View fulltext
View fulltext
In this paper, the Goos–Hanchen shift (GHS) at the interface between air and the aluminum zinc oxide (AZO)/ZnO hyperbolic metamaterial (AZO-HMM) is theoretically examined. The results herein show that AZO-HMM can enhance the GHS at the interface to a value at 3 orders of the incident wavelength under special conditions, which is much larger than conventional GHS values. Moreover, the GHS can be tuned to be negative or positive by changing the incident wavelength or the volume fraction of AZO.
The quasi-phase-matching (QPM) technique has drawn increasing attention due to its promising applications in areas such as nonlinear frequency conversion for generating new laser light sources. In this paper, we will briefly review the main achievements in this field.Wegive a brief introduction of the invention ofQPMtheory, followed by the QPM-material fabrication techniques. When combing QPM with the solid-state laser techniques, various laser light sources, such as single-wavelength visible lasers and ultraviolet lasers, red–green–blue three-fundamentalcolor lasers, optical parametric oscillators in different temporal scales, and passive mode-locking lasers based on cascaded second-order nonlinearity, have been presented. The QPM technique has been extended to quantum optics recently, and prospects for the studies are bright.
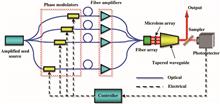
Coherent beam combination (CBC) of fiber lasers based on self-imaging properties of a strongly confined tapered waveguide (SCTW) is studied systematically. Analytical formulas are derived for the positions, amplitudes, and phases of the N self-images at the output of a SCTW, which are important for quantitative analysis of waveguide-based CBC. The formulas are verified with numerical examples by a finite difference beam propagation method (FDBPM) and the errors of the analytical expressions are studied. This study shows that the analytical formulas agree well with the FDBPM simulation results when the taper angle is less than 1.4° and the phase distortion is less than λ/10. The relative errors increase as the taper angle increases. Based on the theoretical model and the FDBPM, we simulated the CBC of fiber laser array and compared the CBC based on the tapered waveguide with that based on the nontapered one. The effects of input beam number, aperture fill factor, and taper angle on the combination performance have been studied. The study reveals that a beam which has near-diffraction limited beam quality (M2≤1.41) and a single beam without side lobe in the far field can be achieved with tapered-waveguide-based CBC. It is shown that beam quality depends on input beam number, aperture fill factor, and taper angle. There exists a best fill factor which will increase as input beam number increases. The tolerance of the system on the fill factor and the taper angle is studied, which is 0.45t0.67 and θ0.8°, respectively. The results may be useful for practical, high-power fiber laser systems.
The implementation of photoinduced linkage isomerism in molecular-based optical materials represents a promising approach for the synthesis of high-contrast, high-resolution photosensitive materials that are necessary for high-density (holographic) data storage and/or real-three-dimensional (holographic) displays. The unsolved task of embedding a photofunctional coordination complex into a matrix like polymer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) with photoinduced isomerism of a SO-bond in the sulfoxide compound [Ru(bpy)2OSO]PF6 is addressed. This approach allows to preserve the spectral properties within the solid dielectric environment, with an impact of PDMS on population and relaxation dynamics. All data are discussed in the framework of photofunctionality, storage, and display applications.
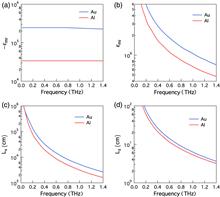
We present experimental measurements that show direct determination of the dielectric properties of various metals relevant to plasmonics. In contrast to traditional measurements that typically rely on transmission and reflectance measurements, we launch surface plasmon-polaritons on a variety of different substrates and measure the propagation properties using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Surprisingly, we find that the extracted values for the dielectric constant for these metals differ by orders of magnitude from published data. In order to validate the obtained results, we separately measure the 1∕e decay length, both along the propagation direction and normal to the metal surface, and show that the results are fully self-consistent with experimental data. The generality of the measurement technique makes it a useful tool to estimate the properties not only of planar conducting substrates but also a wide variety of more complex plasmonic structures.
The optical transmittance properties of single-hole arrays and three-hole chain (vertical) arrays with different geometrical parameters were numerically investigated. It was shown that on increasing the vertical distance between the holes in the hole chain array, the FWHM of the (1,0) resonance mode was decreased and minimum FWHM of 29 nm was obtained for a vertical gap of 48 nm between each side hole. A 1.5–2.0 times larger transmittance enhancement was observed by varying the incident light polarization from the y axis to the x axis. Furthermore, it was found that the optical transmittance of the hole chain array in the case of linearly x-axis polarized incident electromagnetic (EM) field was ~6 times larger than that linearly y-axis polarized incident EM field.
A new integrated plasmonic waveguide sensor is reported with high sensitivity (1600 nm/RIU). The integrated structure, loaded with stratified composite, makes this device robust and easy to fabricate on a chip to use as a sensor probe. The device works on the principle of resonant coupling between surface plasmon and fundamental TM mode. By selecting proper stratified structure (metal–dielectric) and core glass, one can tune the sensitivity and the range of operating wavelength.