the best of our knowledge, the widest tuning range of pulse duration ever achieved in a gigahertz (GHz) repetition rate actively mode-locked 1.5 µm fiber laser oscillator.
A high peak power density and low mechanical stress photonic-band-crystal (PBC) diode laser array based on non-soldered packaging technology is demonstrated. The array consists of the PBC diode laser bars with small fast axis divergence angles. Meanwhile, we design the non-soldered array structure that realizes mechanical stacking of 10 bars in the vertical direction. In the experiment, the peak power density of the PBC array is about 1.75 times that of the conventional array when the same total power is obtained. The peak power of the non-soldered array is 292.2 W, and the “smile” effect is improved by adjusting the mechanical fixing force of the array.
This work presents experimental results of Rabi antenna characteristics using the coupled line microstrip circuit. It was constructed by a modified coupled line microstrip four-port network, which is known as an add-drop multiplexer. The driven AC input enters the device via an input port using the suitable frequency and coupled line microstrip ring radius. The multi-level system is generated by a wave-particle aspect before the two-level system is achieved. At the resonance, the transitions of the states induce the energy called whispering gallery mode (WGM) at the circuit center, which is the squeezed energy. The generated electron oscillation within the WGM envelope oscillated by the frequency is known as the Rabi frequency. By the successive filtering with continuous AC input via the selected port, the electron cloud warp speed can be generated and achieved inside the two-level transition. The constructed microstrip ring radius is 25 mm, and the experimental results of the Rabi antenna characteristics are in good agreement with the simulation results. The obtained resonant antenna oscillation frequency is 2.103 GHz. The electron cloud warp speed of 1.100c and time dilation of 0.006 µs are obtained.
We introduce a simple one-dimensional (1D) structure in the design of 1D color splitters (1D-CSs) with RGB unit cells for color imaging and propose a single-to-double-layer design in 1D-CSs. Based on inverse design metasurfaces, we demonstrate numerically a single-layer 1D-CS with a full-color efficiency of 46.2% and a double-layer 1D-CS with a full-color efficiency of 48.2%; both of them are significantly higher than that of traditional color filters. Moreover, we demonstrate a 1D-CS that has application value by evaluating the double-layer 1D-CS’s performances in terms of incident angle sensitivity, polarization angle sensitivity, and assembly tolerance.
Quantum efficiency is a critical piece of information of a quantum emitter and regulates the emitter’s fluorescence decay dynamics in an optical environment through the Purcell effect. Here, we present a simple way to experimentally probe fluorescence quantum efficiency of single dibenzoterrylene molecules embedded in a thin anthracene microcrystal obtained through a co-sublimation process. In particular, we correlate the fluorescence lifetime change of single dibenzoterrylene molecules with the variation of the matrix thickness due to natural sublimation. With the identification of the molecule emission dipole orientation, we could deduce the near-unity intrinsic quantum efficiency of dibenzoterrylene molecules in the anthracene matrix.
Perfect absorbers (PAs) are devices that can efficiently absorb electromagnetic waves. Great attention has been attracted since metamaterial PAs (MPAs) were first proposed in 2008. In recent years, with the development of nanophotonics and the improvement of nanomanufacturing technology, considerable progresses have been achieved in designing MPAs using new materials and new structures. In this review, we summarized first the latest developments of PAs from five directions: dual-band, multi-band, wideband, narrow-band, and tunable light absorption. The shortcomings of the previous PAs and the latest improvements were introduced as well. Then, the application of perfect absorption in solar cells, sensors, switches, and structural colors was discussed. Finally, we presented the main challenges and prospects in these fields. Novel PAs for applications in a wide field of opto-electronic devices will continuously progress with breakthrough advances in absorbers related technology and science.
Underwater optical wireless communication, which is useful for oceanography, environmental monitoring, and underwater surveillance, suffers the limit of the absorption attenuation and Mie–Rayleigh scattering of the lights. Here, Bessel-like beams generated by a fiber microaxicon is utilized for underwater wireless propagation. Underwater, the cone angle for generating Bessel-like beams starts from 46°, which is smaller than that in air for Bessel-like beams. When the cone angle of the fiber microaxicons is about 140°, the depth of focus underwater, which is four times as long as the depth of focus in air, has enlarged about 28 µm, 36.12 µm, and 50.7 µm for 470 nm, 520 nm, and 632 nm visible lights. The transmission distance of the Bessel beams for visible lights has been simulated by using Henyey–Greenstein–Rayleigh phase function methods and spectral absorption by bio-optical model due to Monte Carlo methods. The results show that the propagation distance could reach 4000 m, which overcome the limit of the Mie–Rayleigh scattering and absorption attenuation underwater.
In this paper, a new optical analysis method for plasma characterization is proposed. Plasma characteristics are obtained directly by measuring the plasma luminous color, rather than the complex spectral diagnosis method, which is difficult to obtain at high speed. By using the light transmittance curve of the human cornea, the RGB coordinates are calculated from the measured plasma spectrum data. Plasma characteristics are diagnosed using the Boltzmann plot method and the Stark broadening method. The corresponding relationship of the electron temperature, electron density data points, and luminous color is established and analyzed. Our research results indicate that this optical analysis method is feasible and promising for fast plasma characterization.