High-precision X-ray imaging diagnosis is the key to understanding the implosion process and revealing unknown physical problems at the ignition scale. X-ray microscope based on grazing incidence reflection, combined with sub-nanometer ultra-smooth spherical or aspherical mirror, can achieve high-resolution imaging with spatial resolution better than 5 μm. This paper introduces the development and application of foreign X-ray microscopic imaging technology in the field of ICF research, highlights the progress of China’s high-resolution X-ray Kirkpatrick-Baez (KB) microscope, multi-channel X-ray KB microscope and large-field X-ray KBA microscope. The research plan for the next stage of ultra-high resolution X-ray microscopic imaging is analyzed. Through continuous technological innovation, China's X-ray microscopic imaging diagnostic capabilities have reached the internationally advanced level.
This article reviews the latest developments of high time- and space-resolving diagnostic technique for laser-driven inertial confinement fusion (ICF) in China. Focusing on the needs of hot spot diagnosis with temporal resolution better than 10 ps, spatial resolution better than 10 μm, and energy range of 10-30 keV, we introduce recent progress in optical, X-ray, and nuclear diagnostics, as well as computational imaging. In optical section, we introduce two diagnostics based on the pump detection technique: all-optical scanning, with temporal resolution up to 200 fs, and all-optical framing, with temporal and spatial resolution up to 5 ps and 5 μm respectively. Since the main components are optical, these systems have great potentials to be applied in the strong electromagnetic, ionizing environment of future ICF research. In X-ray section, we introduce a recently developed high-resolution kirkpatrick-Baez (KB) microscope, which adopts the STTS (S and T represent sagittal and tangential directions respectively) configuration and improves the spatial resolution to 3 μm, meeting the current requirements. Besides, we also discuss a developing technology—the drift tube technology, with temporal resolution up to 10 ps. In nuclear section, we mainly introduce the high-resolution recording system of the neutron imaging, with spatial resolution up to 20-25 μm, as well as the progress in the corresponding aiming technique. In addition, we introduce computational imaging, which is a brand new branch attracting growing attention in ICF field. We also emphasize the three dimensional light field imaging technique and compressed ultrafast photography (CUP) technique, and propose their possible applications in ICF field.
This paper introduces the significance of the research on ultrafast diagnosis technology, summarizes the history and current situation of streak camera and framing camera, analyzes the technical characteristics and main application fields of several mainstream streak tubes, compares the characteristics of domestic and foreign research and development institutions of ultrafast diagnosis equipment. Finally, it presents the achievements and existing problems of ultrafast diagnosis technology in China as well as a preliminary analysis and discussion on further development in this fied.
In the study of laser driven inertial confinement fusion (ICF), the image data obtained through X-ray high-speed photography technology can be used to analyze the spatial and temporal evolution of the plasma with fluid state produced by work and energy transport. The research of X-ray high-speed photography technology has always been an important part of the development of ICF diagnostics. The Laser Fusion Research Center of China Academy of Engineering Physics has made important progresses in the research of X-ray high-speed photography technology in recent years. These advances include: (1) making a success in developing the X-ray camera with 100ps exposure time for Shenguang laser facilities, which has reached the international advanced level as a whole, and is characterised in such aspects as high sensitivity, transmission-type band-pass filtering and miniaturized design; (2) proposing new types of X-ray high-speed photography technologies with 10 ps exposure time such as the micro-sweep gating technology to break the bottleneck of temporal resolution; (3) taking the lead in carrying out theoretical design, technical verification and engineering design of the radiation-hardened X-ray high-speed camera in China; (4) making the efforts on modeling and simulation on target debris and carrying out the special experiments for the first time in China to verify the simulation results.
The streak cameras have very important applications in Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF), including x-ray streak cameras and optical streak cameras. At present, they are still the core diagnostic devices with the highest temporal resolution in this field. This paper introduces the performance and characteristics of two main types of the streak cameras widely used in the field of laser fusion both domestic and international. They are equipped with coaxial electrode double-focus electron optics streak tube and bilamellar electron optics streak tube respectively. In terms of specifications of streak camera, the criteria of dynamic range of streak camera are emphasized, the dynamic range data of today's international high performance streak cameras are presented. The paper also introduces several important research progresses in the development of streak camera technologies, including advanced backlighting ultraviolet fiducial system, neutron radiation tolerant device and gated cathode technology.
Among solid-state laser amplifiers, regenerative amplifiers which have the advantages of high gain, good beam quality and simple structure, have been widely concerned and applied. After decades of development , regenerative amplifiers are able to realize pulse energy of several hundred millijoules and average power of several kilowatts in stable operation. The output performance of regenerative amplifiers is determined by properties of gain media, structure of cavity, pump condition, thermal effect and qualities of components. The properties of gain media are the most essential factors. Because of different properties of materials, regenerative amplifiers based on different kinds of materials present different structure and performance. Based on different material systems, the key common problems encountered in the development process of regenerative amplifiers under various systems, as well as several typical types of regenerative amplifiers and their characteristics are introduced. The future development trend of regenerative amplifiers is discussed.
For a long time, the calibration of soft X-ray diagnostic equipment components of ICF research mainly depends on the synchrotron radiation source X-ray metrology station. This kind of device is usually located in a different place from the large laser facility for ICF research, thus it is difficult to meet the real-time field calibration application requirements of ICF’s research soft X-ray components research. In addition, in view of the great difference between the radiation characteristics of synchrotron radiation X-ray and ICF laser plasma X-ray, the calibration results of synchrotron radiation measurement station can not completely measure the response characteristics of components in ICF experiments. In this paper, a kind of monochromatic technology for compact non-harmonic soft X-ray source is introduced. Based on this technology, a monochromatic system of multi energy channel source based on ICF laser plasma X-ray source with homologous, geometric configuration and double beam comparison calibration is developed for on-line calibration of soft X-ray components in ICF applications. The new system is expected to meet the requirements of real-time calibration application of ICF’s soft X-ray components, while the technical characteristics of its calibration beam will be as close as possible to that of the ICF laser plasma X-ray radiation.
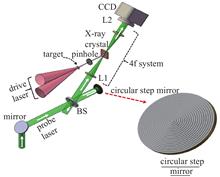
This paper introduces the relationship between X-ray line emission diagnosis and various physical quantities in the study of inertial confinement fusion, and briefly explains the diagnosis method and principle of X-ray crystal spectrometer. For different types of diagnosis, it introduces the functions and principles of different commonly used types of diffraction crystals. In addition, it introduces a new type of X-ray diagnostic method of multi-cone curved crystals, which has high light collection efficiency and at the same time ensures the delicate coupling of the back-end receiving device and reduces aberrations. Based on the study of the diffraction characteristics of the multi-cone curved crystal, X-Chase, an X-ray arbitrary surface crystal diffraction tracking simulation software, was developed. At the same time, the multi-cone crystal of H and He line emissions on the SG laser facility is utilized to demonstrate the code functions. The numerical simulation results show that the variable cone crystal has a good focusing ability.
Low temporal coherence pulse can effectively increase the threshold of parametric instabilities in the laser and plasma interaction. However, frequency conversion efficiency is one of the bottlenecks in its engineering application. The characteristics of frequency conversion technologies of various low-coherence pulse for the high-power laser drivers are summarized in this paper, and based on numerical simulations and experiments, application feasibility of partial deuterium DKDP crystals for frequency doubling and tripling of super-luminescent light are analyzed in detail. The results show that 17% deuterium DKDP crystals can be used for efficient frequency doubling of super-luminescent light in neodymium glass systems, and the conversion efficiency can reach about 80%. 10% gradient deuterium DKDP crystals can be used for triple frequency of 5 THz bandwidth.
The dynamic response of materials is strongly dependent on the temporal evolution of microstructures. As a comprehensive experimental platform integrating dynamic loading and in-situ diagnostic capability, large-scale laser facilities provide technical support to investigate micro-mesoscopic behaviors of materials under extreme conditions of high temperature, high pressure, and high strain rate. The use of high-power pulsed lasers to explore the response of materials under the pressure of tens of GPa up to several TPa, the time duration of nanoseconds, and the strain rate of 106-1010 s-1 is revealing novel mechanisms of plastic deformation and therefore strength evolution. This unique experimental tool, aided by advanced diagnostics, analysis, and characterization, including X-ray diffraction, absorption and imaging, allows us to make real-time observation on these new regimes with high spatial and temporal resolution. In this paper, we review the progress within the last 20 years in micro-mesoscopic dynamic probing techniques, based on large-scale laser facilities, and their applications in the study of dynamic plasticity and strength. At the end, we discuss the significance of these works to promote the multiscale modeling of the dynamic response of materials.