 View fulltext
View fulltext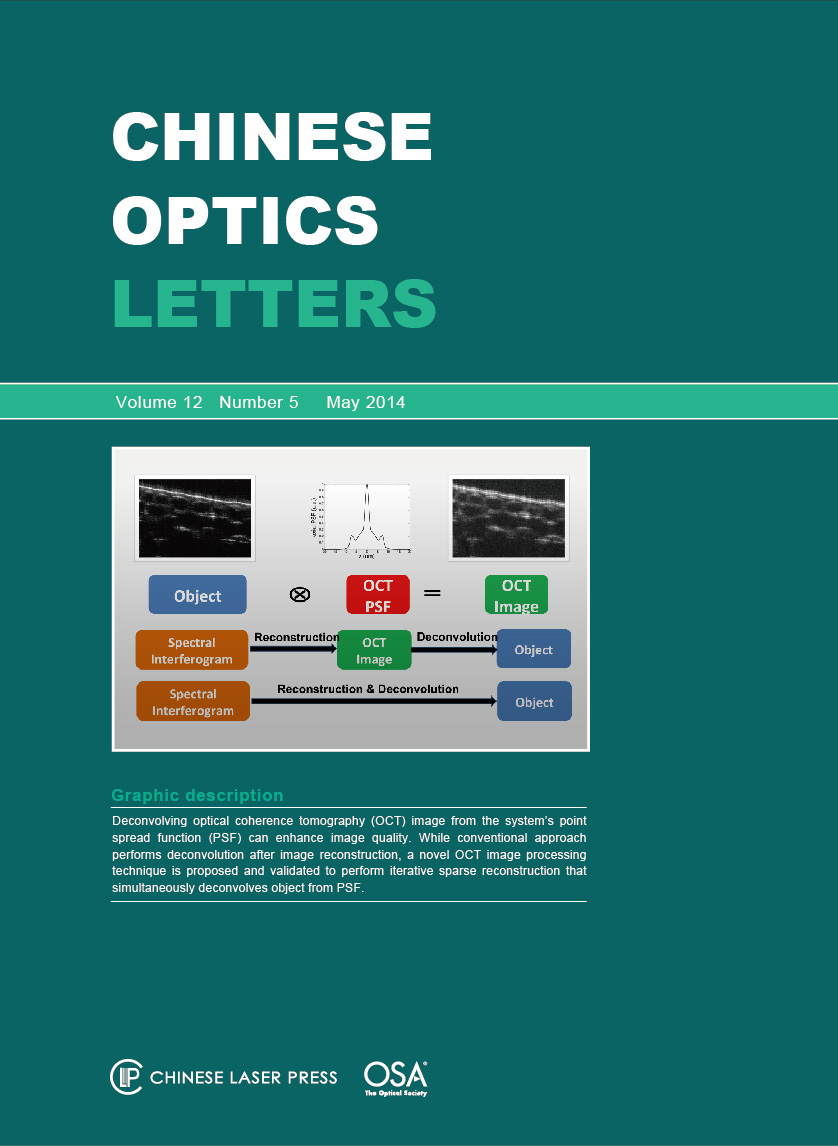
A kind of novel fiber, comprising two fiber cores which are suspended in air inside the outer cladding via a central thin membrane, is proposed for optical switching application. When a hydrostatic pressure applied on the optical fiber, the pressure-induced refractive index change of the two fiber cores will contribute to the periodical change of the intensity of guided light in the fiber core. The mode coupling of two cores under different hydrostatic pressure and influences of each structure parameter of the proposed fiber on the switching pressure have been numerically investigated.
A hybrid optical switch (HOS) with physical layer of wavelength division multiplexing and optical code division multiplexing (WDM/OCDM) scheme is proposed. An additional feature to the HOS than optical cross connect (OXC) is that the controller can process requests for both circuit establishment and burst scheduling. In our study, the measurement criteria of HOS are the blocking probability, probability of error, and probability of outage. To simplify the analysis, no distinction is made between a circuit in progress and a burst in progress. Moreover, a minimum fit (MinF) resource allocation strategy is applied in order to increase the bandwidth efficiency and control the multiplexing interference of the OCDM. A 2D Markov model for the HOS is presented using the MinF strategy. Numerical results reveal that the code parameters and the resource allocation strategy greatly affect the performance. Certain periority can be achieved by assigning shorter codes to high periority users and longer codes to low periority users. Also, the probability of error and outage are reduced by appling the MinF strategy.
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a novel scheme to realize polarization-division-multiplexing quadrature-phase-shift-keying (PDM-QPSK) signal transmission over fiber, wireless and fiber at W-band (75-110 GHz). The generation of polarization multiplexing millimeter-wave (mm-wave) wireless signal is based on the photonic technique. After 20-km fiber transmission, polarization diversity and heterodyne beating are implemented to convert the polarization components of the polarization-multiplexing signals from the optical baseband to W-band so that up to 16 Gb/s mm-wave signals can be delivered over 2-m 2×2 multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) wireless link. At the receiver base station (BS), polarization combination reconstructs the PDM-QPSK signal which is then launched into another 20-km fiber. In the experiment, coherent detection is introduced to improve receiver sensitivity and constant modulus algorithm (CMA) is applied for polarization de-multiplexing. The bit-error-ratio (BER) for 16-Gb/s PDM-QPSK signal delivery is below the forward-error-correction (FEC) threshold of 3.8×10-3 with the optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) above 11.8 dB.
The random phase errors of the optical carriers are discussed and controlled for passive millimeter-wave sparse aperture (PMMW SA) upconversion imaging. A two-channel model is set up for analyzing characteristics of the phase errors, and an active optical control technique based on stochastic parallel gradient decent algorithm (SPGD controller) is proposed to calibrate the phase errors. To demonstrate the feasibility of the SPGD controller, simulations are performed and an experimental system with a two-channel fiber array is set up. Simulation and experiment results show that the SPGD controller can effectively and rapidly compensate the phase errors of the optical carrier, and the accuracy of the phase control is sufficient for imaging systems.
Enhanced 2.7 \mu m emission is obtained in Er3+/Tm3+ and Er3+/Ho3+ codoped ZBYA glasses. Absorption and emission spectra are tested to characterize the 2.7 \mu m emission properties of Er3+/Tm3+ and Er3+/Ho3+ doped ZBYA glasses and a reasonable energy transfer mechanism of 2.7 \mu m emission between Er3+ and Tm3+Ho3+) ion is proposed. Codoping of Tm3+ or Ho3+ significantly reduces the lifetime of the Er3+: 4I13/2 level due to the energy transfer of Er3+:4I13/2 →Tm3+:3F4 or Er3+:4I13/2 →Ho3+: 5I7. Thus, the 2.7 \mu m emission is strengthened and the 1.5 \mu m emission is decreased accordingly especially in the Er3+/Tm3+ sample. The upconversion effects between the Er3+/Tm3+ and Er3+/Ho3+ doped ZBYA glasses are different attribute to the different energy transfer efficiencies. Both of the two codoped samples possess nearly equal large emission cross section (16.6 \times 10-21 cm-2) around 2.7 \mu m. The results indicate that this Er3+/Tm3+ or Er3+/Ho3+ doped ZBYA glass has potential applications in 2.7 -m laser.
Monovalent ions Li+, Na+, and K+, as charge compensators, are introduced into CaYAl3O7: M (M=Eu3+, Ce3+) in this letter. Their crystal phases and photoluminescence properties of different alkali metal ions doped in CaYAl3O7 are investigated. In addition, the influence of charge compensation ion Li+ which has a more obvious role in improving luminescence intensity on CaYAl3O7: Eu3+ phosphor is intentionally discussed in detail and a possible mechanism of charge compensation is given. The enhancement of red emission centered at 618 nm belonging to Eu3+ is achieved by adding alkali metal ion Li+ under 393-nm excitation.
We propose and study an iterative sparse reconstruction for Fourier domain optical coherence tomography (FD OCT) image by solving a constrained optimization problem that minimizes L-1 norm. Our method takes the spectral shape of the OCT light source into consideration in the iterative image reconstruction procedure that allows deconvolution of the axial point spread function from the blurred image during reconstruction rather than after reconstruction. By minimizing the L-1 norm, the axial resolution and the signal to noise ratio of image can both be enhanced. The effectiveness of our method is validated using numerical simulation and experiment.
Measurement of light distribution in biological tissue contributes to selecting strategy and optimizing dose for biomedical application. In this letter, a photoacoustic method combined with Monte Carlo simulation was used to estimate the three-dimensional light distribution in biological tissue. The light distribution was produced by a cylindrical diffuser which interposed into tissues. The light profiles obtained by the method were compared to those detected by photo diodes. The experimental results demonstrate the feasibility of this method. The approach can play a significant role for photo-dosimetry in biomedical phototherapy.
The photoacoustic tomography by using the handheld probe has a great potential in clinical breast imaging. However, the shape of the probe limits the choice of light delivery in this setup. In this letter, we study two commonly used illumination types for handheld probe: bright-field illumination and dark-field illumination. Our results demonstrate several parameters have important impact on the photon fluence in deep breast tissue. The results will help to optimize the design of the photoacoustic breast imaging system with a handheld probe.
Photoacoustic ophthalmoscopy (PAOM) is a novel imaging modality, which is capable of non-invasively detecting optical absorption properties in the retina. We visualize the microvasculature in retina and choroid in albino mouse using PAOM guided by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Since albino mouse characterizes by lacking melanin in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), PAOM illumination laser can penetrate through the RPE onto choroid, and consequently provides volumetric visualization of chorioretinal vasculatures as a result of strong hemoglobin optical absorption. The high-quality chorioretinal microvascular imaging acquired by PAOM implies its great potential in understanding pathological mechanisms and developing therapeutic strategies for major chorioretinal diseases that correlate with vascular disorders.
Autofluorescence (AF) spectra of colonic normal and adenocarcinoma tissues are measured under excitation of 337 nm and analyzed by multivariate curve resolution alternating least squares (MCR-ALS) method using non-negativity constraint. Collagen, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydrate (NADH) and elastin are identified as the main contributing biomedical components. Fisher’s discrminant anlysis (FDA) on the concentration profiles of the principle components (PCs) shows acceptable sensitivity, specificty and accuracy for discrminanting the adenocarcinoma tissues from the normal tissues. MCR-ALS is a powerful tool for characterzing the spectra profiles of the main biochemical components in neoplasm transformation.
In this letter, we present a scheme generating OFDM signals in optical domain instead of electrical domain by transmitting subcarrier signals with multiple LEDs. According to the simulation, this scheme can effectively eliminate signal degradation caused by the high peak-to-average power ratio of OFDM signals in traditional transmitter. Computational complexity in digital part of the transmitter can be reduced by using look-up table. Receiver will stay unchanged.
A model is developed to improve thickness uniformity of coatings on spherical substrates rapidly and automatically using fixed shadow masks in a planetary rotation system. The coating thickness is accurately represented by a function composed of basic thickness, self-shadow effect, and shadow mask function. A type of mask with parabolic contours is proposed, and the thickness uniformity of coatings on spherical substrates can be improved in a large range of ratios of clear aperture (CA) to radius of curvature (RoC) by optimizing shadow masks using a numerical optimization algorithm. Theoretically, the thickness uniformity improves to more than 97.5% of CA/RoC from –1.9 to 1.9. Experimentally, the thickness uniformities of coatings on a convex spherical substrate (CA/RoC = 1.53) and on a concave spherical substrate (CA/RoC=–1.65) improve to be better than 98.5% after corrected by the shadow masks.
We propose a wideband transverse magnetic-reflected polarizing film composed of Cr and SiO2. Based on the polarization characteristics of reflected light from Cr/SiO2 film, the film can serves as a polarizer to severely attenuate the transverse electric (TE)-polarized light and reflect the transverse magnetic (TM)-polarized light in a wavelength range from 600 to 900 nm. By suitably choosing the film thicknesses, the operation angles of such polarizers can be adjusted over a wide angle range greater than the critical angle of total reflection. Cr/SiO2 film has potential use in surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensors based on Kretchmann configuration to form integrated structures.
In this letter, we focus on the high-order quantum image of reference beam. We successfully reduce the noise of reference beam, and achieve a clear high-order quantum image of reference beam. The experimental results convince that the more information from the reference beam, the better visibility will be achieved.
An electro-optic tunable rectangular array illuminator in one-dimensional periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) crystal is presented experimentally which result is in good agreement with results from simulation. The illuminator is formed based on the Talbot self-imaging effect by applying an electric field on PPLN. The intensity distribution of rectangular array could be precisely modulated. Compared with other array illuminators, this tunable illuminator uses a lower voltage and could get a more concentrated intensity distribution. The influence of the incident angle to the self-imaging patterns is studied for the first time.
A pavement reflectance measurement system is established based on a gonio-photometerexisting by changing a bracket to carry the road sample and luminance meter, adding a collimated light source to provide incident light. This automated system could finish the reflection measurement of a road sample in 4 h. An uncertainty budget of this measurement system is made and the combined standard uncertainty of Q0 is 5.26%.
This letter presents a model of an indoor light positioning system (LPS) based on white LEDs and a camera. The position of an LPS receiver is determined through both its relative position to LEDs according to their images captured by the camera and LEDs' absolute position information in the navigation frame, obtained through a visible light communication (VLC) link. The error performance of the proposed LPS is analyzed. The mean error and mean square error (MSE) of estimated receiver position using least squares (LS) and weighted least squares (WLS) estimators are both derived in the presence of non-uniform measurement bias and white Gaussian noise. The effects of communication data rate on the positioning accuracy are also studied through BER performance.
This letter presents an approach based on differential evolution (DE) algorithm for determining the solar cell model parameters from current-voltage (I-V) characteristics. The validity of this approach has been confirmed with experimental and simulated I-V data. It was demonstrated that the I-V curve derived from the parameters extracted by the DE approach is in good agreement with the experimental or simulated I-V data. A low objective function value as well as a high parameter precision can be obtained by the DE algorithm.
A method of detecting dry, icy and wet road surface conditions based on scanning detection of single wavelength backward power is proposed in this letter. The detector is used to receive the backward scattered power which changes with the incidence angle. The relationship between backward power and incidence angle is used to find out the effective angle range and distinguish method. Experiment and simulation show that it is feasible to classify these three conditions within incidence angle of 5.3 degree.










