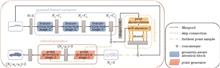
At present, most of the multi-spectral pedestrian detection algorithms focus on the fusion methods of visible light and infrared images, but the number of parameters to fully fuse multi-spectral images is huge, resulting in lower detection speed. To solve this problem, we propose a multi-spectral pedestrian detection algorithm based on YOLOv5s with high timeliness. To ensure the detection speed of the algorithm, we select the merging method of visible light and infrared light channel direction as the input of the network, and improve the detection accuracy by improving the traditional algorithm. First, some standard convolution is replaced by deformable convolution to enhance the ability of the network to extract irregular shape feature objects. Second, the spatial pyramid pooling module in the network is replaced by multi-scale residual attention module, which weakens the interference of the background to the pedestrian target and improves the detection accuracy. Finally, by changing the connection mode and adding the large-scale feature splicing layer, the minimum detection scale of the network is increased, and the detection effect of the network for small targets is improved. Experimental results show that the improved algorithm has obvious advantages in detection speed, and improves the mAP@0.5 and mAP@0.5∶0.95 by 5.1 and 1.9 percentage points over the original algorithm, respectively.
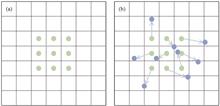
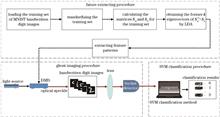
A classification method based on support vector machine and correlation imaging is proposed to address the problem of unknown object recognition. The method utilizes linear discriminant analysis to extract feature vectors from the objects. Based on these feature vectors, the characteristic speckle patterns are designed and applied to a correlation imaging system. By illuminating the objects with the characteristic speckle patterns, the bucket detector values are obtained from the correlation imaging system. The support vector machine is then employed to discriminate and classify the objects based on these bucket detector values. The feasibility of this approach is validated on the MNIST dataset. The results demonstrate that high classification accuracies can be achieved by the proposed method in all ten classification tasks, with an average classification accuracy of 90.5%. The comparison results with other classification methods indicate that the proposed method has more advantages in accuracy.
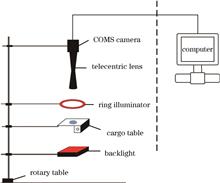
Aiming at the problems of low contrast of the optical lens image and low recognition rate of optical lens surface defects under single illumination when detecting optical lens surface defects by machine vision, a visual detection method of optical lens surface defects under dual light source is proposed. According to the scattering imaging principle, the optical lens images containing defects are obtained by using the image sensor under two different illumination modes, the forward light and the backlight, and then the images are fused into one image by the image fusion algorithm. Finally, the defect size information of optical lens surface is obtained by using the recognition algorithm. Two different defects (scratch, pitting) are detected, and the test results of this system are compared with the processing results of the ZYGO interferometer, and the comparative results show that the pitting error and the scratch error of proposed method are less than 2.7% and 0.8%, respectively, the detection efficiency is inproved by 98.24% compared with the interferometer, and the detection time is shortened. Compared with the detection method under single illumination and manual detection, the identification rate and accuracy of defects detected by the proposed method is higher.
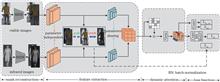
Cross-modal person re-identification is a challenging pedestrian retrieval task. Existing research focuses on reducing inter-modal differences by extracting modal shared features, while ignoring the processing of intra-modal differences and background interference. In this regard, a mask reconstruction and dynamic attention (MRDA) network is proposed to eliminate the influence of background clutter by reconstructing the features of human body regions, thereby enhancing the robustness of the network on background changes. In addition, the dynamic attention mechanism is combined to filter irrelevant information, dynamically mine and enhance the discriminating feature representations, and eliminate the influence of intra-modal differences. The experimental results show that the probability the first search result matches successfully (Rank-1) and mean average precision (mAP) in the all-search mode of the SYSU-MM01 dataset reach 70.55% and 63.89%, respectively. The Rank-1 and mAP in the visible-to-infrared retrieval mode of the RegDB dataset reach 91.80% and 82.08%, respectively. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified on the public datasets.
Point cloud completion refers to the process for reconstructing a complete 3D model using incomplete point cloud data. Most of the existing point cloud completion methods are limited by the point cloud disorder and irregularity, which makes it difficult to reconstruct the local detail information, thus affecting the completion accuracy. To solve this problem, an attention-based multi-stage network for point cloud completion is proposed. A pyramid feature extractor that satisfies the replacement invariance is designed to establish the dependence between points within a localization as well as the correlation between different localizations, so as to enhance the extraction of local information while extracting global feature information. In the point cloud reconstruction process, a coarse-to-fine completion method is adopted to first generate a low-resolution seed point cloud, and then gradually enrich the local details of the seed point cloud to obtain a finer and denser point cloud. Comparison results of the experiments conducted on the public dataset PCN demonstrate that the proposed network can effectively reconstruct the local detail information, and improves the completion accuracy by at least 5.98% over the existing methods. The ablation experimental results also further validate the effectiveness of the designed attention module.
The LiDAR based on single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) is widely used in 3D perception due to its advantages of high sensitivity, long detection distance and high integration level. The LiDAR system based on SPAD contains various sub-modules, and studying the influence of different types of sub-modules on the performance of LiDAR system can help optimizing the system scheme, improving R&D (research and development) efficiency, and reducing R&D cost. Therefore, according to the feature of sub-modules, we use the time-correlated single-photon counting technology (TCSPC) and the Monte Carlo method to establish the LiDAR model based on SPAD. The effects on system performance of passive reset circuit and active reset circuit, single-event first-photon TDC (time to digital converter) and multi-event TDC are obtained. The results show that the system performance of the active reset circuit and the passive reset circuit is basically the same under the conditions of the time of fight of 20 ns, the ambient light of 50×103 lx, and the target reflectivity of 10%. After the target reflectivity increases to 50%, the system performance of the active reset circuit is better than that of the passive reset circuit. Similarly, the system performance of multi-event TDC is better than that of single-event first-photon TDC, mainly because the noise of multi-event TDC is uniformly distributed, and compared with single-event first-photon TDC, the peak value of signal count of multi-event TDC is more likely to be greater than the peak value of noise floor count, and the corresponding solution range algorithm is simpler and requires less computing power. The simulation results show that in order to optimize the system performance, the sub-module of the SPAD integrated chip should adopt the architecture of active reset circuit and multi-event TDC.
Deflecting light waves is an important capability in the manipulation of optical fields and serves as a fundamental aspect in numerous optical applications. With the vigorous development of optical technology, there is an urgent need for optical devices that balance miniaturization and beam deflection ability. Metasurfaces, which are planar devices constructed by arranging sub-wavelength nano-structures with specific order, can redirect light waves towards non-specular directions due to the ability to modulate electromagnetic waves with arbitrary customization, offering the potential to play a significant role in practical applications. In this paper, we first introduce the physical mechanisms underlying the high-efficiency anomalous deflection metasurfaces, then provide a review and discussion of the applications of anomalous deflection metasurfaces and finally summarize potential challenges, offer a glimpse into the future development of anomalous deflection metasurfaces and their applications.