View fulltext
View fulltext
The cover illustrates the concept of deciphering the wavefront aberrations from the acquired image itself via our deep learning methods, without the need of conventional wavefront sensor systems, to recover the high-quality super-resolution image. See Chang Qiao et al., pp. 474.
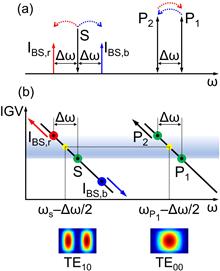
Intermodal four-wave mixing (FWM) processes have recently attracted significant interest for all-optical signal processing applications thanks to the possibility to control the propagation properties of waves exciting distinct spatial modes of the same waveguide. This allows, in principle, to place signals in different spectral regions and satisfy the phase matching condition over considerably larger bandwidths compared to intramodal processes. However, the demonstrations reported so far have shown a limited bandwidth and suffered from the lack of on-chip components designed for broadband manipulation of different modes. We demonstrate here a silicon-rich silicon nitride wavelength converter based on Bragg scattering intermodal FWM, which integrates mode conversion, multiplexing and de-multiplexing functionalities on-chip. The system enables wavelength conversion between pump waves and a signal located in different telecommunication bands (separated by 60 nm) with a 3 dB bandwidth exceeding 70 nm, which represents, to our knowledge, the widest bandwidth ever achieved in an intermodal FWM-based system.
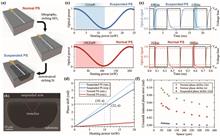
Silicon nitride (SiNx) is an appealing waveguide material choice for large-scale, high-performance photonic integrated circuits (PICs) due to its low optical loss. However, SiNx PICs require high electric power to realize optical reconfiguration via the weak thermo-optic effect, which limits their scalability in terms of device density and chip power dissipation. We report a 6-mode programmable interferometer PIC operating at the wavelength of 1550 nm on a CMOS-compatible low-temperature inductance coupled plasma chemical vapor deposition (ICP-CVD) silicon nitride platform. By employing suspended thermo-optic phase shifters, the PIC achieves 2× improvement in compactness and 10× enhancement in power efficiency compared to conventional devices. Reconfigurable 6-dimensional linear transformations are demonstrated including cyclic transformations and arbitrary unitary matrices. This work demonstrates the feasibility of fabricating power-efficient large-scale reconfigurable PICs on the low-temperature ICP-CVD silicon nitride platform.
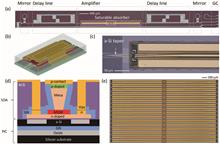
We demonstrate a III-V-on-silicon-nitride mode-locked laser through the heterogeneous integration of a semiconductor optical amplifier on a passive silicon-nitride cavity using the technique of micro-transfer printing. In the initial phase of our study, we focus on optimizing the lasing wavelength to be centered at 1550 nm. This optimization is achieved by conducting experiments with 27 mode-locked lasers, each incorporating optical amplifiers featuring distinct multiple-quantum-well photoluminescence values. Subsequently we present a comprehensive study investigating the behavior of the mode-locking regime when the electrical driving parameters are varied. Specifically, we explore the impact of the gain voltage and saturable absorber current on the locking stability of a tunable mode-locked laser. By manipulating these parameters, we demonstrate the precise control of the optical spectrum across a wide range of wavelengths spanning from 1530 to 1580 nm. Furthermore, we implement an optimization approach based on a Monte Carlo analysis aimed at enhancing the mode overlap within the gain region. This adjustment enables the achievement of a laser emitting a 23-nm-wide spectrum while maintaining a defined 10 dB bandwidth for a pulse repetition rate of 3 GHz.
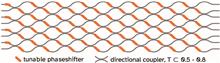
We introduce a programmable eight-port interferometer with the recently proposed error-tolerant architecture capable of performing a broad class of transformations. The interferometer has been fabricated with femtosecond laser writing, and it is the largest programmable interferometer of this kind to date. We have demonstrated its advantageous error tolerance by showing an operation in a broad wavelength range from 920 to 980 nm, which is particularly relevant for quantum photonics due to efficient photon sources existing in this wavelength range. Our work highlights the importance of developing novel architectures of programmable photonics for information processing.
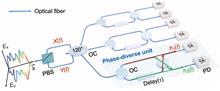
Data centers, the engines of the global Internet, rely on powerful high-speed optical interconnects. In optical fiber communication, classic direct detection captures only the intensity of the optical field, while the coherent detection counterpart utilizes both phase and polarization diversities at the expense of requiring a narrow-linewidth and high-stability local oscillator (LO). Herein, we propose and demonstrate a four-dimensional Jones-space optical field recovery (4-D JSFR) scheme without an LO. The polarization-diverse full-field receiver structure captures information encoded in the intensity and phase of both polarizations, which can be subsequently extracted digitally. To our knowledge, our proposed receiver achieves the highest electrical spectral efficiency among existing direct detection systems and potentially provides similar electrical spectral efficiency as standard intradyne coherent detection systems. The fully recovered optical field extends the transmission distance beyond the limitations imposed by fiber chromatic dispersion. Moreover, the LO-free advantage makes 4-D JSFR suitable for photonic integration, offering a spectrally efficient and cost-effective solution for massively parallel data center interconnects. Our results may contribute to the ongoing developments in the theory of optical field recovery and the potential design considerations for future high-speed optical transceivers.
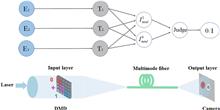
The propagation of coherent light in multimode optical fibers results in a speckled output that is both complex and sensitive to environmental effects. These properties can be a powerful tool for sensing, as small perturbations lead to significant changes in the output of the fiber. However, the mechanism to encode spatially resolved sensing information into the speckle pattern and the ability to extract this information are thus far unclear. In this paper, we demonstrate that spatially dependent mode coupling is crucial to achieving spatially resolved measurements. We leverage machine learning to quantitatively extract the spatially resolved sensing information from three fiber types with dramatically different characteristics and demonstrate that the fiber with the highest degree of spatially dependent mode coupling provides the greatest accuracy.
Multimode fibers (MMFs) are a promising solution for high-throughput signal transmission in the time domain. However, crosstalk among different optical modes within the MMF scrambles input information and creates seemingly random speckle patterns at the output. To characterize this process, a transmission matrix (TM) can be used to relate input and output fields. Recent innovations use TMs to manipulate the output field by shaping the input wavefront for exciting advances in deep-brain imaging, neuron stimulation, quantum networks, and analog operators. However, these approaches consider input/output segments as independent, limiting their use for separate signal processing, such as logic operations. Our proposed method, which makes input/output segments as interdependent, adjusts the phase of corresponding output fields using phase bias maps superimposed on input segments. Coherent superposition enables signal logic operations through a 15-m-long MMF. In experiments, a single optical logic gate containing three basic logic functions and cascading multiple logic gates to handle binary operands is demonstrated. Bitwise operations are performed for multi-bit logic operations, and multiple optical logic gates are reconstructed simultaneously in a single logic gate with polarization multiplexing. The proposed method may open new avenues for long-range logic signal processing and transmission via MMFs.
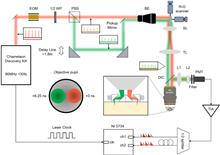
Biodynamical processes, especially in system biology, that occur far apart in space may be highly correlated. To study such biodynamics, simultaneous imaging over a large span at high spatio-temporal resolutions is highly desired. For example, large-scale recording of neural network activities over various brain regions is indispensable in neuroscience. However, limited by the field-of-view (FoV) of conventional microscopes, simultaneous recording of laterally distant regions at high spatio-temporal resolutions is highly challenging. Here, we propose to extend the distance of simultaneous recording regions with a custom micro-mirror unit, taking advantage of the long working distance of the objective and spatio-temporal multiplexing. We demonstrate simultaneous dual-region two-photon imaging, spanning as large as 9 mm, which is 4 times larger than the nominal FoV of the objective. We verify the system performance in in vivo imaging of neural activities and vascular dilations, simultaneously, at two regions in mouse brains as well as in spinal cords, respectively. The adoption of our proposed scheme will promote the study of systematic biology, such as system neuroscience and system immunology.
Optical aberrations degrade the performance of fluorescence microscopy. Conventional adaptive optics (AO) leverages specific devices, such as the Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor and deformable mirror, to measure and correct optical aberrations. However, conventional AO requires either additional hardware or a more complicated imaging procedure, resulting in higher cost or a lower acquisition speed. In this study, we proposed a novel space-frequency encoding network (SFE-Net) that can directly estimate the aberrated point spread functions (PSFs) from biological images, enabling fast optical aberration estimation with high accuracy without engaging extra optics and image acquisition. We showed that with the estimated PSFs, the optical aberration can be computationally removed by the deconvolution algorithm. Furthermore, to fully exploit the benefits of SFE-Net, we incorporated the estimated PSF with neural network architecture design to devise an aberration-aware deep-learning super-resolution model, dubbed SFT-DFCAN. We demonstrated that the combination of SFE-Net and SFT-DFCAN enables instant digital AO and optical aberration-aware super-resolution reconstruction for live-cell imaging.
The exact physical modeling for scattered light modulation is critical in phototherapy, biomedical imaging, and free-space optical communications. In particular, the angular spectrum modeling of scattered light has attracted considerable attention, but the existing angular spectrum models neglect the polarization of photons, degrading their performance. Here, we propose a full-polarization angular spectrum model (fpASM) to take the polarization into account. This model involves a combination of the optical field changes and free-space angular spectrum diffraction, and enables an investigation of the influence of polarization-related factors on the performance of scattered light modulation. By establishing the relationship between various model parameters and macroscopic scattering properties, our model can effectively characterize various depolarization conditions. As a demonstration, we apply the model in the time-reversal data transmission and anti-scattering light focusing. Our method allows the analysis of various depolarization scattering events and benefits applications related to scattered light modulation.
Driven by the large volume demands of data in transmission systems, the number of spatial modes supported by mode-division multiplexing (MDM) systems is being increased to take full advantage of the parallelism of the signals in different spatial modes. As a key element for photonic integrated circuits, the multimode waveguide optical switch (MWOS) is playing an important role for data exchange and signal switching. However, the function of the traditional MWOS is simple, which could only implement the mode-insensitive or mode-selective switching function; it is also difficult to scale to accommodate more spatial modes because of the limitation of the device structure. Therefore, it is still challenging to realize a multifunctional and scalable MWOS that could support multiple modes with low power consumption and high flexibility. Here, we propose and experimentally demonstrate a multifunctional MWOS based on asymmetric Y-junctions and multimode interference (MMI) couplers fabricated on a polymer waveguide platform. Both mode-insensitive and mode-selective switching functions can be achieved via selectively heating different electrode heaters. The fabricated device with the total length of ∼0.8 cm shows an insertion loss of less than 12.1 dB, and an extinction ratio of larger than 8.4 dB with a power consumption of ∼32 mW for both mode-insensitive and mode-selective switching functions, at 1550 nm wavelength. The proposed MWOS can also be scaled to accommodate more spatial modes flexibly and easily, which can serve as an important building block for MDM systems.
We calculate numerically the optical chiral forces in rectangular cross-section dielectric waveguides for potential enantiomer separation. Our study considers force strength and time needed for separating chiral nanoparticles, mainly via quasi-TE guided modes at short wavelengths (405 nm) and the 90°-phase-shifted combination of quasi-TE and quasi-TM modes at longer wavelengths (1310 nm). Particle tracking simulations show successful enantiomer separation within two seconds. These results suggest the feasibility of enantiomeric separation of nanoparticles displaying sufficient chirality using simple silicon photonic integrated circuits, with wavelength selection based on the nanoparticle size.
Distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) technology has been a promising tool in various applications. Currently, the large size and relatively high cost of DAS equipment composed of discrete devices restrict its further popularization to some degree, and the photonic integration technology offers a potential solution. In this paper, we demonstrate an integrated interrogator for DAS on the silicon-on-insulator (SOI) platform. The design of the chip revolves around a Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM) transmitter and a dual-quadrature and dual-polarization coherent receiver. The integrated interrogator supports multiple DAS schemes, including the time-gated digital optical frequency domain reflectometry (TGD-OFDR), which is adopted for system performance evaluation. 59 pε/Hz strain resolution in 12.1 km sensing fiber with 1.14 m spatial resolution (SR) is realized. Besides, along 49.0 km sensing fiber, 81 pε/Hz strain resolution with 3.78 m SR is achieved. The results show that the integrated interrogator has comparable performance to the discrete DAS system. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first dedicated on-chip DAS interrogator, which validates the effectiveness of the blend of photonics integration and DAS technology.
Optical computing has shown immense application prospects in the post-Moore era. However, as a crucial component of logic computing, the digital multiplier can only be realized on a small scale in optics, restrained by the limited functionalities and inevitable loss of optical nonlinearity. In this paper, we propose a time-space multiplexed architecture to realize large-scale photonic-electronic digital multiplication. We experimentally demonstrate an 8×2-bit photonic-electronic digital multiplier, and the multiplication with a 32-bit number is further executed at 25 Mbit/s to demonstrate its extensibility and functionality. Moreover, the proposed architecture has the potential for on-chip implementation, and a feasible integration scheme is provided. We believe the time-space multiplexed photonic-electronic digital multiplier will open up a promising avenue for large-scale photonic digital computing.
Second-order topological photonic crystals support localized corner modes that deviate from the conventional bulk-edge correspondence. However, the frequency shift of corner modes spanning the photonic band gap has not been experimentally reported. Here, we observe the gapless corner modes of photonic crystal slabs within a parameter space by considering translation as an additional synthetic dimension. These corner modes, protected by topological pumping in synthetic translation dimensions, are found to exist independently of the specific corner configuration. The gapless corner modes are experimentally imaged via the near-field scanning measurement and validated numerically by full-wave simulations. We propose a topological rainbow with gradient translation, demonstrating the ability to extract and separate specific frequency components of light into different spatial locations. Our work contributes to the advancement of topological photonics and provides valuable insights into the exploration of gapless corner modes in synthetic dimensions.
Cnoidal waves are a type of nonlinear periodic wave solutions of the nonlinear dynamic equations. They are well known in fluid dynamics, but it is not the case in optics. In this paper we show both experimentally and numerically that cnoidal waves could be formed in a fiber laser either in the net normal or net anomalous cavity dispersion regime, especially because, as the pump power is increased, the formed cnoidal waves could eventually evolve into a train of bright (in the net anomalous cavity dispersion regime) or dark (in the net normal cavity dispersion regime) solitons. Numerical simulations of the laser operation based on the extended nonlinear Schrödinger equation (NLSE) have well reproduced the experimental observations. The result not only explains why solitons can still be formed in a fiber laser even without mode locking but also suggests a new effective way of automatic stable periodic pulse train generation in lasers with a nonlinear cavity.
Yttrium iron garnet (YIG) is a promising material for various terahertz applications due to its special optical properties. At present, a high-quality YIG wafer is the desire of terahertz communities and it is still challenging to prepare substrate-free YIG single crystal films. In this work, we prepared wafer-level substrate-free La:YIG single crystal films, for the first time, to our knowledge. Terahertz optical and magneto-optical properties of La:YIG films were characterized by terahertz time domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS). Results show that the as-prepared La:YIG film has an insertion loss of less than 3 dB and a low absorption coefficient of less than 10 cm-1 below 1.6 THz. Benefitting from the thickness of the substrate-free YIG films and low insertion loss, their terahertz properties could be further manipulated by simply using a wafer-stacking technique. When four La:YIG films were stacked, there was an insertion loss of less than 10 dB in the range of 0.1-1.2 THz. The Faraday rotation angle of the four-layer-stacked La:YIG films reached 19°, and the isolation could reach 17 dB. By further increasing the stacking number to eight pieces, a remarkable Faraday rotation angle of 45° was achieved with an isolation of 23 dB, which is important for practical application in the THz band. This material may provide a milestone opportunity to make various non-reciprocal devices, such as isolators and phase shifters.
The dielectric confinement effect plays an essential role in optoelectronic devices. Existing studies on the relationship between the dielectric confinement and the photoelectric properties are inadequate. Herein, three organic spacers with different dielectric constants are employed to tune the exciton dynamics of quasi-two-dimensional (quasi-2D) Ruddlesden–Popper perovskite films. Femtosecond transient absorption spectroscopy reveals that the small dielectric constant ligand enables a weak dynamic disorder and a large modulation depth of the coherent phonons, resulting in a more complete energy transfer and the inhibition of a trap-mediated nonradiative recombination. Additionally, the increase in the bulk-ligand dielectric constant reduces the corresponding exciton binding energy and then suppresses the Auger recombination, which is beneficial for high-luminance light-emitting diodes. This work emphasizes the importance of dielectric confinement for regulating the exciton dynamics of layered perovskites.
We experimentally demonstrate and numerically analyze large arrays of whispering gallery resonators. Using fluorescent mapping, we measure the spatial distribution of the cavity ensemble’s resonances, revealing that light reaches distant resonators in various ways, including while passing through dark gaps, resonator groups, or resonator lines. Energy spatially decays exponentially in the cavities. Our practically infinite periodic array of resonators, with a quality factor (Q) exceeding 107, might impact a new type of photonic ensembles for nonlinear optics and lasers using our cavity continuum that is distributed, while having high-Q resonators as unit cells.
Polarization is one of the basic characteristics of electromagnetic (EM) waves, and its flexible control is very important in many practical applications. At present, most of the multifunction polarization metasurfaces are electrically tunable based on PIN and varactor diodes, which are easy to operate and have strong real-time performance. However, there are still some problems in them, such as few degrees of freedom of planar structure control, complex circuit, bulky sample, and high cost. In view of these shortcomings, this paper proposes a Miura origami based reconfigurable polarization conversion metasurface for multifunctional control of EM waves. The interaction between the electric dipoles is changed by adjusting the folding angle θ, thereby tuning the operating frequency of the polarization conversion and the polarization state of the reflected wave. This mechanical control method brings more degrees of freedom to manipulate EM waves. And the processed sample is with lightweight and low cost. To verify the performance of the proposed origami polarization converter, a Miura origami structure loaded with metal split rings is designed and fabricated. The operating frequency of the structure can be tuned in different folding states. In addition, by controlling the folding angle θ, linear-to-linear and linear-to-circular polarization converters can be realized at different folding states. The proposed Miura origami polarization conversion metasurface provides a new idea for reconfigurable linear polarization conversion and multifunctional devices.
We propose and experimentally realize a class of quasi-one-dimensional topological lattices whose unit cells are constructed by coupled multiple identical resonators, with uniform hopping and inversion symmetry. In the presence of coupling-path-induced effective zero hopping within the unit cells, the systems are characterized by complete multimerization with degenerate -1 energy edge states for open boundary condition. Su–Schrieffer–Heeger subspaces with fully dimerized limits corresponding to pairs of nontrivial flat bands are derived from the Hilbert spaces. In particular, topological bound states in the continuum (BICs) are inherently present in even multimer chains, manifested by embedding the topological bound states into a continuous band assured by bulk-boundary correspondence. Moreover, we experimentally demonstrate the degenerate topological edge states and topological BICs in radio-frequency circuits.
Exceptional points, as degenerate points of non-Hermitian parity-time symmetric systems, have many unique physical properties. Due to its flexible control of electromagnetic waves, a metasurface is frequently used in the field of nanophotonics. In this work, we developed a parity-time symmetric metasurface and implemented the 2π topological phase surrounding an exceptional point. Compared with Pancharatnam-Berry phase, the topological phase around an exceptional point can achieve independent regulation of several circular polarization beams. We combined the Pancharatnam-Berry phase with the exceptional topological phase and proposed a composite coding metasurface to achieve reflection decoupling of different circular polarizations. This work provides a design idea for polarimetric coding metasurfaces in the future.
Indefinite metacavities (IMCs) made of hyperbolic metamaterials show great advantages in terms of extremely small mode volume due to large wave vectors endowed by the unique hyperbolic dispersion. However, quality (Q) factors of IMCs are limited by Ohmic loss of metals and radiative loss of leaked waves. Despite the fact that Ohmic loss of metals is inevitable in IMCs, the radiative loss can be further suppressed by leakage engineering. Here we propose a mirror coupled IMC structure which is able to operate at Fabry–Pérot bound states in the continuum (BICs) while the hyperbolic nature of IMCs is retained. At the BIC point, the radiative loss of magnetic dipolar cavity modes in IMCs is completely absent, resulting in a considerably increased Q factor (>90). Deviating from the BIC point, perfect absorption bands (>0.99) along with a strong near-field intensity enhancement (>1.8×104) appear when the condition of critical coupling is almost fulfilled. The proposed BICs are robust to the geometry and material composition of IMCs and anomalous scaling law of resonance is verified during the tuning of optical responses. We also demonstrate that the Purcell effect of the structure can be significantly improved under BIC and quasi-BIC regimes due to the further enhanced Q factor to mode volume ratio. Our results provide a new train of thought to design ultra-small optical nanocavities that may find many applications benefitting from strong light–matter interactions.
Multipartite Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) steering admits multipartite entanglement in the presence of uncharacterized verifiers, enabling practical applications in semi-device-independent protocols. Such applications generally require stronger steerability, while the unavoidable noise weakens steerability and consequently degrades the performance of quantum information processing. Here, we propose the local filtering operation that can maximally distill genuine tripartite EPR steering from N copies of three-qubit generalized Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger states, in the context of two semi-device-independent scenarios. The optimal filtering operation is determined by the maximization of assemblage fidelity. Analytical and numerical results indicate the advantage of the proposed filtering operation when N is finite and the steerability of initial assemblages is weak. Experimentally, a proof-of-principle demonstration of two-copy distillation is realized with the optical system. The advantage of the optimal local filtering operation is confirmed by the distilled assemblage in terms of higher assemblage fidelity with perfectly genuine tripartite steerable assemblages, as well as the greater violation of the inequality to witness genuine tripartite steerable assemblages. Our results benefit the distillation of multipartite EPR steering in practice, where the number of copies of initial assemblages is generally finite.
Atomic arrays provide an important quantum optical platform with photon-mediated dipole–dipole interactions that can be engineered to realize key applications in quantum information processing. A major obstacle for such applications is the fast decay of the excited states. By controlling two-band Bloch oscillations of single excitation in an atomic array under an external magnetic field, here we show that exotic subradiance can be realized and maintained with orders of magnitude longer than the spontaneous decay time in atomic arrays with the finite size. The key finding is to show a way for preventing the wavepacket of excited states scattering into the dissipative zone inside the free space light cone, which therefore leads to the excitation staying at a subradiant state for an extremely long decay time. We show that such operation can be achieved by introducing a spatially linear potential from the external magnetic field in the atomic arrays and then manipulating interconnected two-band Bloch oscillations along opposite directions. Our results also point out the possibility of controllable switching between superradiant and subradiant states, which leads to potential applications in quantum storage.
Polarization is crucial in various fields such as imaging, sensing, and substance detection. A compact, fast, and accurate polarization detection device is vital for these applications. Herein, we demonstrate a multifocus metalens for terahertz polarization detection that requires only a single measurement to obtain complete polarization parameters and reconstruct the polarization state of the incident field. The individual subarrays of this metalens convert each of the six polarized components into the same polarization, which in turn links the Stokes parameters to these six foci. The incident linear polarizations and elliptical polarizations are characterized by Stokes parameters and polarization ellipses. Simulations and experimental results show that the scheme can accurately detect the incident polarization with a single measurement. The proposed metasurface polarimetry may find applications in the fields of real-time terahertz detection and integrated optics.
Lead-free perovskite Cs2AgBiBr6 manifests great potential in developing high-performance, environmentally friendly, solution-processable photodetectors (PDs). However, due to the relatively large energy bandgap, the spectrum responses of Cs2AgBiBr6 PDs are limited to the ultraviolet and visible region with wavelengths shorter than 560 nm. In this work, a broadband Cs2AgBiBr6 PD covering the ultraviolet, visible, and near infrared (NIR) range is demonstrated by incorporating titanium nitride (TiN) nanoparticles that are prepared with the assistance of self-assembled polystyrene sphere array. In addition, an atomically thick Al2O3 layer is introduced at the interface between the Cs2AgBiBr6 film and TiN nanoparticles to alleviate the dark current deterioration caused by nanoparticle incorporation. As a result, beyond the spectrum range where Cs2AgBiBr6 absorbs light, the external quantum efficiency (EQE) of the TiN nanoparticle incorporated Cs2AgBiBr6 PD is enhanced significantly compared with that of the control, displaying enhancement factors as high as 2000 over a broadband NIR wavelength range. The demonstrated enhancement in EQE arises from the photocurrent contribution of plasmonic hot holes injected from TiN nanoparticles into Cs2AgBiBr6. This work promotes the development of broadband solution-processable perovskite PDs, providing a promising strategy for realizing photodetection in the NIR region.