View fulltext
View fulltext
A broad light beam propagating through a red-blood-cell suspension may break up into spatial filaments owing to spatial modulation and scattering by the cells. Driven by Brownian motion and spontaneous synchronization, some filaments may exhibit spatial analog of rogue waves. See Yu-Xuan Ren et al., pp. 1838.
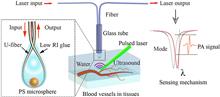
Optical ultrasonic probes, exemplified by Fabry–Perot cavities on optical fibers, have small sizes, high sensitivity, and pure optical characteristics, making them highly attractive in high-resolution ultrasonic/photoacoustic imaging, especially in near-field or endoscopic scenarios. Taking a different approach, we demonstrate an ultrasensitive and broadband ultrasound microprobe formed by an optical whispering-gallery-mode polymer microcavity coupled to a U-shaped microfiber. With the high-quality (Q) factors (>106), the noise equivalent pressure of the ultrasound microprobe reaches 1.07 mPa/√Hz with a record broadband response of 150 MHz and a large detection angle of 180°. Our results show that this optical microprobe can overcome the strong decay resulting from ultrasound diverging and medium absorption through short working distances. We further demonstrate high-quality in vivo whole-body photoacoustic imaging of a zebrafish larva. Our implementation provides a new strategy for developing miniature ultrasound detectors and holds great potential for broad applications.
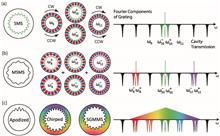
Frequency engineering of whispering-gallery resonances is essential in microcavity nonlinear optics. The key is to control the frequencies of the cavity modes involved in the underlying nonlinear optical process to satisfy its energy conservation criterion. Compared to the conventional method that tailors dispersion by cross-sectional geometry, thereby impacting all cavity mode frequencies, grating-assisted microring cavities, often termed as photonic crystal microrings, provide more enabling capabilities through mode-selective frequency control. For example, a simple single period grating added to a microring has been used for single frequency engineering in Kerr optical parametric oscillation (OPO) and frequency combs. Recently, this approach has been extended to multi-frequency engineering by using multi-period grating functions, but at the cost of increasingly complex grating profiles that require challenging fabrication. Here, we demonstrate a simple approach, which we term as shifted grating multiple mode splitting (SGMMS), where spatial displacement of a single period grating imprinted on the inner boundary of the microring creates a rotational asymmetry that frequency splits multiple adjacent cavity modes. This approach is easy to implement and presents no additional fabrication challenges compared to an un-shifted grating, and yet is very powerful in providing multi-frequency engineering functionality for nonlinear optics. We showcase an example where SGMMS enables OPO across a wide range of pump wavelengths in a normal-dispersion device that otherwise would not support OPO.
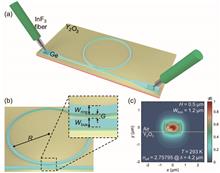
We experimentally demonstrate an all-pass microring resonator (MRR) based on a Y2O3 BOX germanium-on-insulator (GeOI) platform operating in the mid-IR region. The ring resonator was numerically designed to have a high quality (Q) factor in the 4.18 μm to 4.22 μm wavelength range in the fundamental TE mode. According to our design, the GeOI ring resonator was fabricated by the direct wafer-bonding technology with an yttria (Y2O3) buried oxide layer, which is transparent at the mid-IR region, for the bonding interface and the electron beam lithography. The experimental resonant characteristic was obtained using our fiber-based mid-IR measurement setup. The GeOI single MRR exhibited an extinction ratio (ER) of 15.28 dB and an insertion loss (IL) of 1.204 dB, and the racetrack showed an ER of 22.77 dB and an IL of 0.627 dB. Furthermore, the free spectral range of the device was 5.29 nm, and the loaded Q factor of 94,528 (176,158 of intrinsic Q factor) was extracted by the nonlinear least squares method. We believe this demonstration of our GeOI MRR offers a valuable opportunity to implement multipurpose devices such as optical sensors, switches, and filters in the mid-IR range.
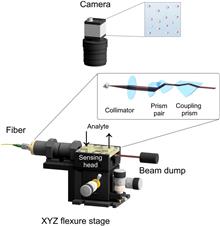
The per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a group of organofluorine chemicals treated as the emerging pollutants that are currently of particularly acute concern. These compounds have been employed intensively as surfactants over multiple decades and are already to be found in surface and ground waters at amounts sufficient to have an effect on human health and ecosystems. Because of the carbon–fluorine bonds, the PFAS have an extreme environmental persistence and their negative impact accumulates with further production and penetration into the environment. In Germany alone, more than thousands of sites have been identified as contaminated with PFAS; thus, timely detection of PFAS residue is becoming a high priority. In this paper, we report on the high performance optical detection method based on whispering gallery mode (WGM) microcavities applied for the first time to detect PFAS contaminants in aqueous solutions. A self-sensing boosted 4D microcavity fabricated with two-photon polymerization is employed as an individual sensing unit. In an example of the multiplexed imaging sensor with multiple hundreds of simultaneously interrogated microcavities we demonstrate the possibility to detect the PFAS chemicals representatives at a level down to 1 ppb (parts per billion).
Self-chaotic dual-mode and tri-mode microcavity lasers have been recently proposed and demonstrated for high-speed random number generation. Here, we report the characteristics of irregular pulse packages and self-chaos operation for a dual-mode circular-sided square microcavity laser. In addition to the mode interaction between the fundamental and first-order transverse modes, we observed irregular pulse packages due to the mode beating of near-degenerate modes for the first time to our best knowledge. Moreover, a successive route from periodic-one and periodic-three states to chaos is first experimentally illustrated by increasing injection current. The chaotic state is observed over a current range of 10 mA, and the maximum chaos effective bandwidth of 22.4 GHz is realized with a flatness of ±4 dB. Chaotic characteristics are also investigated for different longitudinal modes, which indicates that the self-chaotic microlaser can provide robust parallel chaotic outputs for practical application.
Professor John Bowers discusses his career in integrated photonics with his former student, Prof. Lin Chang.
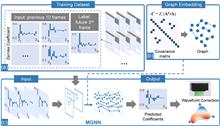
The time-delay problem, which is introduced by the response time of hardware for correction, is a critical and non-ignorable problem of adaptive optics (AO) systems. It will result in significant wavefront correction errors while turbulence changes severely or system responses slowly. Predictive AO is proposed to alleviate the time-delay problem for more accurate and stable corrections in the real time-varying atmosphere. However, the existing prediction approaches either lack the ability to extract non-linear temporal features, or overlook the authenticity of spatial features during prediction, leading to poor robustness in generalization. Here, we propose a mixed graph neural network (MGNN) for spatiotemporal wavefront prediction. The MGNN introduces the Zernike polynomial and takes its inherent covariance matrix as physical constraints. It takes advantage of conventional convolutional layers and graph convolutional layers for temporal feature catch and spatial feature analysis, respectively. In particular, the graph constraints from the covariance matrix and the weight learning of the transformation matrix promote the establishment of a realistic internal spatial pattern from limited data. Furthermore, its prediction accuracy and robustness to varying unknown turbulences, including the generalization from simulation to experiment, are all discussed and verified. In experimental verification, the MGNN trained with simulated data can achieve an approximate effect of that trained with real turbulence. By comparing it with two conventional methods, the demonstrated performance of the proposed method is superior to the conventional AO in terms of root mean square error (RMS). With the prediction of the MGNN, the mean and standard deviation of RMS in the conventional AO are reduced by 54.2% and 58.6% at most, respectively. The stable prediction performance makes it suitable for wavefront predictive correction in astronomical observation, laser communication, and microscopic imaging.
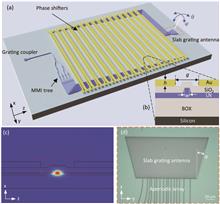
An on-chip optical phased array (OPA) is considered as a promising solution for next generation solid-state beam steering. However, most of the reported OPAs suffer from low operating bandwidths, making them limited in many applications. We propose and demonstrate a high-speed 2D scanning OPA based on thin-film lithium niobate phase modulators with traveling-wave electrodes. The measured modulation bandwidth is up to 2.5 GHz. Moreover, an aperiodic array combined with a slab grating antenna is also used to suppress the grating lobes of far-field beams, which enables a large field of view (FOV) as well as small beam width. A 16-channel OPA demonstrates an FOV of 50°×8.6° and a beam width of 0.73°×2.8° in the phase tuning direction and the wavelength scanning direction, respectively.
Resonant sidebands in soliton fiber lasers have garnered substantial interest in recent years due to their crucial role in understanding soliton propagation and interaction dynamics. However, most previous studies and applications were restricted to focusing on only the first few low-order resonant sidebands because higher-order sidebands usually decay exponentially as their wavelengths shift far away from the soliton center and are negligibly weak. Here we report numerically and experimentally significant enhancement of multiple resonant sidebands in a soliton fiber laser mode-locked by a nonlinear polarization evolution mechanism. The birefringence and the gain profile of the laser cavity were shown to be critical for this phenomenon. Multiple intense resonant sidebands were generated whose maximum intensity was more than 30 dB higher than that of the soliton, which is the highest yet reported, to our knowledge. To accurately predict the wavelengths of all high-order resonant sidebands, an explicit formula was derived by taking the third-order dispersion effect into account. The temporal features of multiple orders of resonant sidebands were characterized, which all exhibit exponentially decaying leading edges. This study provides insight into understanding the properties of high-order resonant sidebands in a soliton laser and opens possibilities for constructing multi-wavelength laser sources.
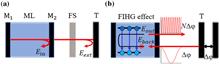
The relative phase change between two light fields can be used as a fundamental parameter to measure the physical quantity causing this change. Therefore, amplifying the relative phase change becomes attractive to improve the measurement resolution. Phase amplification using a many-body entangled state (NOON state) is a well-known method; nevertheless, the preparation process for a high-number NOON state is difficult and sensitive to optical loss. Here, we propose and experimentally verify a concise phase amplification method with a tolerance of about five orders of magnitude for optical loss. The method is based on the optical-feedback-induced intracavity harmonics generation effect to amplify the phase change by 11 times, which is comparable to the highest level of about 10 experimentally reached in NOON states. Furthermore, the 20th intracavity harmonic is generated when the reinjected photon number increases, indicating that 20 times phase amplification is attainable. The proposed method has a prospect for precision measurement applications.
To enhance the strength of chiral light–matter interaction for practical applications, the chirality and quality factors (Q-factors) of current methods need to be strengthened simultaneously. Here, we propose a design of photonic crystal slabs (PhCs) supporting chiral bound states in the continuum (BICs) of transverse electric (TE) and transverse magnetic (TM) modes, exhibiting maximal chiroptical responses with high Q-factors and near-unity circular dichroism (CD=0.98). Different from the past, the PhCs we employed only have reduced in-plane symmetry and can support simultaneously chiral quasi-BICs (q-BICs) of TE and TM mode with two-dimensional ultra-strong external and internal chirality. Based on the temporal coupled-mode theory, two analytical expressions of CD of chiral q-BICs response are revealed, which are consistent with the simulation results. Furthermore, we elucidate these results within the charge-current multipole expansion framework and demonstrate that the co-excitation of higher-order multipole electric/magnetic modes is responsible for near-perfect CD. Our results may provide more flexible opportunities for various applications requiring high Q-factors and chirality control, such as chiral lasing, chiral sensing, and enantiomer separation.
We report on the observation of conical third, fifth, seventh, and ninth harmonics that gradually emerge during the supercontinuum generation by filamentation of femtosecond midinfrared pulses in lithium strontium hexafluoroaluminate crystal. We show that the generation of conical odd harmonics is an optical signature of light-driven material reorganization in the form of volume nanogratings at the site irradiated by repetitive femtosecond filaments. The angle-resolved spectral measurements demonstrate remarkably broad spectra of individual odd harmonics, benefiting from a spectrally broadened pump pulse (supercontinuum), and reveal that filament-inscribed nanogratings represent photonic structures that are able to provide ultrabroad phase-matching bandwidths covering the wavelength range from the ultraviolet to the near infrared. We propose a scenario that interprets the generation of conical fifth, seventh, and ninth harmonics as nanograting phase-matched cascaded noncollinear four-wave mixing processes.
Rogue waves are ubiquitous in nature, appearing in a variety of physical systems ranging from acoustics, microwave cavities, optical fibers, and resonators to plasmas, superfluids, and Bose–Einstein condensates. Unlike nonlinear solitary waves, rogue waves are extreme events that can occur even without nonlinearity by, for example, spontaneous synchronization of waves with different spatial frequencies in a linear system. Here, we report the observation of rogue-wave-like events in human red blood cell (RBC) suspensions under weak light illumination, characterized by an abnormal L-shaped probability distribution. Such biophotonic extreme events arise mostly due to the constructive interference of Mie-scattered waves from the suspended RBCs, whose biconcave shape and mutable orientation give rise to a time-dependent random phase modulation to an incident laser beam. We numerically simulate the beam propagation through the colloidal suspensions with added disorder in both spatial and temporal domains to mimic random scattering due to Brownian motion. In addition, at high power levels, nonlinear beam self-focusing is also observed, leading to a dual-exponential probability distribution associated with the formation of multiple soliton-like spots. Such rogue wave events should also exist in environments with cells of other species such as swimming bacteria, and understanding of their underlying physics may lead to unexpected biophotonic applications.
Optical helicity provides us with an effective means to control the helicity-dependent photocurrent in the spin-momentum-locked surface states of topological insulators (TIs). Also, the TIs show potential in polarization detection as an intrinsic solid-state optical chirality detector for easier integration and fabrication. However, the complex photoresponses with the circular photogalvanic effect, the linear photogalvanic effect, and the photon drag effect in the TIs prevent them from direct chirality detection of the elliptically polarized light. Here, by fitting with the theoretical models to the measured photocurrents, the microscopic origin of different components of the helicity-dependent photocurrent has been demonstrated. We show a comprehensive study of the helicity-dependent photocurrent in (Bi1-xSbx)2Te3 thin films of different thicknesses as a function of the light incident angle and the gate-tuned chemical potential. The observation of the light incident angle dependence of the helicity-dependent photocurrent provides us with a polarization detection strategy using a TI thin film without the use of any additional optical elements, and the detection accuracy can be enhanced by gate tuning. Additionally, the Stokes parameters can be extracted by arithmetic operation of photocurrents measured with different incident angles and gating voltages for complete characterization of the polarization states of a light beam. Using this means, we realize the polarization detection and the Stokes parameters analysis with a single device. Our work provides an alternative solution to develop miniaturized intrinsic polarization-sensitive photodetectors.
In this paper, a 3D meta-atom-based structure is constructed for the multifunctional compatible design of visible, infrared, and microwave. To achieve high performance, a novel dispersion tailoring strategy is proposed. Through the incorporation of multiple controllable losses within the 3D meta-atom, the dispersion characteristics are tailored to the desired target region. The effectiveness of the strategy is verified with an error rate of less than 5%. A proof-of-concept prototype is designed and fabricated, exhibiting high visible transparency, low infrared emission of 0.28, and microwave ultra-broadband absorption with a fractional bandwidth of 150% under 2.7 to 18.7 GHz. This work contributes a novel design strategy for the development of high-performance multispectral stealth materials with wide applications.
Chiral metasurfaces integrated with active materials can dynamically control the chirality of electromagnetic waves, making them highly significant in physics, chemistry, and biology. Herein, we theoretically proposed a general and feasible design scheme to develop a chiral metadevice based on a bilayer anisotropic metasurface and a monolayer liquid crystal (LC), which can construct and flexibly manipulate arbitrary terahertz (THz) chirality. When the twist angle between the anisotropic axes of two metasurfaces θ is not 0°, the spatial mirror symmetry of the chiral metadevice is broken, resulting in a strong THz chiral response. In addition, the introduction of anisotropic LCs not only enhances the chiral response of the metadevice but also induces the flipping modulation and frequency tunability of the chirality. More importantly, by optimizing the θ, we can flexibly design the arbitrary chiral response and the operating frequency of chirality, thereby promoting the emergence of various chiral manipulation devices. The experimental results show that the maximum circular dichroism can reach -33 dB at 0.94 THz and flip to 28 dB at 0.69 THz by rotating the LC optical axis from the x to y axis, with the maximum operating frequency tunable range of ∼120 GHz. We expect this design strategy can create new possibilities for the advancement of active THz chiral devices and their applications, including chiral spectroscopy, molecular recognition, biosensing, and fingerprint detection.
The study of pixelated metamaterials that integrate both the functions of linear and circular polarization filters is rapidly growing due to the need for full-Stokes polarization imaging. However, there is a lack of large-area, ultracompact pixelated full-Stokes metamaterials with excellent performance, especially circular polarization filters with a high extinction ratio, a broad operating bandwidth, and a low-cost, high-quality, efficient manufacturing process, which limits the practical applications of pixelated full-Stokes metamaterials. In this study, we propose a universal design and fabrication scheme for large-area, ultracompact pixelated aluminum wire-grid-based metamaterials used in Vis-NIR full-Stokes polarization imaging. The aluminum wire-grid was designed as a linear polarization filter with an average linear polarization extinction ratio of 36,000 and a circular polarization filter with an average circular polarization extinction ratio of 110 in Vis-NIR. A large-area, ultracompact 320×320 pixelated aluminum wire-grid-based full-Stokes metamaterial was fabricated using nanoimprint lithography and nano transfer printing with the advantages of low cost and high efficiency. This metamaterial was used to achieve full-Stokes polarization imaging with errors within 8.77%, 12.58%, 14.04%, and 25.96% for Stokes parameters S0, S1, S2, and S3, respectively. The inversion errors of the compensated Stokes parameters can be reduced to 0.21%, 0.21%, 0.42%, and 1.96%, respectively.
We develop and experimentally demonstrate a phase-sensitive continuous variable quantum key distribution system with improved secure key rate. This is achieved using multimode coherent states with phase-conjugated subcarrier modulation and phase-sensitive detection. The local oscillator for phase-sensitive detection is regenerated from a polarization-multiplexed carrier wave via optical injection locking. The proposed scheme has a higher classical information capacity at a given number of received photons and exhibits a higher secure key rate when applying the security analysis of the GG02 protocol. Experimental results confirm the higher secret key rate and better excess noise tolerance of the new scheme compared to the typical implementation of GG02.
In the same silicon photonic integrated circuit, we compare two types of integrated degenerate photon-pair sources (microring resonators and waveguides) using Hong–Ou–Mandel (HOM) interference experiments. Two nominally identical microring resonators are coupled to two nominally identical waveguides, which form the arms of a Mach–Zehnder interferometer. This is pumped by two lasers at two different wavelengths to generate, by spontaneous four-wave mixing, degenerate photon pairs. In particular, the microring resonators can be thermally tuned in or out of resonance with the pump wavelengths, thus choosing either the microring resonators or the waveguides as photon-pair sources, respectively. In this way, an on-chip HOM visibility of 94% with microring resonators and 99% with straight waveguides is measured upon filtering. We compare our experimental results with theoretical simulations of the joint spectral intensity and the purity of the degenerate photon pairs. We verify that the visibility is connected to the sources’ indistinguishability, which can be quantified by the overlap between the joint spectral amplitudes (JSA) of the photon pairs generated by the two sources. We estimate a JSA overlap of 98% with waveguides and 89% with microring resonators.
With the rapid development of nanophotonics for enhancing free-electron radiation, bound states in the continuum (BICs) have emerged as a promising approach for emitting intense Smith–Purcell radiation (SPR) with enhanced intensity. However, current BIC-based methods are limited to single-frequency operation, thereby restricting their applications requiring spectral and angular tunability, such as particle detectors and light sources. To overcome this limitation, this work proposes an approach for constructing plasmonic BICs over a broad spectral range in symmetry-broken systems. By leveraging the high-Q resonances near the BICs, we achieve intense SPR with broadband tunability, potentially improving the radiation intensity by six orders compared to traditional methods. Experimentally, we validate the construction of BIC using plasmonic antennas and achieve broadband demonstration. Our proposed concept can be extended to other plasmonic or guided-wave systems, paving the way toward compact and efficient free-electron sources in hard-to-reach frequency regimes.
Owing to their unique optical properties and new degrees of freedom, orbital angular momentum (OAM) beams have been applied in various fields. Detection of the topological charges (TCs) of OAM beams is the key step for their applications. However, on-chip sorting of OAM beams with large TCs still remains a challenge. In this paper, Bloch surface wave (BSW) structures with five semi-ring shaped nanoslits are modeled. A spatial separation of 135 nm on the chip is obtained between two neighboring OAM states. OAM beams with TCs up to 35 can be successfully sorted by the BSW structures, which is much larger than that using metallic structures (only seven). BSW structures exhibit better OAM sorting performances than metallic structures. We systematically show how the lower attenuation of BSW structures leads to far superior separation ability compared to surface plasmons propagating on metallic structures. In addition, sorting of two OAM beams with different TCs simultaneously can be achieved in this way. Our results reveal that BSW structures should be an excellent solution for OAM sorting with large TCs, which is beneficial for applications in integrated on-chip devices and optical communications.
In spintronic applications, there is a constant demand for lower power consumption, high densities, and fast writing speed of data storage. All-optical switching (AOS) is a technique that uses laser pulses to switch the magnetic state of a recording medium without any external devices, offering unsurpassed recording rates and a simple structure. Despite extensive research on the mechanism of AOS, low energy consumption and fast magnetization reversing remain challenging engineering questions. In this paper, we propose a newly designed cavity-enhanced AOS in GdCo alloy, which promotes optical absorption by twofold, leading to a 50% reduction in energy consumption. Additionally, the time-resolved measurement shows that the time of reversing magnetization reduces at the same time. This new approach makes AOS an ideal solution for energy-effective and fast magnetic recording, paving the way for future developments in high-speed, low-power-consumption data recording devices.