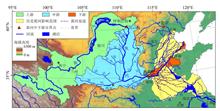
Based on the research on the changes of climate, disasters, vegetation, and land use in the past 40 years, this study made a comprehensive assessment of the characteristics of changes of temperature, dry/wet conditions, and extreme droughts and floods, and the general trend of land cover caused by the agricultural land use, in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River over the past two millennia. We also discussed the general relationships between the above changes and the sedimentation, breaches, and avulsions in the lower Yellow River from a historical perspective. The main conclusions are as follows. (1) During the past two millennia, multi-scale periodic fluctuations of temperature and dry/wet conditions were significant in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, but the dry/wet changes in the middle and the lower reaches were not completely synchronized. Frequencies of extreme droughts and floods varied in different time periods. (2) As early as in the late Western Han Dynasty, the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River had already been developed into an agricultural area with a spatial range similar to today’s, where, especially on relative flat terrains, only limited natural vegetation remained. Since then, the intensity of reclamation showed an increasing trend in general, although it fluctuated greatly over time. (3) The changes of climate and land cover had influenced the water-sediment balance, channel sedimentation, and riverbed stability in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, and driven, as an important trigger, the repeated diking-sedimentation-suspended river-burst and avulsion cycle in the lower Yellow River during the historical period. These understandings can provide historical backgrounds for further revealing the characteristics of environmental change in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River and their impacts on the security of the lower Yellow River region.
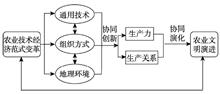
Exploring the core factors promoting the evolution of civilization is the key to facilitating the building of ecological civilization. Based on the transformation of the agricultural technology-economic paradigm, an analytical framework was constructed in this study to discuss the evolutionary process and mechanisms of development of agricultural civilization in the Yellow River Basin. The research shows that: (1) The transformation of agricultural technology-economic paradigm is the fundamental driving force for the evolution of agricultural civilization. It includes the revolution of human-based general agricultural technology, changes in the organization of production, and changes in the agricultural production environment; (2) The evolution of agricultural civilization in the Yellow River Basin can be divided into five stages: Neolithic Age wood axe plowing agricultural civilization, Bronze Age metallic tools plowing agricultural civilization, Iron Age intensive agricultural civilization, Machine Age industrialized agricultural civilization, and Computer Age information ecological agricultural civilization; (3) The evolution of agricultural civilization shows a spiral escalation pattern. The evolution of the form is the result of collaborative innovation among the three components of the agricultural technology-economic paradigm, and co-evolution between the productivity and production relations; (4) Promoting the green transformation of technology-economic paradigm is the key to the construction of ecological civilization. Considering the green information technology as the core, constructing a resource saving and environment-friendly information ecological agriculture civilization will be the future direction of development of agricultural civilization.
The Yellow River Basin plays an important role in China’s social development and ecological security. Ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin have become a significant national strategy, which makes higher requirements on water resources allocation of the basin. The water allocation should not only help ecological system protection but also ensure high-quality development. With the impact of climate change and human activities, the overall runoff of the Yellow River has decreased in recent decades, but it has recovered slightly in the past several years, and the sediment inflow has decreased significantly compared with the historical situation. To meet the water demand of high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin, based on the new situation of runoff and sedimentation and regional water supply and demand, this article estimated the reserved ecological and sediment transport water on the lower reaches (8~12 billion m3), alternative water supply of the Yellow River by the South-to-North Water Diversion Project and seawater utilization (2.5~4.5 billion m3), and water demand for the development of some of the industries on the upper and middle reaches. Then scenarios of the Yellow River water resources allocation scheme were designed. To strengthen water resource security for the strategic development in the Yellow River Basin, it is necessary to improve the institutional arrangements and regulations of water right transfer and compensation, and explore the coupling mechanism of water and land spatial adjustments.
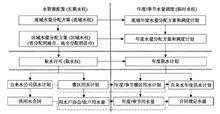
The problem of transboundary river water distribution is related to river health, human - water relationship, regional coordinated development, and security and stability of societies. Water distribution of the Yellow River is one of the major difficulties faced in the implementation of the Yellow River national strategy, which is related to the national economy and people’s livelihood. At present, there are many studies on transboundary river water distribution in China and internationally, but accurate and reasonable conclusions have yet to be reached. The 1987 water distribution scheme for the Yellow River has been implemented for more than 30 years and changes are urgently needed. In this study, through data collection and analysis of a large amount of literature, the thoughts, principles, and rules of water distribution in transboundary rivers were summarized, and a set of systematic calculation methods of water distribution in transboundary rivers was put forward. This new approach is characterized by multi-method synthesis-dynamic analysis-harmonious water distribution based on the thoughts, principles, and rules of water distribution (SDH method for short). On this basis, the theoretical method was applied and the actual situation of the Yellow River Basin and the results of existing scientific research were fully considered. The results are as follows: (1) Water distribution in transboundary rivers is a difficult problem, which involves the complicated relationships between human and nature and between people; (2) The proposed water distribution method takes into account factors such as current water distribution scheme, current water use, future water demand, population, GDP, river basin area, and the overall optimal distribution, changes year on year with the change of the quantity of distributable water, and meets the minimum water demand and water use efficiency constraints; (3) The 1987 water distribution scheme for the Yellow River needs to be adjusted. Considering the change of the total distributable water amount, a new scheme for the Yellow River water distribution under the two scenarios of 37 billion and 30 billion m 3of assumed distributable water is determined respectively (the “19ZQT” water distribution scheme), and the suitability of the scheme was analyzed and demonstrated.
River basin water rights system development is the key for regulating the water and sedimentation relationship in the Yellow River. This article, in accordance with the national water rights system development framework, reviews the development process of and analyzes problems and challenges faced by, and provides recommendations for improving the water rights system in the Yellow River Basin. As the model of modern water rights system development in China, driven by the problems, the Yellow River Basin has formulated water resources allocation plans, conducted water resources regulation, and explored water rights transfer and water rights clarification. But the system has not been completed and problems exist, including inflexible water use plan, no choice for users, no market for trading, and replacement of water extraction management by regulation, among others. More importantly, the system has been facing radical changes in socioeconomic development and in the ecological environment, as well as fundamental changes in water resources, use structure, and water-sedimentation relationship in the basin in the past 40 years. The article recommended to complete water rights clarification, establish eco-environment water rights, introduce water rights trading mechanism, shift management agency functions, and improve water resources management basis for the Yellow River Basin.
Improving water use efficiency is the key measure to realize the sustainable development of water resources. It is of great significance to explore the spatial pattern and dynamic change of water use efficiency in order to promote the ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin. In this study, we built a global Minimum Distance to Strong Efficient Frontier (MinDS model) based on unexpected output to accurately measure the water use efficiency of the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2017. The spatial pattern of water use efficiency of the Yellow River Basin was comprehensively depicted from the perspective of national, regional, and intraregional comparisons. The change of distribution dynamics of water use efficiency was investigated by an extended distribution dynamic model. The results show that the water use efficiency of the Yellow River Basin is higher than the average level in China. The water use efficiency of the lower reaches is higher than that of the upper reaches. A spatial pattern of “high in the east and low in the west” is very clear. The polarization of water use efficiency in the Yellow River Basin is obvious in some years. Spatial factors can significantly affect the regional distribution of water use efficiency. The interaction of water use efficiency in adjacent areas leads to the gradual narrowing of water use efficiency gap in the Yellow River Basin in the long term. And water use efficiency converges to the middle level.
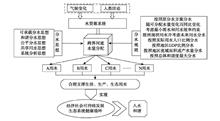
Great achievements have been made in drinking water safety provision in rural China since the 21st century. Tap water supply has reached 80% of the rural population by 2018, and at present the absolute majority of rural residents in China have access to drinking water safety. In some areas of the Yellow River Basin, however, drinking water safety provision projects lagged behind the country average and there are still some problems for rural households to access drinking water safety because of water scarcity, water contamination, waterborne diseases, and insufficient drinking water safety projects. In order to promote ecological protection and high-quality development and safeguard water safety in the Yellow River Basin, this article summarizes the current problems and provides some suggestions, including achieving dynamic water configuration, improving the construction and management of water projects, ensuring source water quality, and so on. Priority to domestic water consumption and quality should be given to ensure the drinking water safety in the rural areas.
As one of the representative regions of the third pole on Earth, Sanjiangyuan has unique species and ecosystems composed of these species. It develops and maintains large areas of original alpine ecosystem, and is an important source of fresh water for China and Asia. It is also the source and key area of ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin. Ecosystem services, natural landscapes, and biodiversity have conservation value of national and global significance. Grassland is the main type of vegetation in the Sanjiangyuan region. Due to many ecological, environmental, and social problems caused by inappropriate grassland use, grassland management and governance is not only a pastoral resource management issue, but also an issue of river basin management of the Yellow River, the Yangtze River, and the Lantsang River Basins. This article summarized the present situation, problems, and demands of grassland management in the Sanjiangyuan region. Multi-objective management goals were proposed based on the ecosystem service functions of the grassland and human demands for production-ecological protection-livelihood security. A multi-objective management framework was put forward, and the regulatory approach and technical support for the multi-objective management of grassland in the Sanjiangyuan region were established. These will provide an important inspiration and guidance for the sustainable ecological development of the region, the construction of national parks, the development of ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin, and subsequent formulation of relevant policies.
Serious soil losses on the Loess Plateau are the main source of sediments in the Yellow River. Large-scale implementation of soil and water conservation measures since the 1950s is one of the key actions for decreasing soil and water losses in this region. Soil and water conservation measures can modify hydrological processes and soil loss processes on hillslopes or in channels by changing hydrological pathway, runoff velocity, and sediment transportation, and then change the spatial and temporal distribution of water and soil resources at corresponding scales. Different types of soil and water conservation measures played substantial roles in sediment trapping, hydrological adjustment, and regional food security maintenance on the Loess Plateau during the past decades. Soil and water conservation measures have a substantial contribution in reducing the sediment loads of the Yellow River, and are important for maintaining ecological security in the Yellow River Basin. This study aimed at (1) systematically summarizing the types and development of soil and water conservation measures on the Loess Plateau for the past seven decades; (2) revealing the effects of soil and water conservation measures on hydrological and soil processes and related critical ecosystem services and underlying mechanisms at multiple spatial scales; and (3) presenting the problems, challenges, and future prospects of soil and water conservation measures on the Loess Plateau. It is suggested that implementation of soil and water conservation measures on the Loess Plateau in the future needs to focus on their maintenance and improvement toward integrated benefits, strengthen their resilience to extreme climate events and natural hazard-induced disasters, and balance tradeoffs among social-economic-ecological benefits. Improvement in the effectiveness of soil and water conservation measures can help maintaining ecological security and enhancing regional ecosystem functions of the Loess Plateau.
Driven by global environmental changes and human activities, the dynamic changes of social systems and ecological systems are increasing. Revealing the interaction mechanisms of this coupled system is the scientific basis for maintaining and enhancing resilience and sustainability. The Loess Plateau (LP) is one of the regions under great pressure from population, resources, and environment in China. It is also an important water and sediment source area of the Yellow River. Rational land use and the coordination of soil and water conservation with water resources use and sediment control are the main requirements of watershed management and regional sustainable development in the lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin. Based on the frontier research of coupled social-ecological system (SES) and the national needs for sustainable development and ecological construction, feedback mechanisms for regional social and ecological systems and coupled SES simulation are the key issues of research. Social-ecological system research in the Loess Plateau needs to illustrate the dynamics and mechanisms of SES evolution, develop methods for analyzing system dynamics and identifying regime shifts, and develop land-use optimization models for sustainable development in the LP, which are useful for the development of theories of SES and practices of sustainable development of the Loess Plateau.
The Yellow River Delta is an internationally important stopover place for waterfowl, but natural factors and human activities have resulted in loss of waterfowl habitat and biological diversity in this area. The habitat quality and diversity of waterfowl can be greatly improved by using fresh water to restore habitat. However, with fresh water shortage and large water consumption in agriculture, domestic use, and industry in this area, ecological water consumption is insufficient. In this case, how to utilize fresh water, sea water, and waste water adaptively considering the local conditions and give full play to the wetland function to protect biodiversity and purify the environment become the key problem to bird habitat restoration. This article summarized the diversity and the habitat requirements of waterfowl in the Yellow River Delta, and examined the water use status and the demands and challenges to the habitat of waterfowl in this area. We also analyzed the measures to restore waterfowl habitat, resource availability, restoration effects, challenges of waterfowl habitat restoration using fresh water, sea water, and waste water, and then proposed some research prospects. We hope that this article can provide a scientific foundation for the optimized measures of waterfowl habitat restoration for improving waterfowl diversity. Bases on the migration of waterfowl, temporal pattern of Yellow River water discharge, patch pattern of waterfowl habitat, status of water utilization, the wetland type after water diversion, and spatial distribution of different kinds of water resources, we recommend to comprehensively use fresh water, sea water, and waste water to restore waterfowl habitat by considering the temporal patterns of water supply, spatial arrangements of habitats, and a combination of the different habitat types at the same patch, with the purpose of giving full play to the wetland function and improving the biological diversity.
To promote the high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin, it is necessary to construct an evaluation index system for a scientific assessment of such development. Based on the two areas of economic and social development and ecological security, and considering five dimensions of economic development, innovation, improvement of people’s livelihood, environmental conditions, and ecological conditions, this study constructed a high-quality development evaluation index system for the Yellow River Basin. Using the data of nine provinces (autonomous regions) in the Yellow River Basin during 2008-2017, the entropy weight method was used in calculation. The results are as follows: The high-quality development level of the Yellow River Basin basically showed the spatial distribution of “high on both sides and low in the central area,” but the gap was decreasing year by year; The high-quality development level in each province (autonomous region) remained stable in 2008-2010, and continued to grow in 2011-2017, with a high growth rate in 2016; The overall high-quality development level of the basin showed an upward trend, with small fluctuations during 2008-2010 and a significantly increase from 2011. Over the last decade, all five dimensions improved. Accordingly, the study put forward specific suggestions and the directions for further research: (1) Strengthen regional linkages and expand the overall opening-up level of the Yellow River Basin. (2) On the basis of protecting the ecological environment, the provinces (autonomous regions) in western China should develop characteristic industries, combining with their factor endowments. (3) Shandong and Henan Provinces should strengthen the protection of the ecological environment while developing the economy. Shanxi and Gansu Provinces should improve people’s living standards urgently. Qinghai Province and Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region need to increase investments in innovation and improve innovation capacity. Finally,the study proposed the further research directions.
The Yellow River Basin is a key area for China’s regional development strategy and national ecological security. However, affected by the location, physical environment, and resource endowments, the economic foundation of the region is relatively weak. It has formed an industrial system dominated by energy and heavy chemical industries, which greatly increased the regional ecological burden. The Yellow River Basin is facing the predicaments of weak economic foundation and weak development ability, the pressures of accelerating social and economic development and transformation of development mode, the contradictions between resource use and ecological protection and between industrial development and environmental carrying capacity, and the challenges of deteriorating local living environment. The core contents of ecological environment protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin is to balance the relationship between resource use and environmental protection, the scale of development and the carrying capacity of resources and the environment, and the development of key areas and the protection of the total ecological security to ensure energy security, ecological security, food security, watershed security, and the health of human settlements. We suggest that the region should optimize the industrial development path, actively promote the new industrialization with green industrial development as its core, and improve the level of industrial development and resource and environmental efficiency; optimize the industrial space based on the resource and environmental carrying capacity, determine suitable industrial development space and ecological protection red line, promote the construction of key energy and chemical bases and the construction of industrial clusters in urban agglomerations, implement strict environmental access policies, and improve environmental control standards for industrial development; strengthen spatial control and ecological restoration of energy and mining development projects, and implement a series of regional ecological environment governance and restoration projects.
The Yellow River Basin is also known as China’s energy basin. Rational and orderly exploitation of mineral resources and overall coordination of the relationship between mineral resources exploitation and ecological environment protection are of great practical significance for the sustainable development of energy and mineral resources and ecological protection in the region. Taking the Yellow River Basin as the study area, this study comprehensively analyzed the characteristics and spatial distribution of environmental stress of regional mineral resources exploitation using multi-indicator comprehensive evaluation method, stress coupling analysis method, and GIS spatial analysis from the perspectives of ecological background fragility, spatial stress to important ecological function areas, and the degree of stress to important ecological environment factors. The 46 mining cities in the Yellow River Basin were divided into eight types, including background stress areas, ecological function stress areas, development stress areas, background with development stress areas, development with ecological function stress areas, background with ecological function stress areas, comprehensive stress areas, and no stress areas. Finally, the article put forward the control path of mineral resources development areas in the Yellow River Basin in view of ecological environment protection, including: (1) Spatial management and control by strictly restricting large-scale and high-intensity industrialization and urbanization development, especially controlling the development boundary of mining areas. (2) Intensity control for areas with fragile ecological background, the intensity and the overall development scale should be controlled simultaneously. (3) Development mode control to pay attention to the structural adjustment and upgrading of energy and mining industries. It is necessary to focus on spatially concentrated development of mining in places where mining is suitable, of industry where industrial development is suitable, and of cities and towns where urban development is suitable.
The Yellow River Basin is an important energy base in China. The comprehensive energy efficiency of the Yellow River basin directly affects the ecological protection and high-quality development of the region. Using the super efficiency slack based measure (SBM) model to measure the comprehensive energy efficiency of nine provinces (autonomous regions) in the Yellow River Basin from 1997 to 2017, the nuclear density estimation method was selected to analyze the temporal and spatial change characteristics of comprehensive energy efficiency, and the driving factors of comprehensive energy efficiency were analyzed with the help of the geographical detector. The results show that: (1) From 1997 to 2017, the comprehensive energy efficiency of the Yellow River Basin showed a U-shaped trend of high-low-high. The comprehensive energy efficiency of the Yellow River Basin decreased from 1997 to 2003, decreased in 2009 after rapid growth from 2004 to 2010, and increased in 2015 after continuous decline from 2011 to 2017. (2) Spatially, the comprehensive energy efficiency of the western provinces of the Yellow River Basin is relatively low, and the comprehensive energy efficiency of the central provinces is greatly affected by multiple factors, while the comprehensive energy efficiency of the eastern province Shandong is significantly higher. The comprehensive energy efficiencies of the eastern, central, and western provinces and the upper, middle, and lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin have all changed from spatially unbalanced to balanced. (3) With regard to the driving factors, the explanation power of factors is in the order of financial decentralization, urbanization level, human capital level, and the degree of opening to the outside world. Expansion of local financial expenditure, acceleration of urbanization, upgrading of talent structure, and improvement of opening-up in the Yellow River Basin jointly drive the improvement of comprehensive energy efficiency. Give full play to the comparative advantages of the Yellow River Basin, and strengthen collaboration within the basin under various policies for promoting the ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin.
Taking the Yellow River Basin as an example, in this study the coupling and coordinated development of new urbanization and ecological environment was examined, and the spatiotemporal differentiation and synchronous development state of the coupling and coordination from 2005 to 2016 were measured. Based on the Tobit model of random effect, the influencing factors of the coupling of new urbanization and ecological environment in the Yellow River Basin were explained. The findings can be summarized as follows: (1) Index values of the new urbanization and ecological environment subsystems and the coupling and coordination degree of the Yellow River Basin were rising first and then declining. (2) The average coupling degree of new urbanization and ecological environment was between 0.34~0.70, which was in the stage of moderate development. The average coordination degree of new urbanization and ecological environment in the Yellow River Basin was between 0.20~0.60, which was in the stage of low coordination and moderate coordination; (3) More than 78% of the cities in the Yellow River Basin lagged behin in ecological environment protection and the pressure of ecological environment are prominent under the background of rapid urbanization. (4) The level of economic development, capacity of the governments, and investment in science and technology have a positive impact on the degree of coupling and coordination; the degree of opening and the level of industrialization have different effects on the coupling and coordination of the upper and middle-lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin. Additional, reducing path dependency has great significance for promoting the coupling of new urbanization and ecological environment. Differentiated strategies should be adopted to promote the coupling development of new urbanization and ecological environment across the Yellow River Basin.
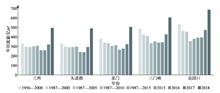
This study constructed a comprehensive evaluation index system for county agricultural modernization level. Theil index and Wolfson polarization index, as well as an obstacle degree model were used to analyze the characteristics of the spatial and temporal patterns of agricultural modernization level and obstacles in Shaanxi Province. We found that: (1) The agricultural modernization development pattern in Shaanxi Province can be divided into three stages, including the rising period (2003-2009), the stable period (2010-2014), and the declining period (2015-2017). (2) Theil index and Wolfson polarization index were slowly rising, and intraregional inequality was the main reason that regional differences of agricultural modernization level in Shaanxi Province expanded, which contributed 86.81% of the overall Theil index. (3) Agricultural modernization level in the Guanzhong Plain Region was higher than that of the Loess Plateau Region and the Qinling-Daba Mountains Region, and the arid area of northern Weihe River and Baoji City, as well as northern Yulin City were the high-level regions and hot spots in Shaanxi Province. Counties with high level of agricultural modernization are distributed along some main rivers and expanded from the Guanzhong Plain Region to the geomorphic transition zone. (4) Agriculture development quality was the biggest sub-index level obstacle factor, with an annual average obstacle degree of 41.58%. The key obstacles that affected agricultural modernization level were facility agriculture development, output efficiency of economic crops, as well as the production of animal products. Finally, this article put forward some suggestions for agricultural modernization development in Shaanxi Province and high-quality development of agriculture in the Yellow River Basin.
China creatively implemented the precision poverty alleviation policy in 2014 and has made significant achievements in reducing population in poverty and poverty reduction, which is remarkable in the anti-poverty history of the world. As the key area of poverty in China, the Yellow River Basin is in urgent need of an overall and systematic analysis of its poverty status and poverty alleviation situation. Based on the data of 356 county-level administrative units and using ArcGIS and geographical detector tools, this study found that: (1) Rural areas in the upper and middle reaches of the Yellow River Basin showed typical characteristics of poor population, deep poverty, and spatial agglomeration of population in poverty. (2) Poverty distribution of the rural Yellow River Basin showed clear spatial heterogeneity; the intensity of the influencing factors basin-wide and in the upper, middle, and lower reaches of the basin was different; and the explanatory power of the economic factors to poverty was stronger than other factors. The interaction between some factors showed a synergetic effect of 1+1> 2. (3) Environmental poverty led to economic poverty, which in turn caused social poverty, and social factors are not conducive to improving the environmental poverty, and thus a “poverty loop” was formed in the rural areas of the Yellow River Basin. Environmental factors were the basic causal factors of poverty, economic factors were the leading factors of poverty development, and social factors were the key factors for solving the problem of rural poverty.
The upper reaches of the Yellow River is the area where poverty is easy and frequent in China. In the context of winning the war against poverty in 2020, it is of great guiding significance to explore the characteristics of poverty reduction turn and high-quality development path for the regional sustainable development. Based on existing research on basin development and governance and national strategies and from the perspective of development geography, an analytical framework of the “five-in-one” geographic capital system and its spatial integration for poverty reduction and development in river basins were constructed. On the basis of defining the scope of the upper reaches of the Yellow River, the issues of poverty alleviation and development in this area was elaborated. The results show that: the incidence of poverty in the upper reaches of the Yellow River continued to decline, the population in poverty had been greatly reduced, and poverty alleviation will be realized after 2020. The geographic capital index values showed a clear upward trend, the increase rate was higher than the Yellow River Basin (0.078) and the national average levels (0.067). However, geographic capital was still restricted by the low income level of urban and rural residents, lower urbanization level, weak research and development intensity of industrial enterprises, weak trade dependence, lower patent density, weak technological market level, and other constraints. Under the background of poverty alleviation and regional convergence, a conceptual model of poverty governance and high-quality development was proposed considering the localization, regionalization, and globalization of regional sustainable poverty reduction and development.