View fulltext
View fulltext
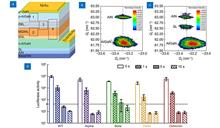
Halide perovskite light-emitting electrochemical cells are a novel type of the perovskite optoelectronic devices that differs from the perovskite light-emitting diodes by a simple monolayered architecture. Here, we develop a perovskite electrochemical cell both for light emission and detection, where the active layer consists of a composite material made of halide perovskite microcrystals, polymer support matrix, and added mobile ions. The perovskite electrochemical cell of CsPbBr3:PEO:LiTFSI composition, emitting light at the wavelength of 523 nm, yields the luminance more than 7000 cd/m2 and electroluminescence efficiency of 1.3×105 lm/W. The device fabricated on a silicon substrate with transparent single-walled carbon nanotube film as a top contact exhibits 40% lower Joule heating compared to the perovskite optoelectronic devices fabricated on conventional ITO/glass substrates. Moreover, the device operates as a photodetector with a sensitivity up to 0.75 A/W, specific detectivity of 8.56×1011 Jones, and linear dynamic range of 48 dB. The technological potential of such a device is proven by demonstration of 24-pixel indicator display as well as by successful device miniaturization by creation of electroluminescent images with the smallest features less than 50 μm.
Deep-ultraviolet (DUV) disinfection technology provides an expeditious and efficient way to suppress the transmission of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, the influences of viral variants (Delta and Omicron) and low temperatures on the DUV virucidal efficacy are still unknown. Here, we developed a reliable and uniform planar light source comprised of 275-nm light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to investigate the effects of these two unknown factors and delineated the principle behind different disinfection performances. We found the lethal effect of DUV at the same radiation dose was reduced by the cryogenic environment, and a negative-U large-relaxation model was used to explain the difference in view of the photoelectronic nature. The chances were higher in the cryogenic environment for the capture of excited electrons within active genetic molecules back to the initial photo-ionised positions. Additionally, the variant of Omicron required a significantly higher DUV dose to achieve the same virucidal efficacy, and this was thanks to the genetic and proteinic characteristics of the Omicron. The findings in this study are important for human society using DUV disinfection in cold conditions (e.g., the food cold chain logistics and the open air in winter), and the relevant DUV disinfection suggestion against COVID-19 is provided.
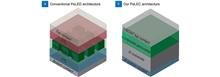
Efficient and eco-friendly disinfection of air-borne human respiratory RNA viruses is pursued in both public environment and portable usage. The AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet (DUV) light-emission diode (LED) has high practical potentials because of its advantages of variable wavelength, rapid sterilization, environmental protection, and miniaturization. Therefore, whether the emission wavelength has effects on the disinfection as well as whether the device is feasible to sterilize various respiratory RNA viruses under portable conditions is crucial. Here, we fabricate AlGaN-based DUV LEDs with different wavelength on high-temperature-annealed (HTA) AlN/Sapphire templates and investigate the inactivation effects for several respiratory RNA viruses. The AlN/AlGaN superlattices are employed between the template and upper n-AlGaN to release the strong compressive stress (SCS), improving the crystal quality and interface roughness. DUV LEDs with the wavelength of 256, 265, and 278 nm, corresponding to the light output power of 6.8, 9.6, and 12.5 mW, are realized, among which the 256 nm-LED shows the most potent inactivation effect in human respiratory RNA viruses, including SARS-CoV-2, influenza A virus (IAV), and human parainfluenza virus (HPIV), at a similar light power density (LPD) of ~0.8 mW/cm2 for 10 s. These results will contribute to the advanced DUV LED application of disinfecting viruses with high potency and broad spectrum in a portable and eco-friendly use.
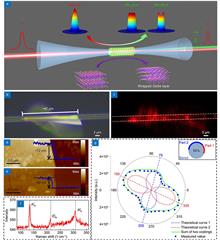
The conversion-efficiency for second-harmonic (SH) in optical fibers is significantly limited by extremely weak second-order nonlinearity of fused silica, and pulse pump lasers with high peak power are widely employed. Here, we propose a simple strategy to efficiently realize the broadband and continuous wave (CW) pumped SH, by transferring a crystalline GaSe coating onto a microfiber with phase-matching diameter. In the experiment, high efficiency up to 0.08 %W-1mm-1 is reached for a C-band pump laser. The high enough efficiency not only guarantees SH at a single frequency pumped by a CW laser, but also multi-frequencies mixing supported by three CW light sources. Moreover, broadband SH spectrum is also achieved under the pump of a superluminescent light-emitting diode source with a 79.3 nm bandwidth. The proposed scheme provides a beneficial method to the enhancement of various nonlinear parameter processes, development of quasi-monochromatic or broadband CW light sources at new wavelength regions.
Deep-ultraviolet (DUV) sterilization technology using DUV-LEDs has attracted considerable attention owing to its portability, eco-friendliness, high potency, and broad-spectrum sterilization. This study compiles the developments of recent DUV sterilization research. Recent works have investigated DUV sterilization from the perspective of device improvement and principle investigation: one employed a novel epitaxial structure to optimize the performance and fabrication cost of DUV-LEDs and realized potent virus disinfection effects for various respiratory RNA viruses, and another work explained the disinfection phenomenon of SARS-CoV-2 and its variants (Delta and Omicron) in a cryogenic environment. These studies have contributed significantly to the development of DUV sterilization.