View fulltext
View fulltext
Two-dimensional (2D) nonlinear optical mediums with high and tunable light modulation capability can significantly stimulate the development of ultrathin, compact, and integrated optoelectronics devices and photonic elements. 2D carbides and nitrides of transition metals (MXenes) are a new class of 2D materials with excellent intrinsic and strong light-matter interaction characteristics. However, the current understanding of their photo-physical properties and strategies for improving optical performance is insufficient. To address this issue, we rationally designed and in situ synthesized a 2D Nb2C/MoS2 heterostructure that outperforms pristine Nb2C in both linear and nonlinear optical performance. Excellent agreement between experimental and theoretical results demonstrated that the Nb2C/MoS2 inherited the preponderance of Nb2C and MoS2 in absorption at different wavelengths, resulting in the broadband enhanced optical absorption characteristics. In addition to linear optical modulation, we also achieved stronger near infrared nonlinear optical modulation, with a nonlinear absorption coefficient of Nb2C/MoS2 being more than two times that of the pristine Nb2C. These results were supported by the band alinement model which was determined by the X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) experiment and first-principal theory calculation. The presented facile synthesis approach and robust light modulation strategy pave the way for broadband optoelectronic devices and optical modulators.
Multiple mode resonance shifts in tilted fiber Bragg gratings (TFBGs) are used to simultaneously measure the thickness and the refractive index of TiO2 thin films formed by Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) on optical fibers. This is achieved by comparing the experimental wavelength shifts of 8 TFBG resonances during the deposition process with simulated shifts from a range of thicknesses (T) and values of the real part of the refractive index (n). The minimization of an error function computed for each (n, T) pair then provides a solution for the thickness and refractive index of the deposited film and, a posteriori, to verify the deposition rate throughout the process from the time evolution of the wavelength shift data. Validations of the results were carried out with a conventional ellipsometer on flat witness samples deposited simultaneously with the fiber and with scanning electron measurements on cut pieces of the fiber itself. The final values obtained by the TFBG (n = 2.25, final thickness of 185 nm) were both within 4% of the validation measurements. This approach provides a method to measure the formation of nanoscale dielectric coatings on fibers in situ for applications that require precise thicknesses and refractive indices, such as the optical fiber sensor field. Furthermore, the TFBG can also be used as a process monitor for deposition on other substrates for deposition methods that produce uniform coatings on dissimilar shaped substrates, such as ALD.
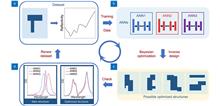
Chiral nanostructures can enhance the weak inherent chiral effects of biomolecules and highlight the important roles in chiral detection. However, the design of the chiral nanostructures is challenged by extensive theoretical simulations and explorative experiments. Recently, Zheyu Fang’s group proposed a chiral nanostructure design method based on reinforcement learning, which can find out metallic chiral nanostructures with a sharp peak in circular dichroism spectra and enhance the chiral detection signals. This work envisions the powerful roles of artificial intelligence in nanophotonic designs.
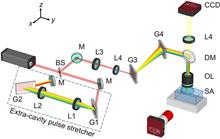
To improve the processing efficiency and extend the tuning range of 3D isotropic fabrication, we apply the simultaneous spatiotemporal focusing (SSTF) technique to a high-repetition-rate femtosecond (fs) fiber laser system. In the SSTF scheme, we propose a pulse compensation scheme for the fiber laser with a narrow spectral bandwidth by building an extra-cavity pulse stretcher. We further demonstrate truly 3D isotropic microfabrication in photosensitive glass with a tunable resolution ranging from 8 μm to 22 μm using the SSTF of fs laser pulses. Moreover, we systematically investigate the influences of pulse energy, writing speed, processing depth, and spherical aberration on the fabrication resolution. As a proof-of-concept demonstration, the SSTF scheme was further employed for the fs laser-assisted etching of complicated glass microfluidic structures with 3D uniform sizes. The developed technique can be extended to many applications such as advanced photonics, 3D biomimetic printing, micro-electromechanical systems, and lab-on-a-chips.
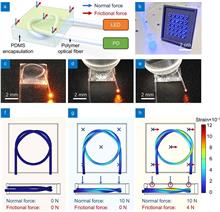
Friction plays a critical role in dexterous robotic manipulation. However, realizing friction sensing remains a challenge due to the difficulty in designing sensing structures to decouple multi-axial forces. Inspired by the topological mechanics of knots, we construct optical fiber knot (OFN) sensors for slip detection and friction measurement. By introducing localized self-contacts along the fiber, the knot structure enables anisotropic responses to normal and frictional forces. By employing OFNs and a change point detection algorithm, we demonstrate adaptive robotic grasping of slipping cups. We further develop a robotic finger that can measure tri-axial forces via a centrosymmetric architecture composed of five OFNs. Such a tactile finger allows a robotic hand to manipulate human tools dexterously. This work could provide a straightforward and cost-effective strategy for promoting adaptive grasping, dexterous manipulation, and human-robot interaction with tactile sensing.