View fulltext
View fulltext
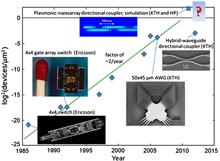
We review the emergence and development of integrated photonics and its status today. The treatise is focused on information and communications technology (ICT) applications, but the technology is generically employable for a wealth of other applications, such as sensors. General properties of the waveguides that form the basis of integrated photonics are reviewed, and several examples of integrated photonics based on silicon and plasmonics are presented. The all-important development of integrated low-power nanophotonics is discussed and current challenges and prospects of the field are elucidated. The treatment is focused on the photonic fabric between source and detector.
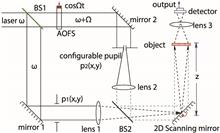
The optical scanning holography (OSH) technique can capture all the three-dimensional volume information of an object in a hologram via a single raster scan. The digital hologram can then be processed to reconstruct individual sectional images of the object. In this paper, we present a scheme to reconstruct sectional images in OSH with enhanced depth resolution, where a spatial light modulator (SLM) is adopted as a configurable point pupil. By switching the SLM between two states, different Fresnel zone plates (FZPs) are generated based on the same optical system. With extra information provided by different FZPs, a depth resolution at 0.7 μm can be achieved.
With the development of semiconductor technology, semiconductor laser devices and semiconductor laser pump solid-state laser devices have been widely applied in z-scan experiments. However, the feedback light-induced output instability of semiconductor laser devices can negatively affect the accurate testing of the nonlinear index. In this work, the influence of feedback light on z-scan measurement is analyzed. Then the calculated formula of feedback light-induced false nonlinear z-scan curves is theoretically derived and experimentally verified. Two methods are proposed to reduce or eliminate the feedback light-induced false nonlinear effect. One is the addition of an attenuator to the z-scan optical path, and the other is the addition of an opto-isolator unit to the z-scan setup. The experimental and theoretical results indicate that the feedback light-induced false nonlinear effect is markedly reduced and can even be ignored if appropriate parameters are chosen. Thus, theoretical and experimental methods of eliminating the negative effect of feedback light on z-scan measurement are useful for accurately obtaining the nonlinear index of a sample.
Wepresent a novel method for engineering ultra-flattened-dispersion photonic crystal fibers with uniform air holes by rotations of inner air-hole rings around the fiber core. By choosing suitable rotation angles of each inner ring, theoretical results show that normal, anomalous, and nearly zero ultra-flattened-dispersion fibers in wide spectra ranges of interest can be obtained alternatively. Moreover, in our dispersion sensitive analysis, these types of fibers are robust to variations from optimal design parameters. The method is suitable for the accurate adjustment of fiber dispersion within a small range, which would be valuable for the fabrication of ultra-flattened-dispersion fibers and also have potential applications in wide-band high-speed optical communication systems.
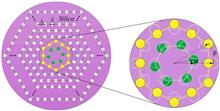
The polarization behavior of elastic scattering at 1473 nm is analyzed from a silicon microsphere on an optical fiber half-coupler. The 0.27 nm angular mode spacing of the resonances correlates well with the optical size of the silicon sphere. The spectral linewidths of the resonances are on the order of 10-3 nm, which corresponds to quality factors on the order of 106. The transverse magnetically polarized elastic scattering signal has higher resonance to modulation depth and background ratio than the transverse electrically polarized elastic scattering signal and is suitable for high-resolution optical filtering applications such as optical monitoring and sensing.
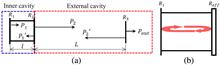
A novel athermal scheme utilizing resonance splitting of a dual-ring structure is proposed. Detailed design and simulation are presented, and a proof of concept structure is optimized to demonstrate an athermal resonator with resonance wavelength variation lower than 5 pm∕K within 30 K temperature range.